INDUCTION HEATING is the industrial heating of metal materials (conductors) placed inside an inductor (inductor) with an industrial frequency of 50 Hz. Induction heating is carried out as follows. An electrically conductive (metal, graphite) part is placed in an inductor, which is made of a round or square tube (usually copper). ZAVODRR - induction heating systems (IHF) and induction heating of metal from professionals!
Induction heating of metal
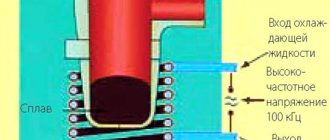
Induction heating of metal combines frequency, temperature, speed and control of the production process. The principle behind induction heating is Faraday's law. a metal part is placed in an inductor, an eddy current arises inside it, which tends to the outer walls.
That is, heat arises directly in the object (metal workpiece), leaving everything around cold, which is an undoubted advantage of this heating method. The heating depth depends on the frequency of the induction heater, and the metal part can be located in isolation from the power source.
Heat in a metal workpiece is not generated uniformly over the entire cross-section, but decreases exponentially with distance from the surface due to the weakening influence of the magnetic field. This process is characterized by a special physical quantity - the depth of penetration of the magnetic field (essentially, the thickness of the surface layer of an object in which the external magnetic field drops to zero). This value depends on the frequency of the inductor current and on the resistivity and relative permeability of the workpiece material at the operating temperature.
Midrange
High frequency
Induction furnaces
Inductors for induction heating
Since the heating efficiency of the material varies depending on the ratio of the inner diameter of the inductor coil and the diameter of the workpiece, it is not advantageous to use one inductor for a large range of diameters.
If you want to order inductors for induction heating, you need to keep in mind that a low diameter ratio is used, as a rule, for surface hardening, and when it is required that the material be heated evenly.
ZAVODRR will manufacture inductors for induction heating with optimal dimensions of the workpiece (which also affects the magnitude of the electric field strength in the heated object). Send us the drawings of the parts, the inductor costs from 15,000 rubles, the production time is 14 working days.
Areas of application of ultrasonic welding
Ultrasonic welding today is the leading method of joining polymer materials, and in some cases the only possible one. Ultrasonic welding of plastics is based on artificially created mechanical vibrations, which are applied to the contact zone and converted into thermal energy.
More than half of the known thermoplastic polymers are welded by ultrasound. Ultrasonic welding of plastics is all the more valuable because for a number of polymers it is the only possible reliable joining method. Polystyrene, one of the most common polymers for the manufacture of various products in large-scale production, is most rationally welded by ultrasound.
Ultrasonic welding machines are used for welding hard polymers and plastics, synthetic fabrics, plastics with metals, soft plastics, artificial leather.
The disadvantages of using an ultrasonic connection are the rather low power of the welding process, which often leads to the need to use a two-way method of supplying energy, and the lack of an accurate and practical method for monitoring the quality of the seam.
Induction heating frequency
heated by high-frequency currents and starts at a frequency of 50 Hz. To select an induction heater, you need to know the induction heating frequencies. The choice of medium, ultra-high frequency or industrial frequency will determine the depth to which the induction current will penetrate. The energy efficiency of induction heating can be improved by using three current frequencies .
The induction heating frequency of an induction heater is:
- 50 Hz ( industrial frequency ) installations, which are powered directly from the network or through step-down transformers;
- ultra-high frequencies (500-10000 Hz), which are powered by frequency converters;
- high-frequency frequencies (66,000 - 440,000 Hz and above), powered by tube electronic generators.
Induction heating systems
Thus, an induction heating system consists, at a minimum, of a generator that converts mains power into the current necessary for operation of the installation, and an inductor that transmits energy for heating. As a rule, a resonant circuit is still needed to match the characteristics of the inductor and generator. To perform more complex tasks, a more complex system is required, including a hardening machine, a cooling system, etc.
Range of high-frequency HDTV installations on transistor IGBT modules
| Parameter/designation | HF-15A | HF-15AV | HF-25A | HF-25AV | HF-40AV | HF-60AV | HF-80AV | HF-100AV | HF-120AV | HF-160AV |
| Power consumption, kVA | 15 | 15 | 25 | 25 | 40 | 60 | 80 | 100 | 120 | 160 |
| Operating frequency range, kHz | 30-80 | 30-80 | 30-80 | 30-80 | 30-60 | 30-60 | 30-60 | 20-50 | 20-50 | 20-50 |
| Supply voltage, V | 220 | 220 | 380 | 380 | 380 | 380 | 380 | 380 | 380 | 380 |
| Number of phases, pcs. | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Maximum current of one phase, A | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 45 | 65 | 120 | 150 | 180 | 240 |
| Efficiency, % | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 |
| Timer, sec | 99 | 99 | 99 | 99 | 99 | 99 | 99 | 99 | 99 | 99 |
| Equipment weight, kg | 18 | 23 | 23 | 31 | 35+30 | 35+30 | 41+42 | 45+47 | 51+49 | 63+55 |
| Cooling system of HDTV installation | ||||||||||
| Water consumption, l/min max. | 5 | 5 | 8 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 12 | 14 | 14 | 16 |
| Water pressure, atm. | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2-3 | 2-3 | 2-3 | 2-3 | 2-3 | 2-3 |
| Pump power, kW | 0,3 | 0,3 | 0,4 | 0,4 | 0,5 | 0,5 | 0,7 | 0,8 | 1,0 | 1,2 |
Induction heating of HDTV pipes and shafts
Induction heating of HDTV pipes at first glance seems expensive due to the price of the equipment, but in fact it allows, with minimal energy costs and high heating rates (which is already a saving), to obtain excellent results when carrying out many works: removal and application of coating, heat treatment welds, bending during pipeline manufacturing and much more.
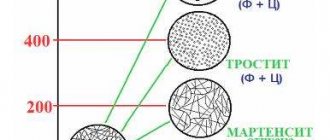
Induction heating of high-frequency shafts allows performing high-frequency hardening operations. High-frequency heating of the shafts can be carried out to a depth of up to 1-2 mm (surface high-frequency heating) or to a depth of up to 5 mm (deep hardening of high-frequency heat). The depth depends on the choice of induction heater and the correct selection of its power.
Anything that has been treated with high-frequency current can be used for much longer and under more unfavorable external influences; induction heating of high-frequency pipes and shafts is different :
- possibility of uninterrupted round-the-clock operation;
- quick setup and connection;
- high-quality uniform heating;
- small overall dimensions.
Muffle furnace for metal hardening
Vacuum muffle furnaces are devices for high-temperature processing and melting of materials with a ceramic base and metal products and various alloys. The principle of operation of the equipment involves the removal of atmospheric air, followed by the injection of inert protective gases and the startup of the furnace within the framework of a preset program.
By type of loading, installations include models with horizontal and vertical orientation. The criteria for selecting units are:
- Dimensions;
- Structure weight;
- Boundary temperature indicators.
The design of muffle-type devices includes the following elements:
- The working chamber with a metal body and a muffle is made of a material with fire-resistant properties;
- Spiral heaters - placed in the groove holes of the muffle;
- Thermal insulating gasket - fills the space formed between the body and the working volume;
- Ceramic door - provides an opening for monitoring temperature indicators;
- Thermostat - provides temperature control to a predetermined level in automatic mode.
Muffle furnace for metal hardening
Muffle hardening devices have three-sided heating, which allows the products to be heated evenly. The presence of multilayer insulation significantly reduces heat loss and saves energy. The working chamber of the unit is made of heat-resistant material, the operator of the unit is protected from thermal radiation thanks to the upward-oriented door opening design. When the door is opened, inductive sensors cut off the current supply.
Induction heating principle
What is the principle of induction heating? And so, the essence of induction heating is that a heated object (conductor) is placed in the alternating magnetic field of an inductor powered by a high-frequency generator. Once the conductor is in an alternating field, then an electromotive force will necessarily arise in it, proportional to the rate of change of the magnetic flux, which will cause Foucault eddy currents, which, in turn (according to the Joule-Lenz law), will cause heating of the workpiece, because it has electrical resistance . An elementary circuit will work productively and for a long time if the frequency is adjusted correctly.
Design of modern high-frequency HDTV installations
High-frequency induction HDTV installations are designated “HF”. Next in the model name is the maximum power consumption, measured in kVA, taking into account both active and reactive components, i.e. capacitive and inductive. The total power depends on the matching of the inductor with the capacitor bank of the HDTV installation and its resonant frequency. The resonant frequency in transistor generators is adjusted automatically in the operating frequency range. Read more >>>
The letter “A” in the model name means the presence of an automatic timer with the ability to pre-set power and time when heating and holding the part. There is also a third timer for cooling down time. There is a mode that allows you to work in an automatic cycle: heating - holding - cooling, without turning off the HDTV installation. In this mode, the third timer setting time can be used to replace the heated part. These functions allow heat treatment to be carried out with a high degree of repeatability.
The letter “B” in the model name means a binary design, in which the high-frequency universal transformer is made as a separate block More details>>>
As a rule, models with a power of 15 and 25 kVA are monoblock and have a duty cycle (continuous operating time) of 80%. When operating these devices in a 100% continuous cycle, you can buy them in a two-block design. Models from 40 kVA are always produced in a two-block design and are designed for a duty cycle of 100%. In this case, excellent cooling of the device is necessary, both high water pressure and low temperature.
Depending on the power of the HDTV installation, the high-frequency transformer unit is connected to the generator and the capacitor bank installed in the generator housing using a cable of various sections. There can be from one to three cables.
Universal high-frequency transformers that are equipped with HDTV installations of this class, as a rule, do not have a variable transformation ratio. A pleasant exception to this rule is the HF-80PKT model (the abbreviation stands for Switchable Transformation Ratio). On this model, you can set three different transformation ratios and use induction coils from one to 5–6 turns, depending on the diameter of the coil. It is precisely this kind of high-frequency installation that is recommended to be used to equip small induction hardening machines. Professional work on high-frequency hardening begins with the use of hardening transformers of the VChTZ series.
When purchasing a HDTV installation, you can order a universal high-frequency transformer with the number of turns of the output winding from one to three. For example, for a HF-60AV HDTV installation, the number of inductor turns for one turn of the output winding will be 1-2 on a diameter of 100 mm, for 2 turns of the output winding - 2-3 turns of the inductor, for three turns - 3-5 turns of the inductor.
Cooling of inductors for models HF-15A and HF-25A is carried out through the device itself. Inductors, starting with the HF-40AV model and more powerful ones, have their own input and output for cooling. The fundamental difference is that in this case, when quenching parts, quenching water or a water-based quenching liquid can be supplied to the inductor. In this case, the inductor simultaneously serves as a quenching sprayer. And the device itself can be cooled, as it should be, with distilled water at the required temperature.
Electrical power supply for HDTV installations with a power of up to 15 kVA is single-phase with a voltage of 220 V. Installations with a power of 25–160 kVA are powered by a three-phase network with a voltage of 380 V. At the rear, lower part of the HDTV installation case there is a grounding connection to protect personnel from electric shock, do not neglect it.
We can say that induction HDTV units are a symbiosis of an electric current converter and a water cooling system. Both of these systems must be maintained and maintained in good condition. Incorrect operation of any of them leads to breakdown of the device as a whole.
All units of transistor HDTV installations are equipped with sensors that turn off the device when the water pressure is low. It is forbidden to readjust them to a lower pressure. Deterioration of the cooling conditions of the device causes its breakdown! Buy a separate or more powerful pump for your installation, and it will reward you with trouble-free operation.
Please note that to create the required pressure in the cooling system, it is often necessary to use multi-blade pumps or run two single-blade pumps in series. The water pressure is checked using a pressure gauge at the inlet of the distribution comb of the cooling system on a device connected to water, i.e. under load.
Use only distilled water for cooling. Bad water causes salt deposits and worsening cooling conditions for device components. Using electrolysis, water corrodes water-cooled aluminum radiators of IGBT modules and diode bridges. Due to electrical conductivity, it disrupts the operation of electronic components and can cause electric shock to operating personnel.
It is necessary to check the supply voltage with the device turned on and at maximum heating power. The supply voltage should not drop under load by more than 5%. All induction HDTV units of the model range from HF-15 to HF-160AV are equipped with a protection system against possible overloads and overvoltages. You can find out more about them in the article here>>>
If any indicator lights up or a buzzer signal appears, remember the name of the indicator, turn off the device and, if possible, find out the cause of the malfunction. The most common reasons for shutdown of HDTV installations are insufficient water pressure, insufficient or excess supply voltage, short circuits in the inductor, and excess temperature in the multipoint control system. If indicators come on indicating internal problems, the HDTV unit should be sent for repair.
All devices of this class are equipped with an input switch - fuse - disconnector. After turning it on, power is supplied to the device and the idle mode is activated, during which the device control boards are powered. Starting and turning off the induction generator of the HDTV installation can be done in various ways. Pressing the green Start button, followed by switching off by pressing the red Stop button. With the foot control pedal connected - press the pedal - Start, release the Stop pedal.
In automatic mode, pressing the Start button starts the cyclic heating mode, pressing the Stop button turns it off. Upon completion of work, turn off the input switch - fuse - disconnector and de-energize the HDTV installation.
A typical circuit design of modern transistor HDTV installations is as follows. The diode bridges of the rectifier convert three-phase electric current into direct current. Then, the IGBT bridged modules generate alternating current. Which is fed to a resonant circuit formed by the primary winding of the HF transformer and a capacitor. The secondary winding of the HF transformer and the inductor connected to it with a heated part contribute to the process of creating frequency resonance. The presence of a high-frequency transformer ensures galvanic isolation of the inductor from the 380V supply network. Which is very important to prevent electric shock to thermal shock workers. The currents flowing in the inductor reach several thousand amperes, but the voltage remains safe for humans and does not exceed 30–50 volts.
The main control board, using sensors, collects information about the operation of the HDTV installation and issues commands to control the generation power and select the resonant frequency. The HDTV installation automatically selects and generates a resonant frequency depending on the number of turns of the inductor and the variable parameters of the heated part. However, only within certain limits. That is why modern HDTV installations have indicators of “Very low” and “Very high” operating frequencies of the device. In this case, you need to measure the generation frequency and select the number of turns of the inductor. Read more >>>
Moreover, the HDTV installation even “sees” the part inserted into the inductor and automatically produces the set power. When the part is removed, the power drops significantly.
Please note! HDTV installations are often transported by truck, almost like firewood. During such transportation, there is a high probability of breaking the connector contacts and loosening the contact bolts. It is for this reason that we recommend ordering commissioning work with the help of qualified service personnel. Miser pays twice! Power switches - transistor IGBT modules are not cheap, up to 10 thousand rubles, and sometimes several pieces burn out. So it's up to you...
Before transporting or storing in an unheated warehouse, thoroughly drain the cooling system, otherwise the remaining water will defrost the radiators.
Application of induction heating
The diverse application of induction heating is due to its properties and functions that facilitate the technological process, allowing it to be automated as much as possible and improve the quality of work results. Practical application of heating:
- molding, melting of ferrous and non-ferrous metals;
- hardening;
- soldering;
- hot pressing;
- welding;
- vacuum melting;
- maintaining the temperature of molten glass;
- processing of very small parts, including jewelry;
- bending pipes and other parts;
- sterilization of laboratory instruments.