Stainless steel has been processed for more than 100 years, but this procedure is still fraught with technological difficulties. Many parts are made from stainless steel, gradually replacing carbon steel, which can no longer withstand increasing loads: for modern mechanisms, the strength threshold of carbon steels is too low. The strength and durability of stainless steel, which does not change its properties at high temperature, pressure and exposure to aggressive environments, entails the complexity of its mechanical processing.
Features of stainless steel processing
processing a stainless steel part on a lathe
The hardness and tensile strength of stainless steel and carbon steel are almost the same. However, only the mechanical values coincide. The microstructure, ability to harden during processing, and corrosion resistance are different.
When processing by cutting, stainless steel is first elastically deformed, then processed easily, after which it enters the hardening stage. At this stage, cutting is only possible with a significant increase in effort. All these stages go through during processing and ordinary steel, but high-alloy steel is strengthened much more noticeably.
The main problems in steel turning are:
- strain hardening;
- removal of chips;
- working tool resource.
Viscosity. The plasticity of steel, especially characteristic of heat-resistant grades, adds additional complexity to processing. The chips do not break off, like carbon steel, but curl in a long spiral.
Low thermal conductivity. The weak thermal conductivity of stainless steel is its advantage when used, but its disadvantage when processed. At the cutting site, the temperature increases significantly, so it is necessary to cool the metal using special liquids. They not only eliminate heat, but also prevent the formation of hardening and facilitate processing. Hardening appears on the working tool, changes its shape and renders it unusable. Therefore, alloy steels are most often processed at low speeds and with special tools.
Saving properties. When exposed to heat, steel does not lose its hardness and strength. This property is most pronounced in heat-resistant steels and, in combination with work hardening, it causes rapid failure of cutters and does not allow them to work at high speeds.
Abrasive compounds. Stainless steel contains microscopic carbide and intermetallic compounds. Increased hardness makes them like an abrasive. The cutters are worn down and require constant editing and sharpening. Friction during turning of stainless steel is an order of magnitude greater than during turning of carbon alloys.
Uneven hardening. During the turning process, the material is hardened unevenly. This is not very important when processing small parts. But it will seriously affect the quality of the shaft or other large part.
Metal bluing
Metal bluing can be done not only in production, but also at home. In this case, the part changes its shade. The presented procedure ensures a beautiful appearance of the product and also improves its anti-corrosion properties. During bluing, the surface of stainless steel is covered with a very thin protective layer. There are several ways to process the material:
Metal bluing
- Alkaline. The process requires an alkaline solution containing an oxidation catalyst. Moreover, the processing is carried out at high temperatures: up to 150 degrees.
- Thermal. Here you need an appropriate environment and elevated temperature: a superheated atmosphere, an ammonia-alcohol solution in a vapor state (but a small layer of varnish is first applied to the surface).
- Acidic. A physicochemical or electrochemical method is needed here.
To make the stainless steel surface smooth and shiny, bluing is carried out in oil. When using chemicals, oxides or the metal itself act as surface dyes. This operation involves the interaction of stainless steel with liquid solutions of metal salts.
Metal bluing agent
With this method, the most dense and close merging of the surface of the product with the paint film occurs. The composition used for bluing contains different components and consistency. It also has a different texture.
You can carry out the procedure at home, but its quality will not be as good as the factory one. It uses saltpeter, citric or phosphoric acid. In any case, the procedure must be approached responsibly and carefully.
Chip removal
Stainless steel shavings form long spirals
The accumulation of long spiral chips disrupts the machining process. Therefore, taking into account the ability of stainless steel to harden during deformation, special designs of chipbreakers are being developed. In addition, intensive surface treatment with cooling lubricant is used.
Lubricant is supplied from inside the torch under high pressure to:
- quickly and noticeably reduce the temperature of the torch;
- remove the chips away from the cutter so as not to accelerate its wear;
- crush the chips into small particles that are easier to wash away from the work area.
High-pressure cooling is widely used in turning stainless steel products. The solution is sprayed directly into the treatment area. When the liquid hits a hot surface, it evaporates and takes away some of the heat. The surface cools down. The disadvantage of this method is the high consumption of coolant. But the service life of the tool increases six times.
In the defense and high-precision industries, steel is cooled with carbon dioxide during processing at a temperature of -78 degrees. This is the most expensive and most effective way.
The shape of the chipbreaker is also very important. Its geometry should be positive to reduce heat generation. A positive rake angle reduces self-hardening of the material and the appearance of bead on the cutter surface, eliminating the main causes of damage during steel turning.
Only a specialized chipbreaker should be used for alloy steels, although chipbreakers are usually produced as universal chipbreakers for working with a wide variety of metals. We produce special chipbreakers and cutters for finishing, roughing and semi-finish cutting of stainless steel. They produce the best results and increase productivity.
Grinding and polishing process
The presented alloy is used not only for the production of various parts, but also for the manufacture of decorative items. To ensure a beautiful appearance of stainless steel surfaces, a procedure of grinding and polishing is carried out.
Grinding
This process allows you to eliminate or reduce the severity of defects on the surface layer of the material. It is performed manually or using automated machines (if a large amount of work needs to be done). The most commonly used machines are:
- belt pneumatic file;
- devices on which sanding belts are attached;
- drum-tape machine.
At home, stainless steel is polished using abrasive sheets. All work is carried out in the following sequence:
- removal of welds and burns;
- limiting the treated area of metal using aluminum tape (2-3 layers);
- carrying out translational and reciprocal movements using hand tools, while it is necessary to control the pressure on stainless steel;
- removing the aluminum tape and sanding subsequent areas of the product.
To avoid damaging the material when grinding stainless steel, you must first select the grain size of the abrasive belt. For this purpose, rough metal blanks are used. Products are also processed using a petal wheel.
Polishing
Polishing stainless steel gives it a metallic shine and makes it look attractive. This procedure is also performed manually or on automatic machines. Chemical, electrical and plasma polishing is also used. At home, mechanical methods are more common.
Polishing stainless steel is the final stage of working with the presented material, giving it a marketable appearance. It is done in production or at home using a felt wheel.
Polishing stainless steel - variations
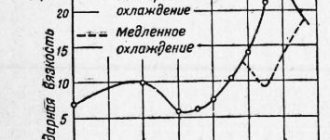
Self-strengthening of steel during deformation
The austenitic type of stainless steel is more prone to self-strengthening, which causes additional difficulties in any type of processing. The more the material is hardened, the faster the cutter wears out. This problem is less pronounced when using special cutting inserts. Their surfaces wear out longer, and the working edges are sharper than usual. Sharp cutting surfaces have time to process the part before the steel self-strengthens and sagging appears.
The task becomes more complicated when working in several stages. Sometimes it is impossible to select enough metal in one approach. Then this is done in stages. It is more effective to remove 3 mm of steel in two approaches than in one 6 mm. It is also recommended to remove an unequal layer of metal in the first and second approaches, for example, 4 mm and 2 mm.
How to drill through stainless steel. Tips for choosing a drill for stainless steel
Parts and objects made from stainless steel are widely used in industry and everyday life. Stainless steel is popular due to its anti-corrosion properties. Corrosion resistance significantly extends the service life of engineering parts, structural metal structures, plumbing elements and household items. In addition, most grades of stainless steel are distinguished by high hardness, strength and, at the same time, toughness of the material. These properties have a positive effect on the performance characteristics of elements made from them, but make them difficult to process.
Often when working with stainless steel parts, it becomes necessary to make holes in them. Drilling holes in stainless steel is somewhat more difficult than in ordinary unalloyed or lightly alloyed steels. In the article below we will discuss how to drill a hole in stainless steel.
Cutting tool
cutters for processing stainless steel
The self-hardening effect leads to rapid wear of the cutters. Therefore, special edge shapes, rake angles and special materials are developed for stainless steel cutters.
There are two types of specialized cutting tools:
- with chemically deposited cutting edge coating (CVD);
- with physically deposited coating (PVD).
Tools with chemically deposited coatings (CVD) allow stainless steel to be processed on lathes at high speeds and do not wear out longer. But these cutters are very difficult to straighten.
Tools with physically deposited coatings (PVD) are used for austenitic stainless steels. They are thinner than CVD, with a smooth surface and a sharp cutting edge. But they wear out faster (since the coating thickness is less) and operate at lower speeds.
Types of incisors
The highest wear resistance is shown by cutters coated with TiC made of hard alloys. During the production process they are cyanidated or nitrided. An expensive and very effective way to strengthen plates is to coat them with cubic boron nitride.
Carbide cutters VK3, T15K6 and T30K4 are quite strong, hard and do not wear out for a long time. T5 K110 and T5K7 are distinguished by higher viscosity; they wear out faster. But for shock loads, it is preferable to use plates with high-viscosity solderings VK8 and VK6A.
Sharpening cutters
Drilling technique
Drilling a hole larger than 6 millimeters must be done in two stages. First, a hole with a diameter of up to 5 mm is drilled, and then brought to the required diameter. The absence of internal stresses before drilling will simplify and expand the range of operating parameters. This will extend the life of the drill and avoid overheating of the surface.
Before drilling into stainless steel, find out its grade, thickness, and recommended drilling parameters. Decide on the coolant. If this is not available, you can use vegetable oil (olive or sunflower), lard, or an emulsion of laundry soap in water.
Source of the article: https://solidiron.ru/steel/osnovy-sverleniya-nerzhaveyushhejj-stali-vybor-sverla-dlya-nerzhavejjki.html
Processing technologies
There are techniques to minimize the negative properties of stainless steel:
- minimize the thickness of the removed metal layer and increase the spindle rotation speed - the surface processed in this way will be more rough;
- using acid as a lubricant significantly increases the wear resistance of cutters, prevents the occurrence of work hardening, but leads to rapid destruction of the lathe, and also has a bad effect on human health.
The video demonstrates the manufacturing process of stainless steel fittings:
Preparatory work
Preparatory work consists of eliminating some of the negative factors associated with drilling stainless steel. Let's look at what properties make this process difficult:
To avoid the disadvantages described above, before drilling it is necessary to decide how the surface will be cooled and what to do to prevent chips from sticking. Among the effective methods, water is suitable. If the volume of metal being drilled is more than one hole with a diameter of 10 mm in a sheet of 2 mm thickness, then you should consider cooling with oil or a special emulsion.
Attention. Cooling with water when drilling stainless steel occurs during the process itself. Cooling by lowering a hot drill into a jar standing nearby leads to hardening and tempering of the metal and loss of basic properties. Coolant is supplied to the contact point when drilling. To reduce consumption, you can place a rubber ring on the surface, surrounding the contact point.
Drilling a sink
The question often arises about how to drill a hole in a stainless steel sink. It is important to understand here that the sink should first be dismantled so as not to damage the plumbing elements and the bedside table. Then the sink needs to be installed on a flat horizontal surface. Next, the location of the future hole is marked and it is cored. If the hole is intended for installing a faucet and has a large diameter, then it is better to use a conical step drill, since the metal of the sink body is thin-walled.
If you are in doubt about how to drill stainless steel with a drill, then there are no big features from the technology described above. The main thing is to use the correct drill and ensure that it is well centered. Use a drill with speed control, set the torque to a position close to the maximum. A hand drill can help produce holes with a diameter of up to 10 - 12 millimeters.
Ways to improve chip removal
Turning is a process that produces long, twisted chips, the accumulation of which makes work difficult. To remove chips from stainless steels, it is proposed to use a cutting tool with an internal coolant supply under pressure, which is especially effective for high-alloy steels. The use of such a tool provides:
- effective cooling of the cutting edge;
- breaking chips into small particles, facilitating their rapid removal from the cutting area.
The disadvantage of this method is the high consumption of coolant. In high-precision production and in the military industry, the most expensive and effective method is used - cooling using carbon dioxide.
The design of the chipbreaker plays an important role in processing stainless steel on a lathe. Specialized tools for corrosion-resistant steels must have a positive outer angle, which reduces self-hardening and metal build-up on the cutting edge.
Satin finishing is... What is Satin finishing?
Satin finishing is a decorative treatment of metal by mechanical, chemical or electrochemical methods to obtain a semi-shiny surface from micro-irregularities. Encyclopedic dictionary of metallurgy. - M.: Intermet Engineering. Editor-in-Chief N.P. Lyakishev. 2000.
Synonyms:
- satin finishing
- weldability
See what “Satinizing” is in other dictionaries:
- satin - calendering, satin Dictionary of Russian synonyms. satin noun, number of synonyms: 2 • calendering (6) • ... Dictionary of synonyms
- satin - I, cf. satiner, German satinieren. Action by sign. verb satin. BAS 1. Lex. Toll 1864: satin; BAS 1: satining ... Historical Dictionary of Gallicisms of the Russian Language
- SATINING - adding shine and gloss to paper, cat. for this purpose they are placed between polished. zinc boards and passed between rollers. Dictionary of foreign words included in the Russian language. Pavlenkov F., 1907 ... Dictionary of foreign words of the Russian language
- satin finishing - Decorative processing of the base metal and (or) coating by mechanical, chemical or electrochemical methods to obtain a semi-shiny surface due to micro-irregularities. Metal coating topics. and non-metal... Technical Translator's Guide
- Satining - (from the French satin satin) is the same as calendering. See also: Paper glazing ... Advertising and printing
- satin finishing atitikmenys: engl. satin finishing rus. satin ... Chemijos terminų aiškinamasis žodynas
- Satin coating - in wallpaper production, see Wallpaper production... Encyclopedic Dictionary F.A. Brockhaus and I.A. Efron
- Satin - cf. process of action on ness. Ch. satin Efremova's Explanatory Dictionary. T. F. Efremova. 2000 ... Modern explanatory dictionary of the Russian language by Efremova
- satinization - satinization, I ... Russian spelling dictionary
- NDP. Satinizing paper (cardboard) - 40. Polishing paper (cardboard) Giving paper (cardboard) a gloss using a friction or polishing calender, machine or cylinder of a paper (cardboard) machine Source: GOST production*: Production of paper and cardboard. Terms and... Dictionary-reference book of terms of normative and technical documentation