The first plasma machines were invented in the 50s of the 20th century. The equipment was bulky and expensive, and was used only in certain industries. But by the end of the twentieth century, plasma cutting of metal became available, and the demand for it grew.
Today, this type of cutting occupies one of the leading positions in the metalworking industry. The equipment used in plasma metal cutting technology is constantly being modernized, becoming more and more practical and convenient.
Types and methods of plasma cutting
Plasma is the cutting of metal under a large flow of plasma, which is formed by blowing an electric arc with gas. When heated, the gas is ionized into positive and negative particles. The temperature of the plasma flow reaches several thousand degrees.
There are different types of plasma cutting:
- separating;
- superficial.
During separation cutting, the electrode sinks into the metal cut. The angle between the metal surface and the electrode should be from 60° to 90°, and with a surface one it cannot be more than 30°.
There are two cutting methods:
- using a plasma arc;
- using a plasma jet.
In the first method, an arc burns between a non-consumable electrode and the metal being cut. In the second case, it is between the forming tip of the plasmatron and the electrode. The product is not included in the electrical circuit during a plasma jet.
Plasma arc cutting is widely used for processing metals, and plasma jet cutting is widely used for processing non-metallic workpieces.
Device elements
The plasma torch device is designed in such a way as to ensure cutting of metals belonging to the refractory class. The electrode (cathode) has a special zirconium or hafnium insert. The use of these metals at high temperatures makes it possible to achieve the effect of knocking out electrons from their surface (thermionic emission).
The nozzle is another consumable element of the plasmatron, which is always isolated from the cathode. The device is also equipped with a mechanism for swirling gas to form plasma.
The consumables are capable of functioning during one 8-hour work shift when we are talking about processing metal up to 1 cm thick. Then they must be replaced, and it is advisable to carry out the latter simultaneously for the cathode and nozzle.
If replacement deadlines are not met, the quality of the resulting cut will deteriorate significantly; waves may appear or the effect of cutting at an angle may be felt. If the hafnium or zirconium insert burns out more than 2 mm, the electrode will burn. The result will be significant overheating of the device.
To prevent the molten material being processed from damaging the elements of the plasma torch, it is equipped with a protective casing. Regular dismantling and cleaning of the casing is the key to long and high-quality operation of the entire device. If basic operating conditions are not observed, you can soon cause serious damage to the plasma cutter. It is equally important to clean other elements.
Classification of plasma torches
Plasma torches for metal cutting are divided into electric arc, high frequency and combined.
By type of arc formation:
- With a direct arc that burns between a metal product and a non-consumable electrode. Power source - direct current.
- With an arc of indirect action. Not connected to the product, it is excited and burns between the anode-nozzle and the cathode-electrode. Power is supplied by alternating current.
By type of cooling:
- air;
- water
Water cooling of the plasma torch is more popular, since the heat capacity of air is lower than that of water. Water cooling allows high thermal loads to be placed on the nozzle and electrode, which increases plasma welding productivity. The disadvantage of this type of cooling is the complexity of the design of the device itself and the need for a constant supply of clean water.
According to the method of arc stabilization:
- water;
- vortex;
- double;
- axial single;
- magnetic.
The water method of arc stabilization is complex in design and has an unreliable system of automatic feeding and regulation of the electrode.
The simplest and most common are vortex, double and axial single types of arc stabilization. The magnetic method of arc stabilization is not very effective. It creates a small compressive arc column, a device that is difficult to operate.
By type of electrode for working with metal:
- gas-protected;
- expendable;
- film-protected.
Most often, gas-protected cathodes with a tungsten rod are used. Consumables are graphite cathodes. Film-protected electrodes are made from zirconium pressed into a copper cage.
High frequency plasma cutters
A feature of devices of this class is the absence of electrodes, since communication with the power source is carried out thanks to the inductive (or capacitive) principle. Accordingly, plasmatrons are divided into induction and capacitive.
The operating principle of plasma torches, which belong to the class of high-frequency devices, implies that the chamber where the discharge occurs is made of non-conducting materials. Glass or ceramics are often used.
The walls are insulated according to the gas-dynamic principle, so the devices are protected from overheating and can be cooled by air.
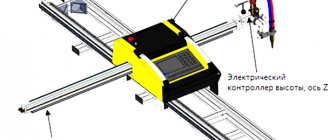
Design of a plasma cutting machine
In essence, a plasma torch is a plasma generator. This is a reliable and compact device in which the start, power and stop of operating modes are easily adjusted.
The plasma torch consists of structural elements:
- Casing.
- The body is fluoroplastic.
- Electrode unit.
- Air flow twisting mechanism.
- Insulating sleeve.
- Electrode.
- Nozzle nut.
- Nozzle.
The main consumables of the device are the nozzle and the electrode. They wear out at the same rate, so they should be replaced at the same time. Untimely replacement will affect the quality of the cut and lead to wear and tear of the remaining elements of the device.
The casing is used to protect the device from metal dust and metal splashes. The casing and plasma torch must be periodically cleaned of dirt.
Device
The burner consists of:
- an electrode holder electrically isolated from both inner tubes;
- a vortex ring that ensures circular motion of the plasma;
- a hollow electrode, inside of which the working and shielding tubes are installed;
- return spring;
- tip;
- protective cap.
Structurally, a plasma torch for plasma cutting also includes hoses through which plasma-forming air is supplied.
The shape of the hole in the nozzle determines the size and configuration of the arc. It is designed in such a way as to withstand a flow of ionized gas heated to 4500...5000°C, at a current density of up to 40000°C/mm2.
The operating sequence of a hand-held plasma torch is as follows. When the equipment is turned off, the working surfaces of the part and the tip are in contact with each other, so the plasma torch head should not be pressed against the metal. When the cutter is turned on, the power source begins to generate direct current, the power of which can reach 500 A. The current ionizes the air in the space between the tubes, which gradually ionizes, acquiring the required temperature. As a result, a flow of plasma-forming gas is initiated. When the gas pressure increases to the required limits, the spring moves the electrode and nozzle apart. A gap is formed in which an electric spark is excited. It converts the air flow into a plasma jet. Then the direction of the direct current is switched along the shortest path between the electrode and the workpiece. This movement continues until the trigger is returned to its previous position.
How the device works
Before work, you need to make sure that the compressor has sufficient pressure, and that the liquid in water devices is heated to the required temperature.
- After pressing the “ignition” button, a high frequency current is supplied from the power source. A pilot electric arc is formed inside the device; the entire channel is filled with an arc column.
- Compressed air begins to flow into the device chamber. Passing through an electric arc, it heats up and increases in volume, ceases to be a dielectric and conducts current.
- At a speed of 2 to 3 m/s, a stream of air begins to burst out of the device’s nozzle, the temperature of which can reach 30 thousand degrees. This hot air is plasma.
- Instead of a duty arc, a cutting arc is lit, which, in contact with the metal workpiece, heats it up at the cutting site. A cut appears in the melting zone, and the particles of molten metal formed on the workpiece fly away from the air flow.
- By releasing the “ignition” button, the arc stops burning.
- Slag is knocked off along the edges of the cut; if necessary, the product is cleaned of it.
Basic knowledge of the operating principle of a plasma torch will not only help you understand how to control the cutting process, but will also make the work easy and the cut smooth and beautiful.
Operating principle of a hand-held plasma torch
In many modern plasma cutters, a primary arc generated between the electrode and the nozzle is used to ionize the gas and generate plasma in the plasma torch itself, before the arc is transferred to the metal being processed.
In hand-held plasma torches, such transfer occurs when the tip comes into contact with the metal. A spark is created, after which a high-frequency circuit is launched, the arc in which begins to burn smoothly and steadily.
The main characteristics of a hand-held plasma torch are:
- Ignition current, A.
- Operating current, A.
- Arc width, mm.
- Plasma flow speed, m/s.
The high cutting speed of the plasma torch is ensured by a specially shaped output nozzle. It causes the ionized gas to compress at high speed. In this case, the concentration of thermal power reaches limits sufficient for local melting of the metal.
The plasma torch burner includes two concentrically located tubes. The plasma flow moves in the inner one, and the gas heated to lower temperatures moves in the outer one. This external flow encloses the perimeter of the cutting zone, ensuring precise cutting, and protects adjacent areas from oxidation.
Types of plasma torches
Enterprises widely use automatic and manual plasma cutting.
You can cut metal using various types of devices.
- Plasma cutters for cutting metals. This group includes air plasma and gas plasma cutters. The air plasma cutter has a simple design and is used for cutting ferrous metals. It can operate from both single-phase and three-phase networks. The gas-plasma apparatus operates on water vapor; hydrogen, argon, oxygen, and nitrogen are used to form plasma.
- Induction cutter. This is a high-frequency device operating on the principle of inductively coupled plasma with temperatures up to 6000 K and a high electron density.
- Combined devices. They are represented by a symbiosis of high frequency currents and an electric arc. The electrical discharge is compressed under the influence of a magnetic field.
- Gas devices that work by compressing the arc column with a plasma-forming gas.
- Water devices whose working fluid is steam gas. High-temperature water steam promotes accelerated combustion of carbon.
- Magnetic cutters. Such devices are ineffective and not popular. Their main advantage is that the compression of the electric arc is adjusted without loss of gas.
Depending on the type of plasmatron, you can easily process any type of steel, including metals with high thermal expansion, as well as materials that do not conduct electric current.
Types of plasmatrons
The entire range of modern technical devices for cutting metals can be divided into three classes:
- electric arc plasmatrons;
- high-frequency plasma cutters;
- combined devices.
To understand the operating features of each type of plasma torch from the designated classes, you should consider them separately.
Advantages and disadvantages of cutting technology
This technology has its advantages compared to other processing methods.
- High performance, easy to learn.
- Plasma cutting has high precision and a variety of cut lines.
- The treated surface does not require additional grinding.
- During operation, environmental pollution is minimal.
- The hand-held equipment used is mobile, light in weight and small in size.
The disadvantages of this method include the small cut thickness, up to 100 mm. You cannot work with two devices at the same time, and also deviate from the perpendicularity of the cut.
Plasma torch selection
To choose the right machine for plasma cutting of metal, you need to decide what characteristics the device should have. The initial data can be:
- automated or manual cutting method;
- duration of work;
- electrical energy consumption;
- metal thickness;
- metal type;
- How often are consumables replaced?
- user reviews about equipment and manufacturers.
A good option for optimal price and power is the Svarog CUN 40 B (R 34) model. This is a lightweight and compact device that is used in cutting thin sheet metals less than 0.12 cm. It is easy to operate, unpretentious in operation, and compressed air consumption is minimal.
The devices with the best energy saving indicators include the AURORA PRO AIRFORCE 60 IGBT model. It is suitable for cutting conductive material. The operating principle is based on non-contact ignition of the arc. The result of cutting is high-quality work without metal deformation.
The BRIMA CUT 120 model is suitable for cutting thick metal. The device is used for cutting non-ferrous, carbon, stainless metal and copper. The thickness of the metal can reach up to 35 mm. It has built-in arc adjustment and smoothly changes the operating parameters of the device.
Read this article on how to assemble a plasma cutter from an inverter yourself.
Read this article on how to assemble a plasma cutter from an inverter yourself.
Cutter CP PT 31
CP PT 31 is widely used due to its simplicity and affordable price. Most budget plasma cutting machines are equipped with just such cutters, which explains the popularity of this model. As a rule, such devices do not have a central Euro connector, and the cutter is connected to the device via an M16x1.5 nut and a 2PIN connector.
The hinged joint at the junction of the sleeve and the handle does not load the cutter's hand, and the light weight of the cutter will allow you to make long-term cuts without straining your hand. The cutter is equipped with a smooth trigger, and the sleeve is covered in denim along its entire length, which minimizes the risk of accidentally damaging the plasmatron hose package. The maximum cut of the cutter is 14 mm .
The CP PT 31 cutter is suitable only for its unique consumable parts, which are not compatible with other cutters - these are nozzles, cathodes, diffusers, a nozzle and a plasma torch head. You can find out more about the components and technical information on our website in the product card.
Plasma cutter CP PT 31
Article: 073.310.106 Plasma cutter CP PT 31 5m (M16x1.5; 2pin) PLA3105 Plasma torch CP PT 31 is connected to air plasma cutting machines via a nut M16x1.5.
Feedback between the cutter and the device occurs using a 2 PIN connector. The thickness of the clean cut is 14 mm. Price: RUB 5,911
Cutter CP SG-55
The plasma cutter CP SG-55, as well as the cutter CP PT 31, is often included in the package of devices in the household segment. The connection is made via a M16x1.5 nut and a 2PIN connector. It features a handle design that is not inferior in convenience and comfortable use. The cutter has a swivel joint, the hose package is protected by a fabric cover.
SG-55 has unique components that are compatible only with this plasma torch (cathode, nozzle and protective cap). Most importantly, the design feature of the cutter head does not require a gas diffuser. The maximum thickness of the metal to be cut is 15 mm .
Plasma cutter CP SG-55
Article: 073.055.105 Plasma cutter CP SG-55 5m (M16x1.5; 2pin) PLA5505
The CP SG-55 plasma torch is connected to air plasma cutting machines via a M16x1.5 nut. Feedback between the cutter and the device occurs using a 2 PIN connector. The thickness of the clean cut is 15 mm.
Price: RUB 5,392
Cutter CP 50
The CP 50 plasma cutter combines improved technical characteristics and a special design, which is certainly suitable for professional use. The plasma torch is connected to air plasma cutting machines via a central Euro adapter. Also, the central adapter can be removed and replaced with a 1/4G connector by installing additional adapters.
A hinge is installed at the junction of the power cable and the handle, which helps to operate the cutter comfortably. Safe operation is guaranteed by a special safety lock on the button, which prevents accidental pressing. Cutting thickness – 15 mm . All components for the cutter are available in a range of branded products - these are the plasma torch head, diffuser, cathode, nozzle and protective nozzle.
Plasma cutter CP 50
Article: 073.500.106 Plasma cutter CP 50 Euro adapter 6m PLA5006
The CP 50 plasma torch is connected to air plasma cutting machines via a central Euro adapter. The thickness of the clean cut is 15 mm.
Price: RUR 18,644
Cutter CP P80
The CP P80 plasma cutter can already be classified as industrial class, but it is still part of the group of popular plasma torches, because They are equipped with most air plasma cutting machines, with a cutting current of up to 80 A. This is a transitional cutter model, which is not much different from the CP 81 cutter, which we will talk about a little later.
The cutter is equipped with a safety device to prevent accidental pressing of the trigger and has the ability to connect a roller attachment for easier cutting of metal. You can also install a special protective attachment on the cutter. The range of branded products also includes nozzles, a cathode and a plasma torch head with a 1/8G internal thread.
In the range of branded products, two connection options are available - with a union nut M16x1.5 and a 2PIN connector, and with a classic Euro adapter. The maximum cutting thickness is 23 mm .
Plasma cutters CP P80
Article: 073.800.106 Plasma cutter CP P80 5m (M16x1.5; 2pin) PLA1615
The CP P80 plasma torch is connected to air plasma cutting machines via M16x1.5 and 2pin. The thickness of the clean cut is 23 mm. Can be equipped with a roller attachment for convenient cutting of metal.
Price: RUB 13,283
Article: 073.800.105 Plasma cutter CP P80 Euro adapter 5m PLA8005
The CP P80 plasma torch is connected to air plasma cutting machines via a central Euro adapter. The thickness of the clean cut is 23 mm. Can be equipped with a roller attachment for convenient cutting of metal.
Price: RUB 14,743
CP 81, CP 101 and CP 141 series cutters
Plasma cutters CP 81, CP 101 and CP 141 have a standard Euro connector with pre-installed 4PIN connectors. PIN connectors are installed in Euroadapter cells 9/1/6/3. We strongly recommend that before installation, make sure that the pins on the plasma cutter match the pins on the CUT air plasma cutting machine; mismatching pins will lead to damage to both the equipment and the cutter. If necessary, the Euro adapter on the plasma cutter can be disassembled and connected to a device that does not have a Euro connector.
The CP series cutters have their own design features, namely: protection of the trigger from accidental pressing, a flexible swivel joint, a rubberized casing covering the hose packages. The protective nozzle of the cutters is equipped with a copper ring that closes the circuit on the plasma torch. Thus, a system for safely changing consumable parts has been implemented, which will prevent short-circuiting or sudden switching on of the plasma torch.
cutter is designed for cutting up to 23 mm , the CP 101 up to 28 mm , and the 141 series cutter for cuts up to 35 mm . When we talk about cutting, we mean a clean cut, not a dirty cut.
A clean cut is the highest quality cut of a material that does not require serious finishing. A dirty cut is a cut that is higher than the stated values of the cutter, but it is possible that during the cut a burr will form, frozen drops of metal on the product. Large burrs will need to be cut off with a grinder, but smaller ones can be beaten off with a hammer.
In addition, the quality of the cut, in addition to the quality of the plasma cutter itself, is also influenced by such factors as: the quality of compressed air, sufficient pressure at the outlet of the compressor, the quality of the plasma source itself and the stability of the mains voltage, as well as timely replacement of nozzles and cathodes. By observing all these parameters, you will achieve the perfect cut.
The range of branded products for these cuts includes special sets of ballerinas, which are used for cutting circles and geometric shapes from sheet metal.
Article: 073.810.007 Set of ballerinas CP 81 BAL5700
Set for cutting circles and geometric shapes from sheet metal. Used in conjunction with the CP 81 plasma cutter.
Price: RUR 7,776
Article: 073.101.077 Set of ballerinas CP 101-141-151 BAL7700
Set for cutting circles and geometric shapes from sheet metal. Used in conjunction with plasma cutters CP 101, CP 141 and CP 151.
Price: RUR 7,828
Plasma cutters series CP 81, CP 101 and CP 141
Article: 073.141.112 Plasma cutter CP 141 Euro adapter 12m PLA1412
The CP 141 plasma torch is connected to air plasma cutting machines via a central Euro adapter. The thickness of the clean cut is 35 mm. The cutter can be used in conjunction with a set of ballerinas from the range of branded products.
Price: RUR 35,183
Article: 073.141.106 Plasma cutter CP 141 Euro adapter 6m PLA1416
The CP 141 plasma torch is connected to air plasma cutting machines via a central Euro adapter. The thickness of the clean cut is 35 mm. The cutter can be used in conjunction with a set of ballerinas from the range of branded products.
Price: RUR 26,173
Article: 073.101.106 Plasma cutter CP 101 Euro adapter 6m PLA1016
The CP 101 plasma torch is connected to air plasma cutting machines via a central Euro adapter. The thickness of the clean cut is 28 mm. The cutter can be used in conjunction with a set of ballerinas from the range of branded products.
Price: RUR 25,162
Article: 073.810.106 Plasma cutter CP 81 Euro adapter 6m PLA8106
The CP 81 plasma torch is connected to air plasma cutting machines via a central Euro adapter. The thickness of the clean cut is 23 mm. The cutter can be used in conjunction with a set of ballerinas from the range of branded products.
Price: RUB 19,565
Plasmatrons marked ACP
Cutters marked ACP are designed for connection to CNC machines. Because of their shape, they are often called "pencils". The ACP 80 cutter is connected to the plasma source with an M16x1.5 nut, and the command to start and stop the cut is passed through a 2PIN connector. The maximum clean cut is 23 mm.
Plasma torches ACP 81 and ACP 141 are connected to the source via a central Euro adapter, which can be disassembled and connected to any plasma source. The maximum cut of 81 models is 23 mm , and 141 plasma torches cut up to 35 mm . Most of the components for automatic cutters are similar to those of standard plasma torches, with the exception of the replaceable element of the CUT torch - the plasma torch head.
Automatic plasma cutters for CNC machines
Article: 073.810.206 Automatic plasma cutter ACP 81 (M16x1.5; 2pin) 6m PLA0681
The automatic plasma torch ACP 81 is connected to air plasma cutting machines via M16x1.5. Feedback between the cutter and the device occurs using a 2 PIN connector. The thickness of the clean cut is 23 mm.
Price: RUR 33,210
Article: 073.800.210 Automatic plasma cutter ACP 80 (M16x1.5; 2pin) 10m PLA1080
The automatic plasma torch ACP 80 is connected to air plasma cutting machines via M16x1.5. Feedback between the cutter and the device occurs using a 2 PIN connector. The thickness of the clean cut is 23 mm.
Price: RUR 30,056
Article: 073.141.212 Automatic plasma cutter ACP 141 Euro adapter 12m PLA1412-1
The automatic plasma torch ACP 141 is connected to air plasma cutting machines via a central Euro adapter. The thickness of the clean cut is 35 mm.
Price: RUB 61,108
Article: 073.141.206 Automatic plasma cutter ACP 141 Euro adapter 6m PLA1416-1
The automatic plasma torch ACP 141 is connected to air plasma cutting machines via a central Euro adapter. The thickness of the clean cut is 35 mm.
Price: RUR 48,324
Plasma cutters are available in various lengths; detailed technical information can be found in the product card on the PTK website or on the websites of our dealers in Russia, Kazakhstan, and the Republic of Belarus.
Safety of operation of the device
Before working with the device, it is necessary to study the manufacturer’s passport and regulatory documentation on safety precautions GOST 12.3.003−86.
- Equipment maintenance and repairs must be carried out with the network disconnected.
- There should be no flammable liquids or combustible materials in the workplace.
- The workplace must be provided with fire extinguishing equipment, well ventilated, and, if necessary, artificial ventilation should be installed.
- The specialist must use special clothing, shoes and other protective equipment when working.
- When cutting, it is better to use special tables that are equipped with a system for removing gases and steam.
- If work is carried out outdoors, a canopy is required.
- Do not leave the plasmatron on for a long time.
Observing safety when operating the device will help avoid occupational diseases and injuries.
Plasma cutting technology
Before you start cutting with plasma, it is worth knowing how the whole process works. Unlike laser cutting, the plasma torch should be placed close to the edge of the material.
After turning on the “start” button, the pilot arc will be lit first, then the cutting arc. The torch with the cutting arc must be moved slowly across the material.
To adjust the cutting speed, it is recommended to control the appearance of sparks on the other side of the metal. When they are not there, it is not possible to completely cut the material.
Several reasons can be noted: high speed of passage of the apparatus, low current, the burner was not at an angle of 90 degrees. to the metal being cut. How to set the cutting angle correctly is shown in the video.
Video:
After completing the process, the burner must be tilted, as the diagrams show. It is worth remembering that after turning off the start, the air will continue to flow for some time.
The plasma cutter will be able to completely melt the metal at the moment when the inclination is 90 degrees or higher.
After turning on the device, wait for the cutting arc to appear, create a right angle between the torch and the material. So any shaped structure can get a hole.
When working with a plasma cutter, it is worth studying the diagrams of the device - they indicate the greatest thickness of metal in which a hole can be made. Plasma cutting technology is shown in detail in the video.
Video: