- Characteristics
- Areas of application
- Operating rules
- Anti-rust application
- Application for metal
Often metal and products made from it are subject to a characteristic “disease”, which manifests itself in the form of a red coating that corrodes the metal. We're talking about rust. Its formation occurs due to the effect of carbon dioxide, oxygen and water on the surface of a metal product. Of course, in order to extend the life of a metal product, it is necessary to begin the fight against corrosion as soon as possible. Treatment with phosphoric acid can help with this.
Characteristics of orthophosphoric acid
Hearing the word acid, a person involuntarily tenses up, because even from old chemistry lessons in school years it is known that acid can have a fairly significant effect on objects or, for example, human skin. What is orthophosphoric acid? Is phosphoric acid, the use of which is recommended as one of the ways to combat rust, dangerous?
Orthophosphoric or simply phosphoric acid is presented in the form of a product of inorganic origin. At normal room temperature, orthophosphoric acid has the form of small diamond-shaped crystals.
Most often, orthophosphoric acid has the form of a syrupy 85% solution that has no characteristic odor. Orthophosphoric acid crystals dissolve quite well in water or ethanol.
Phosphoric acid equation
Phosphoric acid is used in the following sectors of human activity:
- Creation of fertilizers (phosphate),
- Production of special cleaning products belonging to the class of household chemicals,
- Dentistry,
- Substances to combat metal corrosion,
- Fur farming,
- Food industry.
If the ambient temperature, for example, in laboratory conditions exceeds 213 degrees Celsius, orthophosphoric acid is converted into pyrophosphoric acid. The composition of orthophosphoric acid and its chemical formula change accordingly.
Table 1. Physico-chemical parameters of orthophosphoric acid according to GOST 10678-76.
| Indicator name | Norm | ||
| Grade A | Brand B | ||
| 1st grade | 2nd grade | ||
| 1. Appearance | Colorless liquid transparent in a layer of 15-20 mm when viewed against a white background | Colorless or slightly yellowish liquid in a 15-20 mm layer when viewed against a white background | Colorless or colored liquid with a tint from slightly yellow to brown, not transparent in a layer of 15-20 mm when viewed on a white background |
| 2. Mass fraction of orthophosphoric acid (H3PO4), %, not less | 73 | 73 | 73 |
| 3. Mass fraction of chlorides, %, no more | 0,005 | 0,01 | 0,02 |
| 4. Mass fraction of sulfates, %, no more | 0,010 | 0,015 | 0,020 |
| 5. Mass fraction of nitrates, %, no more | 0,0003 | 0,0005 | 0,0010 |
| 6. Mass fraction of iron, %, no more | 0,005 | 0,010 | 0,015 |
| 7. Mass fraction of heavy metals of the hydrogen sulfide group, %, no more | 0,0005 | 0,002 | 0,005 |
| 8. Mass fraction of arsenic, %, no more | 0,0001 | 0,006 | 0,008 |
| 9. Mass fraction of reducing substances, %, no more | 0,1 | 0,2 | Not standardized |
| 10. Presence of metaphosphoric acid | Stands the test | ||
| 11. Mass fraction of suspended particles, %, no more | Stands the test | 0,3 | |
| 12. Presence of yellow phosphorus | Stands the test | Not standardized | |
Table 2. Physico-chemical parameters of orthophosphoric acid according to GOST 6552-80.
| Indicator name | Norm | ||
| Chemically pure (reagent grade) OKP 26 1213 0023 08 | Pure for analysis (analytical grade) OKP 26 1213 0022 09 | Clean (h.) OKP 26 1213 0021 10 | |
| 1. Appearance and color | Transparent, colorless liquid containing no suspended particles | ||
| 2. Mass fraction of orthophosphoric acid (H3PO4), %, not less | 87 | 85 | 85 |
| 3. Density P420, g/cm3, not less | 1,71 | 1,69 | 1,69 |
| 4. Mass fraction of residue after calcination, %, no more | 0,05 | 0,1 | 0,2 |
| 5. Mass fraction of volatile acids (CH3COOH), %, no more | 0,0004 | 0,0010 | 0,0015 |
| 6. Mass fraction of nitrates (NO3), %, no more | 0,0003 | 0,0005 | 0,0005 |
| 7. Mass fraction of sulfates (SO4), %, no more | 0.0005 | 0.002 | 0.003 |
| 8. Mass fraction of chlorides, (Cl)%, no more | 0.0001 | 0.0002 | 0.0003 |
| 9. Mass fraction of ammonium salts (NH4), %, no more | 0,0005 | 0,002 | 0,002 |
| 10. Mass fraction of iron (Fe), %, no more | 0,0005 | 0,001 | 0,002 |
| 11. Mass fraction of arsenic (As), %, no more | 0.00005 | 0.0001 | 0.0002 |
| 12. Mass fraction of heavy metals (Pb), %, no more | 0,0005 | 0,0005 | 0,001 |
| 13. Mass fraction of substances reducing KMnO4 (H3PO3), %, no more | 0.003 | 0.005 | 0.05 |
Price
Phosphoric acid can be purchased in pharmacies, hardware stores, and ordered through Internet sites. For industrial purposes, they are purchased in bulk at discounts. The average cost for Moscow in rubles is:
| Quantity, liter | Average price, rub. | |
| Food thermal | 1 | 400 |
| Technical 85% | 0,8 | 380 |
| 1600 | 13500 | |
| Soldering flux | 0,01 | 180 |
| 0,003 | 40 | |
| Food additive E388 | 1 | 85 |
Applications of phosphoric acid
Modern science quite often allows the same chemical substance or the same chemical composition to be used for completely different purposes. The same can be said about the options for using phosphoric acid.
Today, there are a considerable number of different areas of application of orthophosphoric acid. So, for example, this acid can be used in organic synthesis. It is used in cases where it is necessary to create phosphorus salts of sodium, calcium, aluminum, and manganese.
The use of orthophosphoric acid in the metalworking industry is also of great importance, since orthophosphoric acid is practically irreplaceable here, the effect of which has been proven in removing rust or preventing its occurrence.
Phosphoric acid can also be found in a large number of substances intended for use by housewives in everyday life. It is also known to be used in the medical and food industries.
Other areas where phosphoric acid can be used include:
- Oil industry
- Making matches,
- Film production,
- Production of fire-resistant or fire-resistant items and materials.
The role of orthophosphoric acid is also great in the process of feeding plants, since the beneficial effect of phosphorus on the ability of plants to produce high yields is widely known. Thanks to this acid, agricultural crops become resistant to frost and other unfavorable conditions.
The beneficial effect on the soil is also noted in many sources related to the subject of agriculture or the national economy.
The importance of orthophosphoric acid is also important for animals. Not only does it, together with other organic substances, participate in the metabolic processes of the animal body, but it also helps in the formation of shells and other natural growths in some species of animals, since they contain calcium phosphate.
Phosphoric acid is also used as a food additive in some food products. It has code E 338. This acid finds its purpose in the food industry in the production of sausages, some types of processed cheeses, and carbonated drinks.
It should be noted that you should not abuse food products that contain orthophosphoric acid, since it is not clear what the rate of human consumption per day is. But in any case, the benefit from its consumption is disproportionately small, if not even negligible, in comparison with the harm that it can cause in the form of disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, the occurrence of caries, and the development of osteoporosis.
Receipt
Laboratory methods of obtaining
Phosphoric acid is obtained in laboratory conditions from (V) oxide
P2O5 + 3H2O = 2H3PO4.
The reaction proceeds violently, so it is better to obtain it in this way in industry.
Phosphoric acid can be obtained from phosphates by the action of hydrochloric or sulfuric acid:
Na3PO4 + 3HCI = 3NaCI + H3PO4.
phosphorus (V) can be hydrolyzed
2PCl5+ 8H2O = 2H3PO4 + 10HCl.
Receipt in industry
In industry, the purest phosphoric acid is obtained thermally, for which phosphorus is burned:
4P +5O2 = 2P2O5.
Phosphoric anhydride reacts with water too violently, so phosphoric anhydride is mixed with phosphoric acid heated to 200°C in a concentration of 50-60%. The resulting acid is diluted and partially restarted in the process.
There is an extraction method for obtaining phosphoric acid directly from ores, for example, from apatite:
Ca5(PO4)3F + 5H2SO4 + n H3PO4 + 3H2O = (n+3) H3PO4+ 5CaSO4 H2O + HF.
Rules for working with phosphoric acid
Like any other acid, phosphoric acid requires a person to be extremely attentive, careful and follow all safety rules when working with acids.
Orthophosphoric acid is a rather aggressive chemical if used incorrectly, and neglect of safety precautions when using an orthophosphoric compound can cause burns on the skin. Vapors of phosphoric acid can cause burns to the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract, as well as the manifestation of signs of serious intoxication of the human body. In addition, phosphoric acid is a flammable and explosive compound. That is why it is very important to follow the prescribed rules when working with phosphoric acid.
Rules for working with orthophosphoric acid.
- Work with acid only in a well-ventilated area.
- When working with acid, special attention should be paid to protective equipment in the form of gloves, a mask or, better yet, a respirator and goggles to protect the eyes.
- Do not allow acid to come into contact with exposed areas of the body, otherwise severe burns may occur.
- If acid does get on the skin, it should be washed off as soon as possible with plenty of running water and be sure to go to the hospital.
Transportation and storage of orthophosphoric acid also requires compliance with certain conditions.
Acid can only be stored in glass containers, as well as in polymer and stainless steel vessels.
The reagent can be transported only in special vehicles equipped with metal tanks that are not exposed to acid. Transportation is also permitted by other modes of transport, such as trains or watercraft, but subject to full compliance with safety requirements.
The storage conditions for the acid include placing it in a place where sunlight does not penetrate. The orthophosphorus compound can be stored under such conditions for no more than one year.
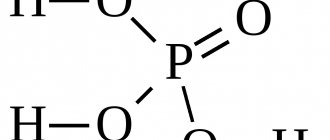
Formula
Phosphoric acid is an inorganic compound that is described by the formula H3PO4. Its molar mass is 98 g/mol. A microparticle of a substance is built in space in such a way that it connects hydrogen and oxygen atoms with each other. The formula shows that the chemical substance has the following composition:
| Number of atoms | Mass percentage | |
| Hydrogen | 3 | 3,1 |
| Phosphorus | 1 | 65,3 |
| Oxygen | 4 | 31,6 |
Use of phosphoric acid against rust
Phosphoric acid, whose effect on rust is widely known, can be used both on an industrial scale and to remove metal corrosion at home. Of course, such actions must be carried out taking into account the safety rules described above.
A clear advantage of phosphoric acid is that under the conditions of chemical cleaning from the surface of a metal using phosphoric acid, it is possible not only to remove loose oxidized masses, but also to create a small protective film on the surface of the metal product. The formation of such a film occurs as follows: the iron oxide is corroded and absorbed by the acid, instead the metal surface is phosphorized. People who carry out a similar cleaning procedure testify that after removing rust by using phosphoric acid, an oily film of a gray hue forms on the surface of the metal product.
At this stage, we can name several basic ways to combat the formation of oxides on metal surfaces:
- Metal etching, which involves complete immersion in an acid solution,
- Spraying the compound using a spray gun or applying it using a roller,
- Mechanical cleaning of metal from oxides followed by the use of acid.
The most suitable and effective method for cleaning metal from corrosion is selected in each specific case, taking into account the individual conditions in which the procedure can be carried out.
Transportation rules
There are special GOSTs that stipulate the rules for transporting phosphoric acid, which is classified as dangerous goods. The substance can be delivered by any type of transport. The chemically active liquid is transported in tightly closed:
- steel tank trucks;
- bottles made of polyethylene, glass;
- plastic cubes;
- barrels;
- cans;
- rubberized railway tanks.
Physical properties
In its pure form, phosphoric acid is a colorless crystalline substance with a melting point of 42.35 °C. The crystals have a monoclinic system. Solid phosphoric acid is hygroscopic and diffuses in air; It is miscible with water in all proportions, but is usually commercially available in three concentrations:
- 75% H3PO4 (mp -20 °C);
- 80% H3PO4 (mp 0 °C);
- 85% H3PO4 (mp 20 °C).
From 85% phosphoric acid, anhydrous acid can be obtained by evaporating water in a vacuum at 80 °C. From concentrated solutions it precipitates in the form of hemihydrate H3PO4 0.5H2O.
In the solid state and concentrated solutions, hydrogen bonds exist between phosphoric acid molecules. When the concentration decreases to 40-50%, the hydrogen bond between phosphate anions and water molecules becomes more stable. Also in solutions, phosphoric acid exchanges oxygen atoms with water.
Recommendations
- Harwood, Lawrence M.; Hodgkinson, Leslie C.; Sutherland, James K.; Towers, Patrick (1984). “Synthesis of anthracyclines. Part 1. Regioselective alkylation of 5-hydroxyquinisarine." Canadian Journal of Chemistry
.
62
(10): 1922–1925. Doi:10.1139/v84-329. - Nakazawa, Koichi; Matsuura, Shin; Kusuda, Kosuke (1954). “Research on the use of polyphosphoric acid as a condensing agent. II". Yakugaku Zasshi
.
74
(5):495–497. doi:10.1248/yakushi1947.74.5_495. - "Phosphoric acid and phosphates." Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology
. New York: Interscience Encyclopedia, Inc., 1953. p. 421. - "Polyphosphates for protection against scale and corrosion." Tramfloc, INC. January 2009. Retrieved December 23, 2010.
- "Ortho-polyphosphate corrosion inhibitors" (PDF). Government Engineering: A Journal of Public Infrastructure
(September–October 2006): 48–49. Retrieved December 23, 2010. - Parmar, Dixit; Sugiono, Early; Raja, Sadia; Ruping, Magnus (2014). “A Complete Guide to Asymmetric Acid BINOL Phosphate and Metal Catalysis: History and Classification by Mode of Activation; Bronsted acidity, hydrogen bonding, ion pairing and metal phosphates.” Chemical Reviews
.
114
(18):9047–9153. Doi:10.1021/cr5001496. PMID 25203602.
external reference
- Determination of polyphosphates using ion chromatography with suppressed conductivity detection, instructions for use 71 from Dionex
- USA 3044851
Phosphorus compounds | |
|
Safety precautions
As a non-flammable and explosion-proof liquid, it is a substance of the second hazard class in terms of its effect on the human body. When its maximum permissible concentration in the indoor air is exceeded, atrophic changes develop in the mucous membranes of the throat and nose, crumbling of teeth, coughing, and if it gets into the eyes and skin - burns and inflammation. When handling the drug, you must wear rubber gloves, a respirator and safety glasses, maintain personal hygiene, turn on the supply and exhaust ventilation or work in a fume hood.
Read also: Turning on centers on a lathe
If there is an acid spill that gets on your body, you must first get rid of the wet parts of your clothing. The affected area of the skin is irrigated abundantly with running water, and it is necessary to apply the liquid rather than rub it with wet wipes or a towel. A one-time rinse lasts up to 20 minutes; if the burning sensation recurs, the procedure is resumed. A loose gauze bandage is applied to the affected area and a doctor is called; if pain is severe, an analgesic is taken. Spilled acid is neutralized with alkali.
No matter how tempting the advertising may be, excessive consumption of foods and carbonated drinks containing phosphoric acid will certainly cause harm to health. Penetrating into the blood, phosphates worsen hemoglobin and density, wash calcium out of the body, and, as a result, lead to osteoporosis, destroy tooth enamel, contribute to an increase in acidity in the body and the occurrence of diseases of the stomach and intestines.