Beginning welders are often faced with a choice: what equipment to purchase for work. Knowing the difference between an inverter welding machine and a conventional one, it will be easier to choose a welder. Transformers and high-tech inverter converters have pros and cons. The devices differ in power indicators, functionality, and dimensions.
What is a welding inverter?
This type of welding machine is characterized by the ability to convert direct electric current into alternating current. This unit contains the following main components:
- rectifiers - network and frequency;
- filter;
- frequency converter - the inverter itself;
- transformer;
- Control block.
This is how a welding inverter works.
Alternating current from the electrical network, which has a frequency of 50 Hz, is supplied to the network rectifier. After this, the current is correspondingly rectified and then smoothed through a filter. Next, it is fed to an inverter, in which it is converted into an alternating voltage with a high frequency - approximately several tens of kHz. Then, through a transformer, the current voltage is reduced to a level of about 50-60 V, while its strength increases to approximately 100-200 A. Then the current is rectified using a frequency rectifier - already during the arc welding process.
The frequency converter - inverter - can be adjusted by the welder, thereby ensuring optimal operating parameters of the unit. To do this, another functional element of the inverter welding machine is used - the control unit.
Main advantages of inverters:
- low weight and dimensions;
- high energy efficiency of welding;
- high welding precision.
- units in many cases require special storage conditions - in terms of temperature, air humidity;
- sensitivity to low temperatures;
- high price, high cost of maintenance and repair.
Principle of operation
Alternating current from the mains is supplied to the rectifier, then a special module converts it into direct current with a higher voltage frequency. Next, the current passes through a transformer, where it is rectified and supplied to the welding arc. This is what an inverter welding machine means.
According to the type of welding arc power source, there are:
- Transformers.
- Inverters.
- Rectifiers.
- Induction devices and others.
Inversion of alternating current into direct current and stepwise rectification ensures a stable arc. All this reduces fluctuations and interference from the electrical network, which affect the quality of the weld. This is how an inverter welding machine differs from a conventional one.
What is a traditional welding machine?
The “classic” welding machine is characterized primarily by its simplicity of design. Its main functional element is a transformer.
This is how a traditional welding machine works.
Alternating current from the electrical network is directed to the primary winding, as a result of which magnetization of the transformer core is formed. The current then passes through the secondary winding - in it the magnetic flux forms an alternating current, characterized by a lower voltage compared to what is supplied to the primary winding. Its voltage depends on the number of turns on the secondary winding.
Thus, a traditional welding machine operates due to electromagnetic induction, which generates a large current strength - sufficient for welding, at a low voltage.
The main advantages of traditional welding units:
- no requirements for special storage conditions;
- lack of sensitivity to low temperatures;
- low price, inexpensive service.
Disadvantages of the corresponding devices:
- heavy weight and dimensions;
- not the most outstanding energy efficiency and accuracy.
Comparison
The main difference between a welding inverter and a traditional welding machine is the presence of a current converter in the first device. In addition, the units under consideration differ in the following aspects:
- weight, dimensions;
- energy efficiency, welding accuracy;
- availability of requirements for storage conditions;
- sensitivity to low temperatures;
- prices, services.
It can be noted that, as a rule, the use of traditional machines requires a more highly qualified welder.
Having determined what the difference is between a welding inverter and a traditional type welding machine, we will reflect in a small table its main criteria in relation to the aspects discussed above.
Inverter and welding machine: what is the difference between them?
Most people involved in welding come across words such as inverter, welding machine or transformer. In some cases, these words are used as synonyms.
This is not surprising, since these two equipment are designed for the same purpose and can replace each other at the right time. However, there are still differences in the form of the principle of application in practice.
The main task for beginners in the welding field is to find out what is the difference between an inverter and a welding machine?
- What is an inverter?
- What is the difference between an inverter and a welding machine, and what characteristics are important?
- Bottom line
Bottom line
Not everyone understands what the difference is between an inverter and a welding machine. They have plenty of different characteristics if you study each design in more detail, but to the average person they will most likely seem identical.
For people who use welding in various situations and for whom the quality of the seam is important, transformer welding equipment will be the best option.
When it is necessary to weld in large quantities, using high power, then a transformer will become a more profitable option, since it is not in danger of overheating. This is the main difference between an inverter and a welding machine.
What is an inverter?
The need for welding work arises not only in industrial activities, but also at home, in the domestic sphere. Often such work appears for owners of private houses or summer cottages. Thanks to the purchase of welding equipment, you can solve any current problem in a short time.
Before choosing a suitable design for your home, you need to understand its purpose, functions and important details of use.
A welding inverter is a device thanks to which you can carry out any welding work at large production enterprises or for private use.
A worthy choice should depend not only on price, capabilities, and quality of work performed, but also taking into account the technical characteristics of the equipment, conditions and specific nuances during operation.
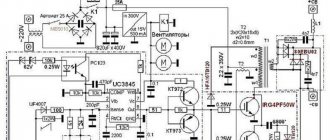
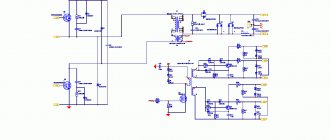
Electrical circuit of a welding inverter.
Important criteria to note when selecting and purchasing inverter welding equipment are as follows:
- The company needs to check the availability of printed circuit boards suitable for a specific design model. They are quite fragile, and repairs are very expensive. In other words, if a specialist has a lot of them, this indicates that the mechanism will most likely break down frequently in the future. In the absence of spare parts and the possibility of purchasing them only for individual order, we can talk about the performance and longevity of the equipment. Additionally, it is recommended to clarify the cost of repairs and production of parts.
- Availability of built-in ventilation. The welding process produces a lot of dust, so it is very important that the design has a cooling fan with a direct purpose. In addition, it must suck up dust. Most manufacturers integrate tunnel ventilation. Thanks to this internal mechanism, additional protection of all main parts from dirt and dust is provided, but the cost increases significantly.
- Protection against sudden voltage changes must be installed. Most welding inverters are sensitive to voltage surges due to built-in protective mechanisms that begin to work when there is a surge of 220 V.
By ensuring that the buyer gets enough information and is able to understand the differences between an inverter and a transformer, the process and task will be successfully completed without any difficulties.
The acquired knowledge will help not only specialists, but also beginners who do not understand the specifics of the instrument. The level of performance depends on the set temperature. It is this that affects the quality of functionality.
For example, due to high temperature - 40+, additional protection mechanisms may start working. However, such an indicator is quite rare in practice. With low temperatures the opposite is true.
Almost every modern equipment contains capacitors, microcontrollers, transistors, etc., which have an individual temperature range.
In cold weather, care must be taken to avoid condensation. At zero temperature, the device may simply not turn on, this will be indicated by a red light with an overload indicator.
When choosing this equipment, you need to familiarize yourself with the passport, operating conditions, permissible temperature, and also find out the possibility of repair services, warranty and the availability of the official website and detailed instructions for use from the manufacturer.
What is the difference between an inverter and a welding machine, and what characteristics are important?
Speaking about the differences between an inverter and a welding machine, it is necessary to highlight several of their characteristics.
- The volume and weight of a welding transformer is much larger than that of an inverter. In industrial structures their weight sometimes reaches 100 kg.
- Welding inverters differ from transformers in their operating principle. The primary rectifier changes the alternating current into a regular one, after which it again converts it into alternating current with a high frequency and again makes a revolution on the secondary rectifier. In transformer welding, the current changes due to a change in the position of the magnetic wires, in other words, from the position of the core, which reduces the equipment or includes a different number of turns in the circuit.
- Inverters have a stable arc, which gives a stable welding current that affects the quality of the seam.
- The inverter has a different design. Its design is more labor-intensive, often has additional functions, such as: changing the current value to improve the ignition of the welding arc or increasing the current to speed up the melting process and prevent the object from sticking together - a function called arc forcing, or reducing the current to increase the time electrode separation and additional protection against overheating.
- The difference also lies in the learning process in working with a transformer and an inverter. It is more difficult to work with a transformer, but once you work with it, the inverter will not present any difficulties.
- Welding machines have a wide range of alternating currents.
- An inverter welding machine differs from a conventional welding machine in its ability to use electrodes required in any type of current.
- With an inverter, regular current operates, while the welding machine uses alternating current with a frequency of 50 Hz.
- The inverter has the highest power of all welding equipment, however, transformers have high efficiency.
- One of the main differences between inverter and transformer equipment is the value of the intermittent functionality coefficient. In the latter case, the indicator is not important, but the inverter needs periodic cooling so as not to overheat and continue to properly fulfill its purpose.
The main differences between an inverter welding machine and a conventional transformer one
Welding machines are becoming indispensable not only in industrial production, but also in everyday life. This is confirmed by the huge selection of household and semi-professional equipment. At the same time, among other types of equipment, inverter devices are becoming increasingly popular. What is the difference between an inverter welding machine and a conventional one?
Operating principle of a transformer welding machine
Modern transformer welding machines are reliable and unpretentious. They operate at a frequency of 50 Hz. Electric current is converted using a transformer. This happens as follows. First, a current of 220V is supplied to the primary winding of the transformer.
It magnetizes the composite core, which creates an alternating magnetic field. As a result, an alternating current appears in the secondary winding, but its parameters are already different: voltage - 50-90V, current - 100-200A. The latter value directly depends on the number of turns in the secondary winding of the transformer. It is adjusted mechanically.
An example of such a device is WESTER ARC 130.
This is what welding transformers look like
Electric welding was first used in practice by the Russian inventor N.N. Benardos in 1881.
Advantages of transformers
Welding transformers have a number of advantages:
- They are inexpensive. With equivalent characteristics, a welding transformer costs half as much as an inverter.
- The devices have a simple and reliable design.
- They can be repaired even at home.
- They can operate at sub-zero temperatures.
Disadvantages of transformers
- Transformers are distinguished by their solid dimensions and heavy weight. They are not well suited for frequent movements.
- When working on alternating current, it is difficult to ensure high quality seams.
- Device efficiency is no more than 80%.
- The devices consume a large amount of electricity.
- They cannot be connected to the intra-house network.
Operating principle of a welding inverter
Serial production of welding inverters was established about 30 years ago. Their more accurate name is rectifiers with a transistor inverter. The main difference between welding machines of this type is the sequence of electric current transformations.
In these devices, it has to change its characteristics several times. First, the current is rectified and becomes constant as it passes through the semiconductor. The next step is to pass it through a filter for additional smoothing.
The current then enters the inverter and is converted into alternating current with a frequency of about 100 kHz. After this, it enters a transformer, in which the voltage decreases and the current increases. It then goes into a high-pass filter and then into a rectifier.
The output produces a direct current of the required parameters.
Due to such complex transformations, it was possible to reduce the dimensions of the welding machine. An example of such a device is ELITECH AIS 200 PNS.
This is what a welding inverter looks like
Advantages of an inverter device
- The efficiency of the devices reaches 95%. Energy losses are minimal.
- The devices are characterized by increased electrical safety.
- They can be connected to a regular household network without consequences.
- The devices have a very wide range of current regulation. Thanks to this, it is possible to use different types of electrodes and select the required welding mode for metals.
- All operation of the devices is regulated by control circuits and microprocessors. This ensures easy ignition and stable arc retention.
- The voltage and current in inverter devices are adjusted smoothly.
- The devices are equipped with protection against surges in mains voltage.
- Welding can be carried out in any spatial position.
Disadvantages of an inverter device
- Their cost significantly exceeds that of welding transformers.
- The devices are sensitive to dust. It may be the cause of failure.
- Inverter welding machines do not tolerate high humidity and low temperatures. They need to be stored only at positive temperatures.
- If the operating rules are violated, the unit with power transistors fails. Replacing it can cost half the cost of the device. Repairing a device is a very expensive procedure.
As a result, the difference between an inverter and a transformer-type welding machine from the user’s point of view is the following: it is mobile, provides excellent quality of seams, and is convenient to work with. These functional advantages are provided by electronics and process automation. For the same reason, such devices are more expensive.
Welding transformers are unique “workhorses”. They should be used when the device is not expected to move and high quality welding is not required.
What is the difference between a welding machine and an inverter?
If you need to carry out welding work yourself, the question arises: what type of welding machine to purchase. Welding is the creation of permanent connections between welded parts at the atomic level. The welded connection is one of the strongest and therefore is used quite often.
During electric welding, heating and melting of the metal occurs due to the formation of an electric arc between the end part of the electrode and the surface to be welded. Sources of arc formation and maintenance are divided into several types:
- Transformer.
- Inverter.
- Rectifiers.
- Welding units based on internal combustion engines.
Let's consider two types that are most widely used: a welding machine based on a transformer and an inverter source of electric arc.
What is the difference between an inverter welding machine and a conventional transformer one: which is better?
If you need to carry out welding work yourself, the question arises: what type of welding machine to purchase.
Welding is the creation of permanent connections between welded parts at the atomic level. The welded connection is one of the strongest and therefore is used quite often.
During electric welding, heating and melting of the metal occurs due to the formation of an electric arc between the end part of the electrode and the surface to be welded.
Sources of arc formation and maintenance are divided into several types:
- Transformer.
- Inverter.
- Rectifiers.
- Welding units based on internal combustion engines.
Let's consider two types that are most widely used: a welding machine based on a transformer and an inverter source of electric arc.
Other types of welding equipment
A rectifier differs from a transformer apparatus by the presence of semiconductors that rectify the electric current, and welding capabilities are expanded. When changing poles, you can shift the area of maximum heating:
- with straight polarity, the electrode heats up more;
- in the reverse case, the workpieces to be welded are in the welding zone.
The difference between semi-automatic machines is the use of welding wire, which is fed into the heating zone automatically. Semi-automatic devices are created on a transformer and inverter basis.
The transformer semiautomatic device with gas equipment is used in auto repair shops and in production; there are no special requirements for storage and transportation conditions.
The inverter is more capricious and is necessary for working with thin metal, stainless alloys, and aluminum.
Separately, there are generators that convert the mechanical energy of the engine into electric current. Such devices produce direct and alternating current, operate on mains power and liquid fuel.
Welders prefer transformer devices for large volumes of work. For beginners, it is advisable to purchase small inverter models. Auto repair shops typically require a variety of equipment.
Design
Despite the fact that externally all the equipment is very similar, since it consists of a housing on which there are sensors and adjustment knobs, as well as connected wires and holders, internally welding transformers differ significantly from inverters.
Transformers appeared earlier, therefore, they are simpler. They consist mainly of coils, the distance between which is adjusted, changing the amount of current. Its design is simpler and more reliable in operation. Due to the smaller number of parts, breakdowns occur much less frequently here.
There is also a dependence on power surges in the network.
Welding transformer
The inverter contains a variety of electronics that control the welding process.
It can overheat faster, so you need to monitor the temperature of the device, and is also sensitive to shocks, shocks and other damage.
They are less reliable in terms of operation, but provide a wider range of parameters. There are often additional functions here due to the design features of the model.
Welding transformer
This type of welding machine appeared earlier than all others. It uses alternating current for welding. Used for working with ferrous metals.
The welding transformer has a very simple design, so it is easy to maintain and repair. The unit has a low price, but is quite reliable and unpretentious. It is also very easy to use. Even a beginner can cope with the job. Unfortunately, due to the unstable welding arc, it is difficult to obtain a high-quality seam.
Another disadvantage of a welding transformer is the high load on the electrical network during operation. For this reason, it is highly recommended not to connect the device to a household electrical outlet. This is fraught with voltage surges or even knocking out plugs.
In addition, the welding transformer is bulky and weighs from 20 kg. Therefore, it is inconvenient to store and move from place to place.
Section: Welding transformers
Welding rectifier
Welding machines of this type are considered to be of higher quality and professional. Direct current is used for welding. You can work with both ferrous and non-ferrous metals. Thanks to a more stable arc, increased penetration depth and improved current control circuitry, it is easier to form a good weld.
Welding rectifiers have a good protection system against moisture, dust and foreign objects. Sparking during operation is noticeably reduced.
However, the cost of such units is noticeably higher, and operation requires skill and experience. For example, it is difficult for a non-professional to avoid constant overheating of the device during operation. The design of a rectifier is also much more complex than that of a transformer. Therefore, independent maintenance and repair will cause a number of difficulties for a beginner.
Section: Welding rectifiers
Welding inverter
The most modern type of welding machines. It has many varieties: there are models both for a specific type of work and universal ones. Thanks to this, it is easy to choose an inverter for different types of welding, as well as for working with any metal.
This type of unit has a very stable arc, so even a beginner can get an even and neat seam. In addition, even simple welding inverters have a flexible adjustment system. Thanks to this, it is easy to configure the device for the task being performed.
During operation, the welding inverter does not load the electrical network. At the same time, welding inverters are lightweight and compact. This means that moving and storing such a device is much easier.
Section: Welding inverters
| Transformer | Rectifier | Inverter | |
| Weldable metals | black | black and colored | black and colored |
| Dimensions/weight | big | big | small |
| Difficulty to use | high | moderate | low |
| Arc stability | low | average | high |
| Multifunctionality | No | No | Yes |
| Flexible settings | No | No | Yes |
| Welding quality | low | average | high |
| Energy efficiency | low | low | high |
| Safety | low | average | high |
| Price | low | low | high |
| Difficulty of maintenance | low | high | high |
Transformer welding machine
This is the simplest of welding machines that uses alternating current. It works using a transformer that regulates the mains voltage to the welding voltage. Transformer or induction welding machines are divided according to the following criteria:
- Power (the greater the welding current, the thicker the metal it can be processed).
- The number of posts, that is, jobs (how many people can work at the same time).
- Voltage (single-phase or three-phase network).
Its advantage is a simpler and more reliable design, low cost, and high maintainability.
Transformer welding machine
The disadvantages include the dependence of the arc on power surges, large weight and overall dimensions, and strong heating during work.
What is an inverter?
An inverter welding machine or simply an inverter is one of the energy sources for electric arc welding, which is based on the use of high frequency current . Its operation is carried out by power electronics and a small transformer.
Inverter welding machine
Its advantages are considered to be low energy consumption, compactness, low weight and size, and fairly high quality seams.
The negative aspects of the inverter include the relatively high cost, fear of moisture, dust and low temperatures (typical of budget models), sensitivity to voltage surges, and expensive repairs.
What do an inverter and a transformer welding machine have in common?
The similarity of these devices in their purpose is the formation and maintenance of an electric arc. But there are still some points that unite them:
- The devices under consideration are united by the presence of a transformer, but of different sizes. Due to the preliminary receipt of high frequency current, inverters do not need to use large transformers. To obtain a current of 160 A, a transformer weighing 0.25 kg is needed. To obtain the same current in inductive devices, a transformer weighing 18-20 kg is required.
- Possibility of smooth current adjustment. Transformer devices have this opportunity due to changing the size of the air gap in the magnetic circuit.
- The devices are powered from a household (220V) or industrial (380V) network.
- Most welding machines have short circuit protection.
What is the difference between an inverter and a transformer source of electric arc?
- The dimensions and weight of a transformer-type welding machine are larger than that of an inverter. Industrial designs can weigh more than one hundred kilograms.
- Operating principle. In the inverter, the alternating current of the network is converted by the primary rectifier into direct current, then again into high-frequency alternating current and then again changes to direct current at the secondary rectifier. In transformer-type welding machines, the current strength changes due to changes in the position of the magnetic core, that is, the core of the step-down transformer or the inclusion of a different number of turns of windings in the circuit.
- The inverter has a more stable arc due to the stability of the welding current, which affects the quality of the seam.
- The difference is in the design. The inverter is more complex and can be equipped with the following additional functions: HOT START - increasing the initial current to improve ignition of the welding arc. ARC FORCE - increasing the welding current to speed up the melting process and prevent sticking, that is, the arc is forced. ANTI-STICK – reduction of current when the electrode sticks to increase the time it takes to tear it off and protect against overload.
- The process of learning to work on a transformer is more complex and time-consuming. However, having mastered these skills, you can easily work on an inverter.
- The inverter produces direct current, the transformer operates on alternating current with a household power supply frequency of 50 Hz.
- The power factor of the inverter is the highest of all welding equipment, and the efficiency exceeds transformer analogues by 20-30%.
- Wide range of welding current changes.
- The inverter has such an indicator as the intermittency coefficient (IC). It determines the time of continuous operation at maximum welding current. That is, if the CP is 50%, then after 10 minutes of operation it needs 5 minutes to cool down. Such requirements are not imposed on a transformer welding machine.
- Possibility of using electrodes designed for both direct and alternating current.
Today there is a fairly wide selection of welding equipment on the market from various manufacturers. The choice of welding machine should be made based on the tasks that will be performed with its help.
Which semi-automatic welding machine is better: inverter or transformer?
To the question: “Which semi-automatic welding machine is better, inverter or transformer?” you can answer in different ways. You can briefly: “Based on the need!”, or you can reasonably understand the pros and cons of each welding technology, and based on this analysis, make an informed decision.
Despite its apparent simplicity, welding several metal elements is an art. As in any other business, to master it you need to gain theoretical knowledge, practical skills and suitable tools.
The first transformers appeared at the end of the 19th century, when electricity became commonplace. At the beginning of the 20th century, it was discovered that using a transformer it was possible to control the arc welding process, which gave impetus to the development of transformer welding machines.
The simplest, so to speak, great-great-grandfather of welding transformers consists of two windings enclosed in a core assembled from insulated metal plates.
When voltage is applied to the primary winding, current begins to flow through it. Under the influence of electromagnetic induction occurring in the transformer core, electric current begins to flow through the turns of the secondary winding.
In a welding transformer, the number of turns of the secondary winding is significantly less than the primary winding, and the winding itself is made of a large cross-section conductor. As a result, the current flowing through the secondary winding is of a significant magnitude, sufficient to ignite and maintain the combustion of an electric arc.
By the way, in the 20–30s of the last century, transformer welding machines became commonplace in production, and by the end of World War II their use was experiencing a real boom. From the 30s to the 80s of the 20th century, the basis of all welding machines was a transformer.
Transformer welding technology is over 100 years old. It is quite simple, but over this time it has been honed almost to perfection.
The welding current can be adjusted in different ways:
- introducing a rheostat into the circuit;
- mechanical change in the distance between the primary and secondary windings;
- changing the gap in the transformer magnetic circuit.
The development of semiconductor technology, its rapid growth and widespread use have opened a new era in welding technology. Inverter welding machines saw the light.
The operating principle of such a device is quite simple. The supply voltage, passing through the rectifier, is converted to DC. In the inverter it is transformed back into alternating power, but at a high frequency (60–80 kHz). After which the voltage rectification process occurs again, since DC welding has a number of advantages.
The use of high-frequency welding currents allows you to get rid of “excess” transformer iron, thereby reducing the weight and dimensions of the welding machine.
Frequency is the fundamental factor in the functioning of an inverter welding machine. With its help, the welding current is regulated - the lower the frequency, the lower the output power, and, accordingly, the welding current.
At the dawn of the development of inverter welding technology, there were disappointments. The first production samples were extremely capricious in terms of welding conditions and not very reliable. But over time, improvements in circuits and components made it possible to eliminate most of the weak points of inverter technology.
Each welding technology has its own advantages and disadvantages. Let's look at the most significant ones in detail.
Reliability
A topic that is still being discussed to this day and has divided welders into two opposing camps. Arguments of the “transformer people” - welding transformers have been improved for more than a hundred years.
The circuitry of the device is simple, but, nevertheless, brought to perfection. To “kill” such a device, you need to try hard. But inverter models cannot boast of this yet.
They are still relatively young, they have room to “grow”.
Modern realities are such that the last argument is shattered to smithereens by the emerging new, more reliable element base and the constant improvement of inverter semiautomatic circuits.
Multifunctionality
In this aspect, the inverter outperforms the transformer. In an inverter semi-automatic device, thanks to the controller, you can set any electrical variable. Moreover, its value will be monitored and adjusted constantly during welding work. And this opens up a wide field of activity not only when welding ferrous, but also non-ferrous metals.
Dimensions, weight
Due to the massive iron that is directly involved in the transformation of energy used for welding, transformer models are heavy and bulky. Even the simplest device weighs close to 20 kg.
Inverter models stand out against their background. With comparable power, they are light and compact.
Quality of arc and welds
The quality of the weld is the calling card of every self-respecting craftsman. To get a good seam, in addition to a steady hand, you need to have a device that will keep the current parameters at a given value.
It is no secret that the simplest transformer models are highly dependent on changes in the supply voltage. When it subsides, the welding current decreases, and the master has to reduce the gap between the parts and the electrode in order to “hold” the arc.
With sudden jumps in the reaction, it may not be enough - with a sharp increase in current, you can often get the workpiece burned through, especially when welding thin-walled metal.
In addition, welding transformers that are not equipped with a rectifier require some getting used to. The fact is that alternating current welding is more physically complex. It leads to the so-called “hard” arc, hissing of the electrode and spattering of metal over the workpiece.
In the figure: on the left is a seam made by a transformer, on the right by an inverter.
Working with a transformer welding machine is somewhat more difficult. But having mastered the welding technique, you can easily “work miracles” with an inverter. The reverse transition without getting used to, developing skills and a certain “additional training” is impossible!
All weather
Based on this feature, the transformer semi-automatic device is a clear favorite. The fact is that inverters stuffed with electronics are afraid of moisture and dust, which can damage the device’s circuit board.
Welding in dusty rooms, especially with metallized dust in the air, is not for the inverter!
Another limitation imposed by manufacturers on inverter devices is the use of equipment for operation in cold weather. The reason for this is possible condensation that can form on the device’s boards.
Transformer devices do not care about all of the above. They will work in hot and cold weather, and even in high humidity. The only thing you shouldn’t do is welding in the rain! Is it dangerous!
Duration of activation
As is known, this parameter characterizes the ratio of the operating time of the device to the downtime necessary for its cooling at maximum loads. The more intense the welding work, the longer the pauses will be required.
When working under loaded conditions, transformer solutions have a better chance of competing for the sympathy of consumers. If you need to make a lot of welds that are not of the best quality, or even just cut metal, then there is no alternative to a transformer. After all, doing the same thing on an inverter device even sounds blasphemous.
Operating under high loads will most likely lead to failure of the electronic components of the inverter apparatus.
Today, when choosing a semi-automatic welding machine, most users will probably give preference to an inverter solution. And this is not surprising, because de facto inverter models are the standard in the field of welding.
But it is still premature to discount transformer models, since there are still certain niches for them in which they have no equal. In the end, it all comes down to specific working conditions and your own informed decision.
Which is better: an inverter or a welding transformer?
Beginning welders are often faced with a choice: what equipment to purchase for work. Knowing the difference between an inverter welding machine and a conventional one, it will be easier to choose a welder. Transformers and high-tech inverter converters have pros and cons. The devices differ in power indicators, functionality, and dimensions.
Which is better: a welding transformer or an inverter. What is the difference
Welding inverter "Elitech IS 220".
As can be seen from the table, both gadgets have their pros and cons.
Welding with a transformer is much more difficult than with an inverter.
Let's say more: if you learn to cook with a transformer, you can easily “switch” to an inverter.
But if it’s the other way around, it won’t be so easy.
If the budget is not limited, then, of course, an inverter. The difference between a transformer and an inverter, we will consider different options in further discussions.
For the dacha
At the dacha there is a lot of work for a welder:
- a “stable” for your “steel horse” - a garage;
- greenhouses and everything connected with them;
- garden watering system;
- Summer shower;
- repair of country equipment, etc.
Note that dachas appeared long before the invention of inverters, and everyone made do with transformers. Many people still use them now. But with an inverter, welding is easier, faster, and of better quality.
For home
In a house, especially a private one, there are no fewer problems than in a country house. But if at the dacha you can take some welding “liberties with unsightly” welding, then at home this will be unforgivable. Therefore, the house must have an inverter.
For garage
In a “men’s club” (some call this establishment a “garage”, although they don’t even have a personal car), a welding machine can have a very wide field of application: from minor repairs (the carrying handle has fallen off) to car body repair. And if the owner of the gadget is a “jack of all trades,” then, of course, he needs an inverter.
For the forge
“Serious men” with large metal parts work here. They need a powerful transformer more. With a certain skill, they will use it to perform all the necessary operations.
For installation of forged products
For the installation of forged products, especially those produced by the “cold forging” method, only an inverter is needed. It will allow you to avoid overheating, sticking, etc. welding defects. This will preserve the artistic value of these forged products.
For car service
It is advisable to use an inverter at a car service center. For body work, there is an automatic welding machine with an inverter source of welding current.
For production
In production, the type of welding equipment prescribed by the technological process should be used. In heavy engineering, a transformer may be used, but in precision engineering - only an inverter current source.
For the construction of a private house
At the construction site of a private house, you can use a transformer to weld reinforcement – it will perfectly “connect” it. Yes, and other welding can be done on it.
For a professional builder or construction company
For construction professionals, of course, only an inverter is needed: it will provide high-quality welding and high productivity. Its cost will “dissolve” in the overhead costs of equipment.
What is a regular welding machine?
The classic current source for generating an electric arc is a transformer. The welder lowers the mains voltage, and the current increases accordingly. Such equipment was used for manual welding everywhere until the beginning of the 21st century.
The operating principle of the transformer is based on the magnetic induction method. Electric current passing through the first winding magnetizes the core. An electromagnetic field arises, and under the influence of waves an electric current is formed in the wire of the secondary transformer winding. The output voltage depends on the number of secondary turns. The equipment generates high-ampere current with parameters necessary for welding.
Advantages and disadvantages of welding transformers
First, about the advantages of transformer devices:
- simplicity of the device, the scheme of operation is clear to the student;
- maintainability, in case of breakdown the transformer can be repaired independently;
- the ability to work for a long time is ensured by low sensitivity to overheating during operation;
- impact resistance – the risk of mechanical damage during transportation is minimal;
- accessible service;
- low price;
- versatility, the device is used for welding various metals;
- there are no special storage requirements, the transformer is resistant to high humidity and dust.
The disadvantages of traditional welders are obvious:
- when the network sags, the transformer turns off; a stable voltage is needed for power supply;
- lack of precise adjustment of current parameters, large adjustment steps, difficult to set up equipment for welding thin-walled workpieces;
- heavy weight, it is difficult to move the equipment independently;
- significant dimensions;
- high power consumption.
What is a welding inverter
The operating principle of the inverter is also based on the induction method; in fact, it is also a transformer converter, only equipped with electronics. The main difference between an inverter welding machine and a transformer one is the presence of semiconductors. The inverter converter is a new generation device, a modern version of classic equipment. Through the use of power electronics, the size of the converter was significantly reduced.
For stable operation of semiconductor elements, the device has a fan. With built-in tunnel-type ventilation, it is possible to protect microcircuits from dirt and dust. A whole class of welding equipment has been created based on inverter converters. It is customary to call an inverter a welder only for manual arc welding; devices operating in TIG, MIG/MAG, and FLUX welding modes are considered semi-automatic.
Advantages and disadvantages of inverters
The device is convenient. There are no problems with igniting the arc thanks to the “easy start” fiction. The electronics maintain stable combustion during voltage surges, and the current is easy to regulate. The difference in setup between an inverter and a transformer is significant. With low energy consumption, it is possible to obtain high-frequency alternating or high-ampere direct current, necessary for the formation of an even seam.
So, the main advantages of the inverter:
- light weight;
- compactness, this largely explains the popularity of inverter power supplies;
- additional functionality that improves the quality of welds;
- ease of setup;
- ability to connect to a standard network (only professional models have an additional input for power supply from a three-phase 380 V network).
Now about the disadvantages, they also exist:
- high price;
- sensitivity to overheating, the inverter must be turned off periodically to prevent the semiconductor unit from overheating;
- increased requirements for operating conditions: equipment should be protected from high humidity, increased dust, low temperatures (professional models are made in a protective case);
- low mechanical strength, the inverter must be handled with care.
Despite all the disadvantages, inverter equipment is gradually replacing traditional transformers.
general information
What is a transformer?
The transformer is the most classic representative of welding machines. Transformer devices were widely used throughout the 20th century and only at the beginning of the 21st century they began to be replaced by inverters.
All modern and old transformers are adapted primarily for manual arc welding using a consumable electrode. This welding technology is also classic and is still used today. It is the simplest and most understandable even for a beginner.
A welding transformer welds using alternating current; in this it differs significantly from an inverter, which welds using direct current. What does this mean for you as a welder? First of all, AC welding is more difficult. The arc is reluctant to ignite and burns unstable. Accordingly, it is very difficult to form seams if you do not have skill in this matter.
Also, the use of a transformer is associated with other difficulties. Often, to adjust the current, it is necessary to change the value of the inductive reactance, or change the value of the secondary open circuit voltage. The inverter has one simple “knob” to adjust the current strength, but with a transformer you will have to learn more.
But transformers are more powerful and are excellent for welding any metals, even thick ones. They are cheaper, unpretentious to storage conditions, and can be repaired quickly and cheaply. The other side of the coin is its large dimensions. A transformer can weigh incomparably a lot. The weight of household models reaches 100 kg.
Surely, many beginners have already decided what to choose: a transformer or an inverter. Do not hurry. Next we will talk about inverters and you may change your mind.
What is an inverter?
An inverter or inverter machine is a modern version of the classic welding machine. Its key advantages are its compactness (weight often does not exceed 10 kg), functionality (there are built-in functions that simplify arc ignition and prevent the formation of defects), and a large selection of devices. At the moment, the inverter is the most popular type of welding equipment all over the world. And most of the buyers are newbies.
There is a little confusion in the names that a new welder may encounter. Inverter equipment is a whole class consisting of different devices, including semi-automatic devices. But among welders, inverters are usually called compact inverter-type welding machines intended ONLY for manual arc welding. If an inverter machine can perform welding in a shielding gas environment, for example, then it is usually called a semi-automatic device, and not an inverter.
Do you remember? An inverter is an inverter machine for manual arc welding. All other inverter machines (performing TIG, MIG/MAG, FLUX welding) are semi-automatic. Therefore, the question “Which is better: a semi-automatic welding machine or a regular inverter?” is a topic for a separate article. We won't talk about this here.
Which welding machine is better: inverter or transformer
Deciding what is best for welding metal in your own garage or home is not difficult. Comparative characteristics of power supplies will help. First, about the similarities: both are necessary for converting electric current, obtaining operating current parameters, only inverters are equipped with electronic converters.
A short example will help you compare the dimensions of inverter and transformer welding machines. To generate 160 A, you need a transformer weighing 20 kg or an inverter weighing 2.5 kg. The inverter has the highest power, however, transformers have high efficiency.
A transformer unit is more difficult to master; special knowledge and skills will be required to set it up. Inverter devices are easier for beginners. Reduces the risk of uneven seams due to built-in functions:
- Hotstart improves arc ignition when the welder is turned on;
- Arcforce prevents the electrode from sticking when a drop falls, forcing the electric arc;
- Anti-stick protects against overload during a short circuit, the arc does not go out.
The capabilities of the inverter are wider; you can obtain a constant electric current of the required strength. High-frequency or pulsed alternating is similar in action to constant.
Transformer welders do not have such a concept: intermittency; the operating mode is indicated on each inverter. If the efficiency is 50%, every half hour the unit is turned off for 15 minutes.
It is impossible to say unequivocally which welder is better. Or rather, such a conclusion makes no sense. Much depends on the working conditions, the nature of the workpieces being welded, and the skill of the welder, finally.
Inexpensive inverter devices are well suited for a summer house and garage, in cases where there is no extensive work experience and they are used a couple of times a year. But you should not forget about storage: protect from high humidity, dust and low temperatures.
Transformer or inverter: which is better?
So now you know what a transformer and an inverter are and what are their differences. At this stage, you probably have a question: “Which welding is better, an inverter or a transformer?” We'll disappoint you, but there is no short answer. Because there are many nuances. But first things first.
First of all, a transformer and an inverter are two completely different devices. They have different devices, different operating principles, and different configuration methods. Even the dimensions and weight differ.
Inverters are more beginner-friendly because they come with additional features that make welding easier. But at the same time they are less reliable and not powerful enough. Transformers are difficult to master, and here the quality of the seam directly depends on the selected settings and the skill of the welder himself. But they are much more powerful and provide you with more opportunities in the future.
A simple conclusion follows from this: transformers are necessary for those who seriously want to master welding, but are not ready to spend a lot of money on a powerful inverter. A transformer for a relatively low price will give you much more options than a household inverter. But you will have to spend a lot of time studying the theory of setting up such a device.
But the inverter will appeal to all summer residents and garage craftsmen who need to weld something up a couple of times a year. They don’t want to spend a long time figuring out the settings and fiddling with transporting the device. But to get a more powerful device, they will have to buy an expensive professional inverter or the same transformer.
What about rectifiers?
Experienced craftsmen have probably noticed that in this article we did not talk about another interesting type of welding equipment. We are talking about rectifiers. Many beginners have not even heard of such devices, although a rectifier may be an ideal option when choosing a first welder.
A rectifier is in many ways similar to a transformer. It is just as bulky and powerful. But there is one key difference. The fact is that the transformer welding machine uses alternating current. Hence there are many difficulties with igniting the arc and making a seam. The rectifier does not have this drawback. It, like the inverter, welds using direct current. Therefore, it is easier for a beginner to light an arc and generally operate the device.
Most rectifiers are also designed for manual arc welding, so you won’t have any problems with this. A rectifier is as reliable as a transformer because it contains rare electronic components. Not a single cheap household inverter can compare in reliability with a rectifier or transformer.
That is why, asking the question “Which is better: a welding transformer or an inverter?” remember the rectifier. This is an excellent device for both beginners and practicing masters.
Other types of welding equipment
A rectifier differs from a transformer apparatus by the presence of semiconductors that rectify the electric current, and welding capabilities are expanded. When changing poles, you can shift the area of maximum heating:
- with straight polarity, the electrode heats up more;
- in the reverse case, the workpieces to be welded are in the welding zone.
The difference between semi-automatic machines is the use of welding wire, which is fed into the heating zone automatically. Semi-automatic devices are created on a transformer and inverter basis. The transformer semiautomatic device with gas equipment is used in auto repair shops and in production; there are no special requirements for storage and transportation conditions. The inverter is more capricious and is necessary for working with thin metal, stainless alloys, and aluminum.
Separately, there are generators that convert the mechanical energy of the engine into electric current. Such devices produce direct and alternating current, operate on mains power and liquid fuel.
Welders prefer transformer devices for large volumes of work. For beginners, it is advisable to purchase small inverter models. Auto repair shops typically require a variety of equipment.
What is the difference between a welding transformer and an inverter?
Author:
Igor
Date of:
18.11.2016
- Article
- Photo
- Video
Many people who are just starting to weld come across such names as welding transformer and inverter, and when they are used almost with an equivalent meaning. This is not surprising, since these types of equipment are used for the same purposes and are completely interchangeable. But the principle of their use is still different and you need to find out how a welding machine differs from an inverter. There are quite a lot of differences, if you go into the nuances, but for the average user it may all look the same.
Pros and cons of an inverter
This type of welding unit has many advantages over other types:
- Stable welding arc, which does not require great skills and experience when working. Significantly saves consumables (electrodes, etc.).
- It is possible to regulate voltage and current.
- Compact dimensions and light weight.
- Low power consumption with high performance.
- Hot-Start system. Provides easy ignition of the welding arc. This is another plus of how welding machines differ from inverters. The former do not have this system.
Despite a large number of positive qualities, inverters still have disadvantages:
- The price is higher compared to other types of welded units.
- High cost of repairing semi-automatic machines. Maintenance of transformer units is significantly lower.
- They do not tolerate dust and low temperatures well.
Design
Despite the fact that externally all the equipment is very similar, since it consists of a housing on which there are sensors and adjustment knobs, as well as connected wires and holders, internally welding transformers differ significantly from inverters. Transformers appeared earlier, therefore, they are simpler. They consist mainly of coils, the distance between which is adjusted, changing the amount of current. Its design is simpler and more reliable in operation. Due to the smaller number of parts, breakdowns occur much less frequently here. There is also a dependence on power surges in the network.
The inverter contains a variety of electronics that control the welding process. It can overheat faster, so you need to monitor the temperature of the device, and is also sensitive to shocks, shocks and other damage. They are less reliable in terms of operation, but provide a wider range of parameters. There are often additional functions here due to the design features of the model.
Welding process
The differences between an inverter and a welding machine during the welding process are as follows. The welding transformer provides an insufficiently stable electric arc. With small fluctuations in the network, the parameters of the welding current change. Inverters do not suffer from this, as they can maintain stability using various built-in circuits, which makes the work of welders easier. This also helps to avoid metal spattering during welding.
The inverter is more technologically advanced and has precise, smooth adjustment of parameters with a scale. The welding transformer has approximate settings and does not have an accurate scale. Modern inverters, even in their budget versions, have such functions as “Hot start”, “Anti-sticking”, as well as “Welding arc force”. The inverter is less energy-consuming and can be connected to a regular outlet, including autonomous power sources
Dimensions and weight
Another noticeable factor that distinguishes an inverter welding machine from a conventional one is its weight. The inverter takes up less volume, with the same power as the transformer, and also weighs less. This became possible due to the fact that the voltage frequency here has increased. According to simple calculations, if you increase the operating frequency of the equipment by 1000 times, then the dimensions will decrease by approximately 10 times. Some models have a transformer the size of a cigarette pack. Thanks to this, compact options are used for welding at heights. For constant transportation, equipment is produced of the inverter type. Most of the useful volume here is occupied by the radiator. Many modern models weigh less than 4 kilograms, while transformers remain unliftable for high-altitude work.
Welding inverters ..Sometimes they are mistakenly called invectors, or even inverters.. How often do we hear this phrase, but how are inverters fundamentally different from conventional transformer welding?
Inverter-type welding machines are designed for manual electric arc welding of metals and metal structures made of black steel. These inverters are characterized by convenient operation, ease of maintenance and portable size. Moreover, due to their design, inverters do not “waste” the network, and can operate in unstable network conditions.
A welding inverter is usually equipped with a rectifier, a converter, a transformer, an output rectifier and a control circuit.
First, a little theory. The operating principle of a welding inverter is based on one of the laws of electrical engineering, which states: The higher the voltage frequency, the smaller the overall dimensions and weight of the transformer must be to transmit the same amount of energy. So, when the frequency of the electric current increases by 1000 times, the dimensions decrease by 10 times. Active developments in the field of inverter welding began at the beginning of the 20th century, and they acquired a recognizable appearance starting in the 90s of the last century, when special power transistors began to be actively introduced. With their help, it was possible to raise the frequency of the current to great heights, while reducing the size of the devices.
For example, the TSS Sai-200 welding inverter operates at a frequency of 100 kHz while weighing only 7 kg. For comparison, for conventional machines the characteristic showing the ratio of welding current to the weight of the machine ranges from 1–1.5 A/kg, while for modern inverters this value has already reached 4–5 A/kg/ Welding inverters have gained leadership positions in the welding equipment market, due to its excellent technical characteristics, ease of transportation and reliability during operation. The most important advantages of inverters are: - Light weight of welding equipment; — Low power consumption; (relative to transformer welding machines) - The area of spark splashing during welding has been reduced; — Ability to regulate the strength of the welding current; — Possibility of operation from the moment of switching on; — High quality weld. Moreover, the inverter is the safest and easiest to operate device among all devices designed for welding a variety of metals. When working with inverters, it is enough to follow a few simple recommendations, following which you will significantly extend the life of your welding machine: - Do not place the inverter in dusty rooms. When working outdoors, place it on a stand to prevent dust from entering. — During operation, do not overload the inverters. The operating instructions for each device indicate a special “PV” characteristic. It shows what percentage of the time the inverter can operate in maximum mode. This parameter is usually calculated for 10 minutes. — After finishing the welding work, let the inverter cool down a little. When the power is turned off, the fan cooling the radio components stops, and if it is turned off immediately, some elements of the circuit may burn out and fail.