Specialists involved in the installation and maintenance of pipeline systems constantly encounter in their work the dimensional parameters of pipes, which are indicated on the drawings or stated orally. Almost each of them can answer the question - what does the nominal diameter of a pipe mean, but if an unqualified user is installing the pipeline, this information can be very useful for him.
It should be noted that the symbolic designation of the nominal diameter, in contrast to colloquial vocabulary, is not so often found on the drawings. This is due to the fact that the terminology and its designation are obsolete and should not be used in modern state industry standards GOST or in symbols.
Rice. 1 Dimensional parameters of threaded pipes
What does nominal pipe bore mean?
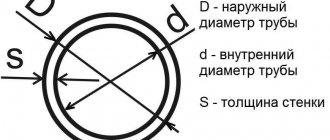
The main dimensional parameters of any pipe: internal and external diameters, wall thickness. The internal size is often called the nominal bore (diameter) and is designated by the symbols Dy.
In modern technical terminology, instead of the name conditional diameter, the phrase “nominal diameter” is used with the symbolic designation DN, the position is regulated by GOST 28338-89. The above document also states that if the production of pipes and fittings was mastered before the introduction of the above-mentioned standard, the conditional passage may be designated by the symbols Dy.
How are pipes marked?
To make it clear what a pipe control is, you need to talk about the generally accepted marking of pipes according to GOST. That is, “DN” is the nominal diameter, and its value is indicated in digital terms. For example, if the nominal diameter of the pipeline is 150 mm, then such products are marked with DN 150.
However, we note that the actual internal cross-section of pipes with similar markings may be completely different. In particular, rolled pipes with an external and internal cross-section of 156/144 or 156/149 mm can be produced with this marking.
This discrepancy is due to the fact that GOST provides only two standard section sizes - 125 and 150 mm. Consequently, these passage values are rounded up to a “conditional” indicator.
Since pipe products of domestic and imported origin must be similar in size, the same standards for conventional dimensions are adopted abroad, and pipes are marked DN.
Standard nominal pipe diameters according to GOST
GOST 28338-89 establishes standard sizes of nominal diameters of any types of pipelines and fittings used in everyday life and the national economy.
The regulatory act also answers the question of what the nominal pipe diameter is, indicating that its analogue, the nominal diameter DN, does not have a specific unit of measurement and is approximately equal to the internal diameter of the pipe in millimeters.
A table of all standard sizes of nominal diameters is shown in Fig. 2, it includes values in the range from 2.5 to 4000 mm.
Rice. 3 Examples of DN designation on pipeline drawings according to GOST 21.601-2011
Indication of the nominal diameter depending on the type of pipe
When indicating the nominal diameter for pipeline fittings, everything is extremely simple. The rounded internal diameter is indicated, for example, like this: DN20, but sometimes an outdated designation can be found: DN20, or Dy20, according to the previously valid CMEA 254-76.
But with the indication for different types of metal and plastic pipes, not everything is so simple, and confusion often occurs due to incorrect indication or uncertainty as to what diameter is indicated, external or internal (nominal diameter).
And the question arises, how is the pipe diameter correctly indicated? The following are examples of correct designations for some types of pipelines.
Designation of water and gas pipe (VGP pipe)
Water and gas pipes (WGP) include metal welded products made of steel in accordance with GOST 1050 and GOST 380, as well as other approved regulations. Applicable:
- In building heating systems;
- Various types of water pipelines;
- In the designs of gas pipeline systems and gas pipelines;
Example notation
Steel pipe manufactured in accordance with GOST 3262-75, with a nominal bore of 32 millimeters and a wall thickness of 3.2 millimeters.
The same thing only with the clutch.
Steel VGP with thread, zinc coating, cut to length. And so on.
Designation of electric-welded straight-seam pipes
Straight-seam electric welded steels are made from low-alloy or carbon steels. Used for the manufacture of pipelines for various applications.
Example notation
Steel pipe, produced in accordance with GOST 10704-91, with an outer diameter of 70.0 millimeters, a wall thickness of 4.0 millimeters, measured length (5000 mm), class II (manufacturing accuracy along the length), made of steel “StZsp”, produced in accordance with group “B” of GOST 10705- 80.
Specifying the diameter of seamless steel pipes
Seamless steel pipes are made from alloy or carbon steels. The absence of seams increases the resistance of the pipeline to various physical influences, such as operating temperature and nominal pressure.
Example notation
Steel pipe produced in accordance with GOST 32528-2013, with an outer diameter of 60.0 millimeters, a wall thickness of 4.0 millimeters, measured length (6000 mm), increased manufacturing accuracy, grade 40X steel, produced according to group “B”.
Unmeasured length, produced in accordance with GOST 32528-2013, with an outer diameter of 95.0 millimeters and an internal diameter of 76.0 millimeters, steel grade 10, produced according to group “B”.
Indication of plastic pipe diameters
Plastic pipes and various fittings are made from the following types of thermoplastics:
They are used for the manufacture of heating pipes, hot and cold water pipelines in accordance with GOST 32415-2013.
Example of designation of plastic pipes and fittings
Manufactured from uPVC, with a nominal outside diameter of 25.0 millimeters, a nominal wall thickness of 2.3 millimeters, and a pressure rating of PN25.
Symbol for plastic fittings:
Coupling made of PVC-U for connecting pipelines with DN 63.0 mm, complies with SDR 13.6, nominal design pressure PN16.
Units of measurement for nominal pipe bore
A wide range of products from foreign manufacturers are supplied to the domestic market; most European countries have adopted the inch system for measuring pipe dimensional parameters. Therefore, their products often indicate conventional pipe passages not in millimeters, but in inches, the unit of which is 25.4 mm.
The minimum pitch of inch markings is 1/16 inch, however, for almost all groups of pipelines the dimensional pitch is accepted as a multiple of 1/4 inch. For example, the most common pipelines for domestic use come with nominal diameters of 1/2, 3/4, 1, 1 1/4, 1 1/2 inches.
Current data table
The current regulatory framework requires marking the nominal diameter of the pipe with the letters DN. Previously, the flow area was designated by the Cyrillic letters DU. GOST stipulates that the clearance is measured in mm. The decoding of the applied markings is carried out as follows. For example, dn25 is indicated on the pipe. This does not mean the internal clearance is equal to the specified value. Markings of this type are found on products whose internal diameter can be, for example, 156/139.
GOST requirements indicate that actual dimensions are rounded up. For example, the table interprets 144 and 149 mm as 150.
In order to calculate the actual parameters, you need to use the formula below:
- External diameter – D(in);
- Wall thickness – S;
- D(in) – 2 x S = DN.
The conditional diameter allows you to accurately select the appropriate pipe for specific needs.
It is easier to disassemble this using an example. For example, DN is indicated as 110 mm. The minimum wall thickness is 6 mm. You can calculate the nominal DN by subtracting the result of multiplying 6 by 2 from 110. The final value is 98 mm.
Marking of ball valves and valves
Probably, many people paid attention to the icons, numbers and letters located on the body of ball valves, fittings and valves.
Let's figure it out, let's start in order.
DN
DN - Standardized representation of diameter according to GOST 28338-89 and GOST R 52720.
DN – translated as nominal diameter. An analogue of the generally accepted designation DN in the Russian segment is the designation in Russian letters as Du.
The nominal bore or (nominal size) is understood as a parameter for pipelines, valves and fittings as a characteristic of the connected parts.
The nominal diameter (nominal size) has no unit of measurement and is approximately equal to the internal diameter of the connected pipeline, expressed in millimeters and corresponds to the nearest value from a series of numbers.
DN is a kind of gradation of diameters, in which, for example, DN 15 means that the diameter of the internal connected pipeline is approximately 15 mm. There are no random numbers in the DN classification, they go strictly as prescribed in GOST - DN 15, DN16 (which, by the way, is rarely found in everyday life), DN 20, DN 25, DN 32, DN 40 and so on.
The nominal diameter values should be selected from the following range:
NOMINAL DIAMETERS DN -Du
| 2,5 | 12 | 50 | 160* | 450 | 1200 | 2600** |
| 3 | 15 | 63* | 175** | 500 | 1400 | 2800 |
| 4 | 16* | 65 | 200 | 600 | 1600 | 3000 |
| 5 | 20 | 80 | 250 | 700 | 1800 | 3200** |
| 6 | 25 | 100 | 300 | 800 | 2000 | 3400 |
| 8 | 32 | 125 | 350 | 900 | 2200 | 3600** |
| 10 | 40 | 150 | 400 | 1000 | 2400 | 3800** |
| 4000 |
* May only be used for hydraulic and pneumatic devices. ** Not allowed for general purpose fittings.
It should be remembered that this standard does not apply to air conditioning and ventilation systems. On most products you can see a duplicate size in English inches. The definition of an inch is the upper quotation mark after the number, our 25.4 millimeters equals 1” English inch.
The half-inch size is written through a ½ dash and is equal to 12.7 mm, but!!!! Attention!!! In terms of dimensions, DN - ½ inch corresponds to DN 15, the same with ¾ inch, ¾ inch in terms of millimeters, it turns out to be 19 mm, but in terms of DN they correspond to DN 20.
It turns out that the conditional diameter corresponds to the nearest DN value from the proposed numbers in GOST!
In a word, nominal diameter!
Conversion table DN-DN to inches
| DN or Du | Inches |
| 6 | 1/8″ |
| 8 | 1/4″ |
| 10 | 3/8″ |
| 15 | 1/2″ |
| 20 | 3/4″ |
| 25 | 1″ |
| 32 | 1 1/4″ |
| 40 | 1 1/2″ |
| 50 | 2″ |
PN
The next most important indicator is the PN value - GOST 26349-84, which indicates what maximum pressure the product can withstand. In the Russian segment, the designation PN is sometimes found as Ru.
This standard applies to pipeline connections and fittings and establishes a number of nominal pressures according to GOST.
Nominal pressure is understood as the highest excess operating pressure at a working medium temperature of 20 °C, at which a specified service life of connections of pipelines and fittings having certain dimensions, justified by strength calculations for the selected materials and their strength characteristics at a temperature of 20 °C, is ensured.
The PN value is calculated in Megapascals. For comparison, PN1 = 0.1 MPa or 1 kgf/cm2 which in turn is equal to 0.98 bar). Simply, if a product bears the designation PN10, then it should be assumed that it is designed for a pressure not exceeding 10 bar.
WOG
This standard is used in the USA and means that the device can be used for different environments, WOG consists of capital letters such as Water - water, Oil - oil, Gas - gas.
Before the WOG designation, the numbers indicate the nominal pressure, which is possible when using the device at room temperature, measured in psi. inch or Psi.
Today, the standard is considered outdated; the nominal pressure it refers to is indicated for cold water, and the nominal pressure for high temperatures, as well as for oil and gas, still needs to be looked at in the product data sheet.
WSP
WSP (Working Steam Pressure) The numbers in front of the WSP icon indicate the maximum operating pressure in Psi when operating the device with steam.
CWP
The numbers in front of the abbreviation CWP indicate (cold working pressure) measured in psi. inch or Psi.
MOP
A designation used in the gas industry, MOP stands for maximum operating gas pressure in a pipeline allowed for continuous operation.
The MOP includes the physical and mechanical characteristics of the pipeline components and the effect of gas on these characteristics. The numbers after the MOP icon are indicated in Bars, for example - MOP5 means that the valve has a maximum operating pressure in the gas system of no more than 5 bar.
Flow direction or → arrow
An arrow marked on the body of the product indicates the direction of flow; this icon absolutely cannot be ignored; it is more often used on check valves, shut-off valves or so-called valves.
GOST 21345-2005 states that the marking of valves with one-way supply of medium must contain an arrow indicating the direction of supply of the working medium. Why direction cannot be neglected for such a crane was discussed in the previous article.
Company logo, country - place of production of the product and release date
By the logo you can understand which manufacturer the product belongs to.
Many manufacturers indicate on the product body the place where it was produced, for example - Made in Italy. Some manufacturing companies put a stamp on their products with the date of manufacture of the product.
C.E.
CE marking means that the product is created in accordance with all European standards and requirements.
LF
“LF” or LEAD FREE means that the material of the product contains very little or no lead.
Grade of steel, alloy
There may be a mark on the faucet indicating the type of material from which the body of the product is made.
It is quite important to know what material the fittings are made of, because this concerns not only how the product will serve, but also means whether it will release harmful impurities into the water.
On stainless steel products, which are quite rare in ordinary water supply, the letter abbreviation NZh or, for example, the digital index 304 or 316, which according to the AISI standard means 304 or 316 grade of stainless steel, can be applied.
For example, the index CW617N means the composition of brass, which approximately corresponds to the Russian analogue LS59-2.
Fighting lead in brass, or lead-free alloys
The stumbling block in the composition of brass is the percentage of lead Pb.
At one time, people in Europe were very puzzled by the fact that brass contained a large amount of lead.
Everyone knows that pipes and fittings with a high lead content negatively affect human health, and therefore, some European enterprises have retrained to produce so-called lead-free brass consisting only of copper and zinc.
But such production required large expenses for the production of the same products, it became necessary to replace and modernize equipment, which led to an increase in the cost of lead-free products by three times compared to the same products produced previously.
Only four countries Germany, France, the Netherlands and the UK use the DIN 50930-6 standard and are gradually replacing lead brass with lead-free alloys. But so far, even in Europe they have not been able to completely abandon lead additives.
According to international standards, lead in the alloy should not exceed 3%. At the moment, the most popular brass alloy used in engineering plumbing is CW617N.
This alloy contains a minimum amount of lead of 1.6-2.6% and is a proven quality standard for brass that is approved for use in European drinking water systems.
Lead-free plumbing fixtures are rarely found on the Russian market. Sometimes you come across counterfeit plumbing products from China, in which the amount of lead can go off scale and cannot be measured.
In this regard, the consumer should pay attention and have a good understanding of the markings of brass in order to avoid purchasing counterfeits with a high content of toxic metal. Having understood the markings, it becomes definitely clear that not all taps are equally useful in one case or another.
The permanent address of the article is https://stroimasterskaya.ru/articles/2858
Watch the video - Marking water fittings
Show more articles from the category - Plumbing
Types of steel pipes
Diameter is not the only characteristic by which “ST” differ; an equally important parameter is the method of their production, which is also a key point in their selection.
- Straight-seam (electric welded). For their production, sheet steel (strip) is used, which, using special equipment, is bent to the required diameter, after which the edges are connected by welding. Welding work guarantees a minimum seam width, which allows the use of these products for the construction of water and gas mains. The most common material is carbon or low-alloy steel. The indicators of finished products are regulated by the following documents: GOST 10704-91, GOST 10705-80 GOST 10706-76 .
- It is necessary to pay attention to the fact that the pipe, which was manufactured in accordance with standard 10706-26 , has increased strength among its peers - after the first connecting seam has been made, it is additionally reinforced with two more from the inside and two from the outside. Regulatory acts indicate the diameters of products manufactured using electric welding. Their size ranges from 10 to 1420 mm .
- Spiral seam . For the manufacture of this type of product, steel in rolls is used. These products also have a seam, but compared to the previous type of product it is wider, and accordingly the ability to withstand internal pressure is lower for such pipes. These products are used in the construction of gas pipeline systems. This type of pipe is regulated by GOST 8696-74 .
- Seamless . The manufacture of products of this type involves the deformation of special steel blanks. Deformation is carried out both with exposure to high temperatures and by the cold method (GOST 8732-78, 8731-74 and GOST 8734-75, respectively). The absence of a seam is a positive reflection on strength - the internal pressure is evenly distributed along the walls (there are no “weak” places).
Regarding external dm., it is worth noting that regulations control their production up to a value of 250 mm . When purchasing products whose diameter is larger than specified, you only have to trust the integrity of the manufacturer.
Calculation
How to calculate the optimal pipe size with your own hands when installing plumbing or heating?
Instructions for heating and water supply systems will differ markedly.
Heating
The key parameter here is the heat flow that the pipe can pass. It can be increased by increasing the internal diameter (which is unprofitable, since with its increase the price per linear meter of pipe increases nonlinearly) or coolant velocity .
The speed, however, is limited from above to a maximum value of 1.5 m/s: as it increases further, the hydraulic noise becomes difficult to bear. In practice, when calculating heating systems, a speed range of 0.4 - 0.6 m/s is used.
Fortunately, modern circulation pumps allow flexible adjustment of performance.
For the convenience of the reader, I will include in the article a table of the dependence of heat flow on the nominal diameter of the pipe.
| DN | Heat flow (kW) at coolant speed | ||
| 0.4 m/s | 0.5 m/s | 0.6 m/s | |
| 15 | 5,8 | 7,2 | 8,6 |
| 20 | 10,2 | 12,8 | 15,3 |
| 25 | 16 | 20 | 24 |
| 32 | 26,2 | 32,7 | 39,2 |
| 40 | 40,9 | 51,1 | 61,3 |
| 50 | 63,9 | 79,8 | 95,8 |
How to use this table? You just need to select the heat flow value that is as close as possible to yours and find the corresponding diameter in the left column.
How to calculate the heat flow in your heating system?
- For an autonomous circuit, when calculating bottling, the thermal load is taken equal to the rated power of the boiler;
- Individual sections of the circuit and connections to radiators are calculated based on the rated power of the devices;
- In the absence of technical documentation for them, the power can be roughly estimated at 200 watts per radiator section.
Thermal power of some heating devices.
Water supply
Accurately calculating the throughput of a steel pipe with a known diameter is extremely difficult, since, in addition to the pressure in the water supply system, it must take into account its hydraulic resistance.
And it, in turn, depends on:
- pipe length;
- number and angle of turns;
- shut-off and control valves;
- pipe wall roughness;
- its service life. Over time, steel pipes become overgrown with rust and lime, which increases their roughness and reduces clearance.
Typical condition of an old water pipe.
In practice, the owner of an apartment or private house just needs to remember a simple rule:
- When the length of the water supply line is up to five meters and the number of simultaneously used plumbing fixtures is no more than three, size DN 15 ;
- With a water pipe length of 5 - 30 meters and the number of simultaneously used plumbing fixtures up to five, the nominal size of the water pipe increases to DN 20 ;
- For a larger length and/or number of toilets and sinks, a DN 25 steel pipe or a plastic pipe equivalent in capacity is used.
Metal-plastic liner for the sink in my basement.
What is the nominal pipe size?
Nominal Pipe Size (NPS) is a North American set of standard sizes for pipes used for high or low pressures and temperatures.
The name NPS is based on the earlier Iron Pipe Sizing (IPS) system. This IPS system was created to indicate pipe size. The size is the approximate internal diameter of the pipe in inches. IPS 6" pipe is pipe that has an internal diameter of approximately 6 inches. Users started referring to the pipe as 2-inch pipe, 4-inch pipe, 6-inch pipe, etc. To begin with, each pipe size was manufactured to have one thickness, which was later named as standard (STD) or standard weight (STD. WT.). The outer diameter of the pipe was standardized.
To meet industrial requirements for higher pressure fluids, pipes were manufactured with thicker walls, which became known as extra strong (XS) or extra heavy (XH). Higher pressure requirements increased with thicker walls. Accordingly, the pipes were manufactured with extra-strong (XXS) or extra-heavy (XXH) walls, while the standardized outer diameters remained unchanged. Please note that this site only uses the terms XS and XXS.