Properties of phosphoric acid
Physical properties
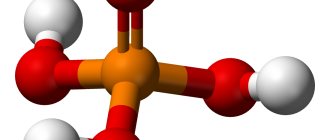
Phosphoric acid is the most stable phosphoric acid at room temperature. In addition to orthophosphoric acid H3PO4, there is metaphosphoric acid HPO3, pyrophosphoric acid H4P2O7, triphosphoric acid H3P3O9 and tetraphosphoric acid H4P4O12. The last three are much stronger than orthophosphoric acid (K1 = 7 ⋅ \cdot ⋅ 10-3).
| Property | Description |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid in aqueous solution, in its pure form - hygroscopic crystals |
| Molar mass, g/mol | 98,0 |
| Density at 20°C, g/cm3 | 1,83 |
| Melting point, °C | +42,35 |
| Boiling point, °C | 213 (dec.) |
Chemical properties
In aqueous solutions, phosphoric acid dissociates into ions :
H3PO4 ⇄ \rightleftarrows ⇄ H+ + H2PO4-, ⇄ \rightleftarrows ⇄ 2H+ + HPO42- ⇄ \rightleftarrows ⇄ 3H+ + PO43-.
Dissociation constants
K1 = 7.1·10-3,
K2 = 6.2·10-8,
K3 = 5.0·10-13.
At room temperature, phosphoric acid reacts only with active metals, oxides and hydroxides:
6Li + 2H3PO4 = 2Li3PO4 + 3H2↑,
3CaO + 2H3PO4 = Ca3(PO4)2 + 3H2O,
3KOH + H3PO4 = K3PO4 + 3H2O.
When heated , it is more active:
3Zn + 2H3PO4 = 2Zn3(PO4)2 ↓+ 3H2↑,
Fe2O3 + 2H3PO4 = 2FePO4↓+ 3H2O.
Phosphoric acid decomposes when heated:
4H3PO4 = 2H4P2O7 + 2H2O.
Phosphoric acid reacts with perchloric acid to form phosphoryl salts:
H3PO4 + HClO4= P(OH)4ClO4.
Therefore, phosphoric acid can be considered an amphoteric phosphorus (V) hydroxide with a predominance of acidic properties.
Molecule structure and physical properties
Phosphorus in the +5 oxidation state forms several acids: ortho-phosphoric H3PO4, meta-phosphoric HPO3, pyro-phosphoric H4P2O7.
Phosphoric acid H3PO4 is a medium strength acid, tribasic, strong and non-volatile. Under normal conditions, phosphoric acid is a solid, highly soluble in water and hygroscopic.
The valency of phosphorus in phosphoric acid is V.
At temperatures above +213 °C, ortho-phosphoric acid transforms into pyrophosphoric acid H4P2O7.
When higher phosphorus oxide reacts with water in the cold, metaphosphoric acid HPO3 is formed, which is a transparent glassy mass.
Receipt
Laboratory methods of obtaining
Phosphoric acid is obtained in laboratory conditions from (V) oxide
P2O5 + 3H2O = 2H3PO4.
The reaction proceeds violently, so it is better to obtain it in this way in industry.
Phosphoric acid can be obtained from phosphates by the action of hydrochloric or sulfuric acid:
Na3PO4 + 3HCI = 3NaCI + H3PO4.
phosphorus (V) can be hydrolyzed
2PCl5+ 8H2O = 2H3PO4 + 10HCl.
Receipt in industry
In industry, the purest phosphoric acid is obtained thermally, for which phosphorus is burned:
4P +5O2 = 2P2O5.
Phosphoric anhydride reacts with water too violently, so phosphoric anhydride is mixed with phosphoric acid heated to 200°C in a concentration of 50-60%. The resulting acid is diluted and partially restarted in the process.
There is an extraction method for obtaining phosphoric acid directly from ores, for example, from apatite:
Ca5(PO4)3F + 5H2SO4 + n H3PO4 + 3H2O = (n+3) H3PO4+ 5CaSO4 H2O + HF.
Application
Phosphoric acid is used in many areas, from industry to dental treatment. The product is used by craftsmen as a flux when soldering, to clean the metal surface from rust. Liquid is used:
- for scientific research in molecular biology;
- as a catalyst for organic synthesis processes;
- for creating anti-corrosion coatings on metals;
- in the production of fire-resistant impregnations for wood.
The substance is used:
- in the oil industry;
- in the manufacture of matches;
- for film production;
- for the purpose of protection against corrosion;
- to clarify sucrose;
- in the manufacture of medicines;
- in refrigeration units as a binder in freon;
- during mechanical processing for polishing and cleaning metals;
- in the textile industry in the production of fabrics with fire retardant impregnation;
- as a component in the production of chemical reagents;
- in veterinary medicine for the treatment of urolithiasis in minks;
- as a component for metal primer.
In the food industry
The use of phosphoric acid in food production has become widespread. It is registered in the register of food additives under code E338. When consumed in acceptable quantities, the substance is considered safe. The following properties of the drug are useful:
- preventing rancidity;
- acidity regulation;
- shelf life extension;
- preservation of taste characteristics;
- enhancing the effect of antioxidants.
Phosphoric acid as an acidifier, leavening agent, and antioxidant is used in the bakery, meat, and dairy industries. Used in the production of confectionery and sugar. The substance gives products a sour, bitter taste. Additive E338 is included in:
- processed cheeses;
- muffins;
- carbonated drinks - Pepsi-Cola, Sprite;
- sausages;
- buns;
- milk;
- baby food;
- marmalade;
- cakes
Research has shown that overconsumption of products containing phosphorus compounds, especially carbonated drinks, can lead to health problems. It is possible:
- leaching of calcium from the body, which can trigger the formation of osteoporosis;
- violation of the acid-base balance - the additive can increase its acidity;
- the appearance of gastrointestinal diseases;
- exacerbation of gastritis;
- destruction of tooth enamel;
- development of caries;
- the appearance of vomiting.
In the non-food industry
The use of phosphoric acid can be observed in many areas of production. This is often due to the chemical properties of the product. The drug is used for the manufacture of:
- combined, phosphorus mineral fertilizers;
- activated carbon;
- phosphorus salts of sodium, ammonium, manganese;
- fire retardant paints;
- glass, ceramics;
- synthetic detergents;
- fire-resistant binding components;
- non-flammable phosphate foam;
- hydraulic fluids for the aviation industry.
- How to treat fingernail fungus
- Symptoms of swine flu in humans
- How to cook pea soup correctly, step-by-step recipes with photos
In medicine
Dentists use orthophosphorus composition to treat the inner surface of the crown. This helps improve its adhesion to the tooth during prosthetics. The substance is used by pharmacists to prepare medicines and dental cement. In medicine, the use of orthophosphorus compounds is associated with the ability to etch tooth enamel. This is necessary when using adhesive materials of the second or third generation for filling. Important points - after etching the surface it is necessary to:
- Rinse;
- dry.
Salts of orthophosphoric acid (orthophosphates, phosphates)
Methods for producing phosphates
Acids are prepared with metals, metal oxides, hydroxides (see Chemical properties of orthophosphoric acid)
Physical properties of phosphates
H3PO4 is a 3-basic acid, therefore it forms 3 types of salts:
| Anion salt | Name | Solubility in water | Examples of salts |
| PO43- | Phosphate (orthophosphate) | most are insoluble (except alkali metal and ammonium phosphates) | Na3PO4; Ca3(PO4)2 |
| HPO42- | Hydrogen phosphate | soluble | Na2HPO4; CaHRO4 |
| H2PO4— | Dihydrogen phosphate | very soluble | NaH2PO4; Ca(H2PO4)2 |
Chemical properties of phosphates
- They have properties characteristic of salts .
- Alkali metal salts are subject to hydrolysis :
Na3PO4 + H2O = Na2HPO4 + NaOH
- A characteristic feature of orthophosphates is their attitude to calcination: monosubstituted salts transform into metaphosphates, dibasic salts into pyrophosphates, and of the trisubstituted ones, only ammonium salts change:
NaH2PO4 = NaPO3 + H2O
Na2HPO4 = Na4P2O7 + H2O
(NH4)3PO4 = 3NH3 + H2O
Phosphorus fertilizers
Calcium and ammonium phosphates and hydrogen phosphates are used as phosphate fertilizers.
With enough phosphorus, plants grow quickly and bear fruit well. The application of phosphorus fertilizers favors the growth of the plant’s root system and increases productivity. In this regard, such fertilizers are important when growing vegetables, grains and fruits and berries.
The table below shows the main types of phosphate fertilizers.
Categories Group V (nitrogen, phosphorus), INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
Levsha1988 › Blog › We chemically treat zinc and rust.
The result of using this case on the body of an OKI. I have long wanted to try galvanizing. Electrolysis is used to deposit zinc on ferrous metals. It will be useful in everyday life, and to study corrosion resistance. There are galvanizing kits on sale, but they are expensive, you have to pay money for such small 2 bubbles and a pair of prichendals. look for where else it is sold. Let's try to figure this out ourselves:
I bought electrolyte for batteries at the car market. This is sulfuric acid with distilled water. The concentration is quite high. Next I took a bunch of dead but not leaking salt batteries. These are the cheapest batteries. I took zinc out of them, cut it into thin strips and dipped it in sulfuric acid. Placed it in a water bath. There was a reaction (photo). I dissolved it while the bubbles were coming, then the acid was produced, supposedly being saturated with dissolved zinc.
But, as it turned out, the resulting solution of zinc sulfate was not permeable. Let's forget about this. Fill it with soda and pour it into a jar with slag.
We buy soldering acid containing zinc from a radio parts store. Composition: zinc chloride. Zinc is already dissolved in hydrochloric acid. There are heaps of zinc there. A liter costs 400 rubles at a local store. A liter is enough for a lot. Immediately, I buy phosphoric acid there. It is also soldering acid. 50 ml. enough. We make 2 electrodes.
A power source will be needed. The main condition here is the ability to adjust the current strength. I have a homemade source from 0 to 24 volts and current stabilization from 0 to 10 amperes. Below I will give a couple of options and a diagram of a simple current regulator if you don’t have a source at hand.
To the clean electrode we connect the + source. To the object being cleared -. We set the voltage to 12-15 volts and the current cutoff to 1.5-2 amperes. We impregnate the felt of the electrode with phosphoric acid. And we begin to drive through the rust. It starts to hiss, the power supply shows that the current has flowed (1.5-2 A). The release of hydrogen and the activity of acid - peels off and dissolves rust that has settled in the pores and the rust remains on the felt. The electrode must be frequently rinsed in water and soaked again in fresh phosphoric acid, because what is in your hand begins to dissolve and deposit on the flywheel. but we don’t need that yet.
Water dripped, the water remained drops. It spreads over bare steel, but here it seems to gather, as if on a greasy surface. Here are a couple more examples of galvanized iron.
Comments 33
And if you first dissolve zinc in orthophosphoric acid, and not hydrochloric acid, will there be the same effect?
Tell me? Can soldering acid (with zinc) corrode the varnish of a car?
Hello. Tell me how to hook up the turn signal lamp, I can’t figure out which wires to connect it to. After all, the negative terminal remains on the body? Thank you
A light bulb into the gap in the positive wire to which the electrode is connected. Those. sequentially.
Respect for the report, but the question is not better to first apply a small current, and then increase it and the surface will be matte, and the soil will fall on it.
In principle, the idea comes in handy. I'll have to try it.
Yes, be careful with fumes there, use a hood and a gas mask, because... during the reaction of hydrochloric acid and zinc, the image of weedy anhydride MPC 0.5 is inhaled and you can get swelling of the lungs!) Well, God forbid.
Where does sulfur dioxide come from in the hydrochloric acid compound? You would also say that pure chlorine is released.)) He didn’t use sulfurous acid. and not sulfite, and not even zinc hydrosulfite, and not copper. There is no sulfur dioxide and there is no sulfuric acid in the reaction. the valence is not the same))) the only thing you should be afraid of is hydrogen.
Phosphorus (III) oxide, phosphorus trioxide (P2O3)
Methods for producing phosphorus (III) oxide
- P2O3 is formed when phosphorus burns in a lack of oxygen or its slow oxidation:
4P + 3O2 = 2P2O3
Physical properties of phosphorus (III) oxide
At room temperature, P2O3 is a white, waxy mass with an unpleasant odor. Easily evaporates, its melting point = 23.5°C
The pairs exist in the form of P4O6 dimers.
!Very poisonous
Chemical properties of phosphorus (III) oxide
- P2O3 as an acidic oxide, when reacting with water, forms phosphorous acid:
Р2О3 + ЗН2О =2H3PO3
- The disproportionation reaction occurs very rapidly when P2O3 is dissolved in hot water :
2Р2О3 + 6Н2О = РН3 + 3H3PO4
- When P2O3 interacts with alkalis, salts of phosphorous acid are formed:
P2O3 + 4NaOH = 2Na2HPO3 + H2O
- When interacting with oxidizing agents , P2O3 exhibits reducing properties:
Oxidation by air oxygen:
P2O3 + O2 = P2O5
Oxidation with halogens:
P2O3 + 2Cl2 + 5H2O = 4HCl + 2H3PO4
Packaging requirements and rules for handling the substance
The container in which the acid is packaged must be marked “Dangerous” or “Corrosive Liquid”.
The additive can be stored and transported in the following packaging:
- polyethylene canisters;
- glass bottles;
- containers and tankers made of stainless steel, which has undergone special treatment;
- plastic cubes.
For convenience, the containers themselves are placed in polyethylene drums or wooden boxes, inside of which there should be soft filler to avoid damage to the packaging.
Contact of the substance on the skin or mucous membranes, in the eyes or in the respiratory tract can cause burns, nausea, vomiting, dizziness and tissue damage. In this case, you must immediately seek medical help.
Acid is dangerous to handle, so you can only work with it away from open sources of fire, in a well-ventilated area.
It is mandatory to have protective clothing: gloves, a respirator, goggles, boots and a suit for working with hazardous substances.
Anti-rust application
A rust converter based on phosphoric acid creates a protective layer on the surface that protects against corrosion during further use. The peculiarity of using the compound is that it is safe for metal when applied. There are several ways to remove rust with phosphoric acid, depending on the size of the damage:
- etching with immersion in a bath or other container;
- repeated application of the composition to the metal with a spray gun or roller;
- covering the surface with pre-treated mechanical cleaning.
The orthophosphorus compound converts rust into iron phosphates. The composition can be used for washing and cleaning:
- rolled metal products;
- wells;
- pipeline surfaces;
- steam generators;
- water supply, heating systems;
- coils;
- boilers;
- water heaters;
- heat exchangers;
- boilers;
- machine parts and mechanisms.
Safety precautions when working with acid
Orthophosphorus compound belongs to the class of hazardous substances and requires caution. Work with the composition must be carried out in a special room equipped with supply and exhaust ventilation, away from sources of fire. The lack of personal protective equipment is unacceptable:
- respirator;
- gloves;
- special clothing;
- non-slip shoes;
- points.
Contact of orthophosphorus composition on the skin or eyes is dangerous, and inhalation of hot vapors is harmful. This may cause burns, dizziness, vomiting, and coughing. In case of emergency you need to:
- remove clothing that has come into contact with the substance;
- rinse the affected area with running water;
- call a doctor;
- apply a loose bandage;
- Neutralize spilled liquid with alkali.