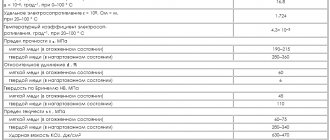
Chemical properties of alkali metals: interaction, preparation
Alkali metals are in the first group of the periodic table. The atoms of these elements contain one electron in their outermost energy level. It is located at a great distance from the core. Like all metals, they are reducing agents and easily give up electrons. The characteristic oxidation state is +1. In the group from top to bottom there is an increase in metallic properties. Due to the increasing ionization energy, the ability to donate electrons, and therefore electronegativity, increases from bottom to top.
Francium is the most active metal because it has an electron at the farthest distance from the nucleus. Accordingly, its ability to recover is the highest.
- Under normal conditions, alkali metals react with oxygen.
They are very active in such reactions, so they are stored under a layer of petroleum jelly. The reaction products can be oxides or peroxides. 4Li + O2 → 2Li2O 2Na + O2 → Na2O2 - Alkali metals react with water under normal conditions.
Hydrogen is displaced from the water, and a soluble base, an alkali, is formed as a reaction product. To recognize alkali, you can use an indicator - phenolphthalein. When added to a solution, it turns crimson. Reactions with water are very violent, lithium “explodes” in water, sodium “boils”. In this case, hydrogen is released in the form of white vapor in clouds. 2Na + 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2↑ 2Li + 2H2O → 2LiOH + H2↑ - React with halogens to form halides.
2K + Cl2 → 2KCl 2Na + Cl2 → 2NaCl - Characteristically, it reacts with hydrogen when heated; the reaction product is hydrides.
For example, the product of the reaction of potassium and hydrogen will be potassium hydride. H2↑ + 2K → 2KH - When heated, they form sulfides with sulfur.
It is a solid, colorless substance, soluble in water. 2Na + S → Na2S - When heated, a reaction occurs with phosphorus, phosphides being the product.
3K + P → K3P - Lithium and sodium can react with carbon when heated.
As a result, carbides are formed. The remaining alkali metals do not enter into these reactions. 2Li + 2C → Li2C2 - Under normal conditions, only lithium reacts with nitrogen; with other alkali metals, reaction is possible only when heated.
6Li + N2 → 2Li3N - They interact with alcohols to form alcoholates.
2C2H5OH + 2Na = 2C2H5ONa + H2↑Many alkali metals are capable of reacting with dilute acids to form hydrogen. However, the reaction proceeds in stages, i.e. First, the metal reacts with water to form an alkali, and then the alkali is neutralized with an acid. Interaction with acids is accompanied by an explosion and therefore such reactions are not carried out in practice.
Receipt
- The main method for obtaining alkali metals is the electrolysis of halide melts. In this case, chlorides that are part of natural minerals are most often used.
- Other methods for obtaining alkali metals can be obtained from their oxides and salts.
For example, sodium can be obtained by calcining soda with coal.Na2CO3 + 2C → 2Na + 3CO↑
Lithium is obtained from its oxide by raising the temperature to 300°C.
2Li2O + Si + 2CaO → 4 Li + Ca2SiO4
From Turkey to Egypt
The history of the discovery of metal has been lost for centuries. Who first discovered the metal, who guessed to “tap” the nugget so that it would turn into a blade or other tool is unknown. Moreover, no one knows who came up with the idea of “welding” the nugget and pouring the liquid metal into the mold.
The next mystery is who was the first to smelt ore into metal. But it is known that archaeologists found the most ancient finds of copper products and smelting slag in modern Turkey. They are incredibly ancient - they are up to 10,000 years old.
Why copper?
The tribes who lived in Europe in ancient times called copper and any metals “mida”. The word “copper” is also found in ancient Russian texts. Scholars consider the word to be related to the Old German "smid" (blacksmith); or a derivative of Media, a country on the territory of present-day Iran.
In Latin, copper is called cuprum (aes cuprium), from the island of Cyprus. There was a rich metal deposit there. Pliny writes:
“...It is known how long the Roman people used only copper coins. Antiquity itself testifies to the importance of this metal.”
For a long time, the main common coin of the Roman Empire was called ass (aes).
Now “copper” and “cuprum” peacefully share their belonging to the non-ferrous metal.
Chemical properties of alkaline earth metals: interaction, preparation
The main subgroup of the second group of the periodic system of chemical elements is formed by metals, which are called alkaline earth metals.
They are so named because the hydrates of their oxides (“earths”), like the hydrates of alkali metal oxides, are alkalis.
The outer electron layer of their atoms consists of two electrons. By giving them away, the atoms of these metals turn into ions that carry two units of positive charge. In all their compounds, the metals of the beryllium subgroup are positively divalent. In the periodic table they are adjacent to the alkali metals. Therefore, these elements exhibit high chemical activity, second only to alkali metals. The properties of the metal increase with increasing atomic number.
- They react with oxygen, the reaction product becomes oxides, except for barium, it forms peroxide BaO2. Beryllium and magnesium interact with oxygen only at very high temperatures, since they are covered with a thin protective oxide film.
2Ca + O2 → 2CaOIn the above reaction, a piece of calcium burns to produce white smoke when heated. It is formed by the finest solid particles of calcium oxide.
- Like alkali metals, they react with water, but less actively. As a result, an oxide hydrate is formed and hydrogen is displaced.
Ca + 2H2O → 2Ca(OH)2 + H2↑Phenolphthalein turns crimson in the resulting solution. This example justifies the expected similarity in the chemical properties of alkaline earth and alkali metals: both react with water to release hydrogen. Alkaline earth metal oxide hydrates, like alkalis, are alkalis, meaning they are soluble in water.
- All metals except beryllium react with halogens.
Beryllium reacts with halogens only at elevated temperatures. The reaction product is halides. Ca + Cl2 → CaCl2 - When heated, all alkaline earth metals, except beryllium, react with hydrogen.
As a result, hydrides are formed. Ca + H2 → CaH2 - React with sulfur, resulting in the formation of sulfides.
Ca + S → CaS - Reacts with nitrogen when heated, with the exception of magnesium. It reacts with nitrogen under normal conditions. The reaction product is nitrides.
3Be + N2 → Be3N2 3Mg + N2 → Mg3N2
- They can react with acids, resulting in the formation of salts of the corresponding acid and hydrogen.
Be + H2SO4 (dil.) → BeSO4 + H2↑
Receipt
The main methods for producing metals of the second group of the main subgroup are electrolysis of melts, aluminothermy and the displacement of other more active metals from their salts.
CaO + Al → Al2O3 + Ca
MgBr2 + Ca → CaBr2 + Mg
Looking for copper
There are considerable reserves of metal on earth. These include native copper (its accumulations can reach 400 tons - take ready-made ones).
There is no native copper-containing minerals available to humans:
Chemical properties of aluminum
Aluminum is in the third group of the periodic table of elements. The charge of the nucleus of an aluminum atom is +13, there are three electrons in the outer electron layer.
Based on the structure of the atoms and their position in the periodic table, it can be assumed that the metallic properties of the elements of the third group should be less pronounced than those of the elements of the second group. This is true.
During chemical reactions, an aluminum atom gives up three electrons from its outer layer, turning into a three-charged positive ion Al3+. Therefore, in all its stable compounds, aluminum is positively trivalent. Its compounds exhibit amphoteric properties.
Aluminum is a reactive metal and acts as a reducing agent. However, its activity is reduced by the oxide film that forms on its surface. Therefore, in many reactions the film is first removed, and then the reaction with substances occurs. Let's look at the chemical properties of aluminum using specific examples.
- Aluminum combines with oxygen in the air both when heated and at ordinary temperatures. A thin, dense film of aluminum oxide quickly forms on its surface. It is difficult to permeate gases and protects the metal from further oxidation.
In a crushed state and at elevated temperatures, aluminum reacts violently with oxygen, releasing a large amount of heat. As a result, aluminum oxide is formed.4Al + 3O2 → 2Al2O3
- Reactions with many nonmetals occur when heated.
2Al + 3S → Al2S3 Al + P → AlP 2Al + N2 → 2AlN 4Al + 3C → Al4C3 - It interacts with water to remove the oxide film.
The reaction proceeds vigorously, displacing hydrogen from water. 2Al + 6H2O → 2Al(OH)3↓ + 3H2 - Interaction with acids. Place aluminum shavings in a test tube containing hydrochloric or dilute sulfuric acid. Aluminum dissolves, displacing hydrogen from the acid and forming a salt.
2Al + 6HCl → 2AlCl3 + 3H2↑ 2Al +3H2SO4(dil.)→ Al2(SO4)3 + 3H2↑Does not react with concentrated nitric and sulfuric acid. Therefore, concentrated nitric acid is stored in aluminum containers and transported in aluminum tanks.
Reacts with dilute nitric acid to form
N2O, N2 or NH4NO3. 8Al + 30HNO3 → 8Al(NO3)3 + 3N2O + 15H2O
- Since aluminum has amphoteric properties, it is characterized by reactions with alkalis.
2Al + 2NaOH + 10H2O → 2Na[Al(H2O)2(OH)4] + 3H2↑ - Aluminum interacts with the oxides of most metals, displacing the less active metal.
This method is used in industry to obtain metals and is called aluminothermy. 2Al + Fe2O3 → 2Fe + Al2O3
Let's sum it up
Their chemical properties depend on the activity of metals. Simple substances - metals - are reducing agents in redox reactions. By the position of a metal in the electrochemical series, one can judge how actively it is capable of entering into chemical reactions (i.e., how strongly the metal exhibits reducing properties).
Finally, we’ll share a table that will help you remember what metals react with and prepare for your chemistry test.
How to smelt cuprum
- pyrometallurgical (with its help, 90% of the metal is produced);
- hydrometallurgical, the remaining 10%.
Hydrometallurgy consists of a single step: treating (usually low-grade) ore with dilute sulfuric acid and then separating copper metal from the solution. In this case, all associated substances from the ore simply disappear.
Pyrometallurgy is more complicated, there are several stages:
- Enrichment by flotation and oxidative roasting.
- Melting for matte at temperatures up to 1500 degrees. Here, crude metal is already isolated, as well as accompanying silver, gold, and nickel.
- Fire refining - purification of the resulting metal from impurities to 99.5% purity.
- Electrolytic refining, bringing purity to 99.95%.
Deposits and production
The origin of copper ores is varied. They are oxide, sulfide, mixed. The majority of sulfide ores on earth (about 90%) contain rich ores. Oxidized minerals are not inferior in metal content.
There are large deposits in Chile (predicted reserves are more than 5 million tons).
The richest deposits of native copper are located in the USA (Lake Superior), on the island of Vancuve (Canada), Corocoro (Bolivia).
Native “cosmic” copper has been found in meteorites and on the Moon.
In Russia, metal mining is carried out in the Krasnoyarsk Territory (the same Norilsk Nickel).
Applications of metal: from telegraphs to fireworks
The widespread use of copper began after the invention of the telegraph. Huge amounts of metal were needed for telegraph wires. Since that time, our hero has not left first place in the ranking of electrical metals.
The use of copper is based on its properties. Electrical wiring in old houses; Now expensive metal is being replaced with cheap aluminum. But the devices contain copper wiring. Computers are equipped with copper heat sinks.
Plumbing equipment, refrigeration equipment, air conditioners - non-ferrous metal with its remarkable properties is used everywhere.
Ships and boats are proud of their copper pipelines (liquid and gas flow into them).
And in many countries, copper pipes are used for water and gas supply to buildings.
Without copper there will be no brazing solder (that's the "glue" for metals).
Dioskourides wrote: “Solder for gold is prepared from children’s urine and Cypriot copper.”
Japan considers copper gas pipeline pipes to be earthquake-resistant.
Copper is used as an alloy for gold alloys; Pure gold is a metal that is too soft and prone to abrasion.
Orange non-ferrous metal gives blue color to pyrotechnic products.
What we didn't know about copper
One of the advantages of this amazing metal is that tools made from it do not produce sparks when struck. It is wise to use them where there is a risk of explosion.
Swedish scientists have come up with a way to bury radioactive waste. Now huge amounts of money are being spent on this. Or you can simply place radioactive trash in copper capsules with walls 5 centimeters thick. According to calculations, corrosion will destroy them no sooner than in half a million years.
Many people know that the Statue of Liberty (the one with the torch and the crown) is made of copper. Not entirely, of course, non-ferrous metal only on top, steel structures inside. There were rumors that it was made of Ural metal, but... It was officially recognized that it came from Norway.
Here is a case when a seemingly useful property of our hero became a disadvantage. A Norwegian cargo ship sank due to the copper ore it was carrying. Electrochemistry is to blame. Copper from the ore created a galvanic couple with the metal hull of the ship, the evaporation of sea water served as the electrolyte. The resulting current provoked such corrosion that it ate through the lining, and water poured into the holds.
For fashionistas and fashionistas
The secret of the “Gold Vision-3000” jeans is the copper biocorset. Copper threads, “built-in” into fashionable pants, help prevent vascular pathologies and stimulate the functioning of the pelvic organs. And they affect digestion, sexual function, hematopoiesis, reduce the harmful effects of household appliances, and the influence of electromagnetic fields.
Alloys, alloys...
Copper is part of many alloys:
- cupronickel;
- brass;
- bronze;
- latten (laton);
- German silver (used in jewelry);
- Abyssinian gold;
- French gold;
- northern gold.
The properties of the metal included in the alloy allow metallurgists to “invent” the required characteristics.
Copper is not cheap, so manufacturers prefer copper alloys (where possible).
In some areas, alloys (especially with aluminum) have confidently outperformed pure metal. “Mama” copper cannot compare with the corrosion resistance, strength, and malleability of alloys.
Blue blood
Everyone has heard this expression. Not everyone knows that blue blood actually exists, but not in people. The hemocyanin protein colors the blood of mollusks, centipedes, and arachnids blue. Hemocyanin itself is an analogue of hemoglobin, which makes our blood red.
Without our hero, man would not have been able to survive as a biological species. The metal promotes the absorption of proteins, carbohydrates, and strengthens the immune system. It’s not for nothing that our great-grandmothers cooked jam in copper basins, because the metal has antiseptic properties.
Metal ions have antifungal and antiviral properties, are able to penetrate the cell membrane and destroy the spread of infection.
There is already fabric containing copper threads. You can’t make an evening dress or a suit out of it, but in hospitals it is necessary. The material was developed in Chile.