What is a hydrochloric acid solution? It is a compound of water (H2O) and hydrogen chloride (HCl), which is a colorless thermal gas with a characteristic odor. Chlorides dissolve well and break down into ions. Hydrochloric acid is the most famous compound that forms HCl, so we can talk about it and its features in detail.
Description
A solution of hydrochloric acid belongs to the class of strong. It is colorless, transparent and caustic. Although technical hydrochloric acid has a yellowish color due to the presence of impurities of chlorine, iron and other elements. The air “smoke”.
It is worth noting that this substance is present in the body of every person. In the stomach, to be more precise, in a concentration of 0.5%. Interestingly, this amount is enough to completely destroy a razor blade. The substance will corrode it in just a week.
Unlike sulfuric acid, by the way, the mass of hydrochloric acid in solution does not exceed 38%. We can say that this indicator is a “critical” point. If you start to increase the concentration, the substance will simply evaporate, as a result of which hydrogen chloride will simply evaporate along with the water. Plus, this concentration is maintained only at 20 °C. The higher the temperature, the faster evaporation occurs.
Physical properties
The physical properties of HCl correlate with the concentration of this compound in solution. In order not to be overloaded with numbers, let's consider the physical properties of hydrogen chloride using the example of its concentrated form (about 36%):
- low boiling point (t=48 degrees Celsius);
- high melting point (t=30 degrees Celsius);
- density is 1.18 g/cm3;
- Hydrogen chloride has the ability to ionize in aqueous solutions.
- at low temperatures it acquires a hydration shell: HCL*H20 or HCl*2H2O;
- solutions of hydrochloric acid, colorless;
- in its pure form it is in a gaseous state of aggregation (and in solutions it is in liquid form);
- in humid air, concentrated HCl solutions can smoke strongly;
- hydrochloric acid is a substance with a pungent odor.
Interaction with metals
A solution of hydrochloric acid can undergo many reactions. First of all, with metals that come before hydrogen in the series of electrochemical potentials. This is the sequence in which the elements proceed as their inherent measure, the electrochemical potential (φ0), increases. This indicator is extremely important in half-reactions of cation reduction. In addition, it is this series that demonstrates the activity of metals in redox reactions.
So, interaction with them occurs with the release of hydrogen in the form of gas and the formation of salt. Here is an example of a reaction with sodium, a soft alkali metal: 2Na + 2HCl → 2NaCl +H2↑.
With other substances, interactions proceed according to similar formulas. This is what the reaction with aluminum, a light metal, looks like: 2Al + 6HCl → 2AlCl3 + 3H2↑.
Means of protection
- Respiratory protection with respirators. Respirators should only be used in the following situations: ✔ Respirators should be used as a last resort (that is, after all engineering and administrative measures have been taken to control the situation). ✔ If the permissible exposure level is exceeded or if there is a risk of such an excess. ✔ In accordance with current regulations. ✔ There is a risk of harmful effects due to air pollution. ✔ As PPE in case of chemical spill response. Laboratory staff using respirator masks must be trained in the use of personal protective equipment.
- Protect your eyes with safety glasses. At high acid concentrations, the use of glasses is mandatory.
- Skin and body protection. Laboratory personnel working with chemicals must wear full-length trousers or equivalent, closed-toe shoes, and a lab coat.
- Compliance with sanitary and hygienic measures: after handling the material, wash your hands thoroughly.
Reactions with oxides
Hydrochloric acid solution also interacts well with these substances. Oxides are binary compounds of an element with oxygen that have an oxidation state of -2. All known examples are sand, water, rust, dyes, carbon dioxide.
Hydrochloric acid does not interact with all compounds, but only with metal oxides. The reaction also produces soluble salt and water. An example is the process that occurs between an acid and magnesium oxide, an alkaline earth metal: MgO + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2O.
Why is intoxication dangerous?
Hydrochloric acid poses a particular danger to the human body. In case of poisoning with such a substance, serious complications and disturbances in the functionality of the body may develop.
Complications:
- Impaired liver function, as a result of toxic hepatitis,
- Bleeding in the stomach due to destroyed walls of the organ,
- Shock from pain when acid hits a large area,
- If it gets in the eyes, visual impairment may occur,
- Serious problems with the kidneys,
- Impaired breathing, suffocation, lack of air,
- Development of a coma.
Such consequences develop gradually depending on the degree of poisoning.
Reactions with hydroxides
This is the name given to inorganic compounds that contain a hydroxyl group –OH, in which the hydrogen and oxygen atoms are connected by a covalent bond. And, since a solution of hydrochloric acid reacts only with metal hydroxides, it is worth mentioning that some of them are called alkalis.
So the resulting reaction is called neutralization. Its result is the formation of a weakly dissociating substance (i.e. water) and salt.
An example is the reaction of a small volume of solution of hydrochloric acid and barium hydroxide, a soft alkaline earth malleable metal: Ba(OH)2 + 2HCl = BaCl2 + 2H2O.
Formula and other names of hydrochloric acid
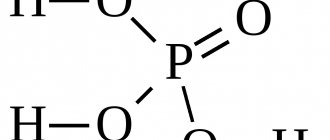
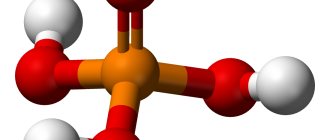
Hydrochloric acid contains two chemical elements: chlorine and hydrogen. This acid consists of two atoms and has the formula: HCl. It is worth noting that hydrochloric acid is a trivial name (i.e., a name used in everyday speech by chemists that does not reflect its composition). According to the international IUPAC nomenclature, a substance with the formula HCl is usually called hydrochloric acid. Sometimes HCl is called hydrochloric acid or hydrogen chloride, or hydrogen chloride is also an acceptable name.
Interaction with other substances
In addition to the above, hydrochloric acid can react with other types of compounds. In particular with:
- Metal salts that are formed by other, weaker acids. Here is an example of one of these reactions: Na2Co3 + 2HCl → 2NaCl +H2O + CO2↑. Shown here is the interaction with a salt formed by carbonic acid (H2CO3).
- Strong oxidizing agents. With manganese dioxide, for example. Or with potassium permanganate. Such reactions are accompanied by the release of chlorine. Here is one example: 2KMnO4 +16HCl → 5Cl2↑ + 2MnCl2 + 2KCl + 8H2O.
- Ammonia. This is hydrogen nitride with the formula NH3, which is a colorless but pungent-smelling gas. The consequence of its reaction with a solution of hydrochloric acid is a mass of thick white smoke consisting of small crystals of ammonium chloride. Which, by the way, is known to everyone as ammonia (NH4Cl). The interaction formula is as follows: NH3 + HCl → NH4CL.
- Silver nitrate is an inorganic compound (AgNO3), which is a salt of nitric acid and silver metal. As a result of the contact of a hydrochloric acid solution with it, a qualitative reaction occurs - the formation of a cheesy precipitate of silver chloride. Which does not dissolve in nitrogen. It looks like this: HCL + AgNO3 → AgCl↓ + HNO3.
How to get rid of blockages?
For tough and targeted cleaning of sewers from organic deposits (fats, food debris, hair, detergents, etc.), dilute hydrochloric acid should be used. This method is not suitable for steel, iron and plastic pipes, since the connection can lead to corrosion and even the formation of through holes.
Before starting the procedure, you need to close the drain holes in other plumbing fixtures and ensure air flow into the room. This step is necessary, since during operation the acid will begin to actively produce toxic gases.
It is recommended to dilute the composition with water until a concentration of 3-10% is reached, then pour directly into the sewer and leave for 1-2 hours. Then you need to rinse the pipes with plenty of water and repeat the procedure if necessary.
Important point! The reagent should not be mixed with other drain cleaners, especially those based on alkalis. Otherwise, the reaction of these connections will cause severe damage to the pipes.
Obtaining the substance
Now we can talk about what is done to form hydrochloric acid.
First, by burning hydrogen in chlorine, the main component, hydrogen chloride gas, is obtained. Which is then dissolved in water. The result of this simple reaction is the formation of a synthetic acid.
This substance can also be obtained from exhaust gases. These are chemical waste (by-product) gases. They are formed through a variety of processes. For example, during the chlorination of hydrocarbons. The hydrogen chloride contained in them is called off-gas. And the acid obtained in this way, respectively.
It should be noted that in recent years the share of waste substances in the total volume of its production has been increasing. And the acid formed due to the combustion of hydrogen in chlorine is displaced. However, to be fair, it should be noted that it contains fewer impurities.
How does poisoning occur?
Hydrochloric acid is a liquid substance without color, but with a characteristic pungent odor. One of the strongest acids, capable of dissolving some metals. Easily turns into gas.
Hydrogen chloride is used in the textile industry, tanning, metallurgy of precious metals, in the production of glue and acids.
The substance is present in the stomach in minimal concentration. Acid helps normalize the digestive process, protects the body from harmful bacteria and microorganisms.
At a concentration exceeding 24%, hydrochloric acid can cause irreversible harm to the human body. Vapors formed upon contact with air cause irritation to the visual and respiratory systems. There are several factors that can provoke the development of poisoning.
Factors:
Intoxication with vapors is possible when working in rooms with poor ventilation, ingestion through negligence, more often occurs in children, contact with hydrochloric acid on the epidermis, mucous membrane if the rules for using the reagent are not followed.
Poisoning of the substance at home in adults occurs as a result of use without protective equipment for the skin, eyes, and respiratory system. Intoxication can occur when acid is inaccurately poured from one container to another.
Use in everyday life
Many cleaning products that householders use regularly contain a certain proportion of hydrochloric acid solution. 2-3 percent, and sometimes less, but it is there. That is why, when putting the plumbing in order (washing tiles, for example), you need to wear gloves. Highly acidic products can harm the skin.
The solution is also used as a stain remover. It helps remove ink or rust from clothes. But for the effect to be noticeable, you need to use a more concentrated substance. A 10% hydrochloric acid solution is suitable. By the way, it removes scale perfectly.
It is important to store the substance correctly. Keep the acid in glass containers and in places where animals and children cannot reach. Even a weak solution that gets on the skin or mucous membrane can cause a chemical burn. If this happens, it is necessary to immediately rinse the areas with water.
Industrial use
It is widely used in the metallurgical, food and medical industries.
- Metallurgy. Application in soldering, tinning and stripping of metals.
- Food industry. Application in the production of food acidity regulators, for example, E507.
- Electrotype. Used for etching.
- Medicine. Finds its application in the production of artificial gastric juice.
Included in synthetic dyes. Used in the production of cleaning products and detergents. But in liquids intended for household use, the concentration of sulfuric acid is insignificant.
In the field of construction
The use of hydrochloric acid and its solutions is a popular way to improve many construction processes. For example, it is often added to a concrete mixture to increase frost resistance. In addition, this way it hardens faster, and the resistance of the masonry to moisture increases.
Hydrochloric acid is also used as a limestone remover. Its 10% solution is the best way to combat dirt and marks on red brick. It is not recommended to use it to clean others. The structure of other bricks is more sensitive to the effects of this substance.
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
What is gastric acidity? This is a characteristic of the concentration of Hydrochloric Acid in the stomach. Acidity is expressed in pH
.
Normally, gastric juice should produce acid and take an active part in the digestive process. Hydrochloric acid formula: HCl
.
It is produced by parietal cells located in the fundic glands, with the participation of H+/K+-ATPase
. These cells line the fundus and body of the stomach. The acidity of gastric juice itself is variable and depends on the number of parietal cells and the intensity of the processes of neutralization of the substance by the alkaline components of gastric juice. The concentration of the drug produced is stable and equal to 160 mmol/l. A healthy person should normally produce no more than 7 and no less than 5 mmol of the substance per hour.
With insufficient or excessive production of Hydrochloric Acid, diseases of the digestive tract occur, and the ability to absorb certain microelements, such as iron, deteriorates. The product stimulates the secretion of gastric juice, reduces pH
.
Activates pepsinogen
, converts it into the active enzyme
pepsin
. The substance has a beneficial effect on the acid reflex of the stomach and slows down the transition of incompletely digested food into the intestines. The fermentation processes of the contents of the digestive tract slow down, pain and belching disappear, and iron is better absorbed.
After oral administration, the drug is partially metabolized by saliva and gastric mucus, the contents of the duodenum. The unbound substance penetrates the duodenum, where it is completely neutralized by its alkaline contents.
In medicine
In this area under consideration, the substance is also actively used. Dilute hydrochloric acid has the following effects:
- Digests proteins in the stomach.
- Stops the development of malignant tumors.
- Helps in the treatment of cancer.
- Normalizes acid-base balance.
- Serves as an effective remedy for the prevention of hepatitis, diabetes, psoriasis, eczema, rheumatoid arthritis, cholelithiasis, rosacea, asthma, urticaria and many other ailments.
In general, a useful drug. If a person has low acidity of gastric juice, then it will not hurt him to take a course of medications that contain hydrochloric acid. A good option is Ortho Taurine Ergo. It increases the level of hydrochloric acid in the gastric environment, helps fight bacteria and parasites.
Did you come up with the idea of diluting the acid and using it internally in this form, and not as part of medications? This is practiced, but it is strictly forbidden to do this without medical advice and instructions. By incorrectly calculating the proportions, you can swallow an excess of hydrochloric acid solution and simply burn your stomach.
By the way, you can still take medications that stimulate the production of this substance. And not only chemical ones. The same calamus, peppermint and wormwood contribute to this. You can make decoctions based on them yourself and drink them for prevention.
How and why they are used
Perhaps this is rightfully one of the important substances that is found and necessary in almost all sectors of human life.
Localization of application:
- Metallurgy. Cleaning surfaces from oxidized areas, dissolving rust, processing before soldering, tinning. Hydrochloric acid helps to extract small inclusions of metals from ores. Zirconium and titanium are obtained using a method of converting oxides into chlorides.
- Food technology industry. A low concentration solution is used as a food additive. Gelatin and fructose for diabetics contain a pure emulsifier. Regular soda also has a high content of this substance. On the product packaging you will see it called E507.
- Field of medicine. In case of insufficient acidity in the stomach and problems with the intestines. Low Ph levels lead to cancer. Even with proper nutrition and plenty of vitamins, the danger does not disappear; it is necessary to carry out tests to obtain juice from the gastric tract, because in an insufficiently acidic environment, beneficial substances are practically not absorbed and digestion is impaired.
- The salt solution is used as an inhibitor - protection against dirt and infections, antiseptic effect. For the production of adhesive mixtures and ceramic products. Heat exchangers are washed with it.
- The procedure for purifying drinking water is also not complete without the participation of chlorine.
- Production of rubber, bleaching of fabric bases.
- You can care for your lenses using this solution.
- Mouth rinse at home
- The substance conducts electricity well.
Burns and poisoning
No matter how effective this remedy is, it is dangerous. Hydrochloric acid, depending on the concentration, can cause four degrees of chemical burns:
- There is only redness and pain.
- Blisters with clear liquid and swelling appear.
- Necrosis of the upper layers of skin is formed. The blisters fill with blood or cloudy contents.
- The lesion reaches the tendons and muscles.
If the substance somehow gets into your eyes, you need to rinse them with water and then with a soda solution. But in any case, the first thing you need to do is call an ambulance.
If acid gets inside, it can cause acute pain in the chest and abdomen, swelling of the larynx, and bloody vomit. As a result - severe pathologies of the liver and kidneys.
And the first signs of vapor poisoning include a dry, frequent cough, choking, damage to teeth, burning in the mucous membranes and abdominal pain. First emergency aid is washing and rinsing the mouth with water, as well as access to fresh air. Only a toxicologist can provide real help.
First aid and emergency therapy
In case of inhalation poisoning, the victim must be immediately taken out into fresh air and given oxygen inhalation. The throat should be rinsed with 2% sodium bicarbonate solution, and the eyes and nose should be rinsed with the same solution. If there is difficulty breathing, instill 4-5 drops of 2-3% ephedrine solution into the nose 3-4 times a day, and inject 1 ml of 0.1% atropine solution subcutaneously. In severe cases of S. aerosol poisoning, inhalation of antibiotic aerosols is used for the prevention and treatment of pneumonia, and a course of treatment with antibiotics and sulfonamides is prescribed.
If a high concentration of S. comes into contact with the skin, it is necessary to immediately wash the skin with water for 5-10 minutes. (preferably 2-4% sodium bicarbonate solution); further treatment is symptomatic (see Burns).
In case of eye damage, after washing with sodium bicarbonate solution, 1 drop of 2% novocaine solution or 0.5% dicaine solution with adrenaline (1:1,000) is instilled into the eyes, then sterile vaseline or peach oil is placed in the conjunctival sac . Subsequent treatment consists of instilling 30% Albucid solution into the eyes and using hydrocortisone eye ointment.
In case of oral poisoning, it is necessary to urgently rinse the stomach through a tube with water and then carry out symptomatic treatment (see Poisoning).
Buffer solution
Solutions that maintain their pH level when a small amount of a strong acid or a strong base is added are mainly composed of:
- A mixture of a weak acid, its corresponding salt and a weak base
- Weak base, corresponding salt and strong acid
To prepare a buffer solution of a certain acidity, it is necessary to mix a weak acid or base with the appropriate salt, taking into account:
- pH range in which the buffer solution will be effective
- Solution capacity - the amount of strong acid or strong base that can be added without affecting the pH of the solution
- There should be no unwanted reactions that could change the composition of the solution
Storage and transportation
Industrial hydrochloric acid is stored and transported in specialized polymer-coated tanks and containers, polyethylene barrels, glass bottles packed in boxes. Hatches of containers and tanks, caps of barrels and bottles must ensure the tightness of the container. The acid solution should not come into contact with metals located in the voltage line to the left of hydrogen, as this can cause explosive mixtures.
History of discovery
It is difficult to say who and when first received hydrochloric acid. It is known that already at the end of the 15th century. alchemist Vasily Valentin and in the 16th century. Andreas Libawe, in an executive search for a miraculous vital elixir, calcined table salt with alum and vitriol in their alchemical instruments and obtained a product that was described as “sour alcohol.” This was the hydrochloric acid we now knew, very unclean.
For the first researchers, it was a completely new substance, with properties that greatly amazed their imagination. Sniffing it, they choked and coughed, “sour alcohol” fumes in the air. When tasted, it burned the tongue and palate, it corroded metals and destroyed tissues.
In 1658, the German chemist I. Glauber (1604-1670) found a new method for producing hydrochloric acid, which he called “hydrochloric alcohol.” This method is still widely used in laboratories. He heated table salt with concentrated sulfuric acid and absorbed the “smoke” that was released with water.
In 1772, the English chemist Joseph Priestley (1733-1804) found that the action of sulfuric acid on table salt releases a colorless gas that can be collected over mercury, and this gas has a very high ability to dissolve in water. An aqueous solution of this gas was called “hydrochloric acid” (acidum muriaticum), and the gas itself was called “pure gaseous hydrochloric acid” by Priestley.
In 1774, the Swedish chemist K.V. Scheele (1742-1786), studying the effect of hydrochloric acid (which he also called “hydrochloric alcohol”) on manganese (IV) oxide, found that it dissolves in hydrochloric acid in the cold, forming a dark brown solution, from which it separates when heated a yellow-green gas with a very pungent odor, the ability to destroy vegetable dyes and affects all metals, not excluding gold. Scheele, as a follower of the phlogiston theory that was dominant at that time, believed that the meaning of this reaction is that under the influence of manganese (IV) oxide with hydrochloric acid, phlogiston leaves it, due to which hydrochloric acid turns into a yellow-green gas. Therefore, he called the gas itself “dephlogisticated with hydrochloric acid.”