Gas Density Table
Table of densities of liquefied propane-butane mixture (in t/m³) depending on its composition and temperature
| Propane/Butane ratio T, °C | −25 | −20 | −15 | −10 | −5 | 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 |
| 100/0 | 0,559 | 0,553 | 0,548 | 0,542 | 0,535 | 0,528 | 0,521 | 0,514 | 0,507 | 0,499 | 0,490 |
| 90/10 | 0,565 | 0,559 | 0,554 | 0,548 | 0,542 | 0,535 | 0,528 | 0,521 | 0,514 | 0,506 | 0,498 |
| 80/20 | 0,571 | 0,565 | 0,561 | 0,555 | 0,548 | 0,541 | 0,535 | 0,528 | 0,521 | 0,514 | 0,505 |
| 70/30 | 0,577 | 0,572 | 0,567 | 0,561 | 0,555 | 0,548 | 0,542 | 0,535 | 0,529 | 0,521 | 0,513 |
| 60/40 | 0,583 | 0,577 | 0,572 | 0,567 | 0,561 | 0,555 | 0,549 | 0,542 | 0,536 | 0,529 | 0,521 |
| 50/50 | 0,589 | 0,584 | 0,579 | 0,574 | 0,568 | 0,564 | 0,556 | 0,549 | 0,543 | 0,536 | 0,529 |
| 40/60 | 0,595 | 0,590 | 0,586 | 0,579 | 0,575 | 0,568 | 0,562 | 0,555 | 0,550 | 0,543 | 0,536 |
| 30/70 | 0,601 | 0,596 | 0,592 | 0,586 | 0,581 | 0,575 | 0,569 | 0,562 | 0,557 | 0,551 | 0,544 |
| 20/80 | 0,607 | 0,603 | 0,598 | 0,592 | 0,588 | 0,582 | 0,576 | 0,569 | 0,565 | 0,558 | 0,552 |
| 10/90 | 0,613 | 0,609 | 0,605 | 0,599 | 0,594 | 0,588 | 0,583 | 0,576 | 0,572 | 0,566 | 0,559 |
| 0/100 | 0,619 | 0,615 | 0,611 | 0,605 | 0,601 | 0,595 | 0,590 | 0,583 | 0,579 | 0,573 | 0,567 |
Distinctive features of liquefied gases:
- high vapor pressure;
- have no smell. To detect leaks in a timely manner, liquefied gases are given a specific odor - odorized with ethylmer-captan (C2H5SH);
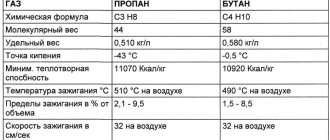
- low temperatures and flammability limits. The ignition temperature of butane is 430°C, propane is 504°C. The lower flammability limit of propane is 2.3%, butane is 1.9%;
- propane, butane and their mixtures are heavier than air. In the event of a leak, liquefied gas can accumulate in wells or basements. It is prohibited to install equipment operating on liquefied gas in basement-type premises;
- transition to the liquid phase with increasing pressure or decreasing temperature;
- high calorific value. To burn LPG, a large amount of air is required (to burn 1 m³ of the gas phase of propane, 24 m³ of air is required, and butane - 31 m³ of air);
- large coefficient of volumetric expansion of the liquid phase (the coefficient of volumetric expansion of the liquid phase of propane is 16 times greater than that of water). Cylinders and tanks are filled to no more than 85% of their geometric volume. Filling more than 85% can lead to their rupture, subsequent rapid flow and evaporation of gas, as well as ignition of the mixture with air;
- as a result of evaporation of 1 kg of liquid phase of LPG at n. u. 450 liters of vapor phase is obtained. In other words, 1 m³ of the vapor phase of a propane-butane mixture has a mass of 2.2 kg;
- When 1 kg of propane-butane mixture is burned, about 11.5 kWh of thermal energy is released;
- liquefied gas evaporates intensely and, when it comes into contact with human skin, causes frostbite.
Example:
The density of a propane-butane mixture of 60% propane, 40% butane at an ambient temperature of -20°C will be 0.577 t/m3 or 577 kg/m3
Specific Gravity Calculations
In order to carry out calculations correctly, it is necessary to define the concept itself.
Specific gravity is the ratio of the weight of a material or substance to its volume. All calculations are carried out according to the formula: y=p*g, where y is specific gravity, p is density, g is gravitational acceleration, which in normal cases is a constant and equals 9.81 m/s*s. The result is measured in Newtons divided by cubic meter (N/m3). In order to convert the value to the SI system, it must be multiplied by 0.102.
Density is the quantitative value of mass in kilograms placed in a cubic meter. A very ambiguous value and depends on many factors. The main one is temperature. So, the density of propane-butane can vary from 490 to 619 kg/m3.
Properties of LPG
To understand why propane is mixed with butane, you need to know the characteristics of each component, including their interaction with the external environment. From a molecular structure point of view, they are hydrocarbon compounds that can be stored in a liquid state, which greatly simplifies transportation and operation.
One of the conditions for the formation of liquid gas is high pressure, so it is stored in special tanks under a pressure of 16 bar. The second condition for the transition of hydrocarbon gases from one state to another is the external air temperature. Propane boils at -43°C, while the transformation from liquid to gaseous state in butane occurs at -0.5°C, which is the main difference between these hydrocarbons.
Table with some other properties of these gases
Additional information about the properties of liquefied hydrocarbon gas can be read in the article: propane-butane for a gas holder - properties and application features.
Video description
What is the pressure in a propane tank?
Here are the main areas of application of liquefied propane in cylinders:
- Domestic use of liquefied propane cylinders is necessary in cases where there is no main connection, that is, in the absence of access to methane. They are used for connecting to cookers (ovens) and for heating boilers with the replacement of nozzles.
- Some small industries use propane for cutting and welding metals.
- As an energy carrier for cars, which is much cheaper than gasoline or diesel.
To determine the nominal pressure in the cylinder, just look at the tag, which should be attached to the valve after each technical check. In addition to the rating, the minimum residual pressure must be indicated, upon reaching which the container is considered unsuitable for use until the next refueling. To determine the amount of gas remaining in the cylinder, which is very important for motorists, a dial pressure gauge is installed on the outlet pipe, which determines the pressure in the container at the current moment. Knowing what the nominal and residual minimum pressure should be, you can determine the amount of propane in the tank using simple arithmetic calculations.
Important! If after refueling the pressure gauge shows the minimum residual pressure, then this indicates two things: either there is a gas leak, or the measuring device itself is faulty. This type of equipment must not be used!
Why do they mix propane and butane in an autonomous gas supply system?
Considering the physicochemical characteristics of saturated hydrocarbons, their use largely depends on climatic conditions. Liquefied butane in its pure form will not work at subzero temperatures. Whereas the use of pure propane is contraindicated in hot climates, since high temperatures cause an excessive increase in pressure in the gas tank.
Since it is not practical to produce a separate grade of gas for each region, for the purpose of unification, GOST provides a mixture with a certain content of two components within the established standards. According to GOST 20448-90, the maximum butane content in this mixture should not exceed 60%, while for the northern regions and in the winter season the share of propane should be no less than 75%.
Percentage of gases at different times of the year
By the way, more articles from our blog about gasification are in this section.
Types of gas cylinders for methane
Today there are 4 types of natural gas tanks, these are:
- Type I.
All metal construction. It is cast in specialized tanks and has no seams. Robust and reliable design, proven over the years. The cylinder has a cylinder-shaped neck for a valve on one side, and a rounded bottom on the other. During the manufacturing process, all tanks are subjected to overpressure testing and ultrasonic testing to identify hidden defects. Despite more modern manufacturing technology for other types, many consider Type 1 to be the most reliable design. - Type II.
Cylinders of the second type are made of metal-plastic construction. They are made of alloyed structural steel. The main part of the structure is covered with a reinforcing shell. It is stated that the steel used in this design does not change its physical properties at low ambient temperatures.
- Type III.
The design of the third type of derailment is similar to the previous one. A distinctive feature is the presence of an aluminum liner, which is reinforced with carbon fiber braid. The breaking force is about 140 kgf/mm2. The braid is impregnated with a specially developed composition based on epoxy resin. The advantage of this type of construction is its resistance to corrosion throughout the entire period of operation. - Type IV.
The fourth type is similar in design to the previous two. A special feature of the design is the material of the liner. In this type, it is polymer, reinforced with a reinforcing shell made of carbon fiber or composite material. The main advantage of this type of cylinder is its low weight, due to the use of modern production technologies. The disadvantages include the high price of the product, rarity on the market, as well as the fragility of the product when exposed to mechanical damage.
Specific gravity of natural gas, weight of 1 m3 of natural gas, table of values
Natural gas is a mixture of gases formed in the bowels of the Earth. This gas is classified as a mineral and is used everywhere. It is believed that this substance is formed due to the decomposition of the remains of living organisms due to high temperatures and pressure.
This type of gas is considered the most environmentally friendly type of organic fuel, because its combustion produces much less harmful substances compared to other types.
Natural gas is used everywhere. They heat living quarters and houses, and heat water. This gas is used to cook food. Used as fuel for cars and as a raw material in the chemical industry.
Temperature processes that occur inside a liquefied gas cylinder
Under normal operating conditions of a cylinder filled with gas, the following conditions apply:
- The theoretical freezing point of liquefied petroleum gas is -188 °C. However, this is only observed in laboratory conditions.
- Liquefied propane boils at -42 ° C, however, such temperatures can only be observed in Antarctica or Yakutia.
- As it cools, some of the butane (which is almost always contained in the mixture) begins to evaporate.
- With such evaporation, the external temperature of the walls of the gas cylinder further decreases. Theoretically - up to -49 ° C, practically - before the process of intensive ice formation begins.
Taking into account the initial humidity of the environment, the evaporation rate decreases, and the gas reducer successfully copes with other issues related to pressure drop.
How much is 1 kg of propane m3 of gas?
Table of densities of liquefied propane-butane mixture (in t/m3) depending on its composition and temperature T, °C
T—temperature of the gas mixture (average daily air temperature); P/B - ratio of propane and butane in the mixture, %
Example: The density of a propane-butane mixture of 60% propane, 40% butane at an ambient temperature of -20°C will be 0.577 t/m3 or 577 kg/m3
How to convert propane-butane from kilograms to liters?
In order to calculate the number of liters in one kilogram of gas, you need to use the formula: Liter=Kilogram/Density Example: It is known that a 50-liter cylinder contains 21 kilograms of gas, whose test density is 0.567. To calculate liters you need to divide 21 by 0.567. The result is 37.04 liters of gas.
How to convert propane-butane from liters to kilograms?
In order to calculate how many kilograms are contained in one liter of gas, you need to use the formula: Kilogram = Liter * Density Example: It is known that 100 liters of gas with a density of 0.567 are filled into a car. To calculate the number of kilograms of gas, you need to multiply 100 by 0.567. The result is 56.7 kg of gas.
How many liters in a cube of liquefied natural gas, compressed, condensed, pipeline, bottled, compressed, oil, associated, gas condensate, propane, butane and propane-butane gas mixture. All of these options are varieties of gaseous fuel or gasfuel
As people call it the “long-suffering” cubic meter – m3. Abbreviations such as cube and cubic meter are especially often used, universally accepted and understood by everyone. Our “people” do not change liters, their mentality does not allow it. The question is how many liters are in 1 cubic meter of liquefied gaseous fuel or one cubic meter of natural gas
, may be of purely educational interest.
Previously, this worried mainly schoolchildren and junior students solving problems in physics. However, today, when various meters are increasingly being installed in apartments and private houses to record the consumption of natural pipeline or liquefied gas, people who are far from the school curriculum are beginning to remember long-forgotten information. In particular, they are interested in the Internet, specifying how many liters are contained in a cubic meter of natural liquefied gas
. For example, an existing meter shows the consumption of natural gas in cubic meters, more precisely in cubic meters, and the tariff is paid based on the number of liters consumed. Therefore, it is useful to check the correctness of gas charges yourself by converting liters to cubes, cubic meters or cubic meters - m3. The task is quite simple, but often “complicated” by incorrect formulations of the question. Therefore, let's take a closer look.
Video description
Propane gas: measure the pressure in the cylinder.
What is important to know about refueling
The price of refilling a gas cylinder is determined as the product of the price of 1 liter of propane by the number of liters equal to 85% of the rated value of the cylinder volume Source mitex-shop.ru
The place where you will refill the propane cylinder is important, if only because not all refillers burden themselves such quality as conscience. As we said above, the tank is only 85% filled, but dishonest workers sometimes demand payment from the buyer for 100% of the capacity. For example, only 42.5 liters of gas are pumped into a 50-liter cylinder, but not 50, and this exactly corresponds to 85%. Therefore, do a simple calculation and find out if you are being deceived at the gas station. Keep in mind that only specialists should fill propane cylinders - this will ensure the quality of the filling and safety for you and everyone around you.
Technological factor
In addition to the climate factor, there is a technological justification for why propane and butane are mixed. At oil refineries, during the processing of associated gases, propane and butane are produced in different quantities. Therefore, to optimize the raw material policy, these hydrocarbons are mixed together in a certain proportion. At the same time, regardless of the technology for producing liquefied hydrocarbon gas, the percentage of the two components must be within the limits established by GOST.