More than one generation of chemists argued about which acid is the strongest. At different times, this title was given to nitric, sulfuric, and hydrochloric acid. Some believed that there could be no compound stronger than hydrofluoric acid. Recently, new compounds with strong acidic properties have been obtained. Perhaps it is among them that the strongest acid in the world is found? This article examines the characteristics of the most powerful persistent acids of our time and gives their brief chemical characteristics.
Properties of acids
All acids have certain chemical properties that can be called common to a given class of chemical compounds.
- The ability to interact with metals, releasing hydrogen.
- The ability to interact with bases, releasing salts.
- The ability to change the color of indicators - for example, cause litmus paper to turn red.
In all of the above properties, another “skill” of any known acid is manifested - this is the ability to give up a hydrogen atom, replacing it with an atom of another chemical substance or a molecule of any compound. It is this ability that characterizes the “strength” of the acid and the degree of its interaction with other chemical elements.
Consequences and prevention
Acid poisoning is often fatal. If treatment is started on time, a favorable prognosis is possible, but in many cases the person remains disabled. The action of all acids negatively affects the condition of the digestive tract, the brain and nervous system suffer.
Intoxication can be avoided by being careful when working with acids. Toxic substances should not be left in places accessible to children and animals. When using toxic compounds, wear protective clothing, hide your eyes behind glasses, and wear gloves on your hands.
The most terrible and dangerous acid is not available to the common man. However, it is important to be careful when using such substances in laboratories. If signs of poisoning occur, you must immediately contact a medical facility.
Super acid
The word “superacid” was introduced into the chemical dictionary in 1927, with the help of the famous chemist James Conant.
The standard for the strength of this chemical compound is concentrated sulfuric acid. A chemical or any mixture that is more acidic than concentrated sulfuric acid is called a super acid. The value of a superacid is determined by its ability to impart a positive electrical charge to any base. The corresponding H2SO4 indicator is taken as the basic parameter for determining acidity. Among strong acids, there are substances with rather unusual names and properties.
Substance concentration
Chemists often have to solve problems that involve determining the percentage of pure acid present in a solution. In such cases, the value sought is concentration.
This is a value that allows you to determine the quantitative composition of a liquid chemical . For example, in order to find out how much pure sulfuric acid is in a dilute solution, you need to pour a small amount of the mixture into a measuring cup, weigh it and determine the desired value using the density table. This table is used in calculations, since density is inextricably linked with concentration.
Known strong acids
The most famous acids from the inorganic chemistry course are hydroiodic (HI), hydrobromic (HBr), hydrochloric (HCl), sulfuric (H2SO4) and nitric (HNO3) acids. All of them have a high acidity index and are able to react with most metals and bases. In this series, the strongest acid is a mixture of nitric and hydrochloric acid, called “aqua regia”. The formula of the strongest acid in this series is HNO3+3 HCl. This compound can even dissolve precious metals such as gold and platinum.
Oddly enough, hydrofluoric acid, which is a compound of hydrogen with the strongest halogen - fluorine, was not included in the contenders for the title of “The Strongest Acid in Chemistry”. The only feature of this substance is its ability to dissolve glass. Therefore, such acid is stored in polyethylene containers.
What is the danger of H2SO4?
This is a colorless and odorless compound obtained by burning sulfur or ores rich in it, followed by the oxidation of sulfur dioxide into anhydrous sulfur and its absorption by water.
The reagent dissolves in water in any proportion and at the same time releases a significant amount of heat. Therefore, to avoid splashing, it is necessary to pour this reagent into water, and not vice versa.
The compound has a destructive effect on animal and plant tissues, absorbing liquid from them and causing them to char. It is capable of dissolving most metals with the formation of sulfuric acid salts, but has little effect on lead. Burns cotton, sugar, wool and wood materials in a short time. Causes very deep burns of the skin and mucous membranes.
Strong organic acids
Contenders for the title “The Strongest Acid in Organic Chemistry” are formic and acetic acids. Formic acid is the strongest in the homologous series of saturated acids. It got its name due to the fact that some of it is contained in the secretions of ants.
Acetic acid is slightly weaker than formic acid, but its distribution spectrum is much wider. It is often found in plant juices and is formed during the oxidation of various organic matter.
Recent developments in the field of chemistry have made it possible to synthesize a new substance that can compete with traditional organic substances. Trifluoromethanesulfonic acid has an acidity index higher than that of sulfuric acid. Moreover, CF3SO3H is a stable hygroscopic liquid with established physicochemical properties under normal conditions. Today the title of “Strongest Organic Acid” can be assigned to this compound.
Many may think that the degree of acidity cannot be significantly higher than that of sulfuric acid. But recently, scientists have synthesized a number of substances whose acidity parameters are several thousand times higher than those of sulfuric acid. Compounds obtained by reacting protic acids with Lewis acids have abnormally high acidity values. In the scientific world they are called: complex protic acids.
How much acid can kill a person?
How much poisonous acid is required to cause poisoning or death? Strong acids react immediately, so in some cases a small drop or one breath is enough.
The amount of acid that can provoke poisoning depends on the person’s age, his physical condition, immune system, and the body’s ability to resist harmful substances. In children, poisoning develops faster than in adults due to accelerated metabolism. A medical professional can determine the exact dosage.
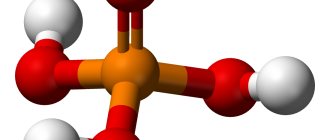
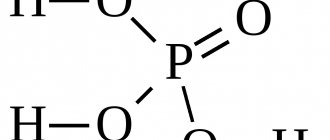
Magic acid
Yes. Everything is correct. Magic acid. That's what it's called. Magic acid is a mixture of hydrogen fluoride or fluorosulforonic acid with antimony pentafluoride. The chemical formula of this compound is shown in the figure:
Magic acid received this strange name at a Christmas party for chemists that took place in the early 1960s. One of the members of J. Olah's research group showed a funny trick by dissolving a wax candle in this amazing liquid. This is one of the strongest acids of the new generation, but a substance that will surpass it in strength and acidity has already been synthesized.
Classification of acids by composition
Acids can be divided into oxygen-containing and oxygen-free. It is not difficult to guess that oxygen-free ones do not contain oxygen atoms, while oxygen-containing ones do. Oxygen-containing acids are formed by corresponding oxides, while oxygen-free acids are formed by direct interaction of simple substances.
Tab. Examples of oxygen-free and oxygen-containing acids formed by the same non-metal
| Oxygen-free | Oxygen-containing |
| HCl | HClO4 |
| H2S | H2SO3 |
| HBr | HBrO |
| HI | HIO2 |
The strongest acid in the world
Carborane acid is carborane acid, which is by far the strongest compound in the world. The formula of the strongest acid looks like this: H(CHB11Cl11).
This monster was created in 2005 at the University of California in close collaboration with the Novosibirsk Institute of Catalysis SB RAS.
The very idea of synthesis arose in the minds of scientists along with the dream of new, hitherto unseen molecules and atoms. The new acid is a million times stronger than sulfuric acid, yet it is not at all aggressive, and the strongest acid can easily be stored in a glass bottle. True, over time the glass does dissolve, and with increasing temperature the rate of this reaction increases significantly.
This amazing softness is due to the high stability of the new compound. Like all acidic chemicals, carborane acid reacts readily, donating its only proton. In this case, the acid base is so stable that the chemical reaction does not proceed further.
Strong and weak reagents
If a reagent in an aqueous solution completely disintegrates into ions, that is, dissociates, then it is strong, since weak chemical compounds never completely dissolve.
In addition, a weak acid can be distinguished by measuring its conductivity. Strong compounds are good electrolytes. Strong bases also disintegrate when placed in water. It should be noted that bases are also called hydroxides or hydroxides.
There are special lists of weak and strong acids and bases. The table below can also be used to classify reagents.
| Strong acid | Weak acid | Strong foundation | Weak foundation |
| HCI hydrochloric or hydrochloric chloride | HF hydrogen fluoride | NaOH sodium hydroxide | Mg(OH)2 magnesium hydroxide |
| HBr hydrogen bromide | CH3COOH acetic | KOH potassium hydroxide | Fe(OH)2 iron(II) hydroxide |
| HI hydrogen iodide | H2SO3 sulfurous | Ca(OH)2 calcium hydroxide | Zn(OH)2 zinc hydroxide |
| HNO3 nitrogen | H2S hydrogen sulfide | Ba(OH)2 barium hydroxide | NH4OH ammonium hydroxide |
| HClO4 chlorine | HNO2 nitrogenous | LiOH lithium hydroxide | Fe(OH)3 iron(III) hydroxide |
| H2SO4 sulfuric | H2SiO3 silicon |
It should also be noted that oxygen-containing carbonic (H2CO3) and orthophosphoric (H3PO4) or phosphoric acids are weak. To the strong ones, it is necessary to add chrome, which is medium in strength.
In addition, it must be taken into account that modern chemistry allows scientists to create new compounds. In this regard, the list of acids, both strong and weak, is constantly updated.
Chemical properties of carborane acid
The new acid is an excellent H+ proton donor. This is what determines the strength of this substance. A solution of carborane acid contains more hydrogen ions than any other acid in the world. In a chemical reaction, SbF5, antimony pentafluoride, binds fluorine ylon. In this case, more and more hydrogen atoms are released. Therefore, carborane acid is the strongest in the world - the suspension of protons in its solution is 2 × 1019 times greater than that of sulfuric acid.
However, the acid base of this compound is amazingly stable. The molecule of this substance consists of eleven bromine atoms and the same number of chlorine atoms. In space, these particles form a complex, geometrically regular figure, which is called an icosahedron. This arrangement of atoms is the most stable, and this explains the stability of carborane acid.
pH value
When carrying out dissociating reactions, it is important to correctly determine the acidity level of the water. To express it quantitatively, a pH value is used, called the strength, weight or potential of hydrogen. It allows you to measure the activity of hydrogen ions. If the pH level exceeds 7, then the substance has acidic properties, but if this indicator is less than 7, then the properties are basic.
Determination methods
The results of chemical reactions in which any substance participates directly depend on the level of its acidity. That’s why chemists always measure this indicator.
There are several methods for determining pH:
- Instrumental method. In this case, a pH meter is used. This device transforms the concentration of protons in a liquid into an electrical signal.
- Indicators. These are substances that change color depending on pH. The use of various indicators allows you to obtain fairly accurate data on the level of acidity.
- Salt. A salt is a compound of ions that dissociates completely in a weak aqueous solution. To determine the acid-base properties of a saline solution, first of all, you need to establish and study the properties of the ions in the solution.
Buffer solution
A buffer solution is a substance characterized by the presence of a constant concentration of hydrogen ions.
When a strong acid or the same base is added in small doses, these solutions retain their original acidity level.
To prepare such a mixture, you need to mix a weak acidic substance or base with an appropriate salt.
When preparing a buffer solution, the following factors must be considered:
- The range of acidity levels at which a substance will become effective.
- The capacity of the solution, that is, how much of a strong acidic compound or base can be added to the mixture without changing its pH.
- When combining substances, there should be no reactions that could affect the composition of the solution.
Meaning of carborane acid
The strongest acid in the world brought its creators well-deserved awards and recognition in the scientific world. Although all the properties of the new substance are not fully understood, it is already becoming clear that the significance of this discovery goes beyond laboratories and research institutes. Carborane acid can be used as a powerful catalyst in various industrial reactions. In addition, the new acid can interact with the most stubborn chemicals - inert gases. Currently, work is underway to allow xenon to react.
Undoubtedly, the amazing properties of new acids will find their application in various fields of science and technology.
Treatment for poisoning
Before doctors arrive, it is permissible to provide first aid to the victim. In case of poisoning, you cannot do without qualified help, but some actions can alleviate the patient’s condition.
We recommend: White snowberry: poisonous or not plant
What to do:
- If the cause of poisoning is gas, the patient is taken out or taken to fresh air;
- The person is placed on a horizontal surface and provided with complete rest;
- It is forbidden to rinse the stomach; this can lead to repeated burns of the esophagus;
- Ice is placed on the abdominal area; this action will help stop internal bleeding;
- You cannot give a person pills and drinks, so as not to provoke negative consequences.
Classification of acids by basicity
Acids can give up as much hydrogen as they contain (in most cases, there are exceptions). If it can donate a maximum of one hydrogen, then the acid is classified as monobasic, if it can donate a maximum of two hydrogen protons, then it is dibasic, and so on.
For example:
HCl ↔ H+ + Cl‒(monobasic)
H2SO4 ↔ 2H+ + SO42‒(dibasic)
H3PO4 ↔ 3H+ + PO43- (tribasic/polybasic)
Tab. Examples of acids with different basicities
| Monobase (one hydrogen) | Dibasic (two hydrogens) | Polybasic (three or more hydrogen protons) |
| HNO3 | H2S | H3PO4 |
| HF | H2SiO3 | H3BO3 |
| HBrO | H2CO3 | H4P2O7 |
Dissociation of water
Dissociation is the breakdown of a substance into its component molecules. The properties of an acid or base depend on the equilibrium that is present in water:
H2O + H2O ↔ H3O+(solution) + OH-(solution) Kc = [H3O+][OH-]/[H2O]2 Equilibrium constant of water at t=25°: Kc = 1.83⋅10-6, also the following equality holds: [H3O+][OH-] = 10-14, which is called the dissociation constant of water. For pure water, [H3O+] = [OH-] = 10-7, hence -log[H3O] = 7.0.
This value (-log[h3O]) is called pH - hydrogen potential. If pH < 7, then the substance has acidic properties, if pH > 7, then the substance has basic properties.
How can you get poisoned?
Hydrocyanic acid is very toxic. When it enters the human body, signs of poisoning appear fairly quickly. This substance can enter the body with products that contain it, as well as with those products that have been treated with cyanide.
Most of this toxic substance is found in almonds. The total amount can reach up to 3%. A person only needs to eat a small handful of almonds to become poisoned. In addition, this dangerous substance is found in the seeds of berries and some fruits. Most acids contain:
- peach – up to 2.8%;
- apricot – up to 1.6%;
- plum – up to 0.95%;
- cherry – about 0.8%;
- apple – approximately 0.6%.
In almond grains and fruit kernels, hydrocyanic acid is not present in pure form, but in the form of amygdalin glycoside. It is this substance that gives the specific taste and aroma to nuts. Once in the human body, amygdalin breaks down into three components, one of which is hydrocyanic acid. Bitter almonds are especially rich in this substance, so adults can eat this product in small quantities, but children should not eat it at all.
Symptoms of hydrocyanic acid poisoning
Acid, entering the blood, forms a compound with oxygen in red blood cells, blocking its release and release to tissues. As a result, the concentration of oxygen in the blood sharply increases, but it does not reach the tissues and organs, and their hypoxia develops.
The most delicate organ, the brain, is affected first and most severely. All its vital centers are suppressed, which leads to oppression of organs and systems, and the entire body quickly fails. External signs of hydrocyanic acid poisoning:
- Rich pink color of the skin and mucous membranes,
- Dizziness, headache, loss of balance, numb lips, dilated pupils,
- Increased heart rate, chest pain,
- Increased breathing, shortness of breath,
- Nausea, vomiting,
- Bitterness in the mouth and metallic taste, frequent urge to defecate.
A victim of hydrocyanic acid poisoning smells the characteristic smell of bitter almonds when breathing.
In severe cases of poisoning, tachycardia is replaced by a slowing of the pulse, loss of consciousness quickly occurs, paralysis of the respiratory center, and convulsions develop. If help is not provided, death occurs within 2-3 minutes.
Reactions with dilute nitric acid
Dilute nitric acid reacts with metals located to the left and to the right of hydrogen. During the reaction with active metals, ammonia is formed, which immediately dissolves and reacts with the nitrate anion, forming another salt. The acid reacts with metals of medium activity to release molecular nitrogen. With low-active ones, the reaction proceeds with the release of divalent nitrogen oxide. Most often, several sulfur reduction products are formed in one reaction. Examples of reactions are provided in the graphical appendix below.