The design of steel ropes and types of deformations, the necessary knowledge when working on soft roofs
Rice.
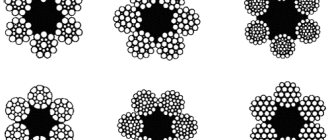
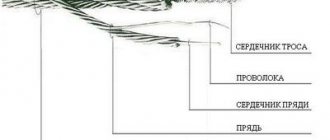
5.1 Double lay steel rope 1 - wire; 2 - strand; 3 - core Table 5.1 Types of strands
| Name | Image |
| Single strand | |
| Three-strand | |
| Five-strand (1 - wire, 2 - strand, 3 - core) | |
| Six-strand | |
| Eight-strand | |
| Eighteen-strand | |
| Closed design with two layers of wedge wire, one layer of Z-wire and TK type core |
The ropes vary in design
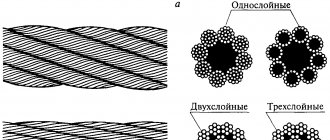
Single lay (spiral) - consisting of one, two or three layers of wire twisted into concentric spirals (Fig. 5.2)
Rice. 5.2 Single lay (spiral)
Double lay - consisting of six or more strands twisted into one concentric layer (Fig. 5.3).
Fig.5.3 Double lay
Triple lay - consisting of strands twisted in a spiral into one concentric layer (Fig. 5.4).
Rice. 5.4 Triple lay
According to the type of contact of the wires between the layers, ropes are distinguished:
With a point touch (type TK) - the wire lays have different steps along the layers of the strand, and the wires intersect between the layers. This arrangement of elements increases their wear during shear during operation, creates significant contact stresses that contribute to the development of fatigue cracks in the wires, and reduces the coefficient of filling of the rope section with metal.
With linear touch (LK type) - such strands are produced in one technological step, while the constancy of the wire laying pitch in all layers of the strand is maintained. To obtain a linear touch, the diameters of the wire and strand are selected depending on the design of the latter. Thus, in the top layer of rope strands of type LK-0, wires of the same diameter are used in layers, strands of type LK-R have wires of different diameters in the outer layer, and in strands of type /7/S-Z, wires are used that fill the space between wires of different diameters . There is a type of rope with a linear touch of the wire between the layers and having layers in the strands with wires of both different and identical diameters - LK-RO. In three-layer linear touch strands, there are various combinations of the above types of strands. It should be noted that the performance of ropes with linear contact of wires in strands, with the correct choice of rope design, is much higher than the performance of ropes with point contact of wires.
With point-linear touch (type TLK) - strands of point-linear touch are obtained by replacing the central wire in strands of linear touch with a seven-wire strand: in this case, a layer of wires of the same diameter with a point touch is laid on a two-layer strand of type LK. The design of these strands makes it possible to produce them on spinning machines with a relatively small number of bobbins. In addition, TLC strands, with appropriate selection of laying parameters, have increased non-twisting properties;
Based on the core material, ropes are distinguished:
With organic core (OC). Most rope designs use lubricated organic cores of hemp, manila, sisal or cotton yarn as the core at the center of the rope, and sometimes at the center of the strands, to provide the required flexibility and resilience. The use of cores made of asbestos cord and artificial materials (polyethylene, nylon, nylon, etc.) is also allowed.
With a metal core (MC). It is advisable to use a metal core in cases where it is necessary to increase the structural strength of the rope when multilayer winding it on a drum, to reduce the structural elongation of the rope during tension, and also when operating the rope under conditions of elevated temperature. One of the most common designs of this type is a double lay rope made of 6-7 wire strands located around a central seven-wire strand. The metal core can be made of ordinary rope or soft wire with a tensile strength of no more than 900 N/mm2.
According to the combination of laying directions of strands and rope:
One-way lay rope - with the same direction of lay of the wires in the strands and the strands in the rope (Fig. 5.5).
Rice. 5.5 Single lay rope
Cross lay rope - with the opposite direction of lay of the strands and the rope (Fig. 5.6).
Strands in ropes (LK strand, TK strand)
Externally, a cross lay rope differs in that the wires on its surface are located parallel to the axis of the rope. The wires of a one-way lay rope are located at an angle to its axis.
One-way laid ropes are less rigid, but are prone to unwinding. In crane mechanisms, as well as for the manufacture of slings, they are used.
cross lay nuts, more rigid, but not prone to unwinding under load. Non-unwinding ropes twisted from pre-deformed wires, which will be described below.
According to the laying method, ropes are divided:
Unwinding - the wires are not freed from internal stresses that arise during the process of twisting wires into strands and strands into a rope. Strands, strands and wires in this case do not retain their position in the rope after removing the bandages from its ends;
Non-untwisting (N) - when laying wires into a strand and strands into a rope, internal stresses are removed by straightening and preliminary deformation in such a way that after removing the dressings from the end of the rope, the strands and wires retain their given position. Non-unwinding ropes have a number of advantages compared to unwinding ones: somewhat greater flexibility and a more uniform distribution of tensile forces on the strands and wires, increased resistance to fatigue stress, and no tendency to disrupt straightness when unfolding.
According to the degree of twist, ropes are divided:
Rotating;
Low-rotating (MK). These ropes should be distinguished from non-unwinding ones. In low-twist ropes, thanks to the selection of laying directions of individual layers of wires (in spiral ropes) or strands (in multi-layer double lay ropes), rotation of the rope around its axis is eliminated when the load is freely suspended. A low-twist rope can be made either non-unwinding or unwinding. A prerequisite for the manufacture of low-twisting ropes is the arrangement of the strands in two or three concentric layers with the opposite direction of lay of each concentric row of strands. In this case, the rotational moments of all strands of the rope are balanced, which prevents the overall rotation of the rope around its axis.
Additional materials:
Symbol of steel rope and signs of deformation of steel ropes
Nylon and vegetable rope
Lifting mechanisms for work on soft roofs
Catalog of waterproofing roofing materials from the TechnoNIKOL company
Catalog of roofing fused materials from the manufacturer JSC “Orgkrovlya”
Anti-unwind rope design
A non-unwinding cable, like a traveling rope, has a strong core braided in a certain sequence of strands, which in turn are made of many small wires. The more strands in the cable, the stronger it is. The core of the product can be of two types, differing in material. In the first case, organic materials are used for its manufacture, and in the second, high-strength steel. The wire used in the production of the cable is characterized by high strength and low bending rigidity.
Unlike unrolling products, non-unwinding products retain their structure after the bandages are removed from their ends. This became possible due to its special straightening and deformation during manufacturing in the factory.
Non-unwinding ropes are more flexible and therefore much easier to use. Some types of products are coated with galvanized coating, allowing them to be used in extreme conditions.
The advantages of non-unwinding steel rope include:
- high degree of flexibility;
- uniform distribution of tension in the cable;
- ability not to delaminate.
Why is cable lubrication needed?
To increase the service life of steel cables, you need to properly care for them. Smoothing of ropes is a mandatory measure, the main task of which is to protect against corrosion and mechanical damage. Experts advise applying lubricants in a thin layer of about 0.2 m. Lubricants are used in the manufacture of cables and their operation.
Regular lubrication of ropes ensures longevity and performs other tasks:
- Prevents deformation by ensuring maximum penetration of individual strands.
- Protects against corrosion, preventing premature failure of the metal product.
- Provides resistance to washout, guaranteeing protection in wet conditions and other external factors.
- Reduces friction, reducing abrasion and wear.
The lubricant guarantees resistance to water, ideal for high pressure spraying - low viscosity product. It exhibits high temperature stability, providing protection at high temperatures. The composition can be used at low temperatures.
Classification of cable products
Steel cable is widely used and there is a large selection of products on the market. There are several classifications of metal cables:
- by appointment;
- according to the shape of the sections;
- the number of strands in the rope, which determines its scope of application;
- material of the main element - the core;
- wire properties;
- direction of strands in the structure – left-sided, right-sided;
- type of wire processing;
- type and genus of Vitya.
To determine the nominal diameter of the cable, you need to take measurements in two sections. There should be a distance of 1 m between them. In sections, the diameter is measured twice along the line of the maximum distance between the limit points.
Application area of the rope
Non-unwinding steel cable, manufactured in accordance with GOST 7668, is widely used in the construction industry, namely as part of various cargo mechanisms and lifting devices. It does its job well under conditions of high shock loads, high compression heat, and lifting loads, both steerable and unsteerable.
During operation, it is not recommended to use the rope together with a swivel . You also need to pay attention to the direction of the lay to avoid overstressing it too much. It is equally important to follow the transportation rules, while maintaining the integrity of the packaging, which will avoid injury.
Purpose of steel cables
Cable products are designed for lifting and moving heavy structures. The hoisting steel cable is also capable of performing the following tasks:
- moving cargo on tower or container cranes;
- holding crane structures;
- installation and dismantling of cranes and others.
If you need to manipulate an uncontrollable load or lift it to great heights, you will need ropes that are resistant to rotation. Only they ensure the stability of the load, so the load is able to rotate. Rotation-resistant ropes attached to the crane structure do not transmit torque to the attachment point. Due to this, it is possible to ensure operational safety. These types of ropes have production requirements in accordance with GOST standards. They differ in the level of rotational resistance depending on the type of structure.
There are several conditions where the use of rotation-resistant ropes is inappropriate and unjustified. For example, if ropes of the same design are used as a pair consisting of right-handed and left-handed ropes. In this case, rotational stability is ensured, so the load does not rotate. This is explained by the balance of torque.
Rotation-resistant ropes are less prone to bending. Therefore, if elastic compounds are needed in a specific situation, then you should not stop at this type of cable. Assess the conditions for using ropes and the risks of using different types of products.
Quality and types of cable materials
The quality of steel used determines the tensile strength of the cable. Modern production technologies offer consumers durable products with anti-corrosion resistance and resistance to external factors. Steel ropes are typically available on the market in tensile ranges from 1570 to 2160 N/mm square.
Galvanized ropes are made from galvanized material to resist corrosion. For the use of heavy equipment (for example, winches, mining machines), there is a demand for the manufacture of ropes with an increased tension range of the rope wire. On the other hand, since strength is not the only criterion when choosing a rope, it is important to evaluate the specific conditions of use of the ropes.
Stainless steel is the most popular material for cable production. Since products made from it can be used in harsh climatic conditions, this indicates high protection against corrosion. Stainless steel has high tensile strength and is considered suitable for almost any environment. Modern steel processing techniques mean that stainless steel can be cut, welded, shaped and manufactured quite easily. The flexibility of cables made from this type of material means that steel can be used to produce products of any size and shape.
There are many different grades of stainless steel, depending on their alloying element content, as well as their mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. They are marked in accordance with GOST and other international standards.
It is important to consider environmental factors when selecting the grade of stainless steel in a cable composition. There are methods for classifying environmental factors that allow you to select a brand for a more precise application.