Duralumin is a group of alloys based on aluminum with the addition of alloying elements (copper, magnesium, manganese, etc.). The name Dural comes from the trademark of the same name. This was the name given to one of the first aluminum alloys that was subjected to heat treatment followed by aging. The alloy was developed by German metallurgical engineer Alfred Wilm in 1903. From the moment of the discovery of duralumin to its mass production at a metallurgical plant in the German city of Duren, 6 years passed. In 1909, a new product under the brand name “duralumin” entered the market. In Russia, since the beginning of the twentieth century, this name has denoted a whole group of aluminum-based alloys. In Russian there can be various variants - “duralumin”, “dural”, “duralumin”.
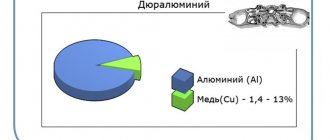
Duralumin, duralumin, duralumin - the main alloying additive of these alloys is copper. The basic composition of the alloy looks like this:
- The main part is aluminum (90-94%);
- Copper 3.5-5.5%;
- Magnesium 0.5-0.8%;
- Manganese 0.6%;
- Impurities - silicon, iron, zinc, etc.
Dural is different:
- Increased strength;
- Low specific gravity;
- High temperature resistance.
Unique physical, mechanical and technological properties have made duralumin one of the most popular structural materials in the world, suitable for use in many areas of production. During the rolling process, duralumin can be given various properties - make it strong and rigid or soft and ductile.
History of the discovery of duralumin
The unique properties of the compound were discovered in 1903 by a German engineer working in the German city of Duren. The term “duralumin” comes from the name of the city. The resulting metal alloy was distinguished by increased strength and low weight, as well as other useful properties.
In 1911, at an exhibition in St. Petersburg, duralumin received a silver medal as one of the best materials for creating aircraft.
This metal became most in demand during the Great Patriotic War. It was used to make parts for weapons, aircraft and tanks.
Over time, the composition of duralumin improved, and new types of alloy appeared.
Normative base
In our country, there are several GOSTs that standardize the requirements for aluminum and its alloys. One of them is GOST 4784-97 Aluminum and wrought aluminum alloys. Brands (with Changes No. 1, 2, 3, as amended). It applies to aluminum and its alloys, which are intended to produce semi-finished products of various types and shapes.
In particular, GOST determines the ratio of aluminum and other components. The same document specifies the requirements.
By the way, in the same document you can also find the names of foreign analogues, for example,
D16 can be replaced with AlCu4Mg1, and D16ch with alloy 2124.
The documents provided by the manufacturer must necessarily indicate not only the brand of the finished product, but also its chemical composition.
Production technology
To obtain duralumin, a charge is first mixed - granules of various metals that will be fused into a single composition. Then the mixture is heated to a temperature of +500°C and sharply cooled with water or saltpeter to room temperature - hardened.
The industrial production of duralumin is based on the use of enormous power electricity.
After this, in most cases, the so-called “artificial aging” of the resulting alloy. This operation consists of additional exposure of the metal at elevated temperature for a long time, for example, at +150...+200°C for 2 hours (all conditions depend on the brand of the compound and the required qualities). The aging process is carried out to ensure that duralumin acquires special strength. Without it, the alloy is characterized by softness and pliability.
After manufacturing, the composition can be covered with a protective film that protects against corrosion.
Industrial production
For industrial production of the alloy, high-power electricity is used.
To obtain duralumin, a compound (charge) is made - these are particles of different metals; later they will be fused into a homogeneous material. After this, the component is heated to a level of +500 ° C, then sharply cooled with water or nitrate. When the temperature of the duralumin workpiece reaches room temperature, hardening is done.
Interesting: What is a coupling, what does it look like and where is it used?
Following this, the so-called “artificial aging” of the manufactured component is most often used. To do this, the material is additionally kept at high temperature for a long period: about 2 hours at +…+200° C. The process is carried out taking into account the brand of the mixture and the required properties. The aging procedure is carried out in order to obtain high strength duralumin. If this process is not applied, the metal will be soft and pliable.
Once formed, the component is sometimes coated with a protective substance that protects against corrosion.
Duralumin: composition
The main part of the alloy is aluminum. The share of this component can reach up to 94% of the total mass. The next component that is present most often is copper. The weight of other additives - manganese, magnesium, iron and others - is small.
This is interesting: What is heat treatment of metals and alloys
An example of the composition of commonly used duralumin grade D16:
- aluminum - 93-94%;
- copper - 3.8-4.9%;
- alloying alloys - 1.5-2%.
Chemical composition of duralumin.
Assortment
Duralumin today is widely used in industry, construction, and mechanical engineering. Conventionally, duralumin is divided into four groups, depending on the saturation of its constituent components, which affects the final price.
1. Classic brand D1. The percentage composition has not changed since 1908, from the moment of the first melting.
2. Increased strength grade D16. Strength is given by the high magnesium content.
3. Increased heat resistance, grades VD17 and D19. They are characterized by a high content of copper and manganese.
4. Increased plasticity of grade D18. Plasticity is achieved due to the increased proportion of magnesium and copper.
Properties of duralumin
The excellent properties of duralumin make it suitable for use in many areas of production, parts manufacturing, and insulation.
Physical and mechanical
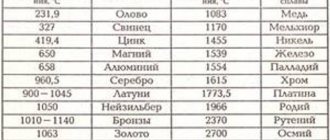
A special feature of duralumin is its lightness with increased strength and heat resistance. Thus, the specific gravity of this metal is 2.8 g/m³, while for steel this figure is 8 g/m³. The melting point of duralumin is +500°C.
The disadvantage of the alloy is the increased susceptibility to corrosion as a result of exposure to elevated temperature or load.
Technological
A distinctive property of duralumin is the ease of its production. This alloy can be made even in domestic conditions: for example, in the garage. It does not need to be heated to extreme temperatures. Thanks to its simple manufacturing technology, this metal is relatively cheap.
The duralumin casting procedure can be done at home.
About the melting point
It must be remembered: aluminum is very easy to cast and begins to turn into a liquid substance already at a temperature of 660 degrees. In order to understand that this indicator is quite low, it is enough to compare it with the melting temperatures of other metals, which are also often used to make certain items needed in everyday life.
For example:
- steel begins to melt only at a temperature of 1300 degrees;
- cast iron - at 1100 degrees.
But still, although the melting point of aluminum in Celsius is not too high compared to many other metals, it is quite difficult to reach 600 degrees at home using an ordinary gas or electric stove .
Decrease temperature
Before subjecting the metal to melting, it is possible to reduce its melting point using special methods, for example, using it in powder form. In this case, it will begin to melt a little faster. But at the same time, it becomes dangerous, since when interacting with atmospheric oxygen, it can oxidize or ignite . And as a result of oxidation , as we remember from the school chemistry course, aluminum oxide is formed; and the temperature at which this substance begins to melt already exceeds two thousand degrees.
In general, it is not possible to avoid the formation of oxide if you melt aluminum, but it is quite possible to reduce the amount of excess substance. When melting aluminum, it is necessary to prevent water from entering the substance. After all, if this happens, there will be an explosion.
Before starting the process, you need to make sure that the raw materials are completely dry. Most often, aluminum wire is used as the starting material. First you need to use scissors to divide it into many small pieces. And in order to reduce the area of contact with the oxygen contained in the atmosphere, these pieces are pressed with pliers.
There is not always a need to create a high quality aluminum product, so it is not always necessary to use powder or finely chopped and tightly compressed wire. You can take any item that has already been used, for example, a jar in which canned food was stored. But before melting, you need to deprive it of the bottom seam or cut the profile. The resulting raw materials can be painted or stained. No need to worry about it. Anything that is superfluous on the surface quickly comes off in the form of waste.
Types of alloys
Depending on the application and the need to acquire the desired characteristics, various substances are added to the alloy.
To avoid corrosion, the metal is anodized, i.e. covered with a special film.
All types of duralumin can be divided into:
- hardened, having the letter “T” in the designation;
- those that have gone through the stage of artificial aging - the designation is “T1”;
- anodized - with the letter “A” in the brand name.
Depending on the formula and heat treatment, the properties of the compounds change. Alloys widely used:
- Aluminum+copper+magnesium with manganese additives. Examples include alloys of grades D1, D16. These compounds are called "duralumin". They are not protected from corrosion and require additional coating.
- Aluminum + magnesium or manganese. In addition to corrosion resistance, this composition allows welding. The alloy is called "magnalium".
- Aluminum+magnesium+silicon. The material is protected from corrosion. It is used at high humidity, in conditions of passage of electric current. It's called "avial".
Heat treatment
Annealing. The alloy is heated to a temperature of 500 °C, and with cooling it acquires flexibility similar to pure aluminum. After the aging process, the leading characteristics of duralumin become hardness and rigidity. Natural aging requires daily exposure and a working temperature of up to 100 degrees Celsius. Artificial aging requires a higher temperature, but much less time. Upon completion of the technology, duralumin becomes a fairly strong and reliable metal that can be used under the highest loads. After annealing, excellent ductility is achieved, and after aging, significant self-strengthening is achieved.
The ability of duralumin to self-strengthen was discovered quite by accident and is now often used when processing the material for use in modern industry. Semi-finished products, depending on the production technology, are supplied in artificially aged, hardened and annealed forms. The heat treatment time is very different - it depends on the structure and thickness of the alloy. After hardening, the alloys are strengthened, but at the same time retain high ductility, which allows them to undergo any deformation. That is why punching and stamping can be done at one time. It is worth noting that natural aging before deformation reduces the tensile strength by 2 kg/mm2 compared to the strength of those parts in which aging occurred after the necessary deformation. The technology requires deformation of rolled steel D1 in the first two hours after hardening. And rolled products D16 and D6 are deformed no later than 30 minutes after hardening.
Areas of application
Sheets, rods, plates, and wire are made from duralumin. These materials are used to make various parts.
This is interesting: What is heat treatment of metals and alloys
Main Applications:
- Aircraft. An important area is the use of duralumin in aircraft construction and the construction of other aircraft - space rockets, airships. This composition is used to make the casing, steering rod parts, power elements, etc.
- Construction. Sheets, pipes, angles, etc. are widely used in this industry.
- Automotive industry. Bodies, radiators and other parts are made from the alloy.
- Drilling industry. Circles, drills, etc. are made from duralumin.
Duralumin is often used in everyday life, for example, in the form of baking foil or candy wrapping.
How to make a casting mold
Before melting aluminum, prepare a blank for casting. There are several ways to pour liquid melt. The open and closed methods are most often used. Each one is worth telling in more detail.
Open form
When aluminum is melted using an open method, after melting the melt is poured into a prepared container, for example, a tin can. The aluminum casting is removed from the can while hot, when the hot melt has set slightly on top. Just tap the container lightly. If an ingot of a given geometry is not needed, the molten metal is poured onto any flat refractory surface; it holds well, does not spread, and looks like mercury.
Closed form
Castings with complex geometries are produced in specially prepared molds. It must correspond to the parameters of the part; it is usually made detachable. To make a mold, a mock-up part is used, from which the casting is made. Silica is used as a molding material; it compacts well and is easy to find. Silica is replaced by:
- a mixture of river sand and liquid glass;
- a mixture of sand, cement, brake fluid is added instead of water;
- gypsum, it is convenient for complex layouts.
Solid, seamless molds are made from gypsum; they are disposable; they are broken after the aluminum has hardened. The mock-up part is made of wax or foam plastic. It is placed inside the container used for the mold, then the voids are filled. The result is smooth parts that do not require additional processing. When plaster is used, it is dried for a couple of days. Plaster is afraid of moisture and swells. It is prone to cracking when dry. When in contact with paraffin or polystyrene foam, gypsum retains its structure and does not form potholes or cavities.
The difference between duralumin and aluminum
Dural has a characteristic gray color. But its main differences from aluminum are the lack of ductility, hardness and fragility. The alloy cannot be bent or made a dent. Duralumin shavings are brittle and brittle. It is easy to scratch; when examining the damage, the fine-crystalline structure of the material is visible.
The type of metal can be determined more accurately by dropping caustic sodium on it. If after 10 minutes the stain darkens, it is duralumin.
Aluminum and duralumin differ from each other in their chemical composition.
Melting process at home
Melting is a rather dangerous process . You must first take care of the means of protection against various toxic substances that will be formed, and also prepare the casting mold.
Means of protection
- You cannot do without special gloves even if you only need to melt aluminum once. This is perhaps the main means of protection, since the molten mass can most likely get on your hands, and then a burn will inevitably appear on the skin, since the temperature of the liquid metal exceeds 600 degrees.
- The next part of the body that also needs to be protected from hot aluminum is the eyes. If you swim frequently, you cannot do without a special protective mask, or at least glasses. But it is best to work in a suit that is resistant to high temperatures of several hundred degrees.
- If it is necessary to obtain pure aluminum, a refining flux will be required. And then you need to work in a chemical respirator.
Selecting a mold for casting
In order to cast aluminum , it is not necessary to stock up on a casting mold. It is enough just to purchase a sheet of a more refractory metal - steel, pour molten aluminum onto it and wait until the latter hardens. But to produce any part from aluminum, you will definitely have to purchase a casting mold.
You can make it yourself at home. Sculpting plaster is usually used for this purpose. It is poured into a mold, then cooled for some time. After this, the model is inserted into it and a second container with plaster is placed on top. In this case, it is important not to forget to make a hole in the plaster using some cylindrical object. Hot aluminum will be poured through this hole.
When melting aluminum, you cannot do without a so-called crucible: that is, a container made of refractory metal. It can be made of porcelain, quartz, steel, cast iron. However, it is not at all necessary to make a crucible yourself, because you can simply buy it in a special store. The volume of the crucible depends on how much metal is required to be obtained.
Advantages and disadvantages
A significant advantage of duralumin is its lighter weight than steel, despite the strength of this material. This allows it to be used in the manufacture of cars, airplanes, and rockets to facilitate construction.
An important property of duralumin is its high heat resistance, which facilitates its use in the production of radiators.
Duralumin is more resistant to vibrations than steel. Due to this, it is widely used in the manufacture of drilling equipment.
This is interesting: What is heat treatment of metals and alloys
Disadvantages include high sensitivity to corrosion. Not all types of duralumin are suitable for welding.
Equipment and methods of smelting
Before melting aluminum, choose a place and method for heating the metal. Two commonly used options:
- In garages or households, aluminum is melted, a smelter is built, it is made of bricks without the use of a binder mortar. A metal frame is convenient as a support; it should have a hole for air injection; for this, use a vacuum cleaner or hair dryer. A homemade stove is lined with coal. The melting container with the crowbar is placed inside. To better retain heat, the bricks are covered with a sheet of metal on top.
- At home, to heat up a small amount of scrap, use:
- with a gas stove, you can melt a small amount of scrap, but the melt yield will be low.
The casting is melted in a steel vessel. To increase the heating rate, a design of two containers is used; they are inserted into one another with a gap of 1 cm. The bottom of the large container is perforated, it serves as a flame divider. When there is a gas burner, combine bottom heating with top heating. You can melt metal faster.
Optional equipment
For small portions of scrap, tin cans are sometimes used. But this container is unreliable, and the tin may burn through. It is safer to use a ceramic or metal refractory crucible for muffle furnaces. A good option is a cut-off fire extinguisher glass. For convenience, a gutter is made through which molten aluminum will flow. When working, use long tongs. You will need a spoon with a long handle to collect the slag.