Often, when you pick up an object shiny with metal, you are surprised at its light weight and realize that it is plastic or wood with a metal coating. Chemical metallization helps to obtain a mirror or matte nickel, chrome, copper or aluminum coating on ordinary ferrous metal or a non-metallic surface. Technology available not only in production, but also at home.
Process technology
Electrolytes are substances that can release ions – charged particles – under the influence of an electric current. This is what the principle of galvanization is based on. In our case, chromic anhydride will be used as an electrolyte. Released particles that will be deposited on the workpiece, forming a film - chromium molecules.
To chrome a part at home, it must be immersed in a bath of solution and connected to the negative wire. The positive anode is immersed in the electrolyte. Under the influence of current, the molecules in the electrolyte will begin to move. Positively charged to the minus (cathode), negative - to the plus. Moreover, some of the molecules form a film, and some will penetrate into the top layer, as a result of which chromium is firmly fixed on the surface. This makes galvanizing significantly different from conventional painting.
In a similar way, not only chrome plating is carried out, but also nickel plating, coating of products with copper and zinc. The processing principle will be the same in any case. The thickness of the spraying will depend on the current strength, heating temperature, processing time, and type of metal.
It is also possible to carry out chemical chrome plating at home. No special equipment is required here. The formation of a metal film on the surface in this case occurs due to chemical reactions in which sodium hypophosphite serves as a reagent. But such a coating is less durable - it is used only for decorative purposes.
This is interesting: KGShP (crank hot stamping press): characteristics and features
Galvanization
The galvanic method is the coating of cast iron, steel, brass or copper structures with a layer of chromium. But not only metal products can be chrome-plated by galvanization. This method can also be used for chrome plating of plastic and wooden products. But in these cases the process will be expensive and technologically complex. To firmly hold the chrome coating on the surface of parts, even metal products require another preliminary coating. For this purpose, nickel, brass or copper are used.
Galvanization requires the creation of a galvanizing plant. In addition, you need a DC source and a set of reagents. This set consists of chromium anhydride, sulfuric acid, soda ash and sodium hydroxide.
It should be noted that when working with this method, it is required that there are no changes in current strength. You also need to constantly monitor the level of salt concentration in the electrolyte and strictly observe the temperature regime for quite a long period (from 5 to 8 hours). Fulfilling all of the above conditions in home workshops is not an easy task. It is for this reason that we will not describe the galvanization process in detail in this review.
Required Equipment
Electroplating (chrome plating) at home is possible if you have the following type of equipment:
- power supply: it should show 1A at the output and be equipped with a voltage regulator; for small volumes of work, a current rectifier is sufficient; the wiring cross-section depends on the size of the workpiece (minimum 6.25 mm);
- wires: the positive one will be immersed in the electrolyte, the negative one, with an alligator holder, will be located at the end towards the workpiece;
- anodes made of tin, lead or antimony alloys;
- containers of suitable size made of chemically resistant, non-conductive material; the ideal option is a plastic bath; for chrome plating of small parts, a glass jar is sufficient;
- a wooden box with thermal insulation made of glass or mineral wool in which the container will be placed; Ordinary sand can also be used as insulation;
- sealed lid: it can be made from a piece of plywood or wooden boards;
- heating element, the power of which is sufficient to heat the liquid in the selected container to a temperature of 60-80°C;
- contact thermometer or thermostat;
- a hollow mold for pouring electrolyte with a tap or brush at the end; to make it, a bundle of copper wire is used, secured and tied with lead wire.
Features of chrome plating
Although chrome plating can instantly change the appearance of a motorcycle or car, this procedure is quite complex and dangerous.
This is due to the use of a special galvanic bath and serious reagents that can be harmful to health if the instructions are not followed. All chemical and physical transformations must occur under the strict supervision of a specialist, even if the procedure is carried out at home. Therefore, it is important to familiarize yourself with the entire theoretical basis before starting. Since chrome plating metal at home became a trend, a lot of different methods have appeared. Chromium deposition is a physical and chemical process that occurs after the part is treated in a galvanic bath. A thin layer of metallic chrome is applied to the product, which hardens almost instantly. As a result, it is easy to obtain a body part with a shiny surface and resistance to external damage. Chrome plating significantly enhances the physical, chemical and decorative characteristics, so it is often used on the lower parts of the vehicle that are exposed to the external environment.
Chrome plating technologies at home
You can order the services of experienced companies that carry out the procedure, or do it yourself, but in any case, the meaning of the operation is to clean the surface followed by treatment with current and reagents. The chemical laws of catalysis and oxidation are at work here, so you need to get a little familiar with this science. Below we will tell you more about the processes.
What you need for chrome plating
The premises have already been mentioned. Now about equipment and materials.
Constant voltage source
Metallization technology involves the use of various electrolytes and containers commensurate with the dimensions of the sample being processed. Therefore, if we are not just talking about chrome plating a single part, then it should be possible to adjust the current strength. The simplest homemade power supply used at home is a transformer + rectifier + rheostat.
Electrical circuit elements
This mainly concerns the cross-section of wires. Practice shows that 3 “squares” is quite enough for home chrome plating of parts. It is also necessary to prepare the clamps with which they will be fastened to the electrodes. There is a crocodile type on sale. The cost is cheap, and the ease of working with them is maximum.
How to ensure constant temperature in the bath? There are two ways. The first and easiest is to use a thermometer and adjust the current value manually. The second one is more difficult to implement, since you will have to install an automatic element - a thermostat. Its inclusion in the circuit will eliminate the need to control the process.
The approximate time for chrome plating is known, so constant presence near the tank is not necessary. But for this you will have to assemble a small electronic circuit. For those who do not understand this, this option is unacceptable.
Bath
Its material must be neutral with respect to liquids, especially aggressive ones. Therefore, glass is best. But this applies mainly to small-sized parts that can fit, say, in a standard 3-liter jar. As an option - containers from industrial batteries with thick walls. Aquarium enthusiasts often raise fry in such aquariums. But getting these vessels is quite difficult.
"External" capacity
You need to assume that the selected glass vessel will be installed in it, which will be lined with insulation on the outside. What can you use? For example, a barrel, a can, a box or a box (even a wooden one).
Thermal insulation material
The choice is large, depending on the size of the containers - sawdust, mineral wool, sand, fiberglass. The goal is to achieve the “thermos” effect. Therefore, it is necessary to make a lid that should completely cover the “outer” tank. If this is a box, then a fragment cut from FC, OSV or something similar will do. It is only necessary to provide waterproofing of the cover from the inside if it is made of a material that includes wood. What to consider? Whatever the cover is made of, it should not be conductive!
A heating element
To make your task easier, you can purchase it. The range of heating elements is quite large, so choosing according to configuration, size and power is not a problem.
Electrodes
They can be plate or rod (for example, made of brass, copper). As a “minus” at home, a clamp is usually used to hold the sample being processed.
bracket
This “detail” cannot be avoided. The workpiece, which is placed in the electrolyte for metallization, must be in a suspended state. Otherwise, the part that will be adjacent to the bottom of the vessel will remain unprocessed. The design of the bracket and the method of its fixation are chosen independently, depending on the work conditions.
Drying cabinet
At the last stage of metallization, the part must be subjected to heat treatment. Otherwise, you will not achieve the characteristic (and desired) shine.
Chrome plating methods
Galvanization technology consists of applying a surface metal layer to a part for a specific purpose - decorative or protective through the use of an electrolyte.
Consequently, electroplating - chrome plating at home suggests that a layer of chromium from an electrolyte of a certain composition will be deposited on the surface being treated when exposed to electric current. This process can be carried out in different ways.
- Carrying out chrome plating using a bath filled with a solution. The technology is accessible for DIY, but is more often used when working with small parts.
- Spraying the coating using a galvanic brush. This technique does not limit the dimensions of the workpiece; it is also optimal for non-removable elements. During the work process, the master has the opportunity to control the thickness of the applied layer and visually assess the quality of the spraying. But this process is more labor-intensive, as it may require up to 20 movements in one place.
Galvanic chrome plating method
Galvanic chrome plating of parts is the most popular method, because all the steps can be done with your own hands. Electroplating involves placing parts in a special solution with a certain composition, from where, under the influence of waves (solitons) of electric current, chromium atoms will be deposited on the surface. Having the right set of tools for chrome plating, you can create a high-quality coating yourself by galvanizing.
Electrolytic chrome plating method
One of the types of galvanizing. When electrolysis is used, tri- or hexavalent chromium gives the product the desired “metallic” appearance. When using a trivalent element, the main substance of the solution is chromic anhydride. The use of hexavalent chromium differs from the previous method by the presence of chromium sulfate in the solution.
When carrying out electrolytic chrome plating of disks or other parts, it is important to strictly observe the proportions of the components. Otherwise, the protective layer will quickly peel off or there will be stains, uneven dullness and insufficient gloss.
Diffusion chromium plating method
Chromium coating is done using a galvanic brush. At home, this method is more preferable, because the master does not need to use a bath. It is especially recommended to perform the technique for parts made of aluminum, carbon steel, and alloys with silicon.
Chemical metallization of surfaces and parts
In the process of this work, chemical reagents, a compressor and a spray gun are used. Almost the same operations are performed as when painting surfaces with acrylic varnish or enamel. When chrome plating in this way, not a protective polymer film is applied to parts and structures, but a mirror-like thin layer of metal. Its thickness is in the range of 0.075-0.25 millimeters. The chemical and physical characteristics of such a coating are comparable to those obtained by vacuum deposition.
Catalytic chrome plating method
A subtype of chemical chrome plating of ferrous or non-ferrous metals, which involves applying a liquid without acids to the part. The technology is safe for humans and helps create original, unusual effects.
Catalytic chrome plating can be used for conventional and flexible products (with electrolysis, the latter is impossible; the coating will peel off).
Typically, silver is used as a reagent in an alkaline ammonia solution, and formaldehyde or hydrazine is used as a reducing agent. The use of silver makes the piece look milky with a mirror surface.
Chrome plating using chemical metallization
The chemical metallization method is most suitable for chrome plating parts at home. There are also special reagents here, but no other complex equipment is required except a spray gun and a compressor.
In many ways, the chrome plating process is reminiscent of conventional painting of products with enamel or acrylic colored varnish, only the result is different. Instead of a polymer protective film, a thin (0.075 - 0.0) is formed on the surface.
25 mm) a metal layer with a mirror shine, not inferior in physical and chemical characteristics to vacuum deposition.
There are two methods of chemical metallization:
- recovery of chromium from salts during chemical reactions;
- coating with specially selected chemicals, as a result of the interaction of which a durable monomolecular layer of silver or other metal is deposited on the surface.
To work with chromium salts, you will need sodium hyposophyte, chromyl fluoride, chromium phosphate, chromium chloride or acetate, caustic soda, acetic acid and other chemicals.
Most of them are unsafe for health, some are very poisonous. If you intend to chrome parts using this method, you need to repeat the chemistry course.
Even with carefully written instructions, it is difficult to achieve the desired result.
Vacuum chrome plating
The technology belongs to chemical metallization and has another name - the PVD process. Gives condensation of chromium vapor on the surface of the part after placing it in a special vacuum chamber. In this installation, under negative pressure, chromium is heated to the evaporation temperature, then settling like fog on the product.
Calculation of pressure and chrome plating period will depend on the degree of wear of the part and the type of material. After vacuum chrome plating, the thickness of the metal layer is minimal, so the part on top is coated with special spray paint or varnished.
Thermochemical chromium plating
Powdered products consisting of fireclay and ferrochrome are used. The technique is similar to that for chemical chrome plating, only the product will be subject to heating during the process.
Spray processing
Sputtering of elements with chromium (catalytic metal working) is performed using the “silver mirror” reaction, in which complex silver layers located in alkaline ammonia solutions act as reagents. The function of a reducing agent is assigned to a formaldehyde or hydrazine solution, or inverted sugar syrup. When silver and a reducing agent are simultaneously sprayed, the steel product acquires a boiling white surface with a mirror shine. Such products are characterized by excellent reflective characteristics. The next stage involves applying a varnish coating to the product to protect it from scratches with the addition of a light-fast coloring toner. To obtain the latter, three pigments are mixed - black, blue and violet in a ratio of 1: 1: 3. Processing using a “silver mirror” is divided into a number of successive steps :
- Analysis and preparation. First, the surface of the product is thoroughly cleaned by rinsing with a specialized composition. To increase adhesion, the surface is sanded with sandpaper with an abrasiveness level of P500−600.
- Application of a glossy base. A glossy black substance is applied to the prepared material, which eliminates the risk of yellowness in the final mirror coating. Then the varnish coating is dried at room temperature from 20°C to 25°C, without the use of specialized equipment, and drying lasts 8 hours. If drying is carried out at a temperature of 60°C, the process duration is reduced to 45 minutes.
- Drying.
- Etching the surface of the product to increase its adhesion to silver, followed by cleaning with distilled water.
- Sensitization or specialized surface treatment using an activator. This allows you to protect the surface with a special film.
- Metallization using silver.
- Application of a protective varnish coating to the product, which reliably protects it from tarnishing and loss of original qualities during long-term use, mechanical stress, or due to the destructive influence of aggressive environments.
Procedure for preparing electrolyte
There are quite a lot of methods, as well as the reagents used. For chrome plating at home, the most common electrolyte option is based on sulfuric acid and chromic anhydride. Component ratio: 2.5 g H2SO4 + 250 g CrO3 per 1 liter of clean water.
- First, the bath is filled. Water (distilled is the best) is poured in approximately ½ full. Its optimal temperature is 60 – 65 ºС. Under such conditions, the dissolution of the chromium compound will occur faster.
- Load CrO3 and mix thoroughly until all grains disappear.
- If necessary, add a certain amount of water (to the required volume), then add sulfuric acid.
After mixing the resulting solution, it is subjected to “processing”. It consists in passing a direct current through it. Its strength is calculated from the ratio: 1 liter - 6.5 A. Visually, the readiness of the electrolyte can be determined by its shade. It should turn dark brown in color. After this, the solution settles in a dark and cool place for at least 24 hours.
When choosing a capacity by volume, you need to focus on the power of the power supply. Accordingly, it should be selected based on the dimensions of the parts to be metallized. This is another reason why chrome plating of large samples at home is impractical and difficult.
Three parts of the galvanic process
Electroplating at home, chrome plating is an electroplating process. Therefore, to carry it out, it is necessary to have three components: a cathode, an anode and an electrolytic medium in which the transfer of charged metal particles will occur.
- Cathode. A plate of pure lead or an alloy of lead and tin. It must be remembered that the cathode area must be larger than the anode area. The cathode is connected to the positive output of the rectifier.
- Anode. This is the chrome-plated part itself. It should hang in the electrolyte medium so as not to touch the walls and bottom of the container. In addition, the anode must never touch the cathode.
- Electrolyte. Chromium plating requires particularly careful preparation of the electrolyte.
Electrolyte preparation
The electrolytic fluid kit for chrome plating includes the following components:
- Chromic anhydride: 250 g/l.
- Sulfuric acid: 2−3 g/l. Chemically pure, concentrated. Technical sulfuric acid is not suitable.
- Distilled water.
The water is heated to a temperature of 60−80 degrees. After this, the anhydride dissolves in it. The solution is cooled slightly and then the required amount of sulfuric acid is added to it in a thin stream.
Preparing the surface of a chrome-plated product
Consists of three stages:
- Mechanical cleaning, grinding and polishing.
- Degreasing.
- Nickel plating.
The peculiarity of chrome plating is that, on the contrary, it emphasizes all existing irregularities, chips and cracks on the surface of the product. Therefore, traces of old paint, rust, chips, cracks and other defects must first be removed from the surface of the chrome-plated part. Preparation of the chrome-plated surface consists of the following steps:
- Sandblasting.
- Polishing with fine sandpaper.
- Sanding with soft materials and polishing paste.
Do not use gasoline or White Spirit for degreasing. Otherwise there will be problems with the quality of chrome plating. The best option is to prepare a special solution:
- Caustic soda: 150 g/l;
- Soda ash: 50 g/l;
- Silicate glue: 5 g/l.
The solution is heated to 90 degrees.
After that, the part is lowered into it and kept for 20-40 minutes, depending on the area and surface relief of the part. Nickel plating is the last stage of preparing a part for chrome plating. The nickel plating process is carried out in a special galvanic bath. The cathode in this case is metallic nickel, and the electrolyte is a solution of sulfuric acid and nickel salts.
Chrome plating in stages
Due to the high toxicity of free chromium, all work must be carried out in a non-residential area equipped with ventilation. It is strictly prohibited to flush electroplating waste down the drain. For them, you should prepare a special chemical-resistant container made of glass or plastic.
- The anode is immersed in the bath. The negative cathode is connected to the transformer.
- The workpiece is suspended at a certain distance from the walls of the container. She shouldn't touch them.
- The current is connected.
- The color of the coating will depend not only on the type of electrolyte, but also on the temperature of its heating. If it is below 35°C, the film will be matte. You can achieve shine by raising the temperature to 35-55°C. Milky chrome plating is obtained by heating above 55°C.
- The exposure time depends on the thickness of the future coating. The average duration is 2-3 minutes.
- Do-it-yourself chrome plating of plastic at home is not much different from electroplating other types of materials. The part is placed in a container with electrolyte and connected to the negative wire.
- Since chromium cannot adhere to all types of metals (only brass, nickel and copper), coating steel products requires the creation of a substrate layer.
- The process begins with a “push” of current. In the first 20-60 seconds, its density should be 2 times higher than the working one. This allows for better treatment of recessed areas. Then the current density is set to the recommended value and the part is processed for another 1-1.5 minutes.
- The temperature must be maintained at the same level throughout.
- The last stage is double rinsing with water. After the first, the electrolyte is neutralized using alkali (regular baking soda).
- The finished product should be polished using paste.
So, chrome plating parts yourself is a real process. Of course, obtaining a wear-resistant coating at home will be problematic - this will require currents of up to 100 A. But a thin, durable film of chromium is quite capable of protecting parts and components from moisture and corrosion. Electroplating also allows you to create original items for interior decoration.
This is interesting: Metal turning - all about turning technology
Chrome plating stages
Chromium plating itself consists of a number of successive stages:
- The process begins by raising the temperature of the electrolyte in the bath to 50-54 degrees.
- A chrome-plated part is placed with the cathode output first connected to it.
- After this, wait for some time without applying voltage to the system. During this time, the temperature of the part and the electrolyte should equalize.
- After applying voltage, the workpiece is in the solution for at least 20 minutes. In some cases, chrome plating can last 2-3 hours. Everything is decided on an individual basis depending on the size of the part and the required final characteristics of the chrome coating.
- After the process is completed, the part is removed from the solution, washed and placed in a drying cabinet for 2-3 hours.
There are a lot of video tutorials on galvanizing on the Internet, in particular, on chrome plating of metals. Therefore, all the details of this process can be found there.
The issues of effective protection and decorative design of the surfaces of products made of various materials are quite relevant both for manufacturers and for many home craftsmen. Chemical metallization, which you can do yourself, allows you to effectively solve such problems.
Chemical metallization technology can be used on virtually any hard surface
Preparing the part for metallization
While the electrolyte is settling, it's time to do this.
Removing contaminants
In order for chrome plating to be of high quality and inexpensive, the layer covering the part must be uniform and thin. This can be achieved if the surface is cleaned down to the very base. How to remove foreign fractions and degrease is up to you to decide. For samples with smooth edges, as a rule, “sandpaper” is sufficient. In other cases, you will have to think about how and with what to remove dirt and rust.
Degreasing
This is the second preparatory stage. Limiting yourself only to traditional means - gasoline, white spirit, solvent “666” or something similar - means you will not achieve high-quality metallization. Chrome plating on such a surface will not last long.
Additional processing is carried out in a solution that is specially prepared for these purposes. There are many recipes, but the most popular for metallization at home is the following:
150 (caustic soda) + 50 (soda ash) + 5 (silicate glue).
*Based on g/l of water.
The pre-treated workpiece is immersed in this solution, which must be brought to a temperature of 85 (±5) ºС. The exposure time depends on the relief of the part and the degree of its residual contamination (from ⅓ to 1.5 hours).
Features of the chrome plating process
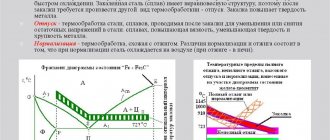
The “installation” diagram with the voltage switching polarity is shown in the figure (see above).
- The current is supplied after the sample is immersed in the electrolyte with some delay. Why? High-quality metallization will occur only if the temperatures of the part and the solution are equal. So you'll have to wait a little. This time can be reduced if the sample is preheated to 40 - 50 degrees. For example, in front of the reflector.
- Recommended current is within 55 ºС.
- After the entire part is covered with a layer of chrome, without “bald spots” (determined visually), it must be dried in an electric cabinet (at least 2.5 - 3 hours).
Before finishing the article, the author with great regret must add a couple of “flies in the ointment”.
Those who are not afraid of the listed difficulties need to take into account a number of other problems that they will have to face. Some - for example, ensuring high quality polishing, maintaining the absolute accuracy of the recipe, the difficulty of determining the optimal dimensions and shape of the electrodes, maintaining a constant current regime - will seem insignificant against the background of just one.
Where can I get anhydride and “pure” acid? The first one is on sale, but only for legal entities, with the preparation of the relevant documents. Store-bought H2SO4, which is purchased for the purpose of preparing electrolyte for batteries, is not suitable. It is not “clean” enough, so it will not provide high-quality chrome plating.
The article turned out to be quite complete. Whether or not to engage in metallization at home is up to you, dear reader, to decide.
Advantage
The purposes of metallization are varied, in most cases it is to impart or increase certain qualities:
- resistance to corrosion processes;
- resistance to mechanical damage;
- wear resistance;
- decorativeness.
The quality of the film depends on the composition of the metal:
the cheapest zinc coating increases anti-corrosion qualities, is actively used in construction to protect embedded parts, steel sheets are coated with zinc before coating with plastics and profiling;
- chromium increases hardness, imparts heat resistance, and makes products attractive in appearance;
- aluminum coating protects parts of equipment operating at elevated temperatures (up to 900°C);
- coating with copper or tin gives a noble appearance even to plastic objects;
- silver produces a mirror-like shine.
When carrying out work, the main condition for obtaining results is adherence to technology.
The essence of technology
Chemical metallization technology can be used to achieve a variety of purposes, most of which are associated with changing the decorative qualities of the surface. In addition, this processing method allows you to hide the main defects of metal or other material: microscopic cracks and pores, other structural defects. In some cases, technology is used to restore coverage.
The essence of the technology is to apply a thin layer of metal. The specifics of the substance application process depend on the specific technology, of which there are quite a few.
Metallization allows you to impart certain performance qualities to parts. Among the achieved characteristics of the processed product, we note the following:
- Hardness increases. Metal is more durable than plastic. By covering the surface of plastic or wooden products with it, you can protect the base from mechanical stress.
- Decorative properties increase. The metallic glossy finish looks very attractive.
- The wear-resistant qualities of the surface are improved. Metallization is often carried out in order to reduce friction between contacting parts.
Parts after chemical metallization
Parts that have high hardness and wear resistance are used in a wide variety of fields. However, high performance can only be ensured if all recommendations are followed.
Classic metallization technology has the following features:
- Several reagents are applied, which react to form a surface layer with certain performance properties. There are many different methods for transferring reagents to workpieces, each with its own characteristics, advantages and disadvantages.
- As a result of metallization, a protective layer is formed on the substrate. In this case, a reliable connection is formed between the coating and the substrate, which is maintained over a long period.
- The resulting coating can be of a wide variety of shades. If necessary, you can create a transition from one color to another without a clear boundary. In some cases, when it is necessary to obtain a surface with special decorative qualities, a dye is added during metallization.
Chemical metallization of different colors
The chemical treatment in question can be carried out in a home workshop, despite the fact that metallization is considered a complex technological process. As a rule, at home the workpiece is subjected to catalytic chrome plating. Due to this, the coating becomes attractive and gains protection from moisture.
Chemical metallization of metal is also in demand because it can be used at home. The work is carried out according to the following algorithm of actions:
- The part is cleaned of contaminants. There should be no layer between the surface layer and the base, as this will significantly reduce the performance characteristics.
- Degreasing is carried out. It is carried out using a special alkaline solution or a special detergent that can remove organic contamination from the surface.
- The degreased surface is additionally washed with clean water. In a similar way, previously used compounds can be removed from the surface during degreasing.
- Surface areas that should not be exposed to the chemical are treated with lead. The tests carried out indicate that lead does not react to the influence of an electrolytic solution.
- Wiring is connected to the solution bath to supply electricity, after which the part is lowered into the prepared reagents.
- After the required period has passed, the product is removed from the solution, dried, and then cooled. If the coating is of high quality, then it is polished.
To carry out the process under consideration at home, you can purchase a special mini-installation designed for chemical metallization, which runs on a small compressor.
The process in question should only be carried out in compliance with the following recommendations:
- Before immersing the part in the bath and applying electricity, you need to check that all contacts are connected securely and can withstand the load.
- The room in which the work in question will be carried out must be ventilated. For this purpose, a ventilation system is installed. This recommendation is due to the fact that during the metal plating process gases are released that can negatively affect vision and breathing.
Parts subjected to chemical metallization
To comply with metallization technology, you must have sufficient experience. You should not expect that when carrying out a complex operation of transferring one material to another for the first time, you will get a result that can be achieved using special industrial equipment.
Methods
For “garage” applications, two main types of processing are suitable:
- galvanic bath method;
- spraying method.
To use the first one you will need:
- a container for immersing parts in a chemical solution (preferably enameled);
- degreasing agents (alkaline solution);
- electrolyte. Ingredients: pure chromium oxide, radicals and distilled water (ordinary water has a high concentration of salts);
- a rectifier capable of providing a constant current density (the required value depends on the area of the chrome-plated part);
- anode (lead);
- electrolyte temperature meter;
- copper wires for hanging cathodes (chrome-plated metal) and supplying current.
For chrome plating of metal parts and plastic by spraying you will need:
- base coat of paint (the surface must be uniform);
- gas burner or chemical solution to create adhesion;
- chrome plating composition;
- means for spraying (spray gun with compressor, electric spray gun). It is possible to use a mini-wash;
- a large amount of distilled water, wetting agent;
- degreasing composition.
Chemical metallization
Chemical metallization is the formation of a thin film of metal on the surface being treated under the influence of various chemical reagents. This method can be used to obtain coatings with zinc (zinc plating), chromium (chrome plating), aluminum (alitizing) and others. Using this technology, it is possible to obtain an even layer of metal on materials with different types of surface: smooth - glass, porcelain, polished stone, or porous: wood, plastic, gypsum.
Silver metallization
Performing chemical metallization at home is quite possible, but requires careful preparation.
Workplace and equipment
As a result of the chemical reaction, a gas is released that negatively affects the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract, so the process must be carried out in a room with forced ventilation or in an open space.
Equipment you will need:
- enamel bath;
- measuring cups with a capacity of 1 l and 250 ml;
- 3 bottles of 100 ml;
- disposable syringes for 5, 20, 50 ml3;
- disposable glasses of 50 ml;
- kitchen electronic scales.
Don’t forget to get rubber gloves, a respirator, sponges, and a set of protective clothing, since when working with concentrated hydrochloric acid, caution is required, otherwise burns are inevitable.
Reagents
Depending on the material of the workpiece and the type of coating, reagents are purchased. For chemical metallization with silver, you will need the following reagents:
- hydrochloric acid;
- silver nitrate;
- tin chloride;
- sodium hydroxide;
- ammonia;
- glucose;
- formalin;
- distilled water.
Preparation of solutions for:
- surface activation - stannous chloride, hydrochloric acid, distilled water;
- recovery - glucose, formaldehyde, distilled water;
- silvering - silver nitrate, sodium hydroxide, ammonia, distilled water.
Surface preparation
the surface is prepared in several stages. Porous and painted products are sanded, the old paint layer is removed, the surface is cleaned of dust, washed and degreased. You can degrease with white spirit, acetone or a solution of sodium hydroxide in water t= +40...+60°C. The surfaces are wiped with a sponge containing a degreasing compound, then washed with distilled water with another sponge. The prepared surface must be completely wetted with water, without dry spots - in these places defects will be inevitable.
Coating the product with an activating composition
The object to be treated is poured with tin chloride evenly over the entire surface for 1 minute, then washed with distilled water for 3 minutes.
Metallization
To obtain a uniform metal film, a solution of a reducing agent and silver plating is sprayed onto the product simultaneously and in equal volumes. Since the resulting mirror film is very thin and not durable, it can be strengthened with a protective varnish - transparent or tinted.
The described method resembles the painting process. There is another, more complex way of performing work - electrochemical metallization.
Chrome plating at home
I would like to share my experience of decorative chrome plating in real home conditions. This can be done using this starting set of reagents for creating a mirror in chrome, gold, copper and any other shade on any surface. The kit contains reagents that are not available in regular stores. These are silver nitrate, stannous chloride, sodium hydroxide, glucose and sodium thiosulfate. Everything else can be bought in regular stores and is available to everyone, this is acetic acid 70% (in grocery stores), ammonia or ammonia 10% (in a pharmacy), distilled water (in auto parts). You will also need scales up to 300 g. (radio parts stores), measuring cups (also suitable for food products), disposable cups, spoons, syringes and hand sprayers. To obtain a chrome-look mirror, you need to go through 4 stages: preparing solutions degreasing the surface activating the surface metallization I’ll start with the recipe for decorative chrome plating, which is so carefully guarded in the depths of their workshops by people who are fluent in the art of chrome plating.
Chemical reagents used
Chemical metallization technology involves the use of various substances that bind together to form a protective coating after undergoing a chemical reaction. Using an activator and reagents for chemical metallization, you can do without special equipment, but the method is not suitable for large parts.
To carry out the processing in question you will need:
- The reducing agent is the main component. Chemical metallization reagents should be stored according to the recommendations provided by the manufacturers.
- The activator is also an important reagent that determines the performance of the surface. Chemical metallization reagents have labels that indicate the name of the metal. Let's take gold, mel and chrome as an example.
- The primer is applied to the surface to ensure the most favorable processing conditions. It significantly increases the adhesion of the applied metal.
- The varnish protects the applied coating from chemical and mechanical influence.
- In order to give the surface a certain color, special toners are used. The specific shade is indicated on the toner packaging.
Reagents for chemical metallization
It is worth considering that when doing the work yourself, it is quite difficult to ensure high quality surfaces. In some cases, you have to use special cleaning compounds.
Considering the disadvantages of chemical metallization, we note that when carrying out this procedure, harmful chemicals are used, work with which must be carried out in strict compliance with safety precautions. This technology is quite simple to implement and resembles the method of coating a surface with a paint and varnish substance.
Types of metallization
Metallization of products, as the name of this process implies, involves applying a thin metal layer to their surface. Not only metal, but also plastic, wood, glass and other materials can be subjected to such processing. The most popular and well-known types of this process are metallization with chromium (chrome plating), coating the surface of the product with a layer of zinc (zinc plating), less known is aluminizing, during which a layer of aluminum is applied to the surface.
Chemical metallization. Mirror frame
Depending on what equipment and what technology is used for metallization, this processing is divided into various types. Thus, today the following methods of applying metal coating are well developed and actively used:
- galvanic metallization, performed in baths with a special electrolyte;
- electric arc metallization, in which the coating is applied to the surface to be treated by electric arc melting of a metal electrode and subsequent spraying of the molten metal using a jet of compressed air;
- gas plasma spraying, in which, as with arc technology, the metal is applied to the surface of the product in a molten, finely dispersed state (like electric arc metallization, gas plasma spraying is a rather complex technological process, so they are used mainly in production conditions);
- cladding – application of a layer of metal to the surface and its subsequent hot rolling;
- diffusion metallization, the essence of which is that atoms of the applied metal, under the influence of high temperature, penetrate into the surface layer of the workpiece;
- hot metallization - the formation of a coating by immersing the product in a bath of molten metal;
- chemical metallization.
It is worth dwelling on the latest technology in more detail, since it is optimally suited for applying metal coatings to various products with your own hands at home.