Forced air burners
In these burners, the air required for combustion of gas is supplied to the burner using a process, a fan, the formation of the gas-air mixture begins in the burner itself and ends in the firebox, the gas burns with a non-luminous and short flame. Burners with forced air supply are often called two-wire and mixing burners, since in them the gas-air mixture is completely mixed.
mixtures of common designs of these burners operate at low gas and air pressure (Fig. 5). However, some designs can also be used at medium gas pressure.
Rice. 5. Burner with low pressure forced air supply: 1 – nozzle; 2 – body; 3 – front plate; 4 – ceramic tunnel
The burners are intended for installation in boiler furnaces and other units with a small firebox volume, as well as in heating and drying gas systems.
in furnaces with a pressure of up to 1200 Pa enters nozzle 1 and exits it through eight holes with a diameter of 4.5 mm. The holes are located at an angle of 30° to the burner axis. The burner housing 2 contains special blades that impart rotational motion to the air flow. Thus, small streams of gas intersect in a swirling air flow and a well-mixed gas-air burner is created. the mixture ends with a ceramic tunnel 4, which has a pilot hole.
The main advantages of such burners: the ability to burn large amounts of gas; wide regulation range of performance; the ability to heat air and gas temperatures above the ignition temperature.
Useful tips
- Cutting a small hole in the back of the forge will improve ventilation. In addition, this cutout allows you to heat long metal workpieces.
- The forge is placed on a special metal stand or table, which makes working with it more convenient. The height is selected individually by the master.
- If a forge shop works with workpieces of different sizes and shapes, then it is advisable to install several forges of different dimensions at once. They are placed close to each other, and gas and air are supplied using flexible hoses. This design solution allows you to quickly reconnect the burners.
- Each gas pipeline must have a shut-off valve. For this purpose, conventional valves are most often used - they provide smoother adjustment, unlike ball analogues.
The main thing in creating a forge with your own hands is to understand the principle of operation, select the right materials and follow safety precautions. Such equipment is created by craftsmen based on personal preferences, wishes and requirements, which provides wide scope for activity.
burner maintenance
In such burners, the air required for gas combustion comes from the surrounding front to the torch space due to diffusion. Gas is supplied to the burner without admixture of primary air and mixed with it outside the burner. Therefore, these burners are called external mixing burners.
Most simple diffusion burners are designed with holes drilled into a pipe. The distance between the holes takes into account the speed of flame propagation from one hole to another.
Industrial diffusion-type hearth burners include slot burners (Fig. 1). They are a pipe with a diameter of up to 50 mm, in which two rows of holes with a diameter of up to 4 mm are drilled. The burner manifold is placed above a grate in a brick channel. The channel is a slot in the bottom of the boiler, the name and where the burners come from is hearth slot.
Rice. 1. diffusion Hearth burner: 1 – air regulator; 2 – burner; 3 – viewing window; 4 – centering glass; 5 – horizontal tunnel; 6 – bricks from the layout; 7 – grate
From burner 2, gas exits into the firebox, where gas flows from under grates 7. air streams are directed at an angle to the air flow and are evenly distributed over its cross section. mixing The process of gas with air is carried out in a specially made slot made of refractory bricks. Thanks to this device, the process of mixing gas with air is enhanced and stable ignition of the gas-air mixture is ensured.
Building a solid fuel forge
The main disadvantage of solid fuel forges is that coal itself cannot produce the required temperature above 1000°C. Therefore, such stoves always require an air stream. Previously, these were bellows, now more often the air is supplied through a pipe with a welded end, also made of steel.
Grate for the forge.
The table plate must be made from a blank with a thickness of at least 5 mm. If you install an open design forge outdoors, you will not need to deal with special ventilation.
Here are the main steps for building a homemade coal-fired forge:
- Build a platform for the foundation with concrete and reinforced rods.
- Fold the bricks into a rectangular base; the table surface can be of any height.
- Make a hole in any wall of the base for the blower.
- Assemble the floor from special refractory bricks onto the base.
- Install a grate with holes, which must also be made of fire-resistant material, for which a cast-iron door from an old stove is perfect.
- After installing the grate, add walls made of the same refractory brick.
- Do not forget to leave a hole in one wall for air supply; it is better to do this immediately when laying bricks.
- Install a fan into the air supply pipe.
- If you are making a closed structure, be sure to build a chimney, which is absolutely necessary for draft.
Such a forge can be made mobile - it all depends on you. An old gas stove can serve as an excellent frame for a solid fuel forge.
Gas burners have advantages
Due to the design features, gas burners are quite durable in use and the most fireproof of the existing types. They are very easy to light, and in addition, these devices have the ability to regulate the intensity of the fire. Improved gas burners can operate even without electricity, are very efficient and economical to use.
Gas burners have many applications; without their use, life is now almost impossible. Therefore, the choice of a gas burner should be taken very seriously. You can now freely obtain the necessary information on the existing variety of gas burners on the Internet, in addition, you can always get professional advice on choosing, installing and using this device from experienced specialists.
Building a gas forge
Before you start building a gas forge with your own hands, you need to determine the parameters of the hearth - its area.
There is a clever formula for this:
N=H×F
N is the productivity of the hearth, which depends on the tension H and the hearth area F. It has been calculated that the gas supply speed in the range from 1 to 1.5 m/sec is sufficient to optimally maintain the required temperature in the hearth.
Diagram of a gas burner for a forge.
You know the area of your workshop and the approximate number of forging parts in kilograms that you plan to produce. With this data you derive the hearth tension with a maximum permissible upper limit of 150 kg/m².
Necessary materials you need to get started:
- fire-resistant brick such as dinas or chamotte;
- plates with a thickness of at least 5 mm made of heat-resistant steel;
- steel profile for the racks, frame and valve of the hearth;
- pipe for the chimney and ventilation duct made of steel;
- putty for sealing cracks between bricks with heat-resistant properties;
- sheet metal or an additional layer of refractory bricks for lining on the outside;
- burners from high-power double-circuit boilers;
- fan;
Gas forges can also be open. With it everything is much simpler; it will be enough to install grate bars with air supply for greater heating efficiency. In this case, combustion substances are removed by a fan made of heat-resistant metal.
It is better to place the support frame close to one of the walls of your workshop. The choice of wall must be made taking into account the fact that a chimney and ventilation pipe will be needed, so it is better not to use adjacent walls, if any.
It is better to weld the racks and the frame itself from low-alloy steel according to drawings that can be downloaded on the Internet. Low-alloy steel is strong, lightweight and, most importantly, resistant to specific high-temperature corrosion. The external lining must be thought out in advance so that holes for its fastening are immediately made in the support frame.
Now about refractory bricks and masonry
It is important to buy real certified fireclay bricks made in accordance with GOST 390-79. If you purchase a brick that does not meet the standard, you risk that ordinary bricks will begin to melt at a temperature of 1000°C.
Construction of a forge.
The second type of refractory bricks is dinas. These bricks are more expensive, but more resistant to high temperatures: they can withstand temperatures of 1800°C. They are lighter than fireclay bricks due to the high proportion of silicon salts in their composition.
If you have the opportunity, it is better to line the forge with silica brick: forges made of refractory silica brick are more durable and can withstand the most severe temperature conditions.
The bricks are laid with a mortar of refractory clay with the addition of chamotte and silica powder in a precise proportion of 60:40. Treat the chimney and fan around the perimeter with metal corners.
The most important final stage is drying the entire structure. After this, you need to check how the fans for the forge work. And only then will it be possible to perform a test run.
Gas burner of injection type. We do it ourselves
Hello friends. In a previous project to make a burr machine, I melted aluminum from a friend of mine. He made a small gas forge from fire bricks and uses it for forging. So I decided to make myself a furnace for melting non-ferrous metals. And we will start with the manufacture of a gas injection burner. There are many different drawings for its manufacture on the Internet. I had to study this whole thing and choose, in my opinion, the optimal design.
Let's talk a little about the principle of operation. There is some kind of tube of a tricky shape. On one side, gas is supplied through the nozzle. But gas without air simply does not burn as we need it to. The burner sucks in air itself due to ejection. This is the process of mixing two media, in our case air and gas, in which one medium, that is, gas, under pressure, affects the air and draws it into the mixer tube. At the point where the air is taken in, a vacuum is created and the air itself goes where it is needed. Mixing takes place in the burner body, and the combustible mixture comes out of it under pressure and creates the required temperature. It's simple.
This burner is sized to accommodate water pipes.
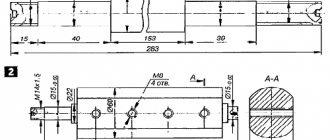
Stage 3: Gas and air supply unit
. Now the mechanism for regulating air and gas supply. We need an M10 bolt with a long thread. The bolt head is not needed. We drill a through hole with a diameter of 5 mm from the end and cut an M6 thread. As a gas jet, I used a wire feed tip from a semi-automatic machine. They cost pennies, and are available in diameters of 0.6 and 0.8 mm. There is one caveat here. The tip is long and needs to be cut so that about 3-4 mm remains after the thread. The remaining part can be threaded and you will get another jet. Now you need a washer with a diameter of about 43 mm. You can look at hardware stores or cut it out of sheet metal.
I turned it on a lathe. A hole with a diameter of 12 mm must be drilled in the center of the washer. We weld an M10 nut to the washer. Now we assemble the structure. Screw the nut onto the bolt. The mount will be welded to it. Next, screw on the adjusting washer and screw in the gas jet. We bend a metal bracket that will attach this unit to the body. I cut it out of 3mm metal. Now you need to rotate the washer to align the nozzle flush with it. The first nut that we screwed must be placed in the center of the thread. In this position, we apply all this to the confuser, then we attach the bracket and you can grab it to the nut and the body
It doesn’t matter where you weld it to the body, but the shorter it is, the tougher it is. If everything is smooth, then we finally weld
Well, everything seems to be ready.
What we have. When screwing in and unscrewing the bolt, we adjust the degree of ejection, so to speak. The best result is when the jet is a couple of mm. enters into confusion. Here you need to twist and see. Using the washer, we regulate the amount of air supplied and, accordingly, the quality of the mixture. In fact, the gas jet needs to be set once and you don’t have to touch it. To prevent it from spinning, you can tighten the nut.
Stage 4: Test.
Let's start testing. We put the hose on the bolt, and on the gearbox we set it to 0.2 kg per cm squared. You can also play with pressure. But too much gas consumption leads to rapid freezing of the cylinder, especially 5 liters. Then it is better to set the jet to 0.6 mm. Before ignition, the washer is completely closed or with a small gap. We ignite the gas and slowly increase the air supply, observing how the flame turns blue and slowly moves away from the burner nose. With a further increase in air, the flame completely breaks away from the burner, and it goes out. This is a feature of her work. To prevent this from happening, you need to install a barrier in the path of the flame or use it in a closed space. Then the escaping fire will ignite the gas, and it itself will support the combustion. In my case, the burner will be installed in a furnace for melting non-ferrous metals. But about her next time. An idea to note. Old cast iron batteries.
We place the burner in the lower part, opposite at the top there is a pipe to the street. Silence the rest. Settings to minimum flow and you can heat the garage. It works well in a closed space and, in theory, at optimal settings it will give a temperature of about 1200 degrees. This is enough for melting aluminum, brass, bronze, lead, hardening and annealing knife blades. You can forge blanks from files. There are a lot of applications.
How do you heat a forge?
To finally take on your own forge, all that remains is to figure out how to light it? Then it will be easier to understand the designs.
The best fuel for the forge is fine coke. Blacksmiths call it koksik, the name was adopted by traders. If there is coke on sale, there is also coke in small packages. The cost of coke, depending on the region, is 3 times more expensive than coal, but it costs 4-5 times less per forging if handled skillfully.
Coke is almost pure amorphous carbon, carbon. Really clean: coke oven gas is a valuable chemical raw material, so metallurgists are not slacking. It ignites at 450-600 degrees, so double kindling is needed: coal is lit with wood, and a layer of 150-170 m of coke is placed on it and the blast is turned on to maximum. When the coal burns out (this can be seen from the flame), the mass of coke is raked, leaving a layer on the grate 1/3-1/4 of the height of the entire pile, the workpiece is introduced into the hearth and raked with burning fuel. The blowing is reduced to normal for this operation and the part is waited until it matures.
To work with Damascus you need charcoal; it ignites at a lower temperature and burns faster, because... preserves the microporous structure of wood. And also, like activated carbon in a gas mask, it additionally absorbs alloying poisons. The fact is that damask steel is forged from a bundle of wires or rods of different hardness. The product itself is obtained by their mutual diffusion during forging. The process is very delicate, and adjustment of the blast requires precision, and light porous charcoal responds instantly to manipulation of air drainage.
Shell for burning a furnace with wood
If you burn with coal, you need to let it burn until it reaches carbon, i.e. volatile components, that same coke oven gas, must burn out. This again can be seen by the color of the flame. But such complete extraction of volatiles as in a coke oven cannot be achieved directly in the forge, so decorative or average-quality household products can be forged using coal. As a rule, one load of coal is not enough and it has to be burned out. The additional load for afterburning is placed on the side of the fireplace on the table and, as it burns, the resulting carbon is raked onto the workpiece.
In general, wood is heated in the same way as coal, but only with deciduous wood. Just a pile of firewood is more likely to burn to ash than to completely release volatiles and form coal. In addition, there is no way to allow unburned wood chips to get on the part; there are too many impurities in the wood that are harmful to steel. Therefore, wood for carbon in the forge is burned in the shell, see fig. The additional load is burned by placing it close to it and, as it burns, the coals are transferred to the shell with tongs.
Flameless panel burner
1 - tunnel; 2 - nipple; 3 - distribution chamber; 4 — injector; 5 - nozzle; 6 — air regulator; 7 - gas pipeline; 8 - ceramic prisms
Flameless combustion of gas has the following advantages: complete combustion of gas; possibility of gas combustion with small excess air; the ability to achieve high combustion temperatures; combustion of gas with high thermal stress of combustion volume; transfer of a significant amount of heat by infrared rays.
Based on the design of their fire part, existing designs of flameless burners with refractory nozzles are divided into burners with nozzles having channels of irregular geometric shape; burners with nozzles having channels of regular geometric shape; burners in which the flame is stabilized on the fireproof surfaces of the firebox.
The most common are burners with nozzles of regular geometric shape. The refractory nozzles of such burners consist of ceramic tiles measuring 65x45x12 mm. Flameless burners are also called infrared burners.
All bodies are sources of thermal radiation arising due to the vibrational motion of atoms. Each temperature corresponds to a certain range of wavelengths emitted by the body. In this case, heat transfer by radiation occurs in the infrared region of the spectrum, and burners operating on this principle are called infrared radiation burners (figure below).
Self-production
Mini horn
The smallest forge you can think of is a mini forge. For a novice blacksmith, this is the best option, intended for use only outdoors. The principles of construction are as follows:
Mini-forge drawing
- 6–8 bricks can be used as the main building material. Having built a stand from them, you can move on.
- The construction of a grate can be done using scraps of metal pipes and a fragment of a steel strip, the thickness of which should be at least 4–6 mm.
- Such a forge can be heated with either coal or coke. For ignition and blowing I use a regular blowtorch. It provides both heat supply and process continuity.
The use of a mini-forge indoors is prohibited due to the lack of a chimney in the structure.
Portable forge
The construction of a mobile forge can be carried out using kitchen utensils such as a goose pan. As a boost system, you can use a fan from a hand siren or any other suitable device.
A portable forge has certain disadvantages:
- its design is non-separable, so it is difficult to get rid of carbon deposits;
- does not allow creating very high temperatures, the maximum possible value is 900 °C;
- operation is quite expensive: only coke or charcoal can be used as fuel.
Despite this, this type of coal forge has many more possibilities than the homemade brick construction described above. This is due to the fact that the work space of a portable structure is open at the top and is much larger.
Stationary forge
This design is the most complex from a construction point of view. Experienced craftsmen manufacture the forge independently, taking into account their own anthropometric data. Its ergonomics must be honed to the smallest detail: the work performed here is often very dangerous.
So, when building a stationary forge, it is necessary to proceed from your own physical data. To do this you need to measure:
- Table height. Stand up straight with your feet shoulder-width apart. The right arm must first be lowered and then bent at the elbow. This will be the height of the table, to which you need to add 5–7 cm.
- Half the diagonal of the table. You need to take large pliers in the same hand and measure the distance from their lips to the stomach. By adding 10–12 cm to the result obtained, you can get the desired result.
- The length of the side of a square table. To do this, the result obtained in step 2 should be multiplied by 1.4.
A forge is an open or closed furnace used in blacksmithing to heat metal
. To make a stationary forge with your own hands, you will need the following materials:
- heat-resistant steel with a sheet thickness of at least 4 mm;
- fireclay brick;
- rolled metal, from which the forge frame should subsequently be assembled;
- steel chimney for carrying out the process of removing gases generated during the combustion process;
- fireproof putty, which must be used to seal cracks;
- steel for lining on the outside.
Materials for making a forge
Rules for the manufacture of a stationary structure
Since the forge is a stationary unit, its location must be clearly defined. Access to one of the walls is necessary because the forge should not be independent. The presence of a wall will allow you to more securely arrange chimneys and install a fan. This design can use a homemade lance.
Support frame for forge
The construction of the forge should begin with the manufacture of a support frame. It is brewed from a metal pipe. The upper part is constructed using refractory bricks. This will make the structure durable and allow you to use the stove more intensively.
The channels provided for ventilation and chimney should be lined with steel corners around the perimeter. The metal is also used in the construction of the lining and damper of the furnace. Sheets used in finishing must have a stiffener.
The forge table must have a forge nest, the optimal depth of which is 10 cm. Below it is an ash chamber into which air is supplied. The size of the table is not regulated, but it is better if it is designed taking into account the master’s data.
A square-shaped pipe should be rolled out of 2 mm thick steel. This will be the ash receptacle. A hole should be made in one of the walls into which a pipe for air supply will later be inserted. This can be done using a vacuum cleaner.
With or without an injector: how does it work?
There are two types of gas burners. Let's look at each of them in detail.
Burners without injector
Design of injection and non-injector burners.
These gas burners operate at high pressure, have a relatively simple design and are extremely efficient to use. Here is the algorithm in which they operate:
- The necessary oxygen is supplied from the air through special rubber slots and a valve, after which it enters the mixer.
- The function of the mixer is to divide the total flow into small jets that enter the nozzle. In the same way, the flow enters a special valve.
- Mixing of gas with oxygen occurs through circulation to ensure that the output is as homogeneous as possible.
- The mouthpiece at the tip is usually made of durable metal, such as copper. The mixture, heated to a very high temperature, comes out through it. The outlet temperature will be even higher than the melting point of metals.
The technical requirements for these devices are simple and specific: the gas flow must be uniform and have a specific speed that can be controlled and very accurately.
An additional requirement applies to the mixture: it must burn completely. The speed of the gas flow must be sufficient to prevent the flame from spreading to the top of the device, which is very, very dangerous due to the high risk of explosion.
On the other hand, the speed of the hot gas flow should not be too high due to the risk of the flame detaching from the mouthpiece with its subsequent attenuation.
How to calculate the optimal gas flow exit speed?
There are several factors to consider:
- composition of the combustible mixture;
- diameter of the inner wall of the nozzle;
- technical device of the mouthpiece.
The average speed is in the range of 70 – 150 m/sec.
Burners with injector
Methane, oxygen or acetylene are used as combustible gases, which are pumped into the mixer using an injector. This is the technological feature of the injection family of welding torches.
Here's how the injector design works:
- Combustible gas is pumped into the mixing chamber by an injector.
- Oxygen comes from the cylinder there too.
- After entering the mixer, the gas is mixed with oxygen in the air.
- The resulting mixture flows through the pipe into the mouthpiece.
- The gas pressure from the mouthpiece must be at least 3.5 atmospheres.
Injection models have a significant technological drawback that must be constantly remembered: the mixture of combustible gas and oxygen is not constant, it changes its composition all the time. As a result, the flame of such a gas burner, by definition, cannot be even and stable.
Such gas burners are used very widely, despite the low pressure and rather complex design. They have a built-in cooling system, since due to the low pressure the nozzle and mouthpiece become very hot. Therefore, the most important point is to control the overheating of the chamber so that it does not explode.
DIY FRIEND
Dear visitors to the “Homemade Friend” website, today we will look at detailed step-by-step instructions for creating a portable forge running on propane with your own hands. A forge using propane as fuel is much more efficient than a coal forge, and the undeniable advantage is that it can be moved to any place in your garage or workshop, and also does not require additional air supply.
In this case, the GAS HORN is a metal structure made of angle, corrugated pipe and 2 mm sheet metal. The hearth chamber is lined with refractory brick, which gives it the ability to withstand maximum temperature loads, and at the same time, fireclay brick has low thermal conductivity, which further increases the efficiency of the hearth.
Having a small blacksmith's forge in your workshop, you can forge all kinds of products: knives, axes, chisels, cores and much more. If you are a creative person... then you can do artistic forging.
So, let's look at the step-by-step process of assembling the forge.
Materials
- corner
- professional pipe
- sheet metal 2 mm
- fire brick
- gas-burner
- gas cylinder (PROPANE)
Tools
- welding inverter
- drill
- Angle grinder (grinder)
- ruler and marker
- hammer
- clamp or pliers
Step-by-step instructions for assembling a forge gas forge with your own hands.
First of all, we make the base of the chamber from a 50x50 corner; at the bends, you need to cut out the corner.
We bend it.
The result was a base for laying refractory bricks.
We weld the lower part with 2 mm sheet metal.
Lay out fire bricks.
We weld the legs from the pro-pipe.
Then you need to make a hole in the base to install the gas burner nozzle.
Drill holes in the brick.
You also need to burn a hole in the metal.
Install the burner.
Then we weld the corners in the corners and make walls with a roof.
The upper part of the rut should be covered with 2 mm metal.
We screw the handle of the gas burner and fix it to the base of the forge legs.
Next, all that remains is to connect a gas cylinder through a flexible rubber hose and start working with metal, for example, forging a knife from a piece of iron.
Thank you for your attention. Tweet
Tweet
18 shared
What is a gas burner?
The prototypes of these devices were wick lamps. Primus stoves without wicks using liquid fuel with burners appeared only in 1892. Gas household appliances began to be used only after the invention of portable cylinders in the 50s. According to their purpose, they are divided into lighting, welding and heating devices. A modern gas burner provides the ability to regulate combustion processes and stable combustion of the working mixture.
Gas burner device
The design of this device may differ depending on its purpose, type of fuel, method of obtaining the air-gas mixture, and size. The simplest portable gas burner consists of the following elements:
- gearbox;
- valve;
- metal case;
- jet;
- heads;
- attachment point.
The principle of operation of a gas burner
The main condition for the normal operation of this device is the effective mixing of fuel with air in the correct proportion and the uninterrupted supply of the finished air-gas mixture to the combustion chamber. The presence of additional elements helps automate ignition, combustion adjustment and shutdown. If we consider this scheme in a simplified way, then a mini gas burner and large units carry out the combustion process according to the following general principle:
- Preparation - gas and air acquire speed, desired temperature and direction of movement.
- Combining air with the required amount of gas to obtain a combustible mixture.
- Combustion - The fuel oxidizes in the firebox or at the exit of the nozzle, releasing intense heat and light.
Rules for safe operation of equipment
If used incorrectly, gas cylinder equipment can become a source of a strong explosion or fire.
When performing welding work, you should definitely use personal protective equipment: glasses, gloves, special shoes.
Before starting work, you need to thoroughly inspect the equipment for damage. If the equipment gets dirty, be sure to remove the dirt
You can work with propane cylinders only in well-ventilated areas, and the air temperature should not be below 0 °C.
Absolutely forbidden:
- Work near open flames.
- Keep the cylinder tilted when working.
- Place the vessels in the sun.
- Carry out work without a gearbox.
- Heat the gearbox over an open fire.
In addition, if you smell gas, you must immediately stop working and turn off the valve on the cylinder. We also recommend that you familiarize yourself with the main reasons for the explosion of gas cylinders.
When working without personal protective equipment, you can get burned, not only from an open flame, but also from accidentally touching hot parts.
If the considered homemade burners are not suitable for you, we recommend that you familiarize yourself with other options for making useful homemade products discussed in our articles - a burner made from a blowtorch and a burner for a sauna stove.
Metal cutting. Equipment and tools for oxygen cutting
The following types of welding are used for metal: oxygen, oxygen-flux, plasma-arc, arc with an electrode, etc. The most widespread are oxygen and plasma cutting, which is divided into separation, the purpose of which is to separate one part of the metal from another, and surface ( fire), the purpose of which is to cut off a layer of metal.
The process of gas plasma oxygen cutting is based on the combustion of metal in an oxygen environment, in which the flame brings the metal to the combustion temperature, and a powerful stream of oxygen burns it and removes the resulting slag. The amount of heat generated when burning metal is quite large. This allows the hot flowing slag to heat the underlying layers of metal (more than 1 mm).
The metal to be cut with oxygen must satisfy the following conditions:
The ignition temperature of a metal in oxygen must be lower than its melting point. This condition is satisfied by steels containing up to 0.7% carbon. Conventional cutting of metals with a high carbon content is not possible. The same thing happens when cutting alloy steels; with increasing impurity content, cutting conditions worsen even with low carbon content;
The melting temperature of metal oxides must be lower than the melting temperature of the base metal. Cast iron and non-ferrous metals do not satisfy this condition, and, therefore, cannot be cut in the usual way;
the cut metal must have minimal thermal conductivity.
For cutting, the same equipment is used as for welding, with the exception of a torch, instead of which a cutter is used (Fig. 4.5).
Figure 4.5. Oxygen cutter
The cutter structurally combines the heating part and the cutting part. The heating part is similar to a welding torch. The cutting part consists of an additional tube 4 for supplying cutting oxygen. The mouthpiece contains two concentrically located holes for the exit of the heating flame 1 and the cutting jet 2. The mouthpiece of the cutter 3 forms a right angle with the barrel. When replacing acetylene with other flammable gases in the cutter, the cross-sections of the injector channels and the mixing chamber are increased. Manual cutting, due to the uneven movement of the cutter and the vibration of the cutting jet, does not provide a high quality cut surface, so the cut cavity is machined.
According to their purpose, cutters are divided into universal ones, which allow cutting of various shapes in any direction, and special ones, intended for certain operations (for cutting holes, etc.), as well as for surface cutting.
Purpose of the forge parts
Now let's go back to the list at the beginning and see what's in the forge for what. And then we’ll get down to making the forge using the samples discussed below or independently, based on the available materials and capabilities.
In industry, tables are mostly lined with quartz refractory brick; it lasts for decades under intense workload. A homemade furnace is usually lined with fireclay bricks, which are cheaper and more accessible. With irregular use, it will also last for years.
A firebox with a grate, an air chamber with drainage and a supply pipe with a valve form the heart of the forge - the tuyere. In industrial designs, replaceable lances are used for different heating methods and heated workpieces. For an amateur or individual craftsman, most often it is enough to have one grate tightly mounted into the table with a solid grate perforated with round holes.
Air drainage is necessary to accurately and quickly regulate the blast without taking your eyes off the workpiece. It will not be possible to forge an underheated part and it will not accept hardening; overheated and overdried, it will tear under a hammer, and in a quenching bath it will at least fail, or even crack. And in any case it will turn out to be unacceptably fragile. How to determine its readiness for forging or hardening by the appearance of a red-hot workpiece is a separate matter. But experienced blacksmiths know that they need to be able to release excess air into the atmosphere in seconds.
The purpose of the chamber, or tent, of the forge, together with its umbrella and chimney, is to remove flue gases from the working area. There are plenty of them released during the preparation of the coal mass (see below), and none of them are good for health. The draft in the chimney needs to be good, because... The front (working) window of the tent and openings for lengthy items (pipes, metal profiles) are constantly open.
As for the quenching bath and gas-air chamber, they may or may not be there, it’s at your discretion. A hardening bath is definitely needed if you are going to forge the so-called. Damascus, damask steel products. They need thermal shock hardening, i.e. from the forge - instantly into the bath.
The gas-air chamber is used in industry:
- For additional drying and heating of air.
- To clean blast air from impurities and condensate.
- For introducing gaseous alloying additives into the air.
At home, super-super special spas are not obtained; The problem of condensation in production occurs when blowing from a common compressed air network. In a low-power furnace, the air heats up sufficiently when passing through the holes of the lance grate, and household gas can be purified from sulfur by passing it through a layer of naphthalene, as mentioned above. In general, make a gas vent, don’t do it, it’s up to you.
Finally, the crucible. This is a heat-resistant cap that expands the extremely high temperature zone. It is installed if non-ferrous or precious metals and alloys are melted in a crucible in a furnace (melting point of gold is 1060 degrees, silver is 960, copper is 1080, brass and bronze is 900), parts are cemented in a muffle, etc. There is no point in looking for an expensive ready-made crucible; in a home forge, it can be completely replaced by a dozen fireclay bricks laid out on a dry surface, piece by piece. In this configuration, a homemade forge will replace an expensive muffle furnace.
Flameless panel burner
1 - tunnel; 2 - nipple; 3 - distribution chamber; 4 — injector; 5 - nozzle; 6 — air regulator; 7 - gas pipeline; 8 - ceramic prisms
Flameless combustion of gas has the following advantages: complete combustion of gas; possibility of gas combustion with small excess air; the ability to achieve high combustion temperatures; combustion of gas with high thermal stress of combustion volume; transfer of a significant amount of heat by infrared rays.
Based on the design of their fire part, existing designs of flameless burners with refractory nozzles are divided into burners with nozzles having channels of irregular geometric shape; burners with nozzles having channels of regular geometric shape; burners in which the flame is stabilized on the fireproof surfaces of the firebox.
The most common are burners with nozzles of regular geometric shape. The refractory nozzles of such burners consist of ceramic tiles measuring 65x45x12 mm. Flameless burners are also called infrared burners.
All bodies are sources of thermal radiation arising due to the vibrational motion of atoms. Each temperature corresponds to a certain range of wavelengths emitted by the body. In this case, heat transfer by radiation occurs in the infrared region of the spectrum, and burners operating on this principle are called infrared radiation burners (figure below).
Which one should I do?
Before we begin manufacturing, we will select the appropriate type of burner from the following list:
- atmospheric injection;
- ejection;
- supercharged.
The second and third types are more difficult to manufacture. And to organize pressurization you will need compressed air or oxygen, which means a compressor or another cylinder.
The easiest way to do it yourself is the first type; it is the one you should prefer.
The atmospheric burner process is controlled by a control valve. Therefore, the choice of type, as well as the model of the device itself, largely depends on which one turns up.
It must be remembered that the combustion of a particular gas depends on the diameter of the nozzle hole. The hydrogen jet has slightly less of it, the propane jet has more.
Designs, diagrams, drawings, assembly technology
First of all, you will need a drawing of the future device, a sketch or diagram of the burner, with dimensions.
It’s easy to find a ready-made one using the Internet. If you understand the general principles of the device’s operation and know how to calculate it, you can develop the project yourself.
An easy option is to use a valve from a propane or oxygen cylinder, known as model VK-74 (see diagram).
A fitting is machined into the side thread, which will also serve as a handle. You can use a pipe of suitable size. On one side, cut an internal thread, on the other, make a shank for putting on the gas hose.
We screw a plug onto the thread with which it is attached to the cylinder. We drill a hole in its end and cut a thread for the jet. We weld a nozzle to the plug on steel spokes, which will also serve as an injection chamber.
It's even easier if you come across an old acetylene cutter or gas cutter. Essentially, this is a finished burner. It is enough to remove the parts connected with the oxygen supply so that they do not interfere, replace the gas nozzle with a nozzle, and attach the injection chamber-nozzle above it.
A very tiny gas burner can be made from a fitting for inflating basketballs, a syringe needle and a couple of droppers, or as they are called medical “systems” for drip administration of drugs. The homemade product can even work from a lighter refill can.
Adjusting roller clamps will act as valves.
True, we will need a forced air supply for this device; the nozzle diameter is too small for injection of atmospheric air. For this purpose, you can use the compressor of an aquarium or an old refrigerator.
Carefully grind off the tip of the syringe needle and fitting. After this, bend the syringe needle slightly and insert it into the side hole of the fitting, so that the end comes out slightly from the cut tip.
We wrap the needle insertion site with copper wire and solder it well with acid.
The burner is ready. All that remains is to connect gas and air to it.
IGK burner: how to buy
Buy IGK burners
various modifications presented in the product catalog of PKF Spetskomplektpribor are possible in several ways.
You can order the required number of Kazantsev injection burners by filling out the intuitive order form at the top of the page. Another purchasing option is to directly contact our managers by phone, email or online dialogue form. If you do not know which specific model of IGK burners you need, our professional consultations will help you avoid making mistakes when selecting this or that equipment.
Return to the general price list for burners
Types of burners used for gas combustion
The choice of the optimal design of the forge burner is related to the issues of the amount of metal waste during heating for forging, the intensity of surface scaling, as well as the total gas consumption. Closed-type furnaces require short-flame burners that provide rapid and intense mixing of the combustible mixture. It is then that the efficiency will be maximum, and the removal of combustion products from the working chamber of the forge will be uniform and efficient.
Thus, the gas burner must provide:
- The greatest angle of inclination of the finished gas-air mixture at the entrance to the working space of the forge.
- High jet exit speed with a low height and large width.
- Gas ignition safety.
- Stability of the combustion process.
- Insensitive to high humidity inside the forge.
- Safety during the so-called “reverse strike”, when a sudden change in the direction of thrust can extinguish the torch, which almost immediately leads to an explosion of the flammable mixture in the furnace.
Gas burner drawings
Gas burner drawing
Burner drawing for a forge
Sketch for a homemade gas burner
Thus, for burning propane (from a cylinder or gas pipeline) the following are used:
- Injector burners providing self-suction of gas. Despite their simplicity, they are characterized by low efficiency, since they allow adjustment of the ratio of components for a relatively small range of values. Regarding a home-made forge, this most often leads to the need to work with a lack of air;
- Burners are tangential type (point jet), when the gas flows along the axis and the air flow tangentially to the mixer body. Mixing here occurs quite intensively, but pressure losses due to turbulence are also large. This affects the unevenness of the amount of air supplied to the forge, and it is greatest where the heated metal comes into contact with the hearth bottom. Accordingly, waste and scale formation increase. The positive quality of tangential burners is their simplicity and reliability;
- Vortex burners, where spiral guide plates are used to mix the flows. In such options, complete mixing occurs only at the mouth, so control by operation in this case is the best, and there is practically no pressure loss. Some of the disadvantages are the design complexity, which is why, even with drawings, making a vortex burner for a forge in a home workshop is very labor-intensive;
- Combined burners that combine tangential and direct-flow supply. The adjustability of the combustible mixture is the best, since by changing the amount of air supplied between the internal and external channels, you can adjust the length of the torch in the forge and, therefore, control the heating time of the workpieces for forging. The disadvantage of such designs is their large dimensions, which may be unacceptable for small forges. Also, the technical complexity of manufacturing a dual-flow burner can be considered a minus.
Scope of application after modification
Gas burners are used in households and agriculture, during construction and repair work, when repairing vehicles and equipment,
In addition to the listed areas, gas appliances are used for the following purposes:
- installation of heat shrink tubes;
- melting the solder before soldering;
- heating metal water pipes;
- heating bitumen for roof repair.
In addition to the above, the device is used for removing paintwork by firing the surface, for welding materials whose melting point is about 1000 C. With its help, you can cook or heat food or boil water for tea right on the construction site.
Blacksmith's forge from a bucket
You can create a forge at home from available materials - for example, an ordinary bucket.
Creating such a furnace is quite simple: holes are made in the walls, the inner surface of the metal is lined with ceramic wool, capable of withstanding temperatures of more than 1200 degrees. Since the bucket has a cone shape, it must be positioned correctly, for which legs are installed.
A hole for the burner is created in the middle part of the forge, and a ventilation hole is cut in the bottom. Fireclay brick, which has increased fire resistance, is placed on the bottom. Finished equipment is often coated with a layer of heat-resistant paint.
Injectorless burners
Considering that high-pressure burners have an injector, the design of such a device is much simpler than that of a low-pressure burner. The figure shows a diagram of the flow of the combustible mixture into a non-injector burner. It works on the following principle:
The polyarylsulfone group contains polymers such as polysulfone, polyphenylsulfone and polyethersulfone, each of which has its own characteristics suitable for a wide range of applications. And therefore they are an excellent choice for electronic applications where high temperature resistance is required.
Plastic products guarantee excellent technical performance, can be easily removed, are more likely to be reused and have a longer service life. These are important features that enable us and our customers to improve sustainable performance.
- Oxygen passes into it through a special rubber hose into valve 1, and then into mixer 3.
- In the mixer, the oxygen flow diverges into small jets and passes further into the mixing nozzle number 4. In the same way, oxygen enters through control valve 2.
- Thanks to mixer 3, the mixture enters mixing chamber 5. An increase in the cross-section of the gas flow helps to reduce its speed, so the mixture of oxygen and gas ends its circulation and provides a homogeneous combustible mixture at the output.
- The resulting mixture enters the tip tube 6, and then through the calibrated channel of the mouthpiece 7, which is made of red copper, comes out and immediately burns, which forms a flammable welding flame.
To provide the correct required flame, this stream must exit the mouthpiece at an exact speed that is equal to the burning rate of the mixture. If this speed is less than normal, then the flame may transfer from the mouthpiece to the top of the burner, which threatens the explosion of the combustible mixture inside the burner itself. If the speed is greater than necessary, the flame will break away from the mouthpiece, move away from its cut and soon die out. Several data will help determine the desired speed: the composition of the combustible mixture, the diameter of the outlet channel and the design of the mouthpiece. It is possible to obtain a constant flow rate of the combustible mixture only by calculating all these values.
These brands are known in the market as materials that guarantee technical quality, reliability and sustainability. This process, which is undergoing continuous development, includes electric servomotors that control the hot needle shut-off system. It accurately, easily and flexibly controls pressure and flow rate during cascade injection. Provides detailed data for the design of plastic parts and injection molds, as well as the injection process as a whole. With the analysis of the molding flow it is also possible to determine the working positions, times and speeds when opening and closing the needles.
High pressure burners are designed for both acetylene and methane or hydrogen. These burners are easy to use and easy to design, and maintain a constant, uninterrupted flow rate of the combustible mixture well. Even with such advantages, injectionless burners are rarely used due to the fact that they require acetylene of sufficient pressure, which is rarely found in production.
The mold was equipped with a five-fold hot system and cavity pressure sensors. Profiling and measuring simple shapes. As a result, the parts showed much better surface quality and the tendency to warp was reduced due to the lower stress. Particularly in the case of cascade injection molding, needle closing servomotors controlling individual nozzles allow precise and individual opening and closing sequences and are matched to selected injection rates.
As a result, the melt flow in the individual hot jets and the volume flow in the cavity can be precisely coordinated and controlled. With the subtle opening and closing of the needle, fears of a drop in the injection pressure of the cascade are prevented and thus eliminate defects arising from the pressure drop in the cavity.
Recommendations
The principle of operation of the device is what you should understand before making the device. You can consider it using the example of a burner for roofing work. How does the burner work?
- The device is connected to the reducers of oxygen and propane cylinders by a system of supply hoses.
- Reducers are placed on the cylinders to create working welding pressure.
- A diagram for gas and oxygen is assembled, the tightness of the connections is checked, the nodes are secured, after which the gas can be opened with valves.
- The gas pressure is set to the operating value and the valve opens.
- The fuel is supplied through hoses to the propane appliance.
- The injector carries out the mixing process to form a gas-air environment.
- A working flame with a temperature reading above 2000 degrees comes out of the device.
When performing any welding work, you must wear personal protective equipment: gloves and goggles, special shoes. You can work with propane cylinders only in a well-ventilated area, and at sub-zero temperatures, any actions with the burner are excluded.
What you should absolutely not do:
- work near open fire;
- keep the cylinder tilted;
- place vessels under the sun;
- carry out work without a gearbox;
- Warm up the gearbox over an open fire.
If you can clearly smell the gas, work with the burner should be stopped by closing the valve on the cylinder. Homemade burners, depending on the purpose of use, can be different: burners with a VK-74 valve, devices converted from an acetylene gas cutter and mini gas burners. It is realistic, profitable, and useful to build every homemade device. Only initially you need to decide on the type of structure and its parameters. The gas burner is also used in private households and for commercial purposes. In plumbing, a metal workpiece is heated with a torch, which ultimately comes out quite hardened.
How to choose a gas burner?
Before purchasing a device, you need to accurately determine the tasks that you plan to solve with its help. We suggest you familiarize yourself with several tips for choosing gas burners for tourism, cottages and home workshops:
- A gas burner with piezo ignition simplifies operation and makes it more comfortable, but often fails in humid conditions.
- Multi-fuel devices are universal; they operate on different types of fuel.
- Simple, unpressurized torch burners are suitable for hiking.
- For delicate work, flame adjustment, ergonomics and balancing are important.
- Travel devices without a hose are more compact, more reliable, but have poor stability.
- Hose-type devices are larger, heavier, but more stable; with an adapter, they can be connected to cylinders of different types.
- The choice of tourist burner by power is 1500 W for two people, up to 3000 W for 4 people, more than 3000 W for a team of 6 people.
- For soldering or firing paint, a power of 500-700 W is required.
- To heat non-ferrous metal and steel up to 3 mm, a power of 1200-1500 W is needed.
- For bending fittings, devices with a power of 2-3 kW are used.
- Devices without an injector produce a less stable flame, especially when turning and tilting, and are not suitable for soldering.
- For soldering cable joints or tubes, a medium-class injection torch with a cone thickness of 3-9 mm is suitable.
- Large devices are used for forging, precision bending, and stamping.
Solid fuel device for forge
The simplest model of a solid fuel device for a private forge is an outdoor open stove, which does not require the installation of a ventilation system. The construction of the structure involves pouring a reinforced concrete base; wall bricks must be laid at the base of the structure. The table is installed at a convenient height; a hole is left in one wall for the blower.
The mountain pit is laid out of fireclay bricks supported on steel corners; a cavity for the grate is left in the middle part of the structure. A chimney or probe will help ensure sufficient draft in the fireplace; the air supply system is installed at the final stage of construction work. Installing an electric fan in the chimney or installing blacksmith bellows will help increase the draft.
In a home forge, a container for hardening parts and a gas-air chamber are not mandatory elements. They can be useful in cases where thermal or shock hardening is required when working with damask steel. In the gas-air chamber the following is carried out:
- drying and heating oxygen;
- filtering oxygen from condensate and foreign impurities;
- mixing air with additives for alloying steel.
To melt precious metals and create an alloy of non-ferrous metals, it is necessary to make a crucible from a heat-resistant material. The device, made in the form of a cap, allows you to increase the operating temperature in the furnace without the risk of overheating the workpiece and the formation of soot.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The injection burner developed by Alexander Kuznetsov is especially popular. In this video, he explains what the structure consists of and how to assemble it:
Example of an injection burner operation:
Properly designed and made with your own hands exactly according to the requirements, the injection burner will become a reliable assistant for a long time. This device will replace expensive factory-made tools. With its help, you can solve many everyday problems without resorting to the help of professionals.
Would you like to tell us about how you assembled an injection torch for blacksmithing with your own hands? Do you have useful information on the topic of the article? Please leave comments in the block form below, ask questions, post photographs.
Video on the topic
In this article we will look at how to make a gas torch for soldering with your own hands. This device is often in demand both in private households and for commercial purposes - for individual technical creativity and various types of construction tasks. In particular, gas burners are used for soldering, metalsmithing, forging, roofing, jewelry work, and for other purposes they produce flames whose temperature exceeds 1500°C.
In metalworking, using a gas torch, you can heat a metal workpiece so that in the end it turns out to be sufficiently hardened. When carrying out welding work with some metals, the areas of future seams must be heated.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The injection burner developed by Alexander Kuznetsov is especially popular. In this video, he explains what the structure consists of and how to assemble it:
Example of an injection burner operation:
Properly designed and made with your own hands exactly according to the requirements, the injection burner will become a reliable assistant for a long time. This device will replace expensive factory-made tools. With its help, you can solve many everyday problems without resorting to the help of professionals.
Would you like to tell us about how you assembled an injection torch for blacksmithing with your own hands? Do you have useful information on the topic of the article? Please leave comments in the block form below, ask questions, post photographs.
Gas safety
Let's start with precautions. Start working with gas from the smallest 5 liter cylinder
Buy a new one and fill it with propane at the nearest gas station. Ask the gas station attendant to tell you how to properly store, transport, refill and use the gas cylinder. He will do this with pleasure, because he is simply bored filling cylinders all day.
Buy a good adjustable gearbox right away. It costs 700-1500 rubles, but this is a small thing when it comes to safety. The pressure gauge should have divisions from 0.1 to 0.6 MPa (mega-pascals)
Attention! The reducer tap does not work like a water tap, but vice versa: to increase the pressure, we need to turn clockwise, i.e. tighten the tap; to reduce the pressure, you need to turn it counterclockwise, i.e.
unscrew the tap
This is important to remember, because in a critical situation we will try to tighten the tap, and this, on the contrary, will only increase the gas pressure - remember this! The burner of a melting furnace, like a burner for a gas forge, usually operates in the pressure range from 0.15 to 0.25 MPa
It’s easier for me to calculate pressure in atmospheres, so it’s 1.5 - 2.5 atmospheres. Don’t turn the gearbox to higher pressure - we simply don’t need it! My gas burner for the melting furnace now operates at a pressure of 1.5 atmospheres, which is enough for liquid aluminum to float in the crucible within 15 minutes
The burner of a melting furnace, like a burner for a gas forge, usually operates in the pressure range from 0.15 to 0.25 MPa. It’s easier for me to calculate pressure in atmospheres, so it’s 1.5 - 2.5 atmospheres. Don’t turn the gearbox to higher pressure - we simply don’t need it! My gas burner for the melting furnace now operates at a pressure of 1.5 atmospheres, which is enough for liquid aluminum to float in the crucible within 15 minutes.
It is strongly recommended to work with gas outdoors. Especially while the gas burner has not yet been configured. In a confined space, 10-15% concentration of propane in the air is enough for an explosion to occur. It is almost impossible to explode in air when working with gas. To explode a 5-liter gas cylinder, you need to throw it into a large fire for 3-4 minutes. Only then will it explode.
It is also highly recommended to use a long gas hose of at least 3-5 meters. The hose must be attached to the gearbox using a clamp with a screw tightening. In addition to the gearbox itself, you also need to acquire some kind of control valve, which would be located directly near the burner. This is necessary so as not to run to the gas cylinder every time to open/close the gas. Fortunately, the cylinder should then be placed around the corner in a special metal cabinet with a padlock. Instead of a faucet, I used another gas torch from an acetylene torch, only instead of a nozzle I connected the hose of my torch.
Portable
The next design is a portable forge made from... goose horn. The design is clear from Fig. The lining is fireclay marl mixed with fireclay sand (ground fireclay bricks, commercially available). Firing the lining after drying - as work progresses.
Portable goose horn
Pressurization is not necessarily a fan from a manual siren, as in Fig. You can use any suitable one, see below, by attaching it with a metal clamp. This, by the way, will make working with long items more convenient. In this case, at the blind end of the air duct, air drainage is required, similar to that for a mobile forge, which will be discussed later.
The capabilities of a goose forge are wider than those of a 6-brick one, because The workspace is larger and open at the top. But there are also significant disadvantages:
- Non-separable design: when cleaning the tuyere (see below about the stationary furnace), carbon deposits fall down and clog the perforation of the air duct, even if its holes are oriented sideways or downwards. To clean you have to break the lining.
- Works only on coke or charcoal, because... There is no table with space for burning.
- Expensive to operate: carbon consumption is comparable to that of coal in real furnaces.
- Low operating temperature, up to 900 degrees, because A lining that is not properly fired will crack.
About cavalry and sewing machines
Cavalry bugle
Once upon a time, every cavalry squadron of all the armies of the world had on its farm a portable forge with a foot drive from a crank mechanism for forging horseshoes and horseshoe nails. It was called cavalry, see fig. If we talk about non-volatile horns, then this is much more convenient than a fan from a siren: both hands are free. Moreover, savvy horsemen taught horses to press the pedal with their hoofs.
Nowadays the cavalry bugle can only be seen in the Red Army Museum. But – let us also be smart – old foot-powered sewing machines are still in use and sold. And this is the same crank with a drive pulley of a suitable diameter and a strong frame for the table. Plus wheels on which you can roll the forge.
Construction of blacksmith bellows
What kind of fan is needed?
Below we will move on to designs that are already quite functional, which require full blowing. And electricity for the fan can be found everywhere. But what kind of fan is needed for a forge? Once upon a time, forges were blown with bellows; For those who are curious about how blacksmith's bellows work, see Fig. on right.
As for productivity, 200-250 l/min is quite enough for a stationary coke furnace. That is, the fan motor power is sufficient from 80-100 W.
Much more important is that we need to push air through a fairly dense mass of sintered fuel
Therefore, when choosing a fan, first of all you need to pay attention to the pressure it creates at zero performance, the so-called
maximum pressure. The meaning of this parameter is simple: the fan will create the maximum pressure by forcing air into a closed cavity.
For the forge you need a maximum pressure of 220-230 mm. Hg Art., which corresponds to approximately 0.3 ati. Axial fans (impellers) of this type are created only by industrial ones, such as VN-2 or its analogues. Household exhaust and industrial cooling systems are not standardized in terms of maximum pressure at all and, as a rule, do not create what is needed.
In addition, they bring the air up to maximum pressure slowly, in minutes, and during delicate forging work, the blast needs to be changed in seconds. It is useless to install a receiver: when the valve is opened, the air in it will expand adiabatically, which at 0.3 ati will only produce zilch.
The final conclusion is that to pressurize the forge you need a centrifugal fan-volute. You don’t need to look at the specification; any centrifugal fan will provide the required maximum pressure based on the very principle of its operation. It is best to take snails from radiation protection systems of military equipment; they also have high productivity. True, the power supply is 12, 24 or 27 V DC, so you will need a transformer and a rectifier of appropriate power.
Any old household vacuum cleaner will work perfectly, but you need to take into account that its power will almost always be excessive. You should not reduce it with an LATR or a thyristor regulator: the motor will work in a difficult mode of excessive rotor slip and the service life of an already worn-out old man will be short. It is best to make a wide air drainage in the tuyere, as in the stationary forge described below.
Waste oil furnace
Considering that petroleum products are expensive, it is beneficial to use a forge using waste oil. To make the forge during mining, parts that have served their useful life are used. After processing the furnaces, a significant drawback emerged - the spent mixture did not ignite well. To eliminate this problem, an additional compartment was built into the mining forge. Here the oil is preheated with coal or wood. To improve combustion, waste fuel passes through filters and diesel fuel or gasoline is added to it.
As a result, the mining forge has the advantages of a yellow flame and stable temperature.
You can make it yourself:
- It is made from fireclay bricks, dimensions: 85×48×40 cm.
- The vault is made in the form of an arch to maintain temperature.
- The body is completely covered with sheets of iron. A thickness of 1.5 mm is used on the sides, and the top and bottom are lined with 2 mm sheets.
- The supports are made from angles based on the weight of the structure.
Air is pumped into the chamber by a fan. A waste tank is installed on a hill. From it, the oil enters the chamber through a pipeline, where it is picked up by air, which moves under a pressure of 2 atm. The waste is broken up and fed into the nozzle.
Scheme of the furnace during development:
DIY burner - drawings
The inner diameter of the liner tube (1) should be 0.5 mm smaller compared to the inner diameter of the nozzle. A washer (2) with air holes is welded inside. The sleeve (2) secures the tube with the nipple.
The design differs in that when moving the tab in the nozzle, it is possible to adjust the air suction through the ventilation holes - and, as a result, adjust the fire temperature over a wide range.
Read also: What washing machines are not made in Russia
Parameters for making a soldering torch
Firstly, the device must be made of refractory metals. With a properly adjusted burner, temperatures in excess of 1000°C can be achieved. Secondly, the burner must be equipped with a reliable operating valve, which will shut off the gas supply in the event of a dangerous situation. Thirdly, you need to use a reliable connection to a tank with a valve or a 5-liter propane tank with a reducer, which will eliminate the risk of accidents.
Below is a typical diagram and principle of operation of an injection gas burner: