Aluminum has occupied a large niche in industrial production for the second hundred years. The material is used in mechanical engineering and the aviation industry, in construction and electronics, in advertising and design, etc. This popularity is due to its unique properties, a combination of which is not found in any other metal. It is plastic and easy to form, has high electrical and thermal conductivity, is light in weight compared to other industrial metals and is not subject to corrosion. After grinding, finished aluminum products have an aesthetic appearance and do not require additional processing.
What is milling
In principle, hand-carved wood can be conditionally classified as milling. But there is a clear difference - only those types of processing that are carried out using a rotating cutter on manual or stationary machines are called milling.
If we exclude other simple woodworking techniques - sawing, hewing, planing, drilling, then there are two main directions in woodworking.
- turning - carving a rotating part to give the desired shape to the diameter of the part;
- milling – the formation of linear (not radial), longitudinal shapes.
The scope of application of milled parts is limitless. Such details can be found in many complex modern products. The operation is quite labor-intensive, but sometimes there is nothing to replace it with. Casting or stamping will not give accurate dimensions, or these methods cannot produce such complex formats. The only way left is milling.
Main technological stages
All milling work begins with determining the dimensions of the future part or product.
When milling with hand tools, mainly in woodworking, most often they work without drawings or even sketches. It is enough to imagine and understand the desired result and decide on the dimensions. The photo below shows the simplest wood milling, edge rounding:
In industrial production, drawings of the future product are necessarily used. Therefore, the milling machine operator must be able not only to operate the machine, but also to read drawings. A fairly high qualification of the machine operator is also required.
When working on modern CNC machines, electronic versions of drawings and appropriate software are required. Here the manual skills of the machine operator fade into the background. And the most important thing is competence in modern computer systems. Although manual work skills are also required - you need to install the cutter, place the workpiece, and control the processing process.
After determining the dimensions for any type of milling, a suitable cutter is selected and installed. The workpiece is placed on the work table and the actual processing takes place.
Setting up the router
In order to do the job, you need to adjust the depth of the cutter. The essence of this setting is that after the cutter reaches a certain depth, the limiter is triggered and it cannot move further. If work must be carried out to great depth, then it must be done in several stages.
If we compare the router with other electric tools, it operates at a much higher speed, it usually exceeds 10,000 rpm.
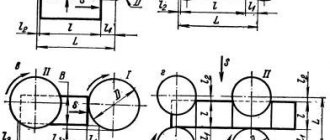
Device of a milling machine.
This is necessary in order to obtain a better cut surface. It is necessary to regulate the speed, since if it is very high, charring of the part may occur. The rotation speed of the cutter depends on its diameter and the material with which the work is being done.
The quality of the surface is not affected as much by the speed of rotation of the cutter as by the speed of its linear movement. The larger the diameter of the working tool, the higher the speed of its movement should be. The higher the hardness of the workpiece, the lower the rotation speed of the working tool should be set. If the cutter has a diameter of 40 mm, then its rotation speed should be within 10,000 rpm, and for a cutter with a diameter of 10 mm it can be 20,000 rpm.
To perform various jobs, you can use parallel or counter rotation of the working tool; counter milling is usually used, in which the cutter and router move in one direction. Climb milling is rarely used, only in cases where there is a possibility of obtaining a flake. This can lead to the router being torn from your hands, so you need to work with even greater care.
Return to contents
Types of milling on machines
There are three main types of milling.
- Terminal . It takes its name from the end mill used with the cutting end (end). It is used for making rectangular grooves, curved holes and windows, pockets and niches for various purposes.
- End _ This is the processing of large surfaces with cylindrical cutters with straight, fairly large cutting edges. The edges, side and horizontal surfaces and ends of workpieces are processed, which is why the operation is called end milling.
- Shaped . The most difficult type of processing. It can be used to manufacture products of any configuration. This could be the spiral teeth of a worm gear, a shaped sample of a wooden baseboard or railing. Milling cutters of various profiles are used, including prefabricated modular ones.
In metalworking, sometimes milling refers to cutting metal using a cutter. But such an operation can be performed in a large number of different ways, both in metal and woodworking, so the operation is conditionally classified as milling.
Industrial portal milling machine manufactured in 1978.
CNC
The machine tool industry today offers hundreds of options for a wide variety of CNC machines for processing any materials. From the smallest for small home workshops, to the most powerful for industrial production.
The main series of such machines:
- lungs;
- professional;
- industrial;
- special.
Light ones (among them the lightest) cost from 150 thousand rubles.
Professional is an intermediate option between light and industrial options. These include wood milling and engraving machines costing from 200 thousand rubles. up to 600 thousand rubles.
Industrial - for continuous production, cost more than 1 million rubles.
Special ones are most often designed individually for specific tasks and details. These include machines for milling stones, as well as small, ultra-precise ones for jewelry.
3D milling
Modern 3-6 axis 3D CNC machines have brought this method of processing various materials to a fundamentally new level. Today there are no parts that such machines cannot make. They even make sculptures with their help.
The most important points are the correct selection of cutters for different materials and the appropriate software. There is both free software on the market, including open source software for possible modification, and paid packages created specifically for the manufacture of specific parts and tasks.
Basic software standards: CAM System and CAD system
As an option, programs are offered for free testing for a month.
The capabilities of such a machine in woodworking can be seen in the following video:
Work order
First, the cutter is properly secured, then the engine is set to the required speed and the milling depth is adjusted. In order to ensure correct movement of the cutter, additional devices are used.
The milling cutter is installed on the workpiece, its guide element is pressed against the guide edge and the engine is turned on. First, the cutter smoothly plunges to the required depth, and then slowly moves along the selected path.
During attachment of the working tool and adjustments, the equipment must be disconnected from the power supply. You need to take a stable position and do the work carefully and carefully.
It is necessary to ensure reliable fastening of the workpiece that is being processed so that it does not tear off during operation. At one time it is necessary to cut off a layer not exceeding 3 mm. Your clothing should not contain any parts that could become wrapped around the cutter during operation and cause injury. It is recommended to connect a vacuum cleaner to the router or use a respirator, as this produces fine dust that can harm the body.
Equipment
The main equipment, of course, is the milling machine itself or a hand router.
The main components are cutters for various purposes and profiles. However, there are no technological lines or small production facilities consisting of only one machine.
Before the workpiece is processed, it is most often prepared on other equipment.
- format cutting machines;
- miter or hand-held circular saws;
- gas cutting or laser cutting of metal.
Sometimes it is necessary to prepare the workpiece in terms of thickness. Then it is adjusted to the desired size using the following equipment:
- wood - trimming on circular saws or band saws, planing on a jointer or planer;
- metal – cutting to thickness in different ways, preliminary rough milling.
Stationary machines
In addition to the modern CNC machines described above, of which there are many, there are also simpler options.
These are the simplest wood milling machines, consisting of a table, a motor, a cutter landing shaft and a guide for manual feeding of the workpiece. There is also an option with installing a manual router into the table upside down.
More complex ones are industrial milling machines for wood and metalworking. They can have automatic feeding of workpieces, regulation of the position of the cutter, positioning of workpieces, etc. Quite a lot of these old machines, manufactured before the 21st century, are still in working order. Although there are fewer and fewer of them left.
Hand milling machines
This type of tool is sometimes called a "milling machine." This is so because a hand router is a completely self-sufficient tool. It has everything that a stationary machine has:
- own electric motor;
- rotating spindle with mount for different cutters;
- working platform with adjustable cutter immersion depth.
This tool is intended for manual work, so there is no point in comparing it with large industrial machines. The manual router copes with its tasks to the fullest extent. Moreover, it has its own number of advantages over stationary options:
- mobility , ability to work anywhere;
- the ability to process large-sized workpieces that do not fit on the desktop of stationary machines;
- great versatility . Unlike special machines, a manual milling machine can perform all basic operations for milling soft materials;
- affordability . The cost of a manual milling machine is tens, sometimes hundreds of times less than the cost of stationary machines;
- compactness . This router does not require large areas to operate and store. When they are not using it, it is simply removed to the side, freeing up space.
Modern manufacturers offer the widest selection of such tools of different power, from 350 W to 2500 W.
In addition to universal ones, there are also special-purpose models - lamella, edge, filler.
List of works that can be performed using the specified tool
As already mentioned, it is possible to make parts of the most varied shapes with a manual milling machine, and all operations that are performed by the specified equipment are conditionally divided into the following categories:
Elevator diagram for a router.
- Making grooves, quarters and grooves. In order to make any grooves in the workpiece that can be open or closed, it is very difficult to do without a manual router. Most often, such elements need to be manufactured when permanent or detachable connections are made.
- Making edges. This operation is performed when elements such as glazing beads, cornices, platbands and other moldings are made. It can be performed when decorating furniture and other wood crafts. In addition to the fact that such elements carry a functional load, they also act as decorative elements.
- Execution of complex contours and surfaces. This operation is performed during the manufacture of exclusive furniture and other artistic works made of wood. When making furniture, when several elements need to be repeated with high precision, templates are used. In this case, it turns out to almost perfectly repeat complex shapes on different workpieces.
- Execution of special elements. A hand router can also be used to make special elements, such as tenons, clamps, grooves and others that carry only a functional load. In mass production, special machines are used to make them, but if you need to make several elements at home, you can do it with a hand milling machine.
Return to contents
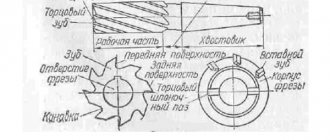
Milling cutters
This small detail makes a huge difference. The machine only serves its work, and it is the milling cutter that directly processes the material. Therefore, the quality of processing depends largely on the cutter. With hundreds of varieties of milling machines and different cutters available, thousands of varieties are used. The main difference is in three respects:
- Mounting method. Shell cutters have a hole in the middle and are mounted on the spindle (shaft) of the machine. The photo shows a shear cutter for woodworking with replaceable knives:
- Milling cutters with shanks are clamped in collets. In the photo, a set of such cutters for a hand router:
- Profile . Simple, straight and profile cutters of various configurations are used. Nozzles with straight cutting edges are used to make the same straight recesses. Profiles form a sample on the workpiece that repeats the profile of the cutter itself.
The exception is 3D CNC machines. They cut complex profiles and reliefs with a simple thin end mill. Profiles on the part are formed due to the mobility of the cutter itself in three coordinates.
On 4-6 axis machines, cutters not only move vertically and horizontally, but can also tilt.
Milling aluminum with a hand router
Very often, home craftsmen perform a number of jobs that cannot be done without a hand router. The most common and versatile is the manual plunge router.
Drawing of a hand router.
Using a hand-held milling cutter, you can make figures of various shapes from wood, from rectilinear to very complex, which is rather an art than just work.
Milling materials
The cutter material must be stronger than the material being processed. If this is not a problem for soft materials, then in metalworking special heavy-duty alloys are used to make cutters. Some machines are equipped with a system for lubrication of the machined surface and the cutter with an oil-water emulsion. It lubricates the cutting area, removes small chips and cools the cutter.
Tree
This is a soft material. It is processed both by hand milling machines and by powerful industrial machines.
A hand router can be used to do almost all types of milling work, but in small quantities.
On industrial machines, moldings are made in-line - lining, floorboards with a groove/tenon connection, baseboards, corners, round products in two passes with a semicircular cutter, etc.
Despite the softness of the material, cutters are made of hard alloys so that they retain their sharpness for a long time and are less abraded by friction. As a rule, these are “high-speed cutters”, alloys such as R6M5, R6MZ and R12 (HSS in Western markings) - steel containing tungsten, molybdenum and vanadium in different proportions.
Plywood
Plywood sheets are large-sized material of small thickness. Sometimes it is necessary to mill edges, cut out non-through and through ornaments, curved or straight lines. Hand-held routers are better suited for working with large sheets. It is better to move a small tool relative to the sheet than to move a bulky sheet relative to a stationary router.
For plywood, universal cutters are used (hardwood, plywood, MDF, etc.). The hard adhesive resins in plywood can dull the cutter faster than when working with wood. Therefore, it is better to use high-quality cutters made of harder alloys.
Furniture board
Furniture board is wood, wooden beams glued together. Processed in the same way as wood. If the sheet is large, it is better to use a hand router, as is the case with large sheets of plywood.
MDF, OSB, laminated chipboard (LDSP) and plain chipboard
These are materials containing wood similar in structure. They are based on crushed wood, sawdust or shavings, compressed and glued under pressure at a certain temperature with adhesive resins. The difference is in the size of the wood particles and the manufacturing method. They are milled in the same way as plywood. Either universal or special cutters for such materials are used.
It is extremely undesirable to allow the cutter to overheat to prevent burning of adhesive resins, wood and the release of acrid smoke. Overheating of the cutter is possible when the cutter moves too quickly, the speed is too high, or the cutting edge of the cutter is dull.
Metal
For metal processing, industrial stationary machines are used, including CNC and 3D CNC. The latter are distinguished by the fact that they can make a part completely in one go. If on simple machines you have to frequently change the position of the workpiece, or use different machines, then a modern 3D CNC machine can cut out the part immediately, according to the programmed program. Dozens of varieties of such machines and hundreds of different types of cutters are produced.
Steel
Durable metal, when significant thickness needs to be removed, this is done little by little in several passes. Manufacturing one complex part on 3D CNC machines can take a long time.
An example of parts that are made on such machines from steel and alloys:
Soft metals: aluminum, brass
Aluminum, brass, copper, bronze are soft metals and alloys. They are processed in the same way on the same machines as steel. The only difference is the processing speed is higher; in one pass it is possible to remove a thicker layer than steel. Cutters wear out less.
Titanium
The processing of titanium is slightly different. This metal is difficult to process. Due to its high chemical activity, titanium sticks to the cutter, which slows down work and wears out the cutter. Titanium conducts and removes heat poorly, so the cut site quickly overheats. This metal is cut with necessarily the supply of coolant (cutting fluid), sometimes under pressure.
Porcelain tiles and marble
These materials, in addition to strength, have high abrasive properties - the ability to quickly erase the cutter. Therefore, it is important to use special cutters to process them:
- polycrystalline diamond;
- pressed (solid-sintered) diamond;
- with diamond coating;
- carbide (nickel, tungsten carbide, cobalt).
Machines of different designs and power are used for stone processing. From mini-machines for making jewelry to large industrial ones for processing architectural elements.
Operation of a CNC machine for stone:
Plexiglas
Refers to soft materials. Processing is possible with universal cutters (wood, plastic, plexiglass) or special ones. The main problem when cutting is the melting of the material and its tendency to crack. That's why:
- The cutter must be sharp; a dull cutter is prone to overheating due to strong friction.
- It is necessary to select the optimal cutter speed.
- To avoid cracks, the material is removed in thin layers.
CSP (cement particle board)
This material does not apply to finishing. Sometimes it is used as intra-wall in frame construction or as insulation on ceilings. The structure is rough and loose. Therefore, during installation, milling of the DSP is practically not required. Sometimes mounting niches are cut out in the DSP (round for electrical sockets, switches, rectangular for communications, etc.). For this purpose, carbide bits on drills, stone discs on angle grinders, jigsaws and diamond-coated saw blades are used.
The material itself is soft, as it is based on wood chips. But cement is a strong abrasive and can quickly erase cutting edges made from insufficiently strong alloys.
DSPs are milled during production on industrial machines. This is one of the stages of technology. You can see how this happens in the following video:
Drywall
This is a soft material. During installation, they are milled with a hand router, and the edge is cut with a regular plasterboard plane. Any cutters that are resistant to abrasion by plaster are used. In sheets of plasterboard it is often necessary to make long grooves (grooves), for example, when you need to recess a load-bearing strip into them. Mounting niches and openings for electrical equipment, wires, and communications are also required. How to mill drywall is fully and clearly shown in the following video:
The above describes milling methods in general terms, with some points. The narrow specialization of each technology is incomparably broader. Textbooks and scientific papers are devoted to metal milling. Practical skills for working with hand routers are also presented in numerous sources. In general, milling is a type of material processing that allows you to make almost any part, and without which it is difficult to imagine modern civilization.
How to mill aluminum
Only TS didn’t indicate what diameter he was cutting with. For a 20mm cutter and a 5mm cutter, you know, the feeds and speeds are different. For example: a 10mm key sawed 35 steel to a depth of 10mm, drilling with a cutter, the depth per pass was 2.5mm. This is 0.03mm per tooth.
Search data for your request:
Schemes, reference books, datasheets: Discussions, articles, manuals:
Wait for the search to complete in all databases. Upon completion, a link will appear to access the found materials.
WATCH THE VIDEO ON THE TOPIC: Is the Chinese CNC 2418 capable of milling aluminum?
processing of 3 mm aluminum with a household milling cutter
There are quite a few types of cutters on the market. Essentially we make a distinction between acute and dull. The sharper the blade, the faster the tip wears out.
The general rule is: the higher the strength of the material, the flatter the sharpening of the blade should be.
Sharper fishtail sharpening for plastics, wood and soft aluminum. Blades are the wear parts of the cutter. In cutters with more than one blade, the load is distributed and durability increases. These cutters run faster and vibrate less in difficult materials such as stainless steel.
Multiple blades - under the same milling conditions - produce thinner chips, resulting in a smoother surface.
In advertising production, 1- and 2-flute cutters are most often used, less often 3-flute cutters. Four-blade or multi-blade cutters cannot cut thick chips in soft materials and are generally not used.
Their main problem when milling soft materials is “baking” in the cavities of the cutter.
Special cutters for aluminum have a large groove. Choosing the “ideal” type of cutter always depends on the material being processed.
In this case, the problem of faster dulling is preferable to the risk of clogging the chip evacuation groove and breaking the cutter. When machining harder metals such as brass, we can recommend 2-flute cutters with a flat grind. The counter-side, counter-milling movement, is “more beautiful” than the synchronous side, down-milling.
This way the “bad” side ends up in the chips. Directions: Do not rout deeper than double or triple the diameter of the cutter. Go through deeper grooves in several passes.
When processing metals, it is imperative to use a lubricant. Note: Aluminum and non-ferrous metals can be milled with alcohol or special emulsions; when processing plexiglass, soapy water can be used. Use a router bit with the shortest cutting edge possible.
Tighten it as much as possible. The right screw thread brings the chips to the top. The cutter has a tendency to lift material. The cutter presses on the material, the opposite of the “corkscrew effect.”
HM carbide is an expensive, man-made product that is produced by agglomeration from tiny powders, such as Wolfram-Carbid.
During the agglomeration process, the shape of the cutter is immediately created and subsequently does not change, only is sharpened.
Carbide is an extremely hard and wear-resistant material, but it is brittle, meaning it is susceptible to vibrations and shocks.
It is important when using carbide cutters to have a stable, possibly heavier and more massive machine, a spindle with precise rotation and high-quality clamping collets.
The material being milled must be rigidly and motionlessly fixed.
High speed steel HSS is used primarily where carbide is too sensitive: when milling stainless steel sheets, on shaky machines, or in cases where the clamping rigidity is not sufficiently ensured.
HSS wears out much faster, but there is less risk of premature failure due to its viscosity. The life of a coated HSS cutter is significantly increased. For example, with a titanium nitride TiN coating, service life is increased sixfold. With Titan-Nitrid coating, HM tools also last longer, although the difference in hardness is negligible.
The main parameters when milling are the number of revolutions and feed. You can check with the supplier what modes he recommends for his instrument.
If the number of revolutions is known, the feed is then calculated using the formula. If the cutting speed of the material varies greatly, check with reference books. From this you calculate:.
High feed rates especially in metals require a rigid and stable machine.
For less stable machines or with increased milling depth, the mode is calculated as follows:. The thickness of the chips will be based on the feed into the material constantly larger. In Fig.
The blade in countermovement is constantly “picking up” material, while in synchronous movement only a small amount is taken in just before the blade goes into the air.
Therefore, the last piece often seems to “break out”.
But in the case when the cutter is already dull, but can still process the material, the surface during up milling will be less smooth than the surface during down milling. This is due to the fact that the angle of entry of the cutter knife into the material is much greater during down milling and, when blunted, it is easier for it to enter the material.
Angle of cutter penetration during up and down milling. When processing hard grades of steel, 4 or more blades are used. Types of cutters by sharpening, geometry and number of knives. Cart Items: 0 Amount: 0 UAH. Feed per tooth based on cutter diameter fz.
Cutting modes
You can easily ask your questions here, or just read useful or interesting information on assembling, setting up and operating a mini CNC machine. How to get a premium account? Why write 2 messages? Where can I download something?
Features of milling aluminum composite panels. Selecting the type of cutter and tool.
Milling an aluminum part on a SkyOne 3D printer
Such widespread use is explained by a number of unique properties inherent in aluminum. Aluminum is ductile and easy to process. It is well known that the economic efficiency of one or another type of material processing varies. It is also known that high-speed BSO processing is the preferred method for processing metals.
Lightweight and durable, impressive and structurally mobile products allow you to hold a seminar, conference or presentation at a high level. Signs and plates, light boxes and volumetric letters acquire high performance characteristics thanks to the aluminum base. During the milling process, the workpiece acquires the planned shape.
Specialists will configure the equipment, select cutting parts, and give the structure an external effect. This is necessary to ensure that the installations correspond to the company’s image and meet modern design requirements.
Aluminum processing is carried out using advanced program-controlled equipment: in automated mode, you can set the required number of revolutions of the cutting wheels.
Aluminum fairing
Sheet metal used in industry and construction is typically stainless steel and aluminum.
Stainless steel has higher mechanical strength, but aluminum sheet has some unique properties that make it possible to use it in some specific conditions.
In its pure form, aluminum is soft, but with the addition of duralumin it becomes harder. It is used everywhere: in cars, in construction, production, etc. Thickness starts from 0.35 mm.
How to mill aluminum?
Do you want to know about discounts and promotions on our equipment? Cutting modes Left-hand cutters Why counter-feed milling is better. Problem: 2-flute cutter melts PVC foam. Solution: choose a lower number of revolutions or mill with a single-thread cutter. Picture 1.
Milling of aluminum products
There are quite a few types of cutters on the market. Essentially we make a distinction between acute and dull. The sharper the blade, the faster the tip wears out.
The general rule is: the higher the strength of the material, the flatter the sharpening of the blade should be. Sharper fishtail sharpening for plastics, wood and soft aluminum. Blades are the wear parts of the cutter.
In cutters with more than one blade, the load is distributed and durability increases.
Milling cutting of aluminum AMG, D The milling machine can mill aluminum up to 20 mm thick. The end is obtained in the color of the material.
Milling aluminum with a hand router
Skip to content. You have JavaScript disabled. Some functions may not work.
Forgot your password? The paragraph has been changed. Explanation and explanations are here. Turk, October 14 in Machining. All the best! Please help me with this question: a theory on milling aluminum and its alloys, in particular D and AK, is urgently needed.
Reduced prices for a wide range of advertising materials in Aluminstroy branches.
Topic in the section “Metal-cutting tools and equipment”, created by user Yur Nikolaich, Search in titles only User messages: Separate the names of participants with a comma.
Newer than: Search this topic only Search this section only Display results as topics. Quick search.
Metal cutters for a hand router Topic in the section “Metal-cutting tools and equipment”, created by user Yur Nikolaich, Registration: Yur Nikolaich I live here.
I will be glad to everyone who can share the secrets of their craft. I tried to mill aluminum on a Reobin machine with a Proxon head. Forum Rules. Rules Advanced search.