Metal marking: technology, equipment, price, consumables
Marking is the application of certain information to an object to identify it for subsequent use.
From the definition it is not difficult to guess that marking metal is also important, because modern industrial production is unthinkable without strict accounting of all units of products. All subsequent control over details is accomplished precisely through a specific sign. Labeling is another way of positive self-promotion for the manufacturer, and for the buyer it is a sure sign of quality. Markings applied to metal have the following functions :
– identifying (allows you to recognize and highlight a specific part);
– informational (carries certain information about the part);
– emotional (works as an element of advertising, used in rare cases).
Marking methods:
– Additional
. Applied to tags, stamps, labels, stickers and other information carriers.
- Straight.
Marking is applied directly to the product in the form of a barcode, letters or numbers, or images. It is carried out by laser engraving and metal marking.
In metallurgy, a direct method of marking is used, since labels and labels can get lost, mixed up, torn, or erased, and laser engraving and metal marking are not influenced by any external factors.
The labeling of metal products is taken extremely seriously and responsibly. The fact is that when constructing and assembling any mechanism, order and accuracy are impossible without special signs that carry specific information. From year to year, the manufacturing technique of a part and its design may change both in terms of quality and design features. Therefore, in such cases, only parts with “old” markings are suitable for repairing old equipment, and for modern ones – with “new” markings. In addition, the marking contains additional information about changes in the design or manufacturing technology, warranty period, and material.
Metal marking technologies:
There are several main types of metal marking technologies:
Each of them has its own specifics in application and use.
How is laser marking carried out?
The technology of metal marking by laser method has its own specifics. The top layer of the part is removed using a non-contact method (without touching the surface of the metal product). This gives a guarantee for the indefinite life of the marking, since it is not susceptible to any possible external damage. If the material is very fragile (glass or plastic), then using this marking method you protect it from deformation. Then, using a laser marker, information is applied to the prepared surface of the metal product: serial number, manufacturer’s logo, bar code and batch number. It is readable, not erasable and contains recommendations for storage and use, as well as sales of parts. Laser marking cannot be removed either physically or chemically, which already indicates its high quality.
The main advantage of laser marking is that almost all materials can be used: wood, glass, plastic, metal products or leather - just determine the correct length of the laser beam.
Regardless of the type of metal or their alloys, laser marking can be carried out at any stage of part manufacturing, without special conditions and requirements.
If consumables for marking metal in different ways are characterized by a high cost, and the marking process itself takes a sufficient amount of time, then laser marking is different in that it does not require large additional costs and is done very quickly.
Advantages of laser metal marking:
– laser marking is carried out using computer modeling;
– products of any parameters and from almost any material can be labeled;
– due to rapid application, laser marking does not affect the level of operation of the enterprise;
– information is applied very clearly, it cannot be changed or erased;
– laser marking requires little energy consumption;
– marking can be done on any uneven surface in the most inaccessible places;
– counterfeiting of the product is excluded;
– laser marking does not stand the test of time.
Why do you need high-quality metal marking?
In addition to keeping records at the enterprise, labeling is also necessary for the buyer. By reading the information on the parts, he can decide what exactly is right for him. Undoubtedly, if the marking was not done very well, or the basic information about the product is impossible to read, the buyer will not want to deal with such details and will refuse to purchase them at his own peril and risk.
This will not happen with laser marking. It is distinguished by its excellent quality, well written letters and numbers. It cannot be faked, it cannot be corrected. This becomes a guarantee that the part was manufactured at the factory. The seller and the buyer can be confident in their choice.
What equipment is used for metal marking?
Industrial metal marking is now widely done using lasers. When producing large batches of products, it is very important to keep records of all elements and not miss anything. For this case, the laser is more suitable than ever. To carry out all the above processes, you need to use metal marking equipment. The equipment may consist of a specific ready-made kit, which consists of:
– computer for process control;
– transmission and control systems;
Alternatively, metal marking equipment may consist of a hand-held marking machine and may also be integrated into a production line. You can use markers on a frame, which are meant as a separate workplace for the marker.
In any case, industrial marking of metal is carried out by serious manufacturers who are ready to take responsibility for their product and provide the buyer with all the information that he may need.
What to do if you need to attach markings to metal?
To attach markings to metal, special tags are used. A metal plate or tape is coated with special ceramic paint, and a row of markings is applied to it using a laser.
If the markings are applied to separate plates, then the markings are attached to the metal using self-tapping screws or self-tapping screws. This method is appropriate only if the introduction into the product does not cause harm to it, does not affect the quality and its size allows such manipulations. Otherwise, the signs can be attached by welding.
If marking according to technology should be carried out only on hot metal, then, naturally, it will not be possible to attach the tag manually. In this case, an automatic fastening unit is used, consisting of the following components:
– installation for making tags;
– manipulator (deliveries the tag to its destination);
– automatic welding machine;
– operator terminal where the control panel is located.
If you use plates for marking, then they can be used on any type of material and regardless of the characteristics of the surface. Such signs are not influenced by external factors. The information is placed in a prominent place and is easy to read.
Using consumables for metal marking
As for consumables, their price and quantity depend on the type of marking you choose. As already mentioned, the least amount of consumables for metal marking is needed for the laser type of marking; you just need to have the appropriate equipment. For other types of marking, a number of consumables are required - you can familiarize yourself with them when purchasing a marking machine or studying the conditions for its use.
Basic consumables:
– carbide needle for marking (the needle is used directly for engraving; when it comes into contact with metal, it is erased and can be changed);
– spring (returns the needle to its place, becomes unusable after using 2-3 needles);
– liquid lubricant (needed to extend the service life of the entire mechanism by regularly lubricating its parts);
– extended marking needles (used if the standard needle length is too short).
Prices for metal marking
When metal marking is carried out to order, prices can vary greatly. It all depends on the financial costs of additional materials. For example, with laser marking you do not need to spend money on anything except electricity - all processes are carried out automatically and without the use of additional equipment.
For attached metal markings, the price will differ, since the price includes plates, screws and paint.
High-quality marking does not mean expensive application. The price depends on the type of marking.
Thus, we can conclude that in any production of metal products, the use of markings is mandatory, since this is the key to quality. It provides the buyer and manufacturer with all the necessary information.
Devices for impact marking of metal
Marking, from him. markieren - mark - applying certain marks or inscriptions to a part in order to be able to identify it. In mass production, this is a point in the technological process
Manufacturing marking – applying symbols to equipment, tools, parts and assemblies.
Application methods:
•branding •electrochemical •thermal transfer printing •drop-jet marking (ink) •laser marking •impact dot marking •drawing application
Branding Branding is the simplest marking, carried out on a surface by striking a metal stamp or stamp on a mechanical press.
The usual set of stamps are stamps with a mirror image of the required size of letters or numbers. A direct image is obtained on the part.
To mark parts from injection molds, inverse inserts are used, then the castings will have a readable inscription. This method allows marking of non-ferrous metals and steel.
Electrochemical Marking method is widely used for marking metals of any hardness. It is an economical and common marking method that rivals laser marking. Often used for marking automotive and aircraft parts.
Thermal transfer printing Thermal transfer printing is a printing method in which the ink layer is transferred from a special tape to the so-called. thermal transfer label to accompany a batch of parts
Inkjet marking This is ink marking. Inkjet printers are used that apply markings directly to the part, mainly on a conveyor
Laser marking A technology in which information is applied by a laser that burns the surface of an object. A laser printer is used to apply graphic information to any solid material. For marking metals, a fiber-optic type of laser is good, which produces reliable markings. Its advantages are speed and quality.
Impact-dot marking The marking process involves applying a group of dots to the metal surface, the sum of which forms the inscription line. The equipment is controlled by CNC.
A pneumatic drive is faster, but an electric drive is more practical for most tasks.
The difference from other methods is that the impact-point method provides an indelible inscription even on parts made of plastic materials and hardened metals.
Drawing marking is done by engraving lines on the surface of a part with a carbide needle. For example, VIN numbers are applied to the body of a passenger car. Limitation: The needle does not mark very hard material (45 HRc) well.
RFID seems to be a promising area. RFID (Radio Frequency IDentification, translated as radio frequency identification) is a method of auto-identification of objects when indicators stored in the so-called radio signals are read. transponders (RFID tags).
Features of marking of technological equipment
When it is not possible to mark a product due to its small size, it must be reflected on a durable label attached to the product. This will help you use it correctly.
The marking is applied on the tongue, depending on the location where the equipment is used. It is also important to indicate on the designation the exact address of the manufacturer or enter a special code by which you can find it on the Internet.
The signs must be a minimum of 5mm in height and spaced proportionally to each other.
Characteristics
Modern paint and varnish coatings are the result of numerous studies of compositions in practice after the introduction of various additives into the mixture that improve the protective coating. The main physical and chemical characteristics of paints are given in the tables. Main characteristics of metal paints
| Comparison criterion | Option | Note |
| Based on composition | oil (MA) | The MA marking indicates the use of oils of plant origin, in particular natural drying oil. Oil paint is used indoors, as it has poor resistance to seasonal air temperature changes. The peculiarity of the paint is that the layer created does not allow air to pass to the metal surface. This is good when painting indoor water pipes, but due to the lack of gas exchange (the paint hermetically seals the metal surface), it is necessary to renew the coating once a year, as the layer peels off. |
| Epoxy (EP) | The paint is intended for use on non-household products (car body, oil pipelines, alkali, gas, acid pipelines), since the epoxy resins included in the composition have a toxic effect on the human body. The protective coating can withstand high temperatures without destroying the layer. | |
| Alkyd (PF and GF) | It has a high degree of adhesion and is used for zinc coated metals. The composition is easily applied to form an alkyd film that is resistant to physical and chemical influences. Poorly withstand high temperatures. Suitable for painting galvanized iron (roofing), zinc coated pipes and fittings. | |
| Acrylic (AK) | The composition includes polyacrylates (polymers of acrylic acids) with high heat resistance. Thanks to these polymers, coatings are weather-resistant and resistant to intense ultraviolet solar radiation. The paint can withstand high temperatures without cracking or deforming the layer. Refers to water-based compositions and is non-toxic. Substances that prevent the development of corrosion are added to the composition. Heating radiators and metal interior elements are painted with acrylic paint to preserve the appearance for a long time (resistant to physical impact). | |
| hammer (ML) | ML – Pigments in a mixture of synthetic resin solutions with the addition of a solvent. The so-called “hammer effect” forms embossed patterns on the painted surface. Hammer paints are used for rust protection and finishing: fences and gates, garden furniture and metal grilles. | |
| Chemical and physical properties | Viscosity | The viscosity index affects the method of applying the composition to the surface (spray gun, brush, roller). If the viscosity is incorrectly selected, the quality of work and the strength of the protective coating are reduced. Domestic manufacturers indicate the viscosity of the dye in seconds; Imported materials are characterized by a different unit of measurement - DIN. The optimal viscosity of the dye, primer or varnish is usually indicated by the manufacturer on the packaging. Most of the compositions, unless otherwise specified by the manufacturer, are intended for painting with a brush or roller. For a roller and brush, the paint viscosity is 18-22 sec or 30 DIN (usually the composition in cans is already ready for use with this particular tool). Before painting with a spray gun, dilute to the consistency of rich milk with a solvent intended for this paint (50 sec or 80 DIN). |
| Covering power | Covering power is expressed in kg/m² or ml/m²; some manufacturers give more understandable values - how many square meters can be covered with a liter of paint m²/l. The properties of the composition to overlap the previous layer depend on this indicator. The higher this indicator, the lower the paint consumption rate. High-quality paints are able to cope with the task in one layer application cycle. One layer for a well-prepared surface has a value of 120 ml/m² or 12 m²/l. | |
| Density | Different surfaces have their own paint density recommendations. For smooth metals one liter of paint per 14-16 m², for rough metals one liter per 6-10 m² | |
| Drying speed | The drying speed is affected by the base of the composition. Alkyd compositions with light fractions of solvents dry the fastest, polyurethane enamels (more viscous) take a little longer, followed by water-based compositions. You will have to wait the longest for oil paint made with natural oils to dry. |
There are standardized designations for all paints. Here is the transcript: Marking paints on metal
| Designation | Letter and number designation |
| Base (film-forming substance) | MA (oil); PF and GF (alkyd); AK (acrylic); BT (bitumen); KCh (rubber); EP (epoxy); NC (nitrocellulose). |
| Type and application of the composition | 1 – external use (weather-resistant); 2 – internal use (limited weather resistance); 3 – conservation products for protective work; 4 – water-resistant; 5 – enamels; 6 – petrol and oil resistant; 7 – chemically resistant; 8 – heat-resistant; 9 – electrically insulating; |
For example, alkyd enamel PF-115. The letter designation “PF” indicates that the enamel is made on the basis of a pentaphthalic binder, the first number 1 is for external use, 15 is the catalog number.
The labeling of imported paints and paints and varnishes differs from the system described above, but the information required by the user must be indicated on the label in Russian.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the offers of paint manufacturers and the range of the most common compositions. The products of these brands meet quality standards and meet the stated characteristics. Summary table of manufacturers
| Manufacturer | Range | Average price per liter |
| 1. Alpina | 9 types of paints for exterior and interior use. The manufacturer offers compositions used indoors and for outdoor use. | 720-800 rubles |
| 2. Dufa | 3 types of enamel applied to rust | 540-700 rubles |
| 3.Hammerite | 3 types of products for indoor, outdoor and non-ferrous metals. | 780-900 rubles |
| 4. TEX | 4 types of universal action compounds | 400-500 rubles |
| 5. KrasKo | 11 types of paints and enamels of various effects | 450-500 rubles |
KrasKo (Russia)
Concept of labeling
Marking is the application of signs characterizing it to a product.
Methods of applying inscriptions on metal
This may include:
- Name,
- options,
- batch number,
- corporate logo,
- quality mark
The inscription should be clear, concise, and durable. Let's look at some ways of applying inscriptions to metal products.
Lettering methods
Branding methods can be different:
- Mechanical
- Chemical
- Electrical
- Photochemical
- Electrochemical
How to choose a labeling method? Usually the designer makes a choice by comparing some product parameters. Namely: product configuration, size, material, surface hardness, production volume, aesthetic requirements, the nature of the marking applied, its constancy, the degree of mechanization and automation of production.
Electric spark pencil
Today you can find several names: electric pencil, electric spark pen, electric marker.
Electric spark pencil
Using an electric marker, inscriptions are applied to a smooth metal surface.
This method is chosen in cases where the impact-point method is not suitable, stamps are inconvenient, laser application is too expensive or impractical.
The marking pencil is mainly used for metal components and parts where bulging of the surface due to the marking is not allowed.
It is often used as a means of adjusting and correcting markings on a flat or relatively flat metal surface. The type and alloy of the metal may be different.
Labels for marking rolled metal products
Labels must be firmly attached and easily visible. The material used for manufacturing is reliable and wear-resistant, so that during transportation and unloading they are not damaged or come off. Sometimes, for safety, labels are placed in special pockets.
When packing rolled metal into bundles, markings are placed in 2 places:
- the top sheet or strip of each bundle;
- marking card or label attached to the pack's binding.
When auto-marking thick and strip metal products, the side edge of the top sheet or strip of each bundle can be branded. On the sheets, the marking area is outlined using paint, bitumen or colored varnish. If the customer so requests, the markings are highlighted in a contrasting color, and the labels are perforated 10 mm from the edge for fastening with wire on all types of metal products.
Marking of rolled products in packs or without packaging if the size exceeds 3 cm and thickness exceeds 4 mm must contain:
- Name of the company;
- steel grade;
- Heat number;
- Batch number;
- all sizes.
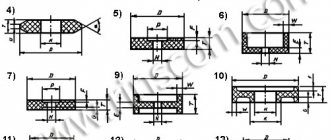
The marking on the label, the end of the roll or the edge of the metal sheet contains the company name, steel grade, heat number, batch number, all sizes, group or strength class, weight. For reliability and clarity of marking, the label can be metal, wood, plastic or moisture-resistant film; their area must be at least 24 cm2, and the letters must have a height of 5-20 mm and a width of 3-12 mm.
Sometimes it is allowed to deviate from the specified font size when marking with paint. It can reach 1 m in height and 7 cm in width; on rods with a diameter of less than 6 cm and strips with a width of less than 5 cm it can be reduced to 2-4 mm.
The consumer may request additional marking with colored paint; for rolled metal made of mild steel, marking with a longitudinal stripe; for rolled metal made of mild steel, a transverse stripe; marking can occur at a specified font depth. Transport marking is regulated by GOST 14192.
Impact dot marking
The impact-point method is used for engraving on products made of soft metals. For example, such as brass, bronze, fittings. You can also order markings on metal for some piece products.
It is recommended to use for metal assembly units (assemblies) and parts, except thin-walled ones.
Impact dot marking
- With this equipment you can apply markings to any surface.
- This method is often used in the production of pipes and other metal structures.
- The main advantage of this method is the high speed of operation and the absence of consumables.
- The markings are clear. Has high resistance and durability.
What are the methods and devices for marking?
Methods and devices for marking metal are divided into the following types.
Drop jet method. This type of marking is notable for the fact that it does not completely damage the metal surface. Drip-jet markings do not corrode or oxidize. The design is created by applying ink drops.
Laser method. It allows you to easily apply markings to any type of metal: nickel, brass, etc. To apply an image in this way, the product is installed in the device and the parameters of the future marker are set. Application occurs like this: the laser beam moves and burns the outline of the marker to the set depth and width.
Laser marking
This marking method is represented by various devices. The following markers are possible:
- Gas laser
- Solid State
- Fiber optic markers for metal and plastic
- Lasers for delicate marking of electronics
- Ultraviolet for products in instrument making
- Double-headed devices for double efficiency
Many large enterprises in mechanical engineering, aircraft manufacturing, and instrument making give preference to this particular marking method.
Electrochemical methods of marking on metal
Along with mechanical marking, electrochemical marking is also used - this is a technology for applying images, logos, alphanumeric information using electric current and acid.
Electrochemical marking
The operating principle is as follows. The power supply supplies electric current to the part through the electrode. The current, passing through the material soaked in the electrolyte and a special dielectric stencil for marking, leaves an etched mark in an empty space. It is necessary to ensure that the stencil fits tightly to the surface of the part to be marked.
The electrolyte for electrochemical marking is a saline solution that speeds up the process of transferring charged electrons between potentials.
The effective voltage for the etching reaction to occur is from 3 to 15 V. The peculiarity of this method of marking metal is that the boundaries are somewhat fuzzy. Therefore, the logo and details on it should be large enough.
Marking using plates (tags)
In recent years, marking using welded plates (tags) has become in demand for many types of metal products. Marking with welded plates provides reliable automatic identification of any metal products, so it has found wide application in marking hot metal. Welded plates do not interfere with technological processes for processing metal products and are reliable during further transportation, warehousing and storage.
The advantages of this marking method in metallurgy include the following:
- a label with markings can be attached to any metal product, regardless of its size, the nature of the surface, the temperature of the product, etc.;
- the marking carrier is a pre-made metal plate with clear markings, which is easy to read (including automatically using detectors or scanners) and is not afraid of bad weather and adverse weather and atmospheric conditions;
- To automatically read information about a product, a bar code is almost always applied to plates, which can carry a very large amount of information about the product and its manufacturer;
- When used on a mass scale, the use of marking plates is economically justified, especially in cases where applying another type of marking is impossible or unreliable.
Plates for marking pipes, sheets, coils, rolled products, pigs, slabs and other things are made of metal with the application of special white ceramic paint. After non-contact CO2 laser application of alphanumeric codes and bar codes, the result is clear, high-contrast markings that are resistant to wear and adverse external conditions. Currently, linear one-dimensional (1D) barcodes in the form of lines are used to encode hardware products. All information about the product and its manufacturer is encoded using transverse lines and spaces between them.
It is possible to use various barcodes used in industry and readable by standard certified detectors (scanners). When selecting the most optimal symbol (Code 128, 39, 2 of 5, etc.), the conditions for applying a barcode for each type of metal product are taken into account, as well as the amount of information that must be used for marking in metallurgy.
A special laser printer is used to produce marking plates. Using a computer, the operator can set on the operating terminal or receive via computer networks from a higher-level process control system all the necessary data for printing plates. The laser printer for the production of marking plates is very compact and can be easily placed next to the personal computer of the installation operator. The choice of the required laser printer is determined by the requirements for marking plates:
- dimensions of the marking plate;
- the amount of information to be encoded, as well as the size of the encoding that must be applied to the plate;
- required performance (sign printing speed).
The starting material for the manufacture of marking plates is a special metal tape with a ceramic coating, on which the markings of pipes, sheets, rolled products, etc. are laser burned.
Laser-marked decals are attached to hardware either manually or using automated welding equipment. For manual fastening of marking plates, construction guns or manual welding machines are used.
The use of automated welding equipment may be determined by working conditions, as well as the desire to reduce the amount of manual labor, which saves not only labor, but also time. Marking of hot metal, when the temperature of metal products reaches 1,000 ºС, is better and safer to carry out using automatic welding machines. Thus, marking of slabs cast on continuous casting machines is possible only with the help of automated equipment, without human intervention.
The choice of method for attaching the marked plate is carried out based on the characteristics of the technological process of the metallurgical enterprise and taking into account safety precautions for personnel. The following operations are most often used to attach marking plates:
- fastening with nails (screws, rivets, slots, etc.);
- fastening with wire or dressing tape;
- welding using MIG technology;
- resistance or arc welding.
The unit for automatic fastening of marking plates consists of the following components:
- equipment for making marking plates (laser printer, scissors, etc.);
- a manipulator for delivering the sign to the place of fastening on the metal product;
- automatic welding machine for attaching the marking plate;
- operator's workstation with control panel and service panel;
- software in a separate secure unit.
Main characteristics
• Possibility to attach permanent, highly secure labels with barcodes and other information
• No impact on metal
• High reliability of connection using welding
• Short marking cycle - about 15 seconds.
To identify and trace products, marking and branding systems are complemented by systems for character and brand recognition.
Drop jet marking of metal
Using drop jet metal marking , you can apply various images and letters to flat or cylindrical steel.
The peculiarity of this method is that it is possible to apply color markings using pigments of any shade. Equipment with two heads is commercially available, allowing complex visualizations to be performed.
Caleslast marking
This method resembles the operation of an inkjet printer on paper, only it prints on metal.
Products sold in steel bottles and small containers are marked. Marking is done on the bottom or neck of the product. There are portable and stationary inkjet printers for marking.
This equipment is often used in production. Industrial engraving is highly productive. Ideal for use on a conveyor without stopping the process.
As a rule, a barcode and a set of certain digital data are stamped.
Although the quality and clarity of the contours is not high, it is sufficient for reading barcodes.
In this article, we have not considered all methods of metal marking.
Recommended viewing:
Color marking of resistors: definition...- How and with what to charge a li-ion (Li-po) battery?…
Online calculator for color resistor markings- What is the best way to connect copper and aluminum...
Marking is a necessary element in any industry
Today, markings are used everywhere. They are used on various types of industrial equipment and tools. Marking is needed because it is a kind of code that tells about the composition of the metal and its quality. Marking is an alphanumeric designation applied to any part of the metal surface.
Metal markings can be of two types:
The first type is an informative marker.
The second type is identification
In order for the marking to be durable and of high quality, it must be applied only with professional equipment, which is selected individually for each metal. Smart Marking company offers a wide range of marking equipment at affordable prices and manufactured to all standards.
Marking of metal products
Almost no modern production can do without labeling its products. The need for it is explained not only by legal requirements (often quite strict), but also by ease of operation. This applies to metal even more than to many other products, since it is sometimes almost impossible to distinguish one or another grade of steel by eye. In addition, applying information to your own products makes it easier to keep records at the enterprise. In our article today we will tell you how to place the necessary data on metal products. And let’s dwell a little more on the laser technology of their application.
Batch accounting at the enterprise
Practical need for batch accounting
or
accounting for manufactured products
is becoming more and more in demand for various manufacturing companies.
What is batch accounting?
This is an accounting of products produced from a certain batch of raw materials, in accordance with a certain specification, marked with data on belonging to a specific production batch, at each section of its processing.
Production batch
- this is a certain quantity of finished products produced on a certain equipment (work center), from a certain batch of raw materials, in a certain period of time, by a certain operator, packaged in a certain way, in a certain container, marked with an appropriate label, indicating a unique batch number on it.
Such information helps to determine: who, when, on what, from what, in what quantity and under what name released the products packaged in this container.
Metal marking functions
1. Informational. This is its main function. Thanks to the data printed on it, the consumer can understand what material the product is made of and what properties it has.
2. Identification. Allows you to recognize a specific product and distinguish it from others.
3. Emotional and motivational. Beautiful labeling can serve as an additional incentive to purchase the product. In turn, carelessly or illegibly printed data can make the buyer wonder whether he should contact this manufacturer.
Technologies and methods of data application
There are 2 application methods - direct and additional. In the case of the latter, the information is placed on a tag, label, sticker or some other item that is attached to the product. This method is not popular in the metallurgical industry because tags and labels can easily come off or get mixed up during transportation.
The main method of application is direct. That is, placement directly on the product. Let's consider several technologies for such marking.
1. Thermal transfer printing. For this method, special thermal transfer tapes are used, the paint layer from which is transferred to the metal under the influence of high temperature. The method is not very popular due to the large amount of consumables and lower marking reliability compared to other technologies.
2. Impact-point. Using a needle-impact printer, a large number of dots are printed on the surface of the product. This method easily applies both alphanumeric information and 2D barcodes, which are later read using a DPM code scanner.
Such marking is very popular among many manufacturers, since it does not require a large amount of consumables (the service life of one tungsten-carbide punch is several million blows) and is very wear-resistant. A paint layer is even applied over the markings without compromising the readability of the information.
3. Electrochemical. Data is applied on a stencil under the influence of an electric current charge. As a result of the reaction, the color or even the surface topography changes, forming the necessary letters and numbers.
4. Stamping (branding). It is carried out using a pre-made stamp on a mechanical press, which makes an impression with the necessary information. The standard set of stamps includes letters and numbers. From a technological point of view, this is the most cost-effective and simplest method.
5. Drop jet. Contactless method of applying data. It is often used in cases where the product is small in size and other data application technologies can deform it. Information is applied with drops of ink.
6. Drawing. It is carried out using a needle pressed tightly to the surface of the metal, which draws grooves on its surface. The technology is used as an alternative to dot-impact marking. The needle deforms the surface to a lesser extent and produces noticeably less noise during operation.
Branding methods
Hallmarking is an assay-technological operation of applying an imprint of the state hallmark on jewelry and household items made of precious metals.
1.
Mechanical method - stamp impressions are applied to the product using the impact method (mechanical hallmarks using a hammer, or on machines for mass stamping).
Imprints are applied both inside and outside. Special stands are also used - anvils that match the shape of the product. It is the most widespread method (70-80% of all products are branded this way). ADVANTAGES: Prints are clear, stable, durable. DISADVANTAGES: When applying stamps, the product may be subject to damage (some deformation from hitting the stamp with a hammer).
2.
Electro-spark method - stamp imprints are applied to the product with copper electrode stamps using an electric-spark installation.
The print is burned with a spark running along the contour of the electrode stamp in an aqueous environment under the influence of an electric current. A distinctive feature of the nameplate for electric spark branding should be the jumpers at the top between the contour of the nameplate and its signs, as well as the entry of the electrode in front from the top. 10-20% of jewelry is branded using this method (approximately 400 items per shift).
ADVANTAGES: Prints are clear, stable, durable. Products are not damaged. Possibility of application to specific shapes, as well as hollow ones, etc. products. DISADVANTAGES: The only caveat is the need for more thorough preparation of the area for the sample impression. The slightest pores, roughness, casting defects or insufficient polishing - and the electric spark method is no longer applicable.
3.
Laser method - carried out using a laser machine.
In this case, mask stamps are used. The outline of the mark is dotted. The surface must be carefully prepared and polished. 10-20% of jewelry is branded using this method (approximately 600 items per shift). ADVANTAGES: Prints are clear. Possibility of application to any surface (convex, concave, hollow). DISADVANTAGES: None, except for careful surface preparation.
Laser marking of metal. Advantages and disadvantages
Laser technology is the most advanced and reliable method of applying information to metal.
This marking has an indefinite lifespan since it is not subject to any physical or chemical influences. It can be applied to any alloy without any additional conditions. In addition, a clear advantage of laser technology is its high speed of operation, which does not affect the level of operation of the enterprise. It does not require large energy consumption, does not require consumables and allows you to apply the necessary information even in hard-to-reach places that are inaccessible to other marking methods. All that is needed to implement it is a computer with a data transmission and control system and a laser itself. The only disadvantage of laser marking is the heating of the surface during the marking process. Before sending the product to the warehouse after applying the data, you have to wait for some time until it cools down.
Product identification in production: quality indicator
What is an industrial marker?
1.1. Ink based markers.
1.2. Markers based on liquid paint.
1.3. Markers based on solid paint.
1.4. Markers for welding work.
The right tool for the job.
When performing multi-stage metal processing, the technologist (or other responsible person) reads the information recorded on the batch of parts, attaches the corresponding accompanying documents to them and moves the batch to the next technological section.
When the batch arrives to the welder, he re-accepts them. If the pieces are cut incorrectly, he has no choice but to reject the entire batch. How did this happen? The welder compares the task specified in the accompanying documentation for the received batch of workpieces with the markings on the workpieces themselves. The instructions in the documentation and the markings on the workpieces coincide only partially. The reason is that the markings on the workpieces are illegible - smeared because they were applied to a dirty surface of the workpieces. The result is rejection of products or repetition of the production cycle.
How can this be avoided?
Metal fabricators spend a lot of time trying to provide the best welding gun, the best stamping equipment, the best cutting tool, but very little attention is paid to one of the most fundamental tools of the metal fabricator - the industrial marker.
Rice. 1. Industrial marker Markal Pro-Line HP
What is an industrial marker?
Industrial markers are not like regular office markers, which are designed for writing on paper in offices, schools and homes. Like any production tool, the industrial marker has been designed to meet the rigorous demands of use in some of the world's most extreme environments.
The four most common categories of markers are:
1.1. Ink based markers. Perhaps the most common liquid ink based markers, they are best suited for marking on paper, cardboard, wood and other porous surfaces. They dry quickly and are easy to use, but do not work well on metal or other materials that are wet, oily, or rusty. Ink-based industrial markers are manufactured with high rigidity tips for longer use in harsh industrial environments. The ink of these markers has a special composition that is more resistant to moisture and wear.
Rice. 2. Marker with Markal DURA INK 60 ink
1.2. Markers based on liquid paint. Contains rich ink and is designed to produce bright marks. The applied markings take longer to dry than ink, but the result is clean, legible marks. The paint includes a number of special components for marking on wet, oily or rusty metals.
Rice. 3. Industrial marker with liquid paint Markal Pro-Line XT
1.3. Markers based on solid paint. They also have rich colors but are not damaged by marking on rough surfaces. Although marks made with hard paint markers can take anywhere from a few minutes to an hour to dry, these markers are durable and economical.
Rice. 4. Marker for rough surfaces Markal B Paintstik
1.4. Markers for welding work. Usually produced in two types. Soapstone markers are the most common, but they are prone to breakage and do not provide reliable, long-lasting markings. Welding pencils allow for precise markings that are clearly visible even through a welder's mask and are more durable.
Rice. 5. Markers for welders Markal
How do liquid paint markers work?
Markers based on liquid paint are becoming increasingly popular in metallurgy. Paint contains various chemical additives that increase the effectiveness of the paint, but the three main components are pigment, solvent and resin. It is the balance and chemical reactions between these components that determine how the markers work.
Pigment gives a marker its color, and the concentration and type of pigment depends on the application of the particular marker. Severe applications such as heat treatment or etching require a marker with special pigments. In fact, most metalworking tasks can be accomplished effectively with liquid ink markers, which can help make part marks brighter and more visible. This allows you to see part numbers from afar and in low light.
Rice. 6. Using a marker with liquid paint Markal SL.100
Once you apply the markings, the resin dries and chemically binds the paint, giving the paint improved water resistance and wear resistance. Some resins can withstand ambient temperatures of up to 66°C (before losing their properties and breaking down), while others can maintain their properties up to 982°C or more.
The solvent keeps the paint in a liquid state inside the marker itself. After you make a mark with a marker, the solvent helps the pigments and resin flow over the surface of the metal. You may notice its specific smell when working with a marker. This is the smell of evaporating solvent. Once the solvent evaporates, the resin will dry on the surface and chemically bond the pigments to the metal.
Industrial markers also differ in the characteristics of the tip (pen). A marker with thinner ink will have a tip with less porosity than a marker with thicker ink. If the tip is "tight" (that is, has less porosity), then it will make it difficult to transfer thick paint through the tip.
The diameter of the tip determines how clear the marking will be. Most users use markers with a 3mm tip. But if you're going to be making very small marks or marks in tight spaces or corners, you may want to consider using a 1.5mm or even 1mm diameter tip. Thicker tips measuring 14mm or larger are well suited for large markings.
Rice. 7. Using Markal Pro-MAX marker
But choosing a marker doesn't end just with tip size. For example, the material from which the tip is made must also be taken into account. For many industrial applications, markers with polyester tips are better suited due to their impact resistance. During the use of a marker, such tips, as a rule, retain their shape well and do not become dull, which leads to thickening of the applied markings and illegible inscriptions.
However, polyester tips are not suitable for every application. For example, if you need to mark a rough or dirty surface, it is better to choose a marker with an acrylic tip, typically used in varnish markers. They are typically processed in a way that allows them to adapt to surface roughness. In these situations, acrylic tips will usually last longer than polyester tips.
The right tool for the job.
Markings made with liquid ink or ink-based markers will bleed slightly after application, and especially on metal, this can result in illegible marks. When someone with an appropriately sized marker writes a "3", the three shouldn't look like an "8", although this happens quite often, and an incorrect part number or any other information can lead to a costly mistake.
These problems usually occur because the surface being marked is oily, rusty, or dirty. Many steel products or workpieces are supplied with an oil-based corrosion inhibitor applied to the surface, which can create marking problems; many conventional markers are not applicable in this situation. The marker paint sits on top of a layer of corrosion inhibitor oil, resulting in blurry or illegible text. In this case, you will need to use a marker with a special, oleophobic, paint, which pushes out the oil at the marking site and allows it to dry through the oil.
Rice. 8. Markal Pro-Line HP marker for oily surfaces
Wet surfaces require a marker with a hydrophobic paint that does not bleed and dries through water or water-based liquids. These markers are ideal for use after machining, plasma cutting, water hardening and marking through cutting fluids and water-based coolants.
Rice. 9. Marker for wet surfaces Markal Pro-Line WP
What about the painted surface? In most cases, manufacturers want to protect the welded joint by painting the weld, the entire equipment, or individual parts of it. Some manufacturers now use markers with water-based or solvent-based inks. Technically, the mark visible after painting is not the original mark, but rather the result of a chemical reaction in which the chemicals in the marker begin to react with the chemicals in the primer and paint. Approximately 30 seconds after applying the paint, the marks will reappear on the painted surface.
Marking rusty, dirty or uneven surfaces will require markers with a more viscous ink that penetrates through rust and dirt to the base material, and a tip that can provide a continuous flow of paint without clogging.
Finally, many materials require heat treatment to achieve the required characteristics, which can cause the applied markings to fade or become illegible. The effectiveness of marking in this case, again, is related to how the liquid paint marker works. Chemical bonds between resin and pigment are reliable only when working within a certain temperature range. When you go beyond this range, these connections are broken and the markings become poorly visible or disappear altogether. Therefore, you should use markers based on special paint with high-temperature pigments and resins.
Rice. 10. Marking clay products with a Markal Pro-Line HT marker after firing at a temperature of 1200 °C
Permanent and removable
Most marking applications require permanent marks; however, whether for product quality control, repairs, or for finished products requiring painting, markings must be removed.
If you need to remove markings from parts before shipping products to customers, you will need to consider using appropriate cleaning chemicals. In the meantime, if possible, try to use a marker whose markings can be removed safely and with minimal effort. Removing markings from extremely aggressive solvent-based paint can cause both personal safety and environmental issues. If mark removal requires the use of cleaners that violate government regulations on volatile organic compounds (VOCs), unexpected costs can add up, all because of the marker you use.
The nature of the resin used in a liquid ink marker determines how the markings are removed. When the resin breaks, the mark is wiped away. Some industrial markers currently produced do not require particularly aggressive cleaning agents. Some resins are destroyed by water. Some are destroyed by the use of slightly acidic detergent solutions (on the order of 10 pH or higher), which allows markings to be applied to products that may be stored outdoors, and therefore the markings must withstand exposure to rain but be easily removable if necessary. However, some resins require more aggressive cleaning.
Rice. 11. Markal Pro-Wash D washable marker
Make sure that the liquid-based marker you choose does not require solvents to remove markings, which are dangerous both for personnel and for the marker itself. For example, the use of xylene, the most well-known solvent for removing varnish markings, has been linked to certain types of cancer. However, today there are cleaning products that are safer alternatives to xylene and are equally as effective. If necessary, markings can be removed using common chemicals, which are not harmful if personnel take appropriate precautions.
Labeling Strategies
No matter how well a commercial marker is suited to your application, a marker can't help you if you can't find it or use it effectively. For example, most workers wear special gloves most of the day, so marker caps or caps should be designed so that people can easily remove them without removing their work gloves.
Rice. 12. Markal Trades-Marker DRY is always at hand
A marker cap sticking out of the front pocket of his work coveralls helps paint a picture of a metal fabricator. If the marker is not constantly with the worker or must be at a specific workplace, some developers have found unusual solutions that prevent the marker from being lost. Some of them apply strong adhesive to the cap of the marker, or use other methods to make the marker an integral part of the workbench or workbench. Workers remove the marker from the cap, use it, and then reinsert it into the cap attached to the workbench. This gives people a direct visual cue. If the cap is missing from your workbench or workbench, the marker is likely lost.
And a little more about markers.
Many employees use markers every day in the production of metal products. Markers are used all the time, they can be completely different from each other, just as one file can be completely different from another file, and one welding gun can be completely different from another welding gun. Ultimately, a marker is more than just a marker, and finding the right marker can help you get the job done better, faster, and easier while reducing waste, waste, and costs.
Rice. 13. Industrial markers Markal
Marking of metals by etching. Acid markers MARKAL
Existing methods (technologies) for industrial marking of finished products made of metals and alloys can be divided into two groups (hanging tags are not considered):
A. Not affecting the marked product (so-called “non-intrusive”):
- paint marking - hand-held markers based on solid or liquid paint, inkjet printers;
- self-adhesive labels on paper or polymer base.
B. Changing properties of the surface of the marked product (so-called “intrusive”):
- chemical etching;
- electrochemical etching;
- hand branding;
- automated dot-impact marking;
- laser marking.
When choosing a labeling method, you must consider:
- the purpose of marking, the volume and complexity of the information applied, requirements for the quality of symbols;
- number of marked products per day (single, small-scale or large-scale production);
- the need for variable marking and the frequency of entering variable data;
- state of the marked surface: physical and chemical properties (surface roughness, material hardness, thickness of the product at the marking site, chemical composition of the material and coating); geometric properties (marking dimensions, surface curvature in the marking area, location of this surface - recessed or protruding);
- requirements for the durability of the marking, taking into account the conditions in which the product will be used (temperature, humidity, atmospheric composition, immersion in liquids, abrasive and frictional effects, gas flows, etc.);
- negative impact of the marking method: the appearance of stress concentrators, corrosion sources, other changes in the surface layer;
- reliability of access and readability of information;
- requirements for the protection of markings from counterfeiting;
- productivity of the marking process and the ability to integrate into conveyor production;
- economic costs and environmental factors.
In this article we will look at the marking of metals and alloys using chemical etching.
Generalized description of chemical etching: controlled removal of the surface layer of material from a product under the influence of specially selected chemical compounds. Typically, in industry, during chemical etching, scale and rust are removed from the surface of products made of ferrous metals using etching solutions. Etching is carried out in solutions of sulfuric or hydrochloric acids, sometimes with the addition of nitric, hydrofluoric and other acids.
Marking of metals and alloys by chemical etching (hereinafter referred to as etching marking) occurs by obtaining a contrasting image of a rich dark gray color, which is the result of anodic oxidation of the surface of the product at the point of contact of the metal with the acid, with incomplete removal of reaction products. The technical literature uses the term "selective etching" .
If the technology is followed, marking metals by etching is a cheap, effective and safe method of obtaining high-contrast and fairly durable markings on products made from various grades of steel, non-ferrous metals and alloys.
This marking method is very widely used in many industries:
- for applying information to various products, especially small ones, where other methods of marking metals (dot-impact, laser) are not applicable or impractical;
- for identification of metal tools, equipment and mechanisms.
Currently, the most effective industrial tool for marking metals by etching is the Markal® SC.800* acid marker, which is a body made of chemically resistant polymer, into which two types of replaceable cartridges are installed:
- cartridge SC.862 (blue) - for etching marking of structural and tool steel;
- cartridge SC.865 (green) - for etching marking of stainless steel, copper, nickel, lead, bronze and alloys based on non-ferrous metals.
The Markal® SC.800 acid marker leaves clear marks and, unlike crayons and paints, does not flake, does not smear and is resistant to abrasion. It does not require additional power supplies or other means to apply etching markings. Also available is neutralizing fluid SC.871, which allows you to control the etching process.
* Markal® SC.800 acid marker is supplied without cartridges.
PROCEDURE FOR WORKING WITH AN ACID MARKER:
- Clean the surface thoroughly using an abrasive cloth.
- The marking surface must be clean - remove any oxide layer, oil or grease.
- For easy marking, make only one pass with the acid marker.
- To obtain more contrast markings, repeat passes until desired result is achieved.
- Lightly wipe the surface after etching with light oil.
- If the etching agent comes into contact with the skin, wash with soap and water.
Materials Science
All metals known in nature belong to two groups - ferrous and non-ferrous metals. Ferrous metals include iron and its alloys (steel and cast iron). In addition, ferrous metals include manganese, a silver-white metal; but in metallurgy and in everyday slang this element is rarely mentioned in the list of ferrous metals. All other metals and alloys that do not contain iron or contain it in small quantities are classified as non-ferrous metals.
This classification is due to a number of reasons, primarily the chemical and mechanical properties of iron-containing metals and alloys with low corrosion resistance (except for some steels with specific additives) and magnetism. Ferrous metals attract machine builders due to their good machinability, mechanical strength, and low price.
Non-ferrous metals have a number of unique properties - high electrical conductivity, resistance to corrosion, low specific gravity with high strength, and in some cases, high aesthetic and jewelry qualities. Generally, non-ferrous metals are more expensive due to their relative rarity in nature, as well as the difficulty of isolating them from rocks.
Non-ferrous metals are most often classified into light, heavy and noble metals.
So, the basis of ferrous metals is iron. However, this metal is practically never found in nature in its pure form due to its relatively low corrosion resistance, so iron in its pure form is not used in mechanical engineering, but alloys are used, the basis of which is compounds of iron and carbon - steels and cast irons. Steels are multicomponent alloys with a carbon content of up to 2.14%. Cast iron is an alloy of iron and carbon with a carbon content of more than 2.14%.
Steels and cast irons are very widely used in mechanical engineering. At the same time, minor additions of non-ferrous metals or non-metallic elements to steel or cast iron alloys make it possible to significantly change their chemical and mechanical properties depending on the needs of machine builders, while slightly affecting the cost of the resulting alloy.
***
Industrial marking of metal products
Metal
Not a single modern enterprise can do without marking equipment. Industrial marking of parts and elements is carried out not only at the last stage of production of finished products, but also during their manufacturing. Parts, assemblies, elements, tools and equipment are marked. The once popular branding method (hand-applied inscriptions using a stamp) is fading into the background in modern production. Automation of all processes requires more effective solutions - for example, the use of point impact and laser equipment.
Both options provide fast, permanent marking and are suitable for installation on high-speed lines.
Types of markings of gearboxes and drive chains.
Marking of the surfaces of gearboxes and chains is used for the purpose of applying identification marks (serial numbers, dates, codes, manufacturer's trademarks, other information), as well as for advertising purposes. Marking can be done either directly on the surface itself or using tags or attached nameplates. There are several types of product labeling from our catalog, which have their own advantages and disadvantages:
- Applying the inscription with paint manually and using inkjet printing, markers, stamping.
- Impact marking (manual and mechanized).
- Drawing marking.
- Needle milling (engraving).
- Electrochemical etching.
- Photochemical method.
- Metallographic method.
- Laser marking.
- Ultraviolet printing.
- Thermal transfer printing.
- Obtaining markings in stamps or injection molds during production directly on the part itself, or casting and stamping of plates.
- Electric spark method.
- Marking with sticky applications, tags, plates.
Applying inscriptions with paint.
The simplest method of marking surfaces is to apply inscriptions with paint using a stencil (brush, roller or spray). Such markings are short-lived, but do not damage the surface of the product. Stencil marking with paint is most often used on the shipping containers of gearboxes and gearmotors. Industrial markers are used for technological marking in the process of manufacturing drive parts. Stationary and portable inkjet markers are more productive and allow you to create high-quality product markings with ink of various colors. Data from a computer to a portable marker can be transferred via a USB port, via radio or via a flash drive (Fig. 1).
Impact marking.
Impact marking can be done using hand stamps, presses or needle impact machines (Fig. 2). The stamps have a mirror image of the inscription. Impact marking is used for metal surfaces of RM type gearboxes, excluding thin-walled parts. Needle-impact machines for impact-dot marking can be stationary, portable, or built into automatic lines. Marking can be done on both flat and cylindrical surfaces. The inscription is created in the form of a sequence of dots formed by the impact of a needle made of high-strength material. The needle is driven by an electromagnetic or pneumatic mechanism. The marking depth (force) can be adjusted, and the spatial position of the marking head relative to the part is also adjusted. After applying the needle-impact marking, it can be covered with paint to increase the contrast of the image. The advantages of dot-impact marking are the stability of the inscription, the possibility of applying a two-dimensional barcode, applicability for wood, plastic, soft and durable metals, the absence of consumables, the possibility of application on hot surfaces, the absence of surface heating during operation, the absence of increased requirements for the production premises, quite high marking speed. The disadvantages are the inability to apply complex images or color designs, rough inscription, low contrast, and limited marking area.
Hot stamping can be used on wood, leather, ceramic and plastic surfaces (with or without foil to add contrast).
Marking with a strike through.
Drawing marking (Fig. 3) is one of the varieties of the needle-impact method. The inscription is also applied with a needle made of durable material (diamond or carbides), which cuts or “scratch” the surface. Drawing markers (scribers) have a reduced noise level compared to impact markers and create “smoother” lines. Marking depth up to 0.5 mm.
LASER MARKING OF PARTS
It is actively used for applying technical information and logos to the surface of industrial products. A high-tech method characterized by high marking speed, reliability, and image durability. The non-contact identification method using a laser is used with metals of different strengths: from ultra-strong titanium alloys and hardened steel, to aluminum, gold and other “soft” metals.
Laser marking machines are divided into two types: stationary and integrated devices. Stationary marking devices are designed for applying identification information to medium and small-sized products. Capable of processing non-standard and complex surfaces: rough, curved, painted, and made of fragile materials.
Integrated laser marking machines , as the name suggests, are integrated into production lines that operate 24/7. The devices produce detailed, clear images at speeds of up to 1300 characters per minute. Depending on the specifics of the production process, integrated markers perform marking both as products move along the conveyor and when the line stops.
If it is necessary to mark curved products, an additional axis of rotation is used. Also, depending on production conditions, it is possible to retrofit laser devices with protective covers, mobile carts, a work table with a tripod and other options.
Steel grades: table of markings with explanations
Steel is the most common alloy. The variety of applications results in a large number of varieties with different requirements, both in terms of mechanical and chemical characteristics of steel. Different grades of steel imply not only a variety of chemical composition, but also manufacturing technology.
Steel grades
The variety of alloys is based on the chemical composition of the metal, since the alloying components determine the final result, and the manufacturing and processing technology only emphasizes and highlights individual characteristics. Some elements included in the composition may impair performance, so individual elements of the label may indicate the absence or low content of such substances.
Deciphering the markings allows you to determine the content of the main elements of the alloy and, in part, the production technology, as well as evaluate the technical characteristics, and with them the scope of possible application.
In addition to differences in composition and processing, steel is also divided into categories based on mechanical strength. There are 5 categories, which differ in test methods for compliance with mechanical strength. Tensile and impact strength tests are carried out on control samples.
Types of steels and features of their markings
Various areas of application of steel require that it have strictly defined properties - physical, chemical. In one case, the highest possible wear resistance is required, in others, increased resistance to corrosion, in others, attention is paid to magnetic properties.
There are many types. The bulk of the smelted metal goes into the production of structural steel, which includes the following types:
- Construction Low alloy steel with good weldability. The main purpose is the production of building structures.
- Spring. They have high elasticity, fatigue strength, and fracture resistance. Used for the production of springs and leaf springs.
- Bearing. The main criterion is high wear resistance, strength, low fluidity. It is used for the production of units and components of bearings for various purposes.
- Corrosion resistant (stainless). High-alloy steel with increased resistance to aggressive substances.
- Heat resistant. It is distinguished by its ability to work for a long time under load at elevated temperatures. Area of application: engine parts, including gas turbine engines.
- Instrumental. Used for the production of metal and woodworking and measuring instruments.
- Fast cutting. For the manufacture of tools for metalworking equipment.
- Cementable. It is used in the manufacture of parts and assemblies operating under high dynamic loads under conditions of surface wear.
- Steel classification
When deciphering the designations, it is necessary to take into account that each of the types corresponds to a strictly defined letter in the marking.
Classification by chemical composition
The main alloying additives are metals. By varying the quantitative composition of additives and their mass fraction, a wide variety of steel grades are obtained. Pure iron itself has low technical properties. Low mechanical strength and high susceptibility to corrosion require the introduction of additional substances into the alloy composition, which are aimed at improving one of the qualities, or several at once.
Often, the improvement of some characteristics entails the deterioration of others. Thus, high-alloy stainless steels may have low mechanical strength, while high-quality carbon steels, along with high strength, receive weakened corrosion properties.
As mentioned above, one of the classifications of steel grades is its chemical composition. The main components of all steels without exception are iron and carbon, the content of which should not exceed 2.14%. Depending on the amount and proportions of additives, the iron content in the composition should be at least 50%.
Based on the amount of carbon contained, steels are classified into three groups:
- Low-carbon – carbon content less than 0.25%;
- Medium carbon – 0.25-0.6% carbon;
- High carbon, with a carbon content of more than 0.6%.
An increase in the percentage of carbon increases the hardness of the metal, but at the same time its strength decreases.
To improve performance, a certain amount of chemical elements is introduced into the alloy. Such steels are called alloyed. For alloy steels there is also a division into three groups:
- Low alloy, containing additives up to 2.5%;
- Medium alloyed, which contain from 2.5 to 10% alloying elements;
- Highly alloyed. alloying impurities varies from 10 to 50%.
The marking of steels reflects the presence and percentage of alloying additives. When deciphered, each element is assigned a specific letter, next to which there is a number corresponding to its content as a percentage. The absence of numbers indicates that the additive is present in the alloy in an amount of less than 1-1.5%. The presence of carbon in the composition is not reflected, since it is included in all compositions, but its content is indicated at the very beginning of the labeling.
The marking can also indicate the purpose of the alloy. Since this classification also uses letter designations, the order of their arrangement is regulated - at the beginning, middle and end of the marking.
Classification by purpose
The classification of steel types by purpose has already been given above. Marking of structural steels includes the following designations:
- Construction - denoted by the letter C and numbers characterizing the yield strength.
- Bearing - designated by the letter Ш. Next comes the designation and content of alloying additives, mainly chromium.
- Instrumental unalloyed - denoted by the letter U and carbon content in tenths of a percent.
- High-speed - denoted by the letter P and symbols of alloying components.
- Unalloyed structural steel has the symbols Cn and a number indicating the carbon content in tenths or hundredths of a percent.
Classification of steel by purpose
The remaining varieties, including tool grades made of alloy steels, do not have special designations other than their chemical composition, so the decoding and purpose of individual types can only be determined from reference literature.
Classification by structure
The structure of steel refers to the internal structure of the metal, which can vary significantly depending on heat treatment conditions and mechanical influences. The shape and size of grains depend on the composition and ratio of alloying additives and production technology.
The basis of steel grains is a crystal lattice of iron, which includes atoms of impurities - carbon, metals. Carbon can form solid solutions in the crystal lattice, or it can create chemical compounds, carbides, with iron.
Metal additives exist in the form of solutions, and many of them affect the state of the carbon solution.
The structure of steel changes with temperature changes. These changes are called phases. Each phase exists in a certain temperature range, but alloying additives can significantly shift the boundaries of the transition of one phase to another.
The following are the main phases of the state of the metal:
- Austenite. Carbon atoms are located inside the iron crystal lattice. This phase exists in the range of 1400-700 °C. If the composition contains from 8 to 10% nickel, the austenite phase can persist at room temperature.
- Ferrite. Solid solution of carbon in iron.
- Martensite. Supersaturated carbon solution. This phase is characteristic of hardened steel.
- Bainite. The phase is formed by rapid cooling of austenite to a temperature of 200-500 °C. Characterized by a mixture of ferrite and iron carbide.
- Perlite. Equilibrium mixture of ferrite and carbide. It is formed when austenite is slowly cooled to a temperature of 727 °C.
IMPACT-POINT INDUSTRIAL MARKING OF PRODUCTS
Using dot-impact devices, identification is applied to metal products with smooth and rough surfaces. The ability to adjust the impact force allows you to apply markings of different depths. Modern software makes it possible to automatically generate inscriptions and apply two-dimensional codes to finished products and their elements for traceability in production and subsequent sales.
Needle impact devices are also divided into stationary and devices integrated into production lines. In addition, there are more compact, portable (mobile) markers.
Integrated needle-impact units are used for industrial marking of products in continuous production enterprises. Allows you to create an effective autonomous identification and traceability system, reducing the human factor. The main components of the equipment are protected from dust and moisture and can be used in difficult technological conditions.
Stationary dot impact markers help create a permanent marking area for identifying medium and small sized products. The devices are characterized by high productivity and speed, which makes it possible to apply even multi-line markings in a matter of seconds.
Portable needle-impact markers solve the problem of applying identification information to large, heavy products and in hard-to-reach places. Mobile devices weigh from 1.5 to 3.5 kg, are easy to carry due to their ergonomic shape and allow you to mark surfaces that are difficult to get to.
Marking with paint or ink
Marking with paints or special inks is one of the oldest marking methods. Today, paint marking is most widespread in the light, electronics and food industries, where equipment such as IMAJE and DOMINO is used. These markers are equipped with special heads with nozzles, with which it is possible to apply any type of marking. Image contrast is provided by a different number of pixels per unit area of the image. The latest paint marking equipment allows you to create multi-colored markings of very high quality.
However, branding hot metal with paints is impossible: the best examples of paint and varnish products can withstand temperatures of no more than 1,000 ºС. Plus, in the conditions of metallurgical enterprises and hot shops, it is difficult to ensure the necessary cleanliness and acceptable temperature conditions required for trouble-free operation of paint blasting nozzles.
The nature of the surface of many metal products also makes it difficult to use paint markers. Scale, dust, roughness, moisture, etc. make paint marking fragmentary and short-lived.
All of the above factors make it impossible or economically unprofitable to use inkjet markers in hot shops and in continuous casting machines.
However, marking in metallurgy with paints is used to indicate cold (cooled) metal products. The only requirement for using paint markings is cleanliness and high adhesiveness of the surface.
Paints are used for marking hot-rolled pipes (at the exit from the rolling mill, when the temperature of the product becomes acceptable), marking slabs and blooms, etc.
Paint marking equipment consists of the following components:
- head with 7 or 9 nozzles;
- manipulator for moving the head with nozzles;
- special panel for paint preparation;
- Remote Control;
- terminal for the operator, with which you can manually set marking parameters;
- electronic control system (software).
The spray nozzles have an increased diameter of the holes, which prevents them from clogging, and are adapted for self-cleaning operations. The minimum height of the applied marking is 19 millimeters, which may limit the use of such equipment for some types of metal products.
Using paint marking equipment, you can apply not only alphanumeric codes, but also barcodes. However, this equipment can only apply binary codes (containing a minimum of information about the metal product), which require special equipment (industrial scanners) to read.
Equipment for applying paint markings has a high degree of reliability. However, when using marking in metallurgy using paints and special inks, it must be taken into account that it takes a certain time for the paint to dry completely, and the hotter the metal product, the longer the time required for the paint to dry. At a high temperature of the metal products being marked, the operating costs of paint-blasting equipment also increase: paint consumption increases, more time is required for unit maintenance, etc.
Main characteristics
• Permanent identification marks
• High degree of character legibility for normal or automatic reading when the tag is not damaged
• Legible markings on rough and uneven surfaces.
• High marking speed.
CONCLUSION
Direct application of information to the surface is the preferred option for identifying metal products and parts. Neither hanging tags nor stickers provide the required level of reliability and long-term safety of markings in industry. The branding method is associated with the human factor: workers often make mistakes during the marking process, the marking is not clear enough and is difficult to read.
Dot-impact and laser marking of metal parts is free of these disadvantages. The use of advanced technologies guarantees high quality of the resulting images, excellent readability and durability of inscriptions on any metal surfaces. The technologies are suitable for such industries as the automotive industry, rolled metal production, equipment and tool production, aviation and military industries.