HSS (High Speed Steel) - denotes a group of high-speed steels, translated as steel for working at high speeds. HSS steel is used to produce a wide range of different metal-cutting tools. This includes twist drills, core drills, step drills, cutters, countersinks, taps, dies, knives and saw blades.
High-speed steel is produced in the classical way - by casting steel into ingots, then rolling and forging, as well as by powder metallurgy - here a jet of liquid steel is sprayed with nitrogen. HSS steels are considered high carbon, typically HSS steel tools have a hardness of 62-64 HRC. The main advantage in comparison with carbide tools is the durability and lower price of the tools. HSS steel performs well in interrupted cutting; the use of HSS may be limited by low cutting speeds compared to carbide alloys.
Characteristics of HSS steels
HSS steels are divided into three main groups:
- Tungsten (T);
- Molybdenum (M);
- High-alloy high-speed steels.
Tungsten steels are now practically not used due to the high price of tungsten and its shortage. The most commonly used steels are T1 general purpose steels and T15 vanadium-cobalt steels. T15 is used for tools used at high temperatures and increased wear.
In molybdenum group steels, the main alloying element is molybdenum, but some of them may contain equal or even greater amounts of tungsten and cobalt. Steels with high vanadium and carbon content are very resistant to abrasive wear. The type of steel from M41 is characterized by high hardness when working at high temperatures, or the term used is red resistance. Molybdenum steels are also used in the production of tools used in “cold” conditions - rolling dies, cutting dies. In such cases, HSS steels are hardened to lower temperatures to increase toughness.
Table of common chemical compositions of HSS steels. Russian analogues.
| Type | Russian analogue | Chemical composition, % | ||||||||
| C | Mn | Si | Cr | V | W | Mo | Co | Ni | ||
| Tungsten HSS steels | ||||||||||
| T1 | P18 | 0,75 | — | — | 4,00 | 1,00 | 18,00 | — | — | — |
| T2 | R18F2 | 0,80 | — | — | 4,00 | 2,00 | 18,00 | — | — | — |
| T4 | R18K5F2 | 0,75 | — | — | 4,00 | 1,00 | 18,00 | — | 5,00 | — |
| T5 | 0,80 | — | — | 4,00 | 2,00 | 18,00 | — | 8,00 | — | |
| T6 | 0,80 | — | — | 4,50 | 1,50 | 20,00 | — | 12,00 | — | |
| T8 | 0,75 | — | — | 4,00 | 2,00 | 14,00 | — | 5,00 | — | |
| T15 | R12F5K5 | 1,50 | — | — | 4,00 | 5,00 | 12,00 | — | 5,00 | — |
| Molybdenum HSS steels | ||||||||||
| M1 | 0,80 | — | — | 4,00 | 1,00 | 1,50 | 8,00 | — | — | |
| M2 | R6M5 | 0,85 | — | — | 4,00 | 2,00 | 6,00 | 5,00 | — | — |
| M3 | R6M5F3 | 1,20 | — | — | 4,00 | 3,00 | 6,00 | 5,00 | — | — |
| M4 | 1,30 | — | — | 4,00 | 4,00 | 5,50 | 4,50 | — | — | |
| M6 | 0,80 | — | — | 4,00 | 2,00 | 4,00 | 5,00 | — | — | |
| M7 | 1,00 | — | — | 4,00 | 2,00 | 1,75 | 8,75 | — | — | |
| M10 | 0,85-1,00 | — | — | 4,00 | 2,00 | — | 8,00 | — | — | |
| M30 | 0,80 | — | — | 4,00 | 1,25 | 2,00 | 8,00 | — | — | |
| M33 | 0,90 | — | — | 4,00 | 1,15 | 1,50 | 9,50 | — | — | |
| M34 | 0,90 | — | — | 4,00 | 2,00 | 2,00 | 8,00 | — | — | |
| M35 | R6M5K5 | 0,82-0,88 | 0,15-0,40 | 0,20-0,45 | 3,75-4,50 | 1,75-2,20 | 5,5-6,75 | 5,00 | 4,5-5,5 | up to 0.30 |
| M36 | 0,80 | — | — | 4,00 | 2,00 | 6,00 | 5,00 | — | — | |
| High alloy HSS steels | ||||||||||
| M41 | R6M3K5F2 | 1,10 | — | — | 4,25 | 2,00 | 6,75 | 3,75 | 5,00 | — |
| M42 | 1,10 | — | — | 3,75 | 1,15 | 1,50 | 9,50 | 8,00 | — | |
| M43 | 1,20 | — | — | 3,75 | 1,60 | 2,75 | 8,00 | 8,25 | — | |
| M44 | 1,15 | — | — | 4,25 | 2,00 | 5,25 | 6,25 | 12,00 | — | |
| M46 | 1,25 | — | — | 4,00 | 3,20 | 2,00 | 8,25 | 8,25 | — | |
| M47 | R2AM9K5 | 1,10 | — | — | 3,75 | 1,25 | 1,50 | 9,5 | 5,00 | — |
| M48 | 1,42-1,52 | 0,15-0,40 | 0,15-0,40 | 3,50-4,00 | 2,75-3,25 | 9,50-10,5 | 0,15-0,40 | 8,00-10,0 | up to 0.30 | |
| M50 | 0,78-0,88 | 0,15-0,45 | 0,20-0,60 | 3,75-4,50 | 0,80-1,25 | up to 0.10 | 3,90-4,75 | — | up to 0.30 | |
| M52 | 0,85-0,95 | 0,15-0,45 | 0,20-0,60 | 3,50-4,30 | 1,65-2,25 | 0,75-1,50 | 4,00-4,90 | — | up to 0.30 | |
| M62 | 1,25-1,35 | 0,15-0,40 | 0,15-0,40 | 3,50-4,00 | 1,80-2,00 | 5,75-6,50 | 10,0-11,0 | — | up to 0.30 | |
A tool containing tungsten (W) will have very useful cutting properties and such qualities as red resistance. This allows the tools to maintain sharp hardness and a sharp cutting edge at red-hot temperatures (up to 530°C). Cobalt (K) further increases red-hardness and wear resistance.
M1.
Used for the production of drills for various applications. M1 steel has less red resistance than M2 steel, but is less susceptible to impacts and is more flexible.
M2.
The most common material for the production of tools is HSS steel. M2 retains its cutting edge for a long time and has good red resistance, unlike other HSS steels with lower tungsten content. It is usually used for the manufacture of tools for high-performance machine work, for example in drilling machines.
M7.
Used for heavy construction drills when drilling hard sheet metal. This HSS steel is used where flexibility and increased service life are required.
M50.
Used to make drills that are used for drilling on portable equipment. Does not have the same red resistance as other tungsten HSS steels
M35.
M35 steel has a higher red resistance compared to M2. At the same time, cobalt slightly reduces the resistance to impact loads.
M42.
M42 “Super Cobalt” steel has excellent abrasion resistance and high red-hardness. Used when working on viscous and complex materials.
Standards
| Name | Code | Standards |
| Long and shaped rolled products | B22 | GOST 1133-71, GOST 2590-2006, GOST 2591-2006, GOST 2879-2006 |
| Test methods. Package. Marking | B09 | GOST 11878-66 |
| Sheets and strips | B23 | GOST 19903-74, GOST 19904-90, GOST 103-2006, GOST 19903-90 |
| Sheets and strips | B33 | GOST 4405-75, GOST 7350-77 |
| Classification, nomenclature and general norms | B30 | GOST 5632-72 |
| Long and shaped rolled products | B32 | GOST 5949-75, GOST 7417-75, GOST 8559-75, GOST 8560-78, GOST 14955-77, TU 14-11-245-88, TU 14-1-1529-2003 |
| Steel pipes and connecting parts for them | B62 | GOST 9940-81, GOST 9941-81, GOST 14162-79, TU 14-159-165-87, TU 14-3-1109-82, TU 14-158-135-2003, TU 14-3-460-2009 , TU 14-3Р-110-2009, TU 14-3Р-55-2001, TU 14-158-137-2003, TU 14-3-460-2003, TU 14-3-1654-89 |
| Blanks. Blanks. Slabs | B31 | OST 3-1686-90, OST 95-29-72, TU 108-938-80, TU 14-1-1214-75, TU 14-1-565-84 |
| Welding and cutting of metals. Soldering, riveting | B05 | OST 95 10441-2002 |
| Castings from non-ferrous metals and alloys | B84 | RD 9257-76 |
| Thermal and thermochemical processing of metals | B04 | STP 26.260.484-2004 |
Legend
The designation of foreign manufacturers does not fully disclose the chemical composition of the HSS steel from which the products are made. A particular tool is assigned a specific task, which is described in the catalog. Other details can be found out by determining the chemical composition, this can be done using a portable metal analyzer, or by testing the products experimentally. Such marking, of course, may be convenient for an unscrupulous manufacturer who may indicate HSS steel on the drill, but it will not meet the necessary requirements. Below are the main markings that characterize the material from which the tool is made and its scope of application.
HSS-R
(or simply HSS) is a designation on products that have undergone roller rolling and heat treatment. Such products have the lowest durability.
HSS-G
- designation on products that are made of HSS steels, the cutting part is ground with CBN (cubic boron nitride). The products have increased durability and less radial runout. HSS-G tools are the most common and are used to solve standard problems.
HSS-E
– cobalt is added to products made from HSS steel type M35. Used when working on viscous and complex materials. There are also such markings as HSS Co 5 and HSS Co 8, which indicate cobalt content of 5 and 8%
HSS-G TiN
– this marking indicates the deposition of titanium nitride. This coating allows increasing surface hardness by approximately 2300 HV and heat resistance up to 600°C.
HSS-G TiAlN
— surface of products coated with titanium-aluminum-nitride. This coating allows increasing surface hardness by approximately 3000 HV and heat resistance up to 900°C.
HSS-E VAP - VAP
-used for processing stainless steels (V2A and V4A). It is obtained by “evaporating” the oxide non-metallic layer. This reduces the adhesion of workpiece chips to the tool surface, which can lead to product failure. As a result, the surface quality is improved and, thanks to VAP, the adhesion of the coolant to the tool surface is improved.
| Characteristics of heat resistance of carbon and red resistance of high-speed tool steels | |||
| steel grade | Temperature, °C | Exposure time, hour | Hardness, HRC e |
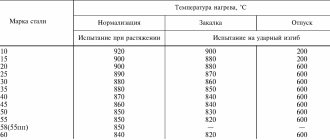
| U7, U8, U10, U12 | 150—160 | 1 | 63 |
| P9 | 580 | 4 | |
| U7, U8, U10, U12 | 200—220 | 1 | 59 |
| R6M5, R6M5K5, R9, R9M4K8, R18 | 620—630 | 4 | |
Mechanical properties of material 12Х18Н12Т according to GOST 5949-2018
| Heat treatment mode | Temporary tensile strength, σв, MPa, min | Yield strength, σ0.2, MPa, min | Elongation at break, δ5, % | Relative narrowing, ψ, % |
| Quenching at 1020-1100 ºС, cooling in air, oil or water | 540 | 196 | 40 | 45 |
Depending on the type of operation of parts made of steel 12Х18Н12Т, they are subjected to various processing operations to improve their properties.
- Austenization
- to prevent intergranular and knife corrosion and increase the ductility of steel. - Stabilization
(annealing) - to reduce the risk of corrosion, or local annealing in the weld area. - Step processing
– prevents corrosive destruction of the product operating in an aggressive environment and in acidic vapors.
Cutting of steel 12Х18Н12Т is carried out in a hardened state at HB 170. Products made of steel 12Х18Н12Т have restrictions on weldability and require subsequent heat treatment. Forging of steel 12Х18Н12Т is performed at temperatures of 1200°C–850°C
. Products with sections up to 350 mm are cooled in air.
DIY file handles
Real craftsmen equip their existing tools with handles made by themselves. With the advent of plastics, there was a wider choice of materials for homemade products.
If you have a lathe, then the handle can be turned from hardwood: walnut, birch, ash. There are quite a lot of drawings on the Internet, using which a suitable handle is made.
Some craftsmen use epoxy resin to make unusual handles.
- First, possible porous materials that can be impregnated with epoxy resin are selected. Most often, fabrics of different colors are used. Micarta is created - a multi-layer fabric impregnated with epoxy.
- They are placed in the desired sequence.
- The epoxy resin is diluted according to the attached recipe.
- Wet each layer.
- Lay in the chosen sequence and place under a press.
- After polymerization is completed, a new material is formed - micarta.
- A file handle is made from micarta.
Video: “Cuban” files.
Analogs
In many countries, a little later than in America, alloys similar in composition and characteristics to D2 steel began to appear. Russia also did not stand aside. The alloys are practically no different from the original sample. And sometimes they surpass it in some indicators. List of analogues:
- X155CrMo12 – analogue of D2 steel in Germany;
- 2379 – steel marking, according to the European designation system;
- SLD – Japanese equivalent;
- SKD-11 – steel marking in Sweden;
- X12MF is an analogue of steel in Russia.
Historical reference
Historically, the alloy belongs to the group of high-carbon and high-chromium steels. Such steel began to be produced back in 1821 in America. The first patent for the alloy was received by Julius Baurum in 1865 in New York. But the use of steel was not found for 70 years.
The problem was forging the metal. During this process, many cracks appeared in the steel structure. And only over time, people learned to process metal correctly. It was not until 1928 that the first patent was issued for a composition that was very close to D2 steel.
And already in 1934, steel was produced with the composition: 1.55% C (carbon), 12% Cr (chromium), 0.25% V (vanadium) and 0.8% Mo (molybdenum). Where alloying impurities improved the characteristics of the alloy when hardening the product. D2 steel gained real popularity during World War II.
It was used on stamping lines. The parts of military aircraft and cars came off the assembly line. It was also used for cutting simpler alloys. In peacetime, knife makers liked steel. Today blades of various directions are made from it.
Comparison of steel with analogues
D2 steel is often compared to Russian-made tool steel X12MF. They are as similar as possible to each other. Functional and production aspects are quite similar. But the controversy surrounding this comparison continues.
No one can give an exact answer as to which steel is better. There are also analogues of D2 steel. These are the following varieties: AUS-8, K110 and 440C. In practice, no one undertakes to compare them. The only thing to consider when purchasing a knife is its cost.
Purpose of files
A file is a universal-purpose hand tool capable of cutting off a thin layer from the surface of the material being processed with one forward movement. It can be used to solve many different problems:
- Clean parts and workpieces from rust and other types of corrosion.
- Remove a layer of dirt or paint.
- Turn the part until the required size is obtained.
- Sharpen other tools used in everyday work.
- Clean electrical contacts in electrical equipment systems.
- Grind and polish the surface of metal and other materials.
Types of notches on the surface of the tool
Based on the nature of the notches, it is customary to speak of a single or double design.
Single execution is more common with rough instruments. Here the tooth has a long cutting edge. Its length corresponds to the width of the file. To make it easier to penetrate into the thickness of the metal being processed, the notch is made inclined at an angle of 25⁰. The result is cutting with some displacement. It makes it easier to penetrate deeper into the part. The effort is slightly reduced.
The double design of the notches is made at an angle to each other. The second cut is made at an angle of 45⁰. Now the cutting teeth are limited in length. Where the lines intersect, places where chips break are formed. Consequently, such files require less physical effort during operation (no need to waste effort on twisting long shavings).
Steel grades for hunting knives
Steel grades for hunting knives
For hand forging a hunting blade, a good option would be to choose the 9XC grade. A knife made of this steel will have good cutting qualities and will also hold an edge perfectly. Steel 95X18 perfectly combines high quality and affordable price, has high strength and hardness, but because of this the blade is difficult to sharpen. The X12MF grade will allow you to create a very durable, wear-resistant hunting blade, provided that it is carefully cared for. Based on this brand, many domestic manufacturers produce damask steel, which indicates the quality characteristics of this brand.
Damascus knives are an excellent option for hunting or hiking. Damascus is very durable and resistant to corrosion. Thanks to the high carbon content of Damascus, the blade is very sharp, but also fragile enough to do household work.
The domestic brand 65G is suitable for making a hunting knife, the purpose of which is not cutting, but chopping. It has excellent viscosity, but should be protected from moisture, because metal is susceptible to corrosion.
Definition and purpose of files
This name is given to a large group of tools designed to work with metal. When producing them, GOST must be taken into account. Among the features we note the following:
- The working part is represented by a metal part with notches. In this case, the form may differ significantly.
- A metal rod is attached to the handle.
Due to the notches during the reciprocating movement, metal processing occurs, chips are formed, which are then removed.