Metal straightening and straightening
During operation or processing, parts made of metal often lose their original configuration. The same phenomenon can be observed if they are not stored carefully. But in order for the parameters of the finished product to meet the requirements of the technical specifications, for the correct implementation of all further stages of processing, it is very important that the dimensions of the workpiece and its shape match the values specified by the project. To do this, an intermediate preparatory technological operation is performed, called “metal straightening”.
Types of editing
A cylindrical workpiece may bend under the influence of an external load, and one with a sheet configuration may become wrinkled. Products in the form of axes that do not even transmit torque, as well as shafts, can bend. The technological operation of straightening metal is understood as a series of actions, upon completion of which the workpiece made of metal returns to its original shape. Defects/flaws come in a variety of forms. The most common ones are:
convex. It appears on flat products in the form of an increase in thickness - the size of the cross-section of the sheet - from the edges towards the center;
dent. A recess on the surface of a metal plate, framed by flat edges;
wave. This is a deviation of the shape of the sheet surface from straightness.
There are two types of editing:
manual. It is carried out when home craftsmen produce uniquely shaped products. Although the set of tools used is quite simple, high demands are placed on the worker’s skill level;
mechanical. Used in industrial production conditions. The equipment is very complex, large-sized and heavy. But it is characterized by a high level of productivity, and its design makes it possible to automate the straightening process.
It is not allowed to perform such an operation at subzero temperatures. In this case, the level of ductility of the material decreases and it becomes brittle. Moreover! Sometimes it is necessary to heat the workpiece to a temperature of 140°C to 400°C. After this, its plasticity increases
Correcting dents with a magnet
It should be noted that this technology is suitable for straightening only minor damage. How to level metal on a car without putty? During operation, the magnet is moved along the surface of the damaged area from the edges to the center of the dent, pulling it towards itself.
To avoid damaging the paintwork, place a soft cloth under the magnet.
External alignment using adhesive technology
This method is also called vacuum, and the essence of this technology is to pull out the dent with a piston attached to the damaged area of the body with glue. However, it is also possible to use non-professional devices represented by suction cups. The applicator is secured with glue to the damaged area of the body.
Once it has dried, the center point of the dent is pulled out using a mini-lifter. The suction cup is used according to the same principle.
This method can correct the defect, but not eliminate it completely. In addition, it is not recommended to use this technology to align parts with cracks, as metal peeling is possible.
In general, the adhesive method of straightening dents is considered one of the simplest and fastest.
Editing metal sheets
The complexity of this operation depends on the type of defect detected. But special difficulties arise when their combination is revealed. For example, a convexity in the center of the plate and at the same time a wavy edge.
Convex
When straightening a convexity, blows should be applied around the circumference. You need to start with the line framing the defect. As work progresses, the radius of the circle must be gradually reduced, moving from the edge of the convexity to its center. As you progress, the frequency of strikes increases, and their strength, on the contrary, becomes less.
A special approach is used when there are several such defects on the sheet. In this case, by striking with a hammer, you need to ensure that the convexities are combined into one common one, after which the editing is carried out according to the method described above.
Waviness
Editing a metal sheet with wavy edges is carried out starting from its edges and then moving towards the center. The waviness of the edges is smoothed out after the plate is stretched in the middle.
Thin sheets
Processing of workpieces with a small thickness in order to return them to a flat configuration using strikers is not carried out. The reason is that metal creases may occur as a result of unforging. A thin sheet is straightened with long, even planes of smoothing bars made of wood or steel. Smoothing is done in different directions with gradually increasing pressure.
What needs to be corrected
Sheet metal: technology, what is special and other important points
The most common surface defects on the sheet that can be eliminated by proper operations are: waviness, convexity or concavity . Moreover, on the same sheet they can be located in different places at the same time - on the edge and in the middle.
Thick and thin sheet blanks
The technology is distinguished by a tool, the choice of which is regulated by the thickness of the sheet. Thin sheets, the thickness of which is measured in tenths of a millimeter , should not be straightened with impact hammers. There is a high probability of breaking through the surface. Here you should use special bars , which are passed along the surfaces of the sheet on both sides.
When editing thicker sheets, there is a certain technological procedure for carrying out the work. to strike directly at the convex part of the sheet . The resulting high stress concentration can lead to the formation of a crack and damage the workpiece. If the bulge is in the center of the workpiece, you should start tapping it from the edges , reducing the impact force and increasing the frequency as you approach the edges of the bulge.
Editing sheet metal using mechanical equipment. Photo Podolsk Equipment Plant
If there is waviness at the edges, blows should be applied, on the contrary, from the center to the periphery . Tensile stresses arising during impact can remove it, reaching the edges of the defect.
Useful video
See how the operation is done manually.
And how this is done using industrial equipment.
Non-ferrous and ferrous metal
Of the entire variety of ferrous and non-ferrous metals, only metals with good plastic properties can be subjected to straightening. Among ferrous metals, these are primarily low-carbon steels . Aluminum, copper, titanium and some of their alloys (brass, duralumin and others) also lend themselves well to straightening.
Strip steel
Defects that can be corrected by straightening on strip steel:
- strip having a bend in the plane;
- strip with a bend along the edge;
- twisted strip;
- There are all kinds of defects in the strip.
Straightening of hardened metal products
In this case, hammers equipped with soft strikers are not used for straightening. For this purpose, a tool with similar elements made of steel with high strength characteristics is used. In this case, the sharp part of the striker - the nose - is rounded, that is, it is given a rounded configuration.
Straightening of hardened metal is carried out by applying pulsed point effects on a concave fragment of the workpiece. As a result of impacts in this area of the workpiece, a stretching of the material structure is observed, due to which the surface becomes more and more flat. This operation is carried out:
on a straightening/straightening headstock, characterized by a hemispherical surface;
with alternating movement of the workpiece from bottom to top and top to bottom. Straightening a hardened square whose right angle is broken is carried out in one of the following two ways (see figure):
if the angle has become acute, the direction of the blows is the internal section of the surface of this part closest to the point of intersection of the rays/sides;
- when the angle has transformed into an obtuse one, the place of striking is the zone close to the top of the outer angle.
The metal in the affected area is subject to tension, as a result of which the 90° angle is restored.
Scraping with abrasives
For ultra-fine leveling with a thickness of the layer being removed up to 0.0001 mm, grinding with abrasive materials is used manually or on machines. During the grinding process, two types of abrasives are used:
Hard abrasives are used for grinding in cast iron and steel parts. Soft abrasives - for parts made of copper, aluminum, tin and other soft metals.
According to the method of performing grinding, there are:
Rules for scraping
Manual abrasive processing is performed using a special tool called a lapping tool.
Depending on the outline of the surface being processed, scraping laps can be:
- flat;
- cylindrical;
- prismatic, etc.
Lapping tools are made of wood, metal, glass, bronze and other materials.
The process of applying abrasive materials to the lap is called caricature.
Mechanical lapping is performed on special lapping or conventional lathes equipped with lapping attachments. One type of mechanical lapping is sandblasting.
Equipment for straightening/straightening
Manual straightening/straightening of metal sheets and structural elements made from them is carried out using hammers on special equipment - straightening headstocks, as well as straightening plates.
Straightening headstocks
For the manufacture of these devices, heat-treated steel alloys are used. The working surface of the straightening head can be:
in the form of a flat circle on a cylindrical base, the radius of which (designation R) ranges from 150 mm≤R≤200 mm:
spherical. This is the lateral surface of a cylinder truncated along the plane of symmetry and along the edges.
Also, in home workshops, a railway rail, cut to a length of 0.5 m to 1 m, is often used as a straightening headstock. It is convenient to move it along the slab. In addition, the rail is not subject to deformation and remains practically motionless when the workpiece is struck with a hammer.
Correct slabs
Straightening slabs are available in two modifications.
Manufacturing material – cast iron. Execution – design with side ribs or solid.
Manufacturing material – steel.
The slab must be heavy and sufficiently stable so that hammer blows do not cause it to shake. As for the requirements for the condition of its surface, they are standard: it must be perfectly smooth, and without the presence of foreign particles in the form of dirt and remnants of metal fragments that interfere with obtaining a high-quality result of straightening work.
The slabs must be installed on supports. They can be either metal or wood. But the most important thing is that these stands provide, in addition to stability, the required horizontal position. To make straightening easier, you need to have enough space around the slab.
There is another interesting option for such equipment. The material used to make the correct slab is dense rubber with many small protrusions, or rather, even tubercles with the same height. Under the influence of impacts, the metal itself determines its place. As a result, there is a significant increase in the productivity of the straightening process when compared with the use of a conventional leveling plate made of steel.
Hammers
The following key requirement is imposed on hammers used for straightening: they must be softer than the material of the workpiece being processed. In view of this, for straightening sheet steel, an impact tool with lead or copper strikers is usually used. Moreover, these elements should be characterized by a rounded shape. A square-shaped firing pin will leave nicks on the metal plate upon impact. When it comes to processing soft metals or non-ferrous alloys, it is necessary to use hammers equipped with rubber or wood strikers.
Convenience of work will be ensured if the ratio of the weight of the impact tool and the same parameter of the correct plate is equal to 1:100.
Equipment and tools: on rollers, presses and more
For manual straightening, the main tools are straightening plates, anvils, straightening headstocks , which act as a base surface for workpieces.
To apply force to the straightening site, various types of hammers . For sheet and strip steel with rough surface treatment, carbon steel hammers with a round striker are used, which, unlike a square striker, does not leave a dent on the surface. Treated surfaces are straightened with wooden mallets or hammers with soft inserts (made of copper or aluminum alloys). When using thin-sheet metal, trowels made from hard wood are used.
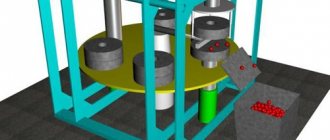
Hydraulic rollers STALEX HER-2070×4.5. Stalex Photos
In production conditions, where rolled products in the form of sheets, strips, rods and other various profiles are widely used, equipment is used for straightening workpieces . Depending on the size and shape of the blanks, several types can be distinguished.
- Correct presses with mechanical or more powerful hydraulic drive. This equipment handles large rolled products: round, square, channel and other profiles, including pipes with a diameter of up to 300 mm. Straightening of thick sheets and strips is carried out on specialized hydraulic presses.
- Roller leveling machines used to work with small and medium-sized rolled products. Roller sheet straightening machines correct defects in sheets and strips of small thickness.
- Tensile leveling machines . They are used for straightening sheets of special alloys and non-ferrous metals.
- Rotary skimmer machines . They are used for straightening pipes and rods from simple to complex profile shapes.
How to straighten sheet metal
Sheet metal straightening
The difficulty of straightening sheet metal depends on what type of defect the sheet has - a waviness on the edge, or a bulge, or a dent in the middle of the sheet, or both at the same time (Fig. 15).
Rice. 15. Techniques for straightening sheet metal: a – with a deformed middle of the sheet; b – with deformed edges of the sheet; c – using a wooden trowel; d – using a metal smoother.
When straightening a convexity, blows must be applied starting from the edge of the sheet towards the convexity (Fig. 15 a, b).
The most common mistake is that the hardest blows are applied to the place where the convexity is greatest, and as a result, small indentations appear in the convex area, which further complicates the uneven surface. In addition, the metal in such cases experiences very strong tensile deformation. You need to do just the opposite: the blows should become weaker, but more frequent, as the edit approaches the center of the convexity. The sheet of metal must be constantly rotated in a horizontal plane so that the impacts are evenly distributed over its entire surface.
Mechanical alignment from inside
Using this technology allows you to smooth out defects without painting.
In this case, vacuum hoods and levers are used. Aligning dents on a car body in this way is based on a pressure difference. The work consists of placing a lever of suitable size, that is, reaching the defect, into the technological hole of the car body and pressing on it until the damaged area returns to its original state. The return of the material to its original state is usually accompanied by a click.
Pressure must be applied carefully to prevent the metal from bending in the opposite direction. If this happens, the area can be leveled with a fluoroplastic bumper.
If the dent is located close to the body opening, then pressure can be applied to it from the inside without using a lever. However, the car body is not always damaged near the technological holes, and it can be difficult to get to the defect from the inside. If this is not possible, damage can be leveled using one of the methods discussed below.