Plasma cutting is a technological operation for separating materials, in which a plasma jet plays the role of a cutting tool. The essence of the plasma cutting process is the high-speed passage of a stream of ionized gas, i.e., plasma, through a tapering hole (nozzle), which acts as a conductor of electric current between the torch (plasma torch) and the material being cut. It heats and melts the products. A high-speed plasma stream then mechanically blows away the melt, separating it.
The temperature of the plasma flow varies from 5000 °C to 30000 °C, speed - from 500 m/s to 1500 m/s.
The main purpose of the operation is cutting metal elements with a thickness of up to 25 mm. The maximum material thickness for plasma cutting does not exceed 200 mm. The thickness of the metal cut by plasma depends on its thermal conductivity. Namely: the greater the thermal conductivity of the metal, the thinner the product that can be cut. To obtain a plasma jet use:
- inactive gases (nitrogen, hydrogen, water steam) - plasma cutting of non-ferrous metals;
- active gases (oxygen, air) for cutting ferrous metals.
Advantages and disadvantages of the plasma cutting method
Let us note the main advantages of this technological operation:
- Plasma cutting is used for both ferrous (steel, cast iron) and non-ferrous (aluminum, copper) metals. Non-metallic materials (concrete) can also be cut;
- high speed, productivity, accuracy;
- the ability to cut out shapes of complex configurations;
- excellent edge surface quality. The edge does not need to be subjected to additional machining;
- safety, environmental friendliness of the technological process. It does not use flammable gas or compressed oxygen, and there are practically no harmful emissions;
- versatility of the operation: the ability to cut large-width parts, pipe blanks, and perform cuts at a certain angle;
- The workpiece does not need to be preheated before use. This significantly saves the time of the technological operation.
But in the modern, innovative plasma cutting process there are also negative aspects:
- when cutting thick workpieces, it is necessary to use high-power sources of electricity;
- the need to attract trained qualified personnel for work;
- limitation on the thickness of processed parts;
- Plasma cutting work is accompanied by a high noise level;
- high price of equipment.
Equipment for plasma cutting of metal
To carry out cutting using plasma, it is necessary to obtain the plasma arc itself. For this purpose, a special apparatus is used - a plasmatron, which consists of:
- nozzle - plasma outlet;
- an electrode made of a metal with a high melting point (tungsten, zirconium);
- channel for supplying compressed gas (air, purified oxygen);
- an insulating element that simultaneously plays the role of a cooler.
Some of the structural elements of the plasma torch, which operate in areas of high temperatures and significant dynamic loads, may wear out and require periodic replacement. Such elements include:
— electrodes;
— plasmatron nozzle;
— insulating units;
— a diffuser where the swirling of the working gas flow occurs.
In addition, various protective screens and casings are considered consumable items, which make working with the plasma torch more comfortable.
Wear of consumable parts can lead to deterioration in cut quality and breakdown of expensive equipment. Therefore, it is necessary to promptly identify wear of consumables and replace them.
The installation for plasma cutting includes:
- transformer or inverter, current converter to create an electric arc;
- compressor for supplying gas under pressure;
- plasmatron for generating flow;
- air supply tube connected to an electrical cable.
Although the most important technological process occurs in the plasma torch, plasma cutting is impossible in the absence of any other piece of equipment.
Optimal solutions for living conditions
Cutting cast iron at home eliminates the use of complex, expensive tools. Preference is given to simple and affordable solutions that require minimal training on the part of the master.
As an auxiliary tool you can use:
- grinder;
- hacksaw;
- reciprocating saw (electric hacksaw);
- pipe cutter
Working with each of the listed tools has a number of features.
Cutting cast iron with a grinder
The use of an angle grinder will help to form cuts with a thickness of 2.3 - 2.5 mm on the surface of the cast iron part. The device is highly maneuverable and has moderate weight.
To carry out the work effectively, you will need diamond blades for cutting cast iron. The use of general-purpose equipment will reduce labor efficiency and lead to rapid wear of the disks.
Diamond wheel 12A2-45 150x10x3x32 AC4 125/100 B2-01 100% 58.0 Bestseller
RUR 2,989
Add to cart
Diamond wheel 12A2-45 150x10x3x32 AC4 100/80 B2-01 100% 58.0 Bestseller
RUR 2,742
Add to cart
Diamond wheel 1A1 125x10x5x32 AC4 125/100 B2-01 100% 83.0 Bestseller
RUR 3,837
Add to cart
Diamond wheel 1A1 125x10x5x32 AC4 100/80 B2-01 100% 83.0 Bestseller
RUR 3,748
Add to cart
Diamond wheel 1A1 125x10x3x32 AC4 125/100 B2-01 100% 51.0 Bestseller
RUR 2,577
Add to cart
Diamond wheel 12A2-20 125x10x2x32 AC4 125/100 B2-01 100% 32.0 Bestseller
RUR 2,890
Add to cart
Recommendations for cutting cast iron with a grinder.
- Make only straight cuts. Trying to form a curly cutout increases the risk of injury, biting and breaking the circle.
- During operation, a large number of sparks are generated. Before starting the event, you should remove all flammable objects within 2 m2.
- Cutting is carried out only in protective clothing. Gloves and goggles (masks) are required.
Upon completion of the operation, you should wait until the working surface of the part cools down.
Rice. 1 Cutting cast iron with a grinder
Application of a hacksaw
Using a hacksaw it is possible to cut thin workpieces. The event takes a lot of time and effort and requires significant physical training from the master.
Given the design and dimensions of the hacksaw, the mechanic will not be able to work in confined spaces, for example, in a pipe box.
The main advantage of a hand tool is its safety. During operation, no sparks are formed and no excessive heating of the surface occurs.
Rice. 2 Hand hacksaw for metal
Cutting workpieces with an electric hacksaw
An electric hacksaw (reciprocating saw) is an order of magnitude more productive than its classic counterpart. It is light in weight and moderate in size, creating minimal stress on the craftsman. As with a regular hacksaw, there are no sparks at all. This has a positive effect on the safety of the procedure.
When choosing a blade for a tool, you should prefer products marked BIM and HSS. It has increased strength and tolerates heat and intense mechanical stress.
Rice. 3 Working with an electric hacksaw (reciprocating saw)
Working with a pipe cutter
The method is suitable for cutting pipes and cast iron rods. When working in domestic conditions, manual pipe cutters are used. They are designed for workpieces with a diameter of 6–23 mm; they form a cut using movable pointed circles pressed to the part with a ratchet mechanism.
Pipe cutter, 3-28 mm Matrix 550 rub.
Add to cart
Pipe cutter, 25-75 mm Sibrteh RUR 4,630
Add to cart
Pipe cutter, 12-50 mm Sibrteh RUR 3,062
Add to cart
Palm pipe cutter "Piranha", 22 mm, 3/4, auto. reg., ratchet, hole 1/4 Gross 530 rub.
Add to cart
Palm pipe cutter “Piranha”, 16 mm, 1/2, auto. reg., ratchet, hole 1/4 Gross 853 RUR
Add to cart
Manual pipe cutter “Piranha”, 6-23 mm, 1/4-7/8, fur. reg. light up pipes, crackling with snoring fur.Gross (out of stock)
More details
In most cases, home pipes are located in hard-to-reach places. This complicates the use of pipe cutters and eliminates the possibility of working with large-diameter components. If free space allows, using a manual pipe cutter would be a good solution.
Rice. 4 Working with a manual pipe cutter
If only dismantling is required
In cases where maintaining the integrity of the part is not a priority, a chisel and hammer can be used. Cast iron is a brittle material that is quickly destroyed by impact.
Instead of a chisel, you can use a sledgehammer. At the same time, it is worth taking care of the availability of free space for a good scope.
Plasma torch operation process
After pressing the button, an electric current flows into the device and the primary electric arc with a temperature of about 8000 °C lights up inside and spreads over the entire area of the channel.
The compressor begins to supply compressed air into the channel with the primary arc, which, passing through the channel, heats up and acquires the properties of an ionized gas that conducts electric current. Due to high heating temperatures, air expands in volume by 50-100 times. This significantly increases gas pressure.
Then, through the channel, the hot, expanded gas flow enters the nozzle, which narrows it and makes it more concentrated. The air flow, converted into plasma, flies out of the nozzle opening at enormous speed (about 3 km/s). In this case, the temperature of the ionized flow increases several times.
It is this ionized gas, heated to enormous temperatures, that is the plasma through which cutting is carried out.
What is plasma used for and what is laser used for?
The laser is suitable where accuracy, cleanliness of cuts and edges and speed are needed. And plasma cuts slowly, relative to a laser, and with a dirty cut, so it is impossible to cut out complex technical parts. And on a metal laser machine it is possible to cut, for example, small nameplates and plates, thin grilles and complex design elements, as well as rotary wheels.
Plasma is needed to make simple products. In the shape of a rectangle, oval or square, because they can be processed later. But cutting out a star with holes inside will be difficult. Plus, sanding will take a lot of time. And post-processing equipment will cost several times more than a metal cutter.
Plasma is used where there are large thicknesses and for simple cutting, for example, rails, metal frame elements or welded structures, etc.
Types of plasma cutting
Separation using plasma is classified according to a number of characteristics.
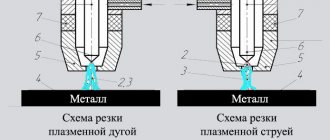
By cutting method:
- arc. In this case, the material being cut acts as part of an electrical circuit;
- jet. The material is not part of the chain. An electric arc is formed between the electrodes.
Based on the depth of cut, there are:
- superficial, in which the product is not divided into parts;
- separation, in which the metal is divided into several separate parts.
Separation plasma cutting is used more often.
According to the properties of the environment in which the technological process occurs:
- the usual type of cutting using ambient air.
- cutting using protective gas.
- cut using water.
In the latter case, water protects the cut from environmental influences, cools the cutter (plasma torch), and absorbs harmful fumes.
Technology
When carrying out work, you should adhere to the following metal plasma cutting technology:
- The nozzle, from which a stream of air will burst out, is located at the edge of the metal sheet.
- The wizard starts the device using the power button. The initial arc is turned on, which gradually turns into a cutting arc.
- The burner is tilted at 90 degrees. Cutting is done slowly and carefully.
- The master must control the appearance of splashes of molten metal. If they do not appear, it means that the metal workpiece could not be cut through.
- Do not touch the nozzle or point it towards other objects immediately after turning it off, as hot air will continue to flow from it for some time.
If you cannot cut through a metal sheet, you need to change the angle of inclination, slow down the pace of work, or increase the voltage.
Plasma cutting technology
Types of cutting systems
Systems differ depending on the type of plasma gas provided by the technology.
Conventional systems use ambient air as gas. The current strength in this process ranges from 12-20 thousand A/in². The shape of the plasma flow depends on the nozzle opening. Such systems are used for both manual and mechanized cutting. Deviations in the dimensions of the cut part are allowed.
High frequency (high current density) systems are used for plasma cutting with increased precision. Purified air, oxygen, and mixtures of hydrogen and nitrogen are used as plasma gas. Plasmatrons and consumables of a more complex design are used in the technological process. The current strength for high-frequency separation is 40-50 thousand A/in². The main goal is to achieve increased accuracy when focusing the arc and obtain high quality cutting.
How to choose the correct current strength?
In order to obtain an even and careful cut, without scale, sagging and slag, it is necessary to properly set the current strength on the machine required to cut a specific workpiece. To do this, you need to know how much current is needed to melt 1 mm of material. For different types of alloy there will be different meanings:
- When working with cast iron and steel - 4 A.
- When working with non-ferrous alloys and their alloys - 6 A.
Interesting read: Is it possible to cut threads in cast iron?
For example, to process an iron sheet 20 mm wide, the machine must be set to a current of at least 80 A, and to work with a duralumin sheet of the same thickness - 120 A. But this is not all that needs to be taken into account when working. So that the alloy has time to melt at the cutting site, but at the same time does not deform under the thermal action of the plasma, it is important to choose the best cutting speed . It can be from 0.2 to 2 m/min, depending on the set current strength, the thickness of the workpiece and the type of alloy. Naturally, at first it will be difficult for a new person to measure the speed and choose a more suitable one, this will come with experience. And for the first time, remember the usual rule: move the torch so that the sparks are visible from the reverse side of the workpiece being cut . If they are not visible, the alloy is not cut through, the speed is high. But moving the torch very slowly, especially at high current levels, can lead to the formation of scale, arc extinction, and deterioration of the cutting properties.