- Product certificates
Instructions for use
Attention: In the old Rules POT R M-012-2000, the lower height limit was 1.3 m, now it is 1.8 m above the level of scaffolding or scaffolding, as well as 5 m in height, and the angle must be at least 75°. The “Rules...” sets out the best definition of working at height, reflecting many realistic aspects. a) there are risks associated with a possible fall of an employee from a height of 1.8 m or more; b) the employee ascends a height exceeding 5 m, or descends a height exceeding 5 m, along a vertical ladder, the angle of inclination of which to a horizontal surface is more than 75°; c) work is carried out on sites at a distance closer than 2 m from unfenced differences in height of more than 1.8 m, and also if the height of the fencing of these sites is less than 1.1 m; d) there are risks associated with a possible fall of a worker from a height of less than 1.8 m if work is carried out on machines or mechanisms, water surfaces or protruding objects.
- analysis of documents - availability of certificates of conformity, operating instructions, markings;
- studying the history of operation of the safety equipment - PPE record card, forms based on the results of previous inspections;
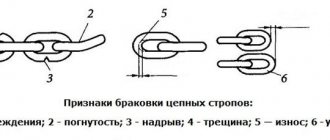
- visual and tactile inspection of the product - the use of a magnifying glass, probe and other special tools is acceptable;
- function check;
- documenting the results of the inspection;
- formulation of recommendations.
The time interval between mandatory checks of protective equipment used during work at height is determined by the manufacturer and indicated in the operating instructions for a specific type of product. Typically, harnesses are inspected at least once every 12 months. However, the person responsible for the operation of such products may reduce this period depending on the conditions in which the harness is used. For example, insurance that is exposed to the risk of high temperatures, aggressive chemical elements, and high humidity is checked more than once a year. Moreover, paragraph 96 of the Labor Code obliges the worker who uses the harness to check it before starting work and at the end of it. This is done by visual and tactile inspection of PPE, including:
- Shock Absorber Band:
- a cut;
- wear;
- burned areas;
- marks;
- chemical pollution;
- weak areas;
- Threads in the seams of the shock absorber, tape base of the sling body, power sewing:
- circumcised;
- worn out;
- tattered;
- elongated;
- with traces of chemical exposure;
- Rope sling base:
- cuts;
- wear;
- rigidity;
- fraying;
- bloating;
- traces of exposure to high temperatures;
- chemical pollution;
- hernias;
- Cable base of steel sling:
- cuts;
- wear;
- chemical exposure;
- traces of corrosion;
- folds;
- twists;
- Sealing loops;
- Protective thimbles:
- Availability;
- deformation;
- Connecting elements (body, bolt, locking mechanism, axles, rivets) and length adjustment mechanism:
- Availability;
- corrosion;
- deformation;
- marks;
- cracks;
- wear;
- Protective covers:
- Availability;
- wear.
Loads weighing 100 kg and 150 kg must have a nominal diameter of 200 mm. The ring bolt should be in a central position at one end of the load. It is also possible to deviate the bolt location from the central position (Figure 2) in order to balance horizontal loads when testing certain types of PPE.
The dummy for static and dynamic testing of certain components and systems must meet the dimensions and requirements specified in Figure 1. The mass of the dummy is (100 ± 1) kg. The center of gravity should be located above the crotch by (200±25) mm. The rings for hanging the mannequin must have an internal diameter of 40 mm and a cross-sectional diameter of 15 mm. The surface of the mannequin should be smooth. If the mannequin is made of wood, then the surface should be shellac or varnished.
The test bench must be designed in such a way that its natural frequency (vibration) along the vertical axis at the attachment point is at least 100 Hz and so that the application of a force of 20 kN to the attachment point does not cause a displacement of more than 1 mm. The attachment point on the test bench shall be a ring or rod with a cross-sectional diameter of (15 ± 1) mm.
The load measuring device must be designed to measure force from 2,0
up to 20.0 kN with an error of no more than
±5%,
must have a passband width of 1000 Hz and include a low-pass filter with unevenness of 0.5-1.0 dB in the passband and
3 dB
with a passband width of 60 Hz. The passband rejection must be at least 12 dB per octave.
The chamber should be a cube with an edge of 1 m (Figure 3), in which dust particles can be sprayed with a stream of air under a pressure of 6 bar. The chamber must have a ventilation hole with a filter. A cord should hang from above to control the mechanism during testing.
Is it necessary to test harnesses according to the new rules? Answer from a lawyer 2022
Manufacturers for the most part rely on previously existing regulations, departmental and industry regulations, indicating approximately the same testing requirements in the passports for staircase structures.
Meanwhile, when comparing various regulations (industry, departmental), there is a difference in approaches to the static load standard and test time. Finally, where and what tests are carried out? we can compose a magazine ourselves we can compose a magazine ourselves we must conduct periodic inspections of safety harnesses we must conduct periodic inspections of safety harnesses Clause 95 RBDTL ensures regular checks of the serviceability of safety systems at height in accordance with the instructions in their operational documentation.
Who should perform the harness test?
General safety requirements 1.1. A safety belt is a means of personal protection for a person when falling from a height. The static breaking load for the belt must be at least 7000N (7OOkgs). 1.2. The belt must withstand the dynamic load that occurs when a load weighing 100 kgf falls at a height equal to two sling lengths. 1.3. A carabiner - a belt element designed for fastening to structures - should provide quick and reliable fastening and unfastening with one hand when wearing an insulated mitten.
When testing, a static load is applied to each claw or hole for 5 minutes. directly onto the fastening straps so that the load axis passes through the center of the step. Safety rules for working on roofs. Work on the rack lines is carried out only with a safety belt, which is secured with a carabiner to the safety rope when moving along the roof and to the rack when working with it, a helmet and wearing shoes with rubber soles or galoshes. Before going out onto the iron roof, the worker must check with an indicator that there is no stress on all metal objects encountered along the route of his journey through the attic, and before entering the roof - on the metal stairs, the roof itself and the safety cable. If voltage is detected, access to the roof is prohibited.
Harness testing period
Safety harnesses are a mandatory means of personal protection for workers during high-altitude work and are used in such activities as high-altitude work on construction sites, high-altitude installation and roofing work, when lowering or ascending long distances and other areas where there is a risk of falling from a height.
- a violation of safe operation requirements was detected during pre-operation or periodic inspection;
- the product was used to stop a fall;
- the product was not used for its intended purpose;
- manufacturer's markings are missing or unreadable;
- the history of use of PPE against falls from height is unknown;
- the service life or storage period has expired;
- the product has been subject to repairs that were not authorized by the manufacturer;
- doubts have arisen about the integrity, completeness or compatibility of PPE.
And imagine that somewhere next to a 20-30 meter cliff (the height of a 9-story building is about 30 meters, which imitates working heights) someone will throw off a mannequin in the belts until they break or something? But how will he and the mannequin simulate the fall height and the rate of fall until the safety mechanism is triggered, so that the doll becomes heavier in the jerk up to half a ton?
- shoulder straps, which should be located at an optimal distance from each other so as not to injure the neck;
- leg straps equipped with elastic pads for comfortable use;
- back rods that connect the shoulder and leg straps;
- webbing safety belt for additional back support, which reduces fatigue;
- special loops into which carabiners are inserted and equipment can be stored;
- a set of self-locking buckles that adjust the length of the shoulder and leg straps, the back anchor point in height, and the total volume of the belt. The purpose of these buckles is to prevent spontaneous loosening or unfastening of belts and straps when working at height.
The safety belt is designed to ensure the safety of work on overhead power lines, power stations, oil rigs and other structures as a means of individual protection for a person when falling from a height and retains its operational properties at temperatures from minus 40 to plus 40°C. The system with a shock absorber must be operated with at least 3 meters of free space under the supporting surface.
Testing of safety belts (2020)
Paragraph 633 of the Safety Rules for explosion- and fire-hazardous production facilities for storing and processing plant raw materials (approved by order of Rostechnadzor dated November 21, 2013 No. 560) establishes that “... During operation, safety belts must be tested every six months, as well as before the start of operation, with a static load equal to 4000 N (400 kgf), which must be recorded at the place where the marking is applied. When testing the belt with a static load, the mass of the suspended load of 400 kg is maintained for 5 minutes.”
Thus, paragraph 36 of the Safety Rules in the Oil and Gas Industry (approved by order of Rostechnadzor dated March 12, 2013 No. 101) establishes that “...Safety belts and halyards should be tested at least once every 6 months with the static load specified in the plant operating instructions - the manufacturer, by a special commission with the execution of the act. In the absence of such data in the operating instructions, the test should be carried out with a static load of 225 kgf for five minutes.”
Harness Inspection Log Form
Vacuum drying – vacuum drying technology. Categories of chambers for vacuum drying. Features in the process of vacuum freeze drying.
Before being put into operation, as well as every 6 months, safety belts must be subjected to a static load test according to the method given in the standard or technical specifications for belts of specific designs. During operation of the belts, dynamic tests are not carried out. The metal parts of the safety belt must not have cracks, holes, tears or burrs.
At this training (unless, of course, you buy scabs in bulk for a thousand rubles) you will be told how to inspect safety harnesses, how to look for places where the safety lanyard may break internally, the basics and rules of marking, how to properly check locking devices and even tripods. Well, it’s mandatory to fill out all forms and inspection reports.
Dynamic tests are carried out with loads weighing 100 kilograms (±1 kg). Depending on the type of belt, you can use bags filled with dry sand (types A and B) as cargo; mannequins that imitate the upper part of the human torso (types B and D); mannequins imitating the human torso (types D and E).
Before putting into operation and every 6 months during operation, the consumer should test with a static load: - a sling without a shock absorber with a load weighing 700 kg; — a sling with a shock absorber weighing 400 kg (in this case, the shock absorber is not tested); — a buckle with a belt weighing 300 kg.
That is why the right choice of first aid kit for the workplace and medical office is immeasurably important. The composition of each first aid kit must be selected based on all possible risks of injury during the production cycle.
Safety belts are intended to protect against falls from a height when working on poles or wires of power lines and on structures or equipment of distribution devices. Durable, non-stretch material is used for the belts. The width of the belts must be at least 100 mm, length - from 900 to 1000 mm.
Mounting belt test protocol
Versions A and B are not intended for work involving fire. Testing of mounting belts In addition to acceptance and type tests, safety belts must also be subjected to periodic inspections.
1 Scope of application 2.1 Safety belt is a personal protective equipment attached to the human body and used independently or jointly with other means of protection to prevent a person from falling from a height or evacuating him from dangerous areas. 2.2 Strapless - safety, including: a load-bearing belt covering the waist or chest of a person, having a widened support in the back (hereinafter referred to as the sash), a sling with a carabiner or a catcher for fastening to the supports.
GOST R 50849-96 Construction safety belts
4.2.4 The sash must be made of materials with warming and hygroscopic properties; the design of the sash should facilitate uniform distribution of the load across its entire width; for this, the rigidity of the sash in the transverse direction must be significantly greater than in the longitudinal direction. For insurance and emergency evacuation of a person working in trenches, wells, tanks or other confined spaces, in cases of gas poisoning, fire, explosion. These belts cannot be used as a means to prevent a worker from falling from a height.
Are belts tested according to the new rules?
American mixed martial arts fighter Matt Mitrione, after winning the Bellator 180 tournament in the first round over Fedor Emelianenko, feels one step away from the champion title. After the fight, Matt talked about the mutual knockdown and Fedor’s career.
On the victory: “Crazy. He is so smart that right during the fight he started looking at my knees and feet. I changed my stance at the same time as him and it may have confused him. I attacked the moment he started attacking. I didn't realize that we both fell. I just saw him on his back and thought I should quickly pounce on him. I told the coaches all week that it would happen the same way I knocked out Derrick Lewis. I knew that we would deliver the blow at the same time and then the strongest would win.”
Personal fall protection equipment (PPE)
As you know, on May 5, 2015, new “Rules on labor protection when working at height” come into force. The new Rules, in comparison with the previously in force POT RM-012-2000 (Inter-industry rules for labor protection when working at height), carry quite dramatic changes. Let's look at the most important innovations and offer our solutions.
We recommend reading: How to find out who is the owner of a property
It turns out that from May 5, 2015, any personal protective equipment must undergo periodic testing of suitability for further use. Periodic inspections must be carried out by competent employees who have undergone appropriate training, or by organizations accredited by the manufacturer, depending on the operating conditions and taking into account the requirements of the manufacturer, based on his conclusion, PPE is either accepted or rejected.
Who should test mounting belts, ladders and stepladders?
According to clause 5.1.33 of the “Safety Rules for Working with Tools and Devices,” the person responsible for the condition of stepladders and ladders is an engineering and technical worker, who is appointed by order for the department of the enterprise. Before use, the inspection of ladders and stepladders is carried out by the worker himself, and during testing by an engineering and technical worker. According to clause 4.1.18 of the “Inter-industry Rules on labor protection when working at height” POT R M-012-2000, safety belts (assembly belts) must be tested every 6 months, as well as before putting into operation with a static load according to the method given in standards or technical specifications. After the load test, a thorough inspection of the belt is carried out (visually) and in the absence of visible damage, the safety (assembly) belt is allowed into operation.
24 Dec 2022 marketur 666
Share this post
- Related Posts
- Antenna in a high-rise building
- Who is provided with tax benefits?
- Responsible for maintaining egais
- Benefit when paying for a landline phone for a labor veteran of the Murmansk region
Mounting belt
Before putting into operation and during use (once every six months), mounting belts are subjected to certain testing for a static load of 4000 N. Testing of mounting belts is carried out using two methods:
Whatever type of belt is chosen, it is important that it maintains its performance characteristics at critical low and high temperatures - the average operating temperature range of such devices is defined as -40°...+40°.
Polar Industrial Forum
A person trained in industrial training, on the contrary, would say that the manufacturers of modern ASC are categorically against regular testing of equipment under high loads, even static ones. I don’t remember where, but I read that the problem is the use of synthetic fibers, which under repeated “test” loads become deformed and lose their properties. I don’t know a single person who would give his safety system for testing, and after their successful results, would continue to work on it, only to tear it to the end in order to find out the maximum load, and then with peace of mind buy the same new one.
GOST R EN 365-2010: clause 4.1-4.7 states that all instructions about the need for repairs, maintenance, inspections, etc. must be given in the product documentation. And clause 3.2 provides a definition of periodic inspection - the action of periodically performing an in-depth check of PPE for defects, such as damage or wear. Clause 4.2 f) states that the instructions for use must indicate the inadmissibility of making any changes or additions without the prior written permission of the manufacturer.
Are belts tested according to the new rules?
The rules have been introduced, but none of the labor safety inspectors yet knows what to do with all this. Soon it will become unprofitable to carry out work at heights: you need to train people and buy equipment, and all this for money. By the way, about checking:
It's clear. And by our enterprise order, several people in each workshop (linemen, repair and inspection workshop, substations) received the right to conduct mechanical tests of protective equipment. What is noted in the certificates in the columns for the right to carry out special work. In our workshop, the right to conduct mechanical tests of protective equipment was given to the head of the workshop and the foreman of one of the teams.
Who has the right to test safety belts?
In accordance with GOST R 12.4.184-95, there was a need to conduct tests at least twice a year. (Clause 9.2 The consumer must subject each belt to a static load test of 4000 N before putting it into operation, as well as during operation every 6 months.) According to order of the Federal Agency for Technical Regulation and Metrology No. 134 dated April 10, 2009.
The spikes must be turned all the way in and sharpened correctly. After inspection and elimination of detected defects, the claws and manholes are tested. During testing, the claws and manholes are installed in their working position on a special test bench that simulates the configuration of the power line support for which they are intended. The test is carried out by applying a static load of 135 kg.
Safety belt inspection inspection dates 2022
The design of the carabiner should ensure that its lock can be opened with one hand. The carabiner must have a safety device that prevents its spontaneous opening. The lock and safety device must close automatically.
As the person moves, the rope gradually unwinds from the drum, allowing the person to move away from the place of fastening a certain distance, and if he falls during a jerk, the rope is blocked and automatically stops the person’s further fall.
GOST R 50849-96 Group Zh07 BUILDING SAFETY BELTS General technical conditions. Test methods (Modified version.
For safety systems (systems with a shock absorber), the fastening point is a support (structural element), which must be located above the worker and have a strength of at least 15 kN; to stop a fall, it is necessary to use the harness fastening elements intended for this purpose.
Topic: Do safety belts need to be tested?
We use safety belts for working at heights. We test it every six months. New safety regulations for working at height have been released, coming into force this year, where: clause 95 “Dynamic and static tests of personal protective equipment against falls from a height with an increased load are not carried out by operating organizations.” What to do now, test it or not? If tested, then according to what and with what load?
Indeed, in the new rules on labor protection when working at height, there is an indication that although the employer ensures regular checks of the serviceability of safety systems for working at height in accordance with the instructions in their operational documentation, as well as timely replacement of elements, components or subsystems with decreased protective properties, but dynamic and static tests of PPE against falls from a height with an increased load are not carried out by operating organizations. This means that it is not at all necessary to test the safety (mounting) belts with a static load.
How often to check the harness
All personal protective equipment used for working at height requires special attention. The technical condition of such products must be monitored by specially appointed persons, whose responsibilities include organizing the acceptance of new PPE, their inspection and testing.
Currently, the labor protection rules (Order 155n) exclude the clause obliging the employer to test PPE with loads (dynamic and static). Thus, when considering the issue of the frequency of checking the safety harness, it is worth drawing the attention of those assigned to the insurance equipment to this point. However, if industry regulations require insurance to be tested in this manner, it must be done.
The time interval between mandatory checks of protective equipment used during work at height is determined by the manufacturer and indicated in the operating instructions for a specific type of product. Typically, harnesses are inspected at least once every 12 months. However, the person responsible for the operation of such products may reduce this period depending on the conditions in which the harness is used. For example, insurance that is exposed to the risk of high temperatures, aggressive chemical elements, and high humidity is checked more than once a year. Moreover, paragraph 96 of the Labor Code obliges the worker who uses the harness to check it before starting work and at the end of it. This is done by visual and tactile inspection of PPE, including:
One of the elements of anchor safety lines is a safety harness. A device of this type consists of a system of belts, slings, buckles and special fasteners that hold the worker’s body in a certain position and prevent him from falling from a height. The frequency of checking the safety harness is determined by the Labor Safety Rules approved by the Ministry of Labor and Social Protection of the Russian Federation (Order 155n), as well as industry regulations. At the same time, only factory-made harnesses that have a quality certificate are allowed for use.
- document analysis;
- checking operating instructions;
- visual and tactile inspection;
- performance check;
- documentation of research results;
- issuing recommendations for further use of the harness.
Physiotherapeutic belt Fizomed for kidney treatment
Right now you can buy belts for kidney treatment - not only for yourself, but also for your relatives suffering from common diseases of the urinary system. This is possible thanks to affordable prices, online ordering and delivery anywhere in Russia and even to other countries. By purchasing a belt for the treatment of kidneys "Fizomed", you receive a unique physiotherapeutic product that has no contraindications or side effects - the development is registered with the Ministry of Health and is approved for use at any age.
The kidney treatment belt developed by our company is necessary at any stage: for prevention, during treatment or after medical intervention. It prevents damage and disorders, relieves pain and regenerates tissue. At the same time, it is easy to use and does not require special skills - its use is accessible to anyone. Our belts for treating kidneys at home are simply necessary for people who have long and constantly experienced problems with the functioning of these organs. If you are already desperate and accustomed to living with pain and anxiety about your health, our modern development will give you a chance to feel good.
Terms and rules for testing assembly belts and manholes
Work (construction, painting, maintenance of lamps, etc.) can be carried out from the cradle of an automobile tower, provided that it is carried out safely and measures are taken to prevent people from falling from the cradle and being electrocuted.
Workers must put on protective clothing and arrange it in order so that it does not restrict movement and does not have loose or hanging ends. Work from the vehicle tower must be carried out by at least two workers (not counting the driver), one of whom must be a signalman. If two people work in the cradle, then a third person must be allocated - a signalman. The responsibilities of the signalman include:
Order 93
Belts submitted for testing are first inspected. As a result of the inspection, it should be established that the belt fabric has no local damage (cuts, burns, etc.), the rivet connection has no play, the stitching of the belt, belts and overlays is completely intact, the nylon sling has no broken threads, places the welds of the chain links and rings are smooth and free of burrs, the outer lock of the carabiner is in good working order, its surface is smooth without burrs, gouges, scratches and other similar defects.
A static load of 225 kg (depending on its design) is applied to the belt, fixed to a rigid support, for 5 minutes, while the breaking force can be obtained by hanging a load (operational tests) or in a tensile testing machine. The belt is considered to have passed the test if no damage is found during inspection and the carabiner is operating normally.
Are belts tested according to the new rules?
4.5.1. Safety belts are personal protective equipment for workers against falling when working at heights and steeplejack operations, as well as means of insuring and evacuating a person from dangerous areas. 4.5.2. Safety belts must comply with state standards and technical specifications for belts of specific designs. 4.5.3. Depending on the design, belts are divided into strapless and strapless, as well as belts with or without a shock absorber. 4.5.4. The design of the belt buckle (closing device) must exclude the possibility of incorrect or incomplete closure. The design of the carabiner should ensure that its lock can be opened with one hand. The carabiner must have a safety device that prevents its spontaneous opening. The lock and safety device must close automatically. 4.5.5. When working in electrical installations without removing voltage from live parts, you should use safety belts only with a sling made of synthetic materials. When working on an overhead line or in a switchgear with the removal of voltage from live parts, it is allowed to use belts with a sling made of steel rope or chain. When performing hot work, you should use belts with a sling made of steel rope or chain. 4.5.6. The static breaking load of the belt must be at least 7000 N for a belt with a shock absorber and at least 10,000 N for a belt without a shock absorber. The dynamic force during protective action for a strapless belt with a shock absorber should be no more than 4000 N, and for a shoulder belt with a shock absorber - no more than 6000 N. 4.5.7. The safety rope is an additional safety feature. Its use is mandatory in cases where the place of work is located at a distance that does not allow the belt to be secured to the structure of the equipment with a sling. For insurance, steel, cotton ropes or ropes made of nylon halyard are used. Steel ropes must comply with state standards. A cotton rope must have a diameter of at least 15 mm, a rope made of nylon halyard - no less than 10 mm, and their length - no more than 10 m. The breaking static load of a steel rope must correspond to that specified in the state standard, and that of a cotton rope and a rope made of nylon halyard - not less than 7000 N. Safety ropes can be equipped with carabiners.
4.5.9. Before starting work, the belt must be inspected to check the condition of it as a whole and of the load-bearing elements separately. A belt that has been subjected to a dynamic jerk, as well as a belt that has thread breaks in the stitching, tears, burns, cuts in the waist belt, sling, shock absorber, violations of rivet joints, deformed or corroded metal components and parts, cracks in metal parts must be removed from service. and safety latch malfunction. Self-repair of belts is not allowed. 4.5.10. Belts and ropes should be stored in dry rooms in the absence of aggressive environments, at a distance from heat-generating devices, in a suspended state or laid out on shelves in one row. After work, as well as before storage, they must be cleaned of dirt, dried, metal parts must be wiped, and leather parts must be greased.
GOST R 50849-96 Construction safety belts
2.9 A lanyard is an integral element of a belt, consisting of a halyard and one carabiner rigidly attached to its end, or a halyard and two carabiners attached to both ends, which serves to directly (or through a connecting element) secure a person to a support. - buckle, connecting rings, carabiners used to connect or adjust the length of shoulder or hip straps - 5 kN (500 kgf);
- load-bearing elements and parts of a belt of type G, except for shoulder chest straps, the strength of which is established in the technical specifications for belts of specific designs - 3 kN (300 kgf).
Inspection and testing of mounting belts
The static load on the belt as a whole is checked as indicated in Figure 1. Individual elements of the belt are tested for compliance with the standard, as indicated in Figures 2 and 3. The belt without shock absorber passes the test if it does not collapse or break completely or partially under a static load of 10 kN , which corresponds to 1000 kgf. The belt with a shock absorber must withstand a load of 7 kN, which corresponds to 700 kgf, without rupture or destruction. Minimum load that individual elements of the mounting belt must withstand:
Construction protective belts must also withstand the dynamic load that occurs when a load weighing 100 kg (plus or minus 1 kg) falls from a height equal to two maximum sling lengths. Testing of the mounting belt for compliance with these requirements is carried out according to the diagrams shown in Figures 4 and 5. The free fall height of the dummy load must correspond to two lengths of the sling.