What is forging? Stages of the forging manufacturing process
Today, metal forming is the most common and technically sound method of producing blanks, called forgings, which are subsequently machined to achieve the required dimensions and configuration of the part.
The forging manufacturing process goes through the following stages:
1. Cutting rolled products of various configurations into the required sizes.
The rolled products used can have round, square, rectangular and polygonal sections. Sometimes it is allowed to use a workpiece in the form of a special profile (angle, I-beam, channel)
2. The process of metal deformation.
3. Heat treatment of forgings (normalization and tempering)
4. Reception of the finished forging by the technical control department.
Methods used to make forgings
Today there are two main methods for obtaining forgings:
• Forging is the process of deforming a metal workpiece, which is in a plastic state, and giving it the desired shape by exposure to the impact load of the hammer or press strikers. Forging also includes bending, drawing, and drawing. A distinctive feature of forging is that the workpiece is in a free position during the deformation process; it does not have a clear location.
The allowance for processing a forged forging is almost 2 times greater than for a forging obtained by stamping. In production, forging is used only in small-scale and single-piece production, using two main methods: manual or machine.
• Stamping is the process of deforming the original metal workpiece under pressure, which occurs using additional equipment (special stamp).
The process of plastic deformation is carried out in the die matrix, the shape of which is completely identical to the manufactured forging. The impact element that exerts the load is the punch.
Stamping can be performed with or without preheating the original workpiece.
Stamping, in contrast to forging, has a fairly high productivity, it does not require highly qualified workers, and the resulting forging has higher dimensional accuracy and low surface layer roughness. However, the use of stamps is only advisable in mass and serial production in order to justify the costs of their expensive production.
Alloy steel grade 5ХНМ (tool die) is widely used in industries where high demands are placed on manufactured products in terms of hardness, strength, wear resistance, and where high manufacturing precision is required. Often this is tool production and machine tool manufacturing.
Forgings produced from 5ХНМ steel have found their main application in the design and production of press dies, forging units, and hammers.
Steel 5ХНМ has the following mechanical properties:
Tensile strength B - 1570 MPa Yield strength T - 1420 MPa Hardness after annealing - 241 MPa
Impact strength KCU – 340 kJ/m2
Analyzing the physical properties and composition of the basic alloying elements of 5KhNM steel, it can be noted that due to the high content of chromium - up to 0.8% and nickel up to 1.8%, the steel has high hardness, strength and elasticity, which helps to avoid cracks on the surface of the forging after its thermal treatment processing. The molybdenum content of up to 0.3% contributes to good impact strength, thereby preventing the steel from becoming brittle after tempering.
Forgings made of die steel 5ХНМ are subjected to annealing, preparing them for subsequent heat treatment and ensuring the removal of internal stresses in the structure.
In order for a tool made from die alloy steel 5ХНМ to have maximum hardness and have a long service life, finishing heat treatment is required. Hardening is carried out at a temperature that reaches 850°C, and then subsequent tempering is carried out at a temperature of 460-520°C.
The environment in which quenching and tempering will be carried out, as well as the temperature regime, is selected by the technologist depending on the operating conditions and the shock load of the tool being manufactured. However, it must be remembered that high temperatures during the hardening process can cause an increase in the hardenability of steel and, as a result, a decrease in impact strength.
There are also foreign analogues of die alloy steel 5ХНМ, which has also gained great popularity in the USA and European Union countries.
Here it is labeled in accordance with its standards in force in the country. For example, T61206 or L6 in the USA and 55NiCrMoV7 in the European Union.
Application benefits
The production of the products in question is carried out by foundries. They are supplied with forging blanks, where they undergo a full technological cycle, including heat treatment. The finished product has the following advantages:
- excellent performance characteristics;
- stable mechanical properties;
- high Brinell resistance;
- low cost.
The workpiece does not require special storage conditions. If necessary, they can even be stored on an open construction site. They retain their properties for a long time.
The surface of the product is of high quality. There are no cavities, burrs, sagging or other defects on the workpieces. In addition, during metal processing there is no decarbonization of the material.
What is the correct way to pack or forge?
» Other »
Question for experts: what is forging???
Sincerely, Shura Kiselev
Best answers
Forging - circle, square, strip from various steel grades
Do you need to manufacture a forging product with specified dimensions according to drawings: a circle or a square of large diameter from various steels? You can contact Alfa-Soyuz LLC - we work directly with manufacturers, which allows us to work at reasonable prices without sacrificing quality.
All products (custom forgings, etc.) have passed quality control and received certificates. You can order and buy forgings and other products at retail (from 1 piece or from 1 m) or wholesale.
We deliver rolled metal throughout St. Petersburg and the region, as well as throughout Russia.
Forging is a blank or finished product obtained by forging or hot stamping in a forging and stamping industry. Stamped forgings, after cutting and heat treatment, are transformed into various parts: connecting rods, crankshafts, levers, gears, turbine blades, fasteners, balls, rollers and bearing rings, etc.
Forgings are made from structural, heat-resistant, stainless, heat-resistant, tool and other steels. From these types of steels, forgings are made according to the following nomenclature: smooth shafts of round and rectangular cross-section, disks with and without holes, cylinders, plates, die cubes, rolled rings.
When they pack. Packing. Parking, when you park, you park your car in a certain place.
metallurgical operation (from the word “forge”) - a method of processing metal to give it certain useful properties
Forging is a rough blank or a finished metal product with mechanical processing, manufactured in accordance with drawings and final dimensions, free forging methods, and hot stamping.
A forging is a rough blank or an intermediate part made during the process of forging (stamping) or pressing a metal or alloy
partalstalina /shop/item/3454
-answer
This video will help you figure it out
Answers from experts
A circle is a geometric figure! A forging is a workpiece (sometimes a product) obtained by metal forming methods - forging or stamping. The question had to be formulated: “What is the difference between forging and rolled stock? ". Forging, see above, and a billet from rolled stock is obtained by cutting (from a rod) or cutting (from sheet metal) depending on the diameter of the workpiece.
1. Forging - a blank or finished product obtained by forging or hot stamping in a forging and stamping industry. 2. Stamping is the process of plastic deformation of a material with a change in the shape and size of the body. Once again, to secure the material: 1-workpiece
2-process
Stamping, when the product is made with a stamp. Forging is a product made in a forge using the forging method.
a forging is like a blank. and stamping is an operation
Stamping of the product itself. The packaging is what the stamping is wrapped in, so to speak. Sort of like that.
Forging is a product obtained as a result of numerous blows with a universal hammer. Stamping is a product obtained as a result of a single application of pressure (impact or slow pressure) using a figured (individual) stamp.
You will have to work a lot to become a blacksmith. Look into any forge. They are stamped on presses at the factory.
die forging is one of the methods for producing forgings. It involves the production of small-sized forgings (die cubes, plates) in closed dies. A cheaper and faster method of mass production of forgings compared to open forging.
Forging is a blank, and stamping is a process of plastic deformation
Stamped forging - produced by deforming an alloy or metal in the limiting form of a die. Stamped forging is highly accurate. Stamping can be hot with preheating of the metal or alloy and cold, without heating the forging. High heating of the metal gives the forging plasticity and fluidity. Allows you to give the workpiece the required shape at a lower cost.
Forged forging (press, hammer) - differs in the independent position of the workpiece during forging. Increased ductility and strength. A forged forging is inferior to a stamped forging in exact compliance with dimensions and shapes.
GOST 7509-89
This interstate standard determines the amount of tolerances, allowances and forging allowances for steel forgings manufactured by hot die forging. There are restrictions on weight and size. The standard states that for workpieces weighing more than 250 kg and dimensions more than 2500 mm, permissible deviations, radii of rounding of external corners and other parameters are established through negotiations between the manufacturer and the customer.
Forgings are a product in demand in various industries. They are obtained by forging and stamping the workpiece. Do you think casting parts can compete in quality with forgings? Write your opinion in the comments block.
Manufacturing of forgings and stampings: technology features
Forging and hot stamping is one of the three main areas of pressure processing of piece workpieces made of metals and alloys.
Due to the fact that the ability of a metal to deform significantly increases with increasing temperature, using hot pressure treatment methods it is possible to produce products of arbitrarily complex shapes, even from steels with relatively low ductility (for example, high-alloy steels). Moreover, some alloys are pressed exclusively when hot.
The production of forgings and stampings by hot deformation is determined by the temperature at which the deformed metal ceases to be hardened. Hardening manifests itself as constantly increasing values of the plastic limit.
As a result, more and more force has to be applied to the metal, which negatively affects the energy consumption of deforming machines. During hot pressure treatment, the mobility of the grains of the macrostructure increases, and their movement becomes easier.
Therefore, the specific forces are noticeably reduced, so it becomes possible to shape steel with high degrees of deformation without fear of destruction of the workpiece.
Forging and stamping are the main types of hot forming. Accordingly, the production equipment in the first case is called forging, and in the second - forging and stamping.
The uncontrollability of thermal expansion of metal during hot forming in most cases does not make it possible to manufacture products without tolerances and allowances. Therefore, forgings and stampings are blanks that are then subject to mechanical modification along the contour, drilling holes, making grooves or fillet grooves.
Thus, by forging and stamping we understand the technology of hot metal forming, which is carried out at temperatures at the end of the austenitic transformation. For low-carbon and unalloyed steels this is a temperature range of 1050...12000C, and for high-carbon and alloyed steels - 850...9500C.
Metal forging
During forging, the flow of metal under the action of a deforming tool is not limited in any way, since the shape change occurs by pressing smooth strikers on the surface of the workpiece.
In this case, the deformation force is the smallest, however, the possibilities for precise deformation of the metal are minimal: plastic flow always occurs in the direction of least resistance, i.e., into the gap between the strikers.
Therefore, forging is a purely procurement operation and is performed in the following cases:
Basic forging operations:
- Upsetting (reduction in the height of the workpiece with a corresponding increase in its diameter).
- Broaching (increasing the length of the workpiece while decreasing its height).
- Firmware closed and open - obtaining blind or through holes.
- Torsion is a helical change in the longitudinal axis of the workpiece.
- Chopping – dividing a workpiece into several parts.
Forging is carried out on steam-air forging hammers, and steam-hydraulic forging presses are used to deform especially large forgings (for example, crankshafts). A workpiece that has undergone forging transitions is called a forging.
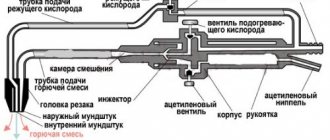
Hot stamping
During hot stamping (by the way, it can be either volumetric or sheet: the latter is used for hard-to-deform steels, which are supplied as thick sheets with a thickness of more than 15...20 mm), the flow of metal under the influence of working force is limited by the shape of the cavity of the working tool - the die. Sometimes the finished product after such a change in shape is called “stamping,” but the term “forging” is practically more common, since it is initially already known whether the metal is processed by forging or stamping.
The stamp is a complex tool consisting of two halves - movable and stationary. In this case, the movable part of the stamp is attached to the press slide or to the head of a steam-air stamping hammer, and the stationary part is placed on the table of hot stamping equipment.
The presence of side walls of the die increases the deformation force due to the appearance of friction forces. However, finished stampings have significantly higher dimensional accuracy, so the tolerances are much tighter.
In addition, the availability of modern hot stamping equipment - hot stamping machines, screw and crank presses - also allows us to minimize machining allowances.
In some cases, stamped forgings only need to be descaled.
Thus, forging, stamping - the differences between them lie in the degree of accuracy of the final product and in its shape.
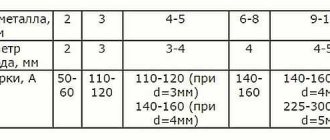
Sequence of hot stamping technological processes:
- Heating of the workpiece using flame or electric furnaces.
- The actual deformation (the main patterns of metal flow are upsetting and extrusion).
- Trimming flash - a technological residue, the presence of which ensures the filling of difficult-to-fill die cavities.
- Editing-calibration, as a result of which the longitudinal axis of the product, bent by thermal stresses arising during deformation, is aligned.
So, forging, stamping - the difference between them is that after deformation, forging is always subject to subsequent processing, while stamping already has a shape approaching the shape of the final part.
Forging is a metal processing process, types and main operations, what is free forging
Let's start with definitions. Forging is a method of processing metal in order to change it. This is not welding, although the metal is processed primarily using high heat.
Forging is the heating of metal to its forging temperature so that it becomes malleable to form new shapes into workpieces. Each metal has its own characteristics, which include the level of forging temperature.
Aluminum and its alloys can be forged at a temperature of 400°C, copper at 1000°C, and to forge iron it will have to be heated to 1250°C.
Types of processing
The types of forging are as follows:
- Using pneumatic, hydraulic, steam hammers;
- Manual, in which the impact on the metal is direct, with a hammer or sledgehammer.
- Stamping, in which the part, when exposed to it, takes the shape of a stamp.
Forging is the products obtained as a result of forging, including semi-finished products.
Open-loop forging is an alternative to stamping: the part is deformed freely without being placed in a die mold. Additionally, this method is used to improve the quality and structure of the substance, then this is called forging.
After forging, the alloy changes significantly for the better; it becomes stronger and finer-grained due to the destruction of large crystals.
Here you cannot do without powerful cranes and special manipulators of various calibers. This processing method is the most economical of all existing ones. If we talk about mass industrial production, then stamping takes first place in popularity.
Free forging is the domain of single or small-scale forging production.
Forging operations and tools
There are many such operations, these are some types of metal forging, the names speak for themselves:
- draft;
- firmware;
- broach;
- running in;
- rolling out, etc.
This is what a self-respecting blacksmith master should stock up on before work:
- hammer or sledgehammer;
- anvil;
- forge or oven;
- small hand and mechanical hammers;
- pliers for gripping hot pieces of metal
- “holder” – a rod with claws for gripping a blank.
Physics of the process
Let's take a closer look at processing using forging.
Heating the workpiece
The fateful stage: as soon as you heat it up, the forging process will continue. A metal blank is taken that needs to be heated. This is done in forges or heating furnaces - it depends on the size of the workpiece.
First of all, preheat the oven, the criterion for readiness is dark red color. The next stage is placing the workpiece in a hot oven. The workpiece must be hot, otherwise you will get cracks in the inner layers of the alloy.
The preheating temperature will be quite sufficient at 300°C: you can check by the appearance of smoke and the slight ignition of oil on the surface of the part.
When parts or several parts are inside the furnace, the heat is gradually increased to the required level. The relationship here is direct: the higher the temperature, the softer and more ductile the part. But it is absolutely forbidden to overheat the workpieces.
The higher the heating of steel, the higher the risk of the formation of individual crystals with weak bonds, which makes the alloy after forging brittle, with tears and cracks. This undesirable phenomenon is called overheating of steel.
It is important to understand that for efficient and high-quality forging, two things are equally important: the correct temperature level and the gradual heating.
Crimping a metal workpiece
It only seems that metal is a homogeneous and dense substance. In fact, inside you can find various voids and so-called shells. Therefore, the workpiece removed from the oven must be immediately compacted: it is hit with a hammer from the middle to the ends.
The actions performed by the hammer are divided into two stages: preparation and final finishing.
Preparation
The main thing in preparation is to “put in order” the alloy of the workpiece: compact it and give it “rough” the desired shape and size. The preparation stage is also divided into types in terms of shape: solid or hollow cylinders, flat things, rings, stretching, etc.
The method of forging at this stage may also vary; their names are just as funny.
As a result, an octahedron should form. It is pressed again - blows with a hammer with a 1/8 turn, after which a shape with sixteen edges is formed. Then everything goes according to the same scenario to get a cylinder with a significantly reduced diameter.
The workpiece becomes longer, the metal moves along the axis. This processing is called pulling.
During work, you need to monitor the condition of the metal. If, for example, cracks are found on the surface, forging must be stopped and the cracks cut out using a forge chisel.
Examples of free forging - 10 photos.
If the metal part for forging is too large, processing is done in two stages: first, the lower part is crimped and prepared, then the remaining part is heated and processed.
The end of this stage is “profit cutting,” which involves removing the upper “profitable” part of the workpiece due to the void content in it.
To form a part in the form of a ring, a piece of the workpiece needs nothing at all: crimp, stretch, clean from scale, chop off the profit and... cut into pieces. We heat these pieces thoroughly a second time and do a wonderful thing - we form cakes from them.
Holes in these cakes are punched on both sides to create real rings. Next, processing is carried out called “layout” in a special anvil of a stand-up type.
One of the most common shapes of workpieces are parts with a rectangular cross-section. Their forging is carried out according to its own rules. Firstly, you need to work on special flat anvils. First, they are crimped, and then they are flattened “flat”.
The next stage is to rotate the workpiece along the axis by 90°C and flatten it “on edge”. Under impacts and flattening, the part becomes longer along the axis.
To ensure that it does not turn into a thin ribbon, it is simultaneously “rolled out” to expand the dimensions, and all resulting irregularities are smoothed out with a hammer. This is how armor plates are forged.
There are a huge number of options for blanks based on the shape and nature of the metal. There are also many ways of forging. You need to be able to choose the most optimal one and plan the sequence of open forging operations.
The quality of forging and the consumption of resources in the form of energy for repeated heating and other consumables will depend on the correctness of this choice.