Classification of non-destructive testing methods according to GOST 18353-79
The main methods of non-destructive testing are based on the use of various physical phenomena and the measurement of physical quantities characterizing these phenomena. The most widely used types of non-destructive testing are:
- ultrasonic;
- radio wave;
- electric;
- acoustic;
- eddy currents;
- magnetic;
- thermal;
- radiation;
- penetrating substances;
- optic.
General types of non-destructive testing may include several specific methods, differing in characteristics such as:
- method of interaction with the controlled object;
- physical quantities measured during observation;
- method of obtaining and interpreting data.
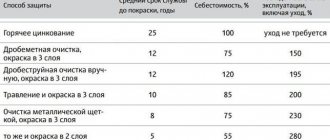
The correct choice of method allows the enterprise to save money and ensure high reliability of the controlled equipment and structures.
Visual
Optical is one of the most technically accessible types of NDT which requires the simplest instruments and devices: magnifying glasses, squares, rulers, calipers, micrometers, etc. Using these tools, the shape and dimensions of butting edges, seats, the depth of overlap at joints and etc. Products are visually inspected to detect rust, burns, dents, sagging, etc.
For optical NDT, it offers devices of its own production:
- “string” to control straightness;
- indicator devices for measuring the depth of the undercut and incomplete filling of the edge groove;
- standard set of control and measuring instruments: magnifying glasses, ruler, tape measure, square, calipers, sets of radius templates and probes, flashlight, metal marker.
Optical inspection is used in any production; product acceptance begins with it.
Radio wave method of non-destructive testing
It consists of irradiating the object under study with radio frequency radiation and measuring the parameters of the transmitted, reflected or scattered electromagnetic wave.
Radio wave method
It is applicable to dielectric, semiconductor materials, as well as thin-walled metal shells and structures in which radio waves propagate well. Used to check the uniformity, dimensions and shape of products made of plastic, rubber, and composite materials. In this case, the amplitude, phase or polarization characteristics of the wave are measured. Non-destructive testing using the radio wave method makes it possible to detect inhomogeneities, foreign inclusions, poor-quality adhesive and welded joints and other defects in the mass of material.
UD2-70 (NPK "LUCH")
at a price of RUB 247,000.
In 2014, NPK Luch released the fourth generation UD2-70, which indicates the demand and constant improvement of this model. What remains from past developments is the aluminum body, ease of learning and use of the device.
Model features
The device is designed for NDT of metal, polymer and composite products for deviations in the homogeneity of the material structure and violation of its continuity. The model allows you to determine the location of the defect and is suitable for studying finished products and welds.
The device is lightweight - only 2.2 kg. At the same time, it comes in a rugged case with a degree of protection IP64. In the previous version there were problems with the durability of the handle, now they have been corrected - the reliability of the design has been increased.
In the new version, the battery is removable and to replace it you only need to unscrew 4 screws. Continuous operation time is 14 hours. There is a network connection. The keyboard has also been changed, now it has a more strict appearance.
When ordering equipment, it is possible to purchase a version with ARD diagrams. Work is carried out with two independent ASD strobes. The built-in memory allows you to store 400 settings and Type A scan images, as well as 4000 depth gauge values.
In addition to the general purpose version, the manufacturer offers “locomotive”, “carriage”, “metro TR-2” and “metro TR-3” versions with expanded equipment to increase the efficiency of specific work.
Technical characteristics* UD2-70
| Parameter | Meaning |
| Operating frequencies, MHz | 0,4; 1,25; 1,8; 2,5; 5; 10 |
| Depth of inspection for steel, mm | 1-7500 |
| Speed of ultrasonic vibrations, m/s | 100-15000 |
| Gain adjustment, dB | 0-100 in steps of 0.5 and 1 |
| Temporary sensitivity adjustment, dB | 0-80 |
| Cut-off function | linear up to 100% display height |
| Sweep type | A, B |
| Distance measurement accuracy, mm | 0,1 |
| Screen size, mm | 111,4×83,5 |
| Operating temperatures, °C | -10…+50 |
| Dimensions, mm | 245×77×145 |
| Weight, kg | 2,2 |
*See the full list on the official website.
Watch a short video review of this ultrasonic flaw detector:
Electrical non-destructive testing method
A group of methods for non-destructive testing of metals and dielectrics is based on the measurement and interpretation of the characteristics of the electrostatic field applied to the controlled object. The most common measurements are electrical potential and capacitance.
To work with conductive materials, the equipotential method is used; for dielectric materials, the capacitive method is more often used. The thermoelectric method is applicable for fairly accurate determination of the chemical composition of a material without taking samples and using expensive mass spectrographic equipment.
Non-destructive testing electrical
Using electrical techniques, various hidden defects are found:
- voids and porosity in castings;
- microcracks in rolled metal;
- lack of penetration and other welding defects;
- poor-quality paint coatings and adhesive seams.
Acoustic or ultrasonic testing
The method is based on excitation of vibrations in a structure of a certain frequency, amplitude, duty cycle of pulses and analysis of the structure’s response to these vibrations. Interpretation of the results using specialized computer programs allows you to recreate two-dimensional sections of the object under study without destroying it. There are two main groups of acoustic flaw detection techniques:
- Active - the installation emits vibrations and subsequently receives a response from the structure.
- Passive - only measurements of oscillations and impulses are carried out.
Ultrasonic non-destructive testing
Sound vibrations with a frequency above 20 kilohertz are called ultrasound. Ultrasound is one of the most popular methods of acoustic flaw detection in industry and allows you to check the quality and spatial configuration of almost any materials. The popularity of ultrasound is determined by its advantages over other methods:
- low price of equipment;
- compactness of installations;
- safety for personnel;
- high sensitivity and spatial resolution.
The ultrasonic method is of little use for structures that have a coarse-grained structure or a very rough surface.
The safety of ultrasound for humans allows it to be widely used in medical diagnostics, including examination of a child in the womb and early determination of its gender.
Eddy current non-destructive testing method
The method is based on inducing low-intensity eddy (near-surface) currents in the object under study with a frequency of up to several megahertz, placing it in an electromagnetic field created by eddy current measurement transducers. Suitable for metals and other electrically conductive materials. Based on the inhomogeneities of the near-surface vortex field, one can judge the presence of inhomogeneities and other defects in the outer layer of the metal (up to a depth of several millimeters). The measurements also accurately determine defects in paint and protective coatings applied to a metal part. A powerful inductor coil that generates a high-frequency electromagnetic field serves as an eddy current transducer. Eddy currents induced by this field in the surface layer of the metal are measured with the same coil (combined circuit) or a separate one (separated circuit). Based on the spatial pattern of the intensity distribution of the measured currents, the locations of inhomogeneities that introduce distortion into the field are determined.
Eddy current non-destructive testing method
The use of eddy currents is the basis for a large number of different designs of flaw detectors, specializing in determining the thickness and uniformity of rolled metal sheets and coatings on structures, continuous measurement of the diameter of wire and rolled rods during their production. Eddy current devices, along with ultrasonic ones, are also used to determine the condition of turbine blades and other critical highly loaded components.
Scope of application
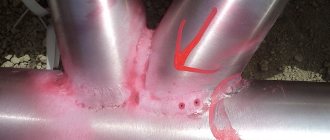
Power elements of structures experience large static and dynamic loads. This leads to the occurrence of fatigue cracks and subsequent destruction of parts. Timely detection of cracks and other defects helps prevent emergency failure of a part of a structure, one of the components or an entire unit. The use of flaw detection methods is one of the few options for solving this problem.
Depending on the technology for determining defects, visual-optical, ultrasonic, X-ray, capillary, magnetic particle, and eddy current flaw detection methods are used.
Types of flaw detectors
| Method | When to use | Principle of operation | Peculiarities |
| Ultrasonic testing (UT) | Used for inspection of welds, pipes, beams, rails, and other cast and composite structures. Allows you to detect cracks, sunsets, pores, looseness and other discontinuities on the surface or in the depths of parts made of metal, plastic and other materials. | Ultrasonic vibrations propagate into the part in the form of a directed beam. The vibrations reflected from the defect lead to the appearance of an intermediate pulse on the flaw detector screen. |
|
| Radiographic | Allows you to detect defects in welded and soldered seams, cracks, pores, deep corrosion, as well as damage to the structure of the material that occurs during machining. | It is based on exposing a part to x-rays and obtaining an image of the internal structure on film or digitally on a display. Allows you to identify the shape and exact dimensions of the defect. |
|
| Eddy current | This method detects cracks, intergranular corrosion, and inclusions of foreign metals at a depth of up to 2 mm without the need to remove the coating. | To excite eddy currents, a sensor with an inductance coil inside is used. The alternating current passing through its winding forms an alternating magnetic field in space. Penetrating inside the part, it excites eddy currents. Using a flaw detector, the eddy current parameter is converted into an observable signal. |
|
| Capillary | To detect invisible defects on the surface of parts made of aluminum, magnesium, titanium or nickel alloys and steel, subject to prior removal of the coating and thorough surface preparation. | Based on the use of the property of a liquid to wet a solid under the action of capillary pressure and fill narrow cracks and small holes. A penetrating liquid (penetrant) is applied to the test area, removed, and then a developer composition is used, against which the area with the defect becomes visually noticeable. |
|
| Magnetic particle | To control parts and assemblies directly in the structure, without the need to dismantle them. It is used at repair plants to detect cracks that are invisible during visual inspection. | The metal part is magnetized using a magnetic flaw detector. A stray field appears above the defects, which reveals itself when parts are processed with ferromagnetic particles in a liquid or gas mixture. The presence and location of cracks are judged from the indicator pattern. |
|
* There are dozens of NDT methods; we consider the most popular solutions.
Summary table of flaw detector models
| Model | Peculiarities | Equipment | Approximate price |
| 1. Ultrasonic device UD2-70 (NPK “LUCH”, Russian Federation) |
|
| RUB 247,000 |
| 2. Ultrasonic device USM-Go+ (GE Sensing & Inspection Technologies, USA) |
|
| 370,000 rub. |
| 3. Ultrasonic device Isonic 2010 (Sonotron NDT, Israel) |
|
| RUB 1,670,000 |
| 4. X-ray apparatus Arion-300 (PF “Arion”, Russian Federation) |
|
| 506,000 rub. |
| 5. X-ray machine Mart-250 (Spectroflash LLC, RF) |
|
| 695,000 rub. |
| 6. Eddy current device Vector-50 (NPC “Kropus”, Russian Federation) |
|
| 280,000 rub. |
| 7. Eddy current device VD-70 (NPK “Luch”, Russian Federation) |
|
| 220,000 rub. |
| 8. Set for penetrant testing Spotcheck SK3 (MAGNAFLUX, UK) |
|
| 15,000 rub. |
| 9. Device for magnetic particle testing Magnaflux Y1 (Magnaflux, UK) |
|
| 94,000 rub. |
Magnetic non-destructive testing method
This group of techniques is based on the physical measurement of the interaction of the object under study with a magnetic field. Used for flaw detection of ferromagnetic materials and alloys. The three main types of magnetic research are:
- magnetic particle;
- fluxgate;
- Magnetographic.
Magnetic method
To detect heterogeneity in the structure of a magnetic material, it is magnetized, and the surface is lubricated with a special suspension or gel containing calibrated metal particles. These particles are concentrated along the magnetic field lines, visualizing it in a simple and visual way. In places of inhomogeneities and defects, the magnetic field is distorted, and its lines will be curved. Magnetographic experiments were carried out by scientists back in the 18th century, but were adapted for flaw detection purposes only in the 20th century.
Capillary
Surface and through defects are easily detected using a simple and effective NDT method. Its essence lies in the capillary staining of the white surface of the product with a colored penetrant, obtained by treating it with a developer. After applying the developer, the penetrant appears on the surface in places of discontinuities, cracks, lack of fusion, and folds. Defect zones contrast with the rest of the background and are easily distinguished.
A significant disadvantage of the method is the toxicity of the chemicals, which places special demands on forced ventilation of the flaw detector's workplace, as well as the correct use of personal protective equipment. Through defects are detected in other ways.
offers laboratories and enterprises using the capillary method in their activities:
- colored and luminescent penetrants;
- developers, incl. low temperature;
- aerosol cleaners.
The method is effective, simple and relatively inexpensive, which is why it is popular.
Thermal method
Thermal techniques are based on measuring the intensity of thermal fields emitted by a controlled device or structure. The distribution of temperatures on the surface and the gradient of their change reflect the distribution of heat inside the object. In places of defects and inhomogeneities, the uniform thermal picture will be distorted.
Using a thermal imager for non-destructive testing
Researchers, through calculations and experiments, have identified typical changes in the thermal portrait of a product that are characteristic of certain defects, and currently, computers and neural networks are trusted to recognize such features. The thermal pattern on the surface is measured using both contact thermometers and remote pyrometry. Using a thermal portrait, welding and soldering defects, leaks in blood vessels, areas of internal stress concentration, and faulty electronic components are detected. The thermal method is most widely used in electronics and instrument making.
Vector-50 (NPC "Kropus")
at a price of 280,000 rubles.
Vector-50 is a model of an eddy current flaw detector from a constantly updated line from the Kropus Research and Production Center. This is the largest Russian manufacturer of NDT equipment, so its products could not fail to be included in our review.
Model features
The device is universal, because Supports any eddy current and impedance converters. This makes it possible to assess the condition of metal, carbon fiber and composite products, to identify surface and subsurface cracks and discontinuities in them. The device can be used as a thickness gauge and to determine the electrical conductivity of non-ferrous metals.
In addition to its compact dimensions (200x225x80 mm) and low weight (1.5 kg), the equipment has a color display with a resolution of 640x480 pixels and connects to a computer via USB. The device memory can store 100 settings and 500 control protocols.
Among the features is the display of the signal on the display in two planes: complex and amplitude-time. Various signal visualization modes are available. There is also the possibility of separate amplification along the abscissa and ordinate axis. The device can be used with rotary transducers for hole inspection.
The flaw detector is powered from a 220V network or battery.
In the second case, the maximum battery life is 10 hours. Technical characteristics* Vector-50
| Parameter | Meaning |
| Operating mode | standard, synchronous, frequency scanning |
| Gain adjustment, dB | 0-70 in steps, 0.1, 1, 2, 6 or 10 |
| Frequency change, Hz | 1-20×106 in increments of 1, 10, 100 or 1000 |
| Low-pass/high-pass filter, Hz | 5-1000/2,5-500 |
| Types of suitable converters | rotary, absolute, differential |
| Operating temperature, °C | -30…+55 |
| Dimensions, mm | 200×225×80 |
| Weight, kg | 1,5 |
*See the full list on the official website.
See how this flaw detector works in tandem with a rotary sensor to detect surface cracks in bolted process holes:
Radiation non-destructive testing method
This method is extremely effective; it allows you to obtain information about the largest installations and structures (with virtually no size restrictions) by shining them with penetrating ionizing radiation.
Radiation non-destructive testing method
Applicable in the following ranges:
- gamma rays;
- x-ray radiation;
- neutron radiation.
The physical basis of the method is an increase in the flux density of charged particles in places of hidden defects. Based on a comparison of the intensity of the transmitted and reflected flow, a conclusion is made about the depth of the heterogeneity. It is used to determine the quality of welds on large products, such as nuclear or chemical reactor vessels, turbines, main pipelines and their shut-off valves.
Arion-300 (PF "Arion")
at a price of RUB 506,000.
Pulse X-ray machine Arion-300 from, specializing in the production of X-ray machines for industrial flaw detection. The company is a partner of the Italian company Bosello and the American company Varian, which over the past decades have been leaders in the development of X-ray television systems.
Model features
Weighing 5.1 kg, this portable, portable unit is suitable for quality control of industrial products where high precision defect detection is required. Allows you to identify deep corrosion, determine the location and size of cracks and pores. It is used to examine the seams of gas pipelines, in the aviation industry, in cases where, for technical reasons, the ultrasonic testing method is not applicable.
It has a gas-filled X-ray tube with an anode voltage of 300 kV. The absence of water or oil cooling made it possible to reduce the weight of the device and make it portable. However, this affects the duration of uninterrupted operation. To protect against overheating, an automatic system is installed that operates every 500 pulses. The technological break is 1.5 minutes. The device operates in a temperature range from -35 to +50°C.
The kit includes an 18 Ah battery in a case, a generator, a power supply unit and a control unit, a high-voltage cable and a 220 V power cable, a voltage converter, a charger and a warning lamp.
Everything is packed into a case. Technical characteristics* Arion-300
| Parameter | Meaning |
| Operating voltage at the anode, kV | 300 |
| Translucent steel thickness from a distance of 500 mm, mm | 35-60 |
| Focal spot diameter, mm | 2,3 |
| Power consumption, W | 200 |
| Operating temperature, °C | -35…+50 |
| Dimensions, mm | high-voltage unit – 485×85×115 control panel – 150×255×95 |
| Weight, kg | high-voltage unit - 3.9 control panel - 1.2 |
*See the full list on the official website.
Watch a five-minute video demonstrating the operation of the device in the field:
Penetrant non-destructive testing method
The essence of the method is that a specially prepared liquid, less often a chemically active or radioactive substance, is released into the internal cavities of the controlled device or structure. The location of the defect is determined by its accumulation or traces.
There are two varieties:
- capillary, for finding surface capillary cracks through which the indicator substance leaks;
- leak detection - to detect leaks in pipelines and containers.
Penetrant non-destructive testing method
The surface is thoroughly cleaned, then an indicator substance, or penetrant, is applied to it. After a certain exposure, a developer substance is applied and the picture of defects is observed visually. If radioactive markers are used, defects are detected using appropriate radiographic equipment. The technique has the following advantages:
- high sensitivity;
- ease of use;
- clarity of presentation.
It combines well with other methods and serves them for mutual verification.
VD-70 (NPK "Luch")
at a price of 220,000 rubles.
VD-70 is a simple and relatively affordable model of an eddy current flaw detector that allows you to determine the location of surface cracks and estimate their depth. Suitable for examining metal products only.
Model features
This is a very lightweight device (0.5 kg), housed in a durable aluminum case with IP63 protection degree. The display has a resolution of 320x240 pixels and occupies half the area of the front part of the case.
The device has a memory for 1000 studies and 300 program settings. The manufacturer offers several delivery versions: general, locomotive, wagon, for depot TR-2 and TR-3.
VD-70 operates from a built-in battery, the capacity of which lasts for 8 hours.
Technical characteristics* VD-70
| Parameter | Meaning |
| Depth of detected defect, mm | from 0.3** |
| Working gap, mm | up to 0.7** |
| Frequency, kHz | 10-250 |
| Radius of curvature of products, mm | from 12** |
| Operating temperature, °C | -10…+50 |
| Dimensions, mm | 170×85×35 |
| Weight, kg | 0,5 |
*See the full list on the official website.
** depends on the type of converter.
The video below shows the equipment of the previous version of the device. It has not changed, but the flaw detector itself has become more compact and ergonomic:
Optical non-destructive testing method
The optical flaw detection method is based on the analysis of optical effects associated with reflection, refraction and scattering of light rays by the surface or volume of an object.
Optical method
External optical techniques make it possible to determine the cleanliness and roughness of surfaces, which is especially important in precision engineering. When measuring the dimensions of small parts, the physical phenomenon of diffraction is used, and the roughness of surfaces is determined based on interference measurements.
Internal defects can only be identified for transparent materials, and here optical techniques have no equal in terms of cheapness and efficiency.
They stand out due to their simplicity and low labor intensity in detecting surface defects, such as cracks, burrs and nicks.
Features of the structure and operation of microhardness testers
An efficient and accurate instrument for determining Vickers hardness. This is the optimal ratio of quality and price.
Digital microhardness testers are presented, as well as hardness testers operating on the Brinell and Rockwell scales.
The standard microhardness tester system includes:
- digital lens;
- LCD screen;
- operating system with a simple and intuitive interface;
- automatic starting lever;
- automated load application;
- positioning table;
- built-in PC.
When working with a microhardness tester, the operator can independently select the parameters. Information about all studies is saved in the computer’s memory and can be printed if necessary.
Hardness values are automatically converted to other scales.