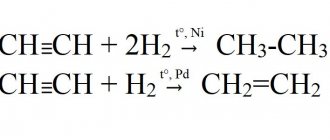C2H2 acetylene. Properties of acetylene. Preparation of acetylene.
Properties of acetylene.
The most widely used flammable gas for oxy-fuel cutting is acetylene, which is a chemical compound of carbon and hydrogen ( C2H2 ).
At normal temperature and pressure, acetylene is in a gaseous state. Chemically pure acetylene is a colorless gas with a weak ethereal odor and a slightly sweet taste. Technical acetylene, used for oxygen cutting, due to the presence of certain impurities in it (hydrogen sulfide, ammonia, hydrogen phosphorous, etc.), has a strong unpleasant odor and is harmful to the human body.
At a pressure above 2 kg/cm2, acetylene in large volumes acquires the properties of an explosive gas and, upon contact with a heated surface or from an electric spark, explodes, with the temperature reaching 3000°C and the pressure increasing by more than 10 times.
With oxygen and air, acetylene forms explosive mixtures that explode when exposed to fire. Acetylene - air mixture is explosive in the presence of from 2.3 to 81% acetylene in the air. Even more dangerous is the acetylene-oxygen mixture, which explodes from fire when the oxygen content is from 2.3 to 93% acetylene, while the speed of propagation of the blast wave reaches 3000 m/sec, so you need to especially carefully monitor the density of all acetylene devices and pipelines etc.
Also read: What are the properties of oxygen. Weight of 1 m3 of oxygen. Weight of liquid oxygen. Methods for obtaining oxygen.
The explosiveness of acetylene is greatly reduced when placed in capillary (very thin) channels. This property of acetylene is used when filling cylinders under pressure - acetylene cylinders are filled with a special porous mass.
Reaction of acetylene with acetone.
Acetylene is highly soluble in many liquids, especially acetone . In one volume of acetone at 15°C and normal pressure, 23 volumes of acetylene are dissolved, and at elevated pressure - proportionally more. This property of acetylene is also used when filling cylinders. The solubility of acetylene in acetone largely depends on temperature: with increasing temperature, the solubility decreases, and with decreasing temperature it increases sharply.
The ability of dissolved acetylene to explode is reduced.
Acetylene combustion reaction.
Acetylene, when burned in a mixture with pure oxygen, produces a flame with a temperature of 3050 - 3150 ° C, and when burned in a mixture with air, it produces a flame with a temperature of 2350 ° C.
Complete combustion of acetylene.
For complete combustion of 1 m3 of acetylene, 2.5 m3 of oxygen or 12.5 m3 of air is required.
Acetylene is lighter than oxygen and air. Specific gravity of acetylene at 0°C and 760 mm Hg. Art. 1.17 kg/m3.
With prolonged interaction with red copper and silver, acetylene produces compounds that explode when heated or upon strong impact. Therefore, in the manufacture of acetylene equipment and fittings, the use of silver solders and red copper in their pure form is prohibited. Only technical copper alloys containing no more than 70% copper are allowed.
Preparation of acetylene.
The main industrial method for producing acetylene is the decomposition of calcium carbide with water. Calcium carbide is a chemical compound of calcium with carbon ( CaC2 ) and is a dark gray or grey-colored solid.
Technical calcium carbide is obtained by fusing quicklime with coal (coke or anthracite). The charge, consisting of a mixture of coal and lime in a certain proportion, is immersed in an electric arc furnace, where, under the influence of the heat of the electric arc, it melts to form calcium carbide.
Molten carbide is poured from the furnace into molds, in which it solidifies. The solidified calcium carbide is then crushed, sorted into pieces of certain sizes and packaged in special drums for storage and transportation. Drums for packaging calcium carbide are made of sheet iron with a thickness of at least 0.5-0.6 mm with a hermetically sealed lid. Corrugations are rolled onto the cylindrical surface of the drums to increase their strength. The drum holds 50-130 kg of calcium carbide.
Carbide drums should be opened very carefully, since for one reason or another moisture may penetrate inside the drum and an explosive acetylene-air mixture may form. It is best to cover the drum cover with a layer of grease and remove it with a special knife . Under no circumstances should you resort to hammer blows.
When uncorking carbide drums, it is strictly forbidden to use a flame or cut out the drum cover with a chisel.
Acetylene decomposition.
When exposed to water, calcium carbide decomposes, forming acetylene and slaked lime. The reaction proceeds according to the equation
CaC2 + 2H2O = C2H2 + Ca(OH)2
and is accompanied by significant heat release.
Calcium carbide, when in contact with atmospheric air containing water vapor, decomposes with the release of acetylene. From 1 kg of calcium carbide usually produces from 230 to 300 liters of acetylene.
The decomposition of 1 kg of calcium carbide theoretically requires 0.56 liters of water . The decomposition reaction of carbide proceeds with the release of a large amount of heat, so a lack of water can lead to significant overheating and even ignition of acetylene at the site of carbide decomposition. To avoid this, the carbide decomposition process is always carried out with an excess amount of water, which is used for cooling. Almost 1 kg of calcium carbide requires 5 to 20 liters of water.
Was the article useful?! Share with your friends on social networks!!!
Combustion of acetylene water gas
Acetylene is used in industry as a fuel for gas welding and metal cutting, and also as a raw material for various chemical industries.
Acetylene is a chemical compound of carbon and hydrogen. Technical acetylene is a colorless gas with a sharp, characteristic odor. Inhaling it for a long time causes dizziness, nausea and can lead to poisoning. Acetylene is lighter than air and dissolves well in various liquids. It dissolves especially well in acetone. Acetylene, when burned in a mixture with pure oxygen, produces a flame with a temperature of 3050-3150 ° C. It is an explosive gas.
Acetylene explodes under the following conditions:
1) with an increase in temperature above 500 ° C and pressure above 1.5 at\
2) a mixture of acetylene and oxygen with a content of acetylene from 2.8 to 93% explodes at atmospheric pressure from a spark, flame, strong local heating, etc.;
3) under the same conditions, the acetylene-air mixture explodes when it contains from 2.8 to 80.7% acetylene;
4) with prolonged contact of acetylene with copper or silver, explosive acetylene copper or acetylene silver is formed, which explode upon impact or increased temperature.
An acetylene explosion is accompanied by a sharp increase in pressure and temperature and can cause serious accidents and significant damage.
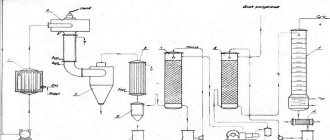
When acetylene is placed in narrow channels, its ability to explode with increasing pressure is significantly reduced. In industry, acetylene is obtained by decomposing calcium carbide with water in special devices - acetylene generators. The technical acetylene obtained in this way usually contains harmful impurities: hydrogen sulfide, ammonia, hydrogen phosphide, silicon hydrogen, which give acetylene a pungent odor and impair the quality of welding. Impurities are removed from acetylene by washing in water and chemical cleaning with special cleaning agents. In addition, acetylene may contain water vapor and mechanical particles (lime and coal dust). To remove moisture, acetylene is dried. Dust is removed using a fabric filter. For welding, acetylene can be taken from an acetylene pipeline coming from an acetylene generator station, or directly from a single-station generator. Acetylene can also be supplied in cylinders under 16 at pressure, dissolved in acetone.
In addition to acetylene, other flammable gases or vapors of flammable liquids can be used when welding and cutting metals: hydrogen, petroleum gas, gasoline vapors, kerosene, etc.
Hydrogen is a flammable, colorless and odorless gas. Hydrogen is one of the lightest gases. The flame temperature during combustion in oxygen is 2300° C. Hydrogen easily ignites and in a certain mixture with oxygen or air produces an explosive mixture, which is called detonating gas. Therefore, when carrying out welding and cutting work with hydrogen, it is necessary to strictly follow safety regulations to avoid explosions. Hydrogen is produced by decomposing water with electric current. It is stored and transported in steel cylinders in gaseous form under a pressure of 150 atm.
Propane-butane mixture is obtained during the extraction and processing of natural petroleum gases and oil. The flame temperature during combustion of the mixture in oxygen reaches 2100° C.
At low pressure, mixtures of propane and butane liquefy. They are stored and transported in steel cylinders with a capacity of 33 and 45 kg under a pressure of up to 16 atm, filled with a liquid mixture to half the volume, since when the cylinder is heated, the pressure can increase significantly, which can lead to an explosion of the cylinder. The mixture is used for cutting, soldering, hardening, welding lead, aluminum and thin steel.
Petroleum gas is a mixture of flammable gases, has an unpleasant odor, and is colorless. Obtained from the processing of oil and petroleum products. The flame temperature during combustion in oxygen is 2300° C. It is stored and transported in a gaseous state in cylinders under a pressure of 150 at. At this pressure it partially liquefies. An oil gas cutting and welding machine requires an evaporator. Used for cutting, soldering, hardening, welding steel up to 2-3 mm thick, welding brass, lead, aluminum.
Coke oven gas is a gaseous mixture of flammable products obtained at coke plants when coke is produced from coal. The flame temperature during combustion in oxygen is about 2000° C.
Delivered to the welding site via a gas pipeline or in cylinders under a pressure of 150 at. Coke oven gases are contaminated with cyanide compounds, which can lead to poisoning. Therefore, they are thoroughly cleaned before use. Used for cutting, soldering and welding low-melting metals.
Methane at normal temperature and pressure is a colorless gas. Methane is found in large quantities in natural gases, where its content reaches 95-98%, the flame temperature during combustion in oxygen is 1850 ° C for Dashavsky and 2000 ° C for Saratov gas.
Natural gases are usually supplied to places of consumption through pipelines and are relatively rarely transported in a gaseous state in cylinders under a pressure of 150 atm. Used for welding low-melting metals, cutting and soldering.
City gas (Moscow) is a mixture of coke oven, oil and natural gases. It is obtained by gasification of solid fuel. The flame temperature during combustion in oxygen is about 2000° C.
Low-melting metals are supplied to places of consumption for cutting and welding through gas pipelines or in compressed form in cylinders under a pressure of 150 at.
Gasoline is a transparent liquid that evaporates easily. Gasoline vapors, when burned in oxygen, give a temperature of 2400° C. Gasoline is obtained by refining oil. Stored and transported in liquid form in vessels at atmospheric pressure. Special equipment is used for welding and cutting. Gasoline is more often used for cutting than for welding.
Kerosene for gas-flame processing is used, like gasoline, in the form of vapor. For this purpose, special burners and cutters equipped with evaporators are used. Kerosene-oxygen flame has a lower temperature (2700°C) than gasoline-oxygen flame. Nevertheless, kerosene is widely used in gas cutting.
It should be borne in mind that all the gases discussed, as well as gasoline vapors, are explosive.
Source
Storage and safety precautions
Acetylene should be stored indoors away from oxygen and flammable gases. Do not allow the gas to come into contact with silver or copper. In a storage room, not only the gas content in the air must be controlled. It is advisable to always keep an eye on the pressure and temperature. When the pressure rises to a critical level, acetylene explodes. The same thing happens when the temperature rises.
Where acetylene is stored and used, open flame sources are prohibited. The premises must always be maintained at an optimal temperature. Fires are especially dangerous in such places. If a fire suddenly occurs, acetylene cylinders should be cooled and removed. In some cases, acetylene leaks occur. To avoid an explosion, you need to use a special non-sparking key and close the cylinder.
When extinguishing, it is better to use asbestos cloth, sand, fire extinguishers containing nitrogen and carbon dioxide. In case of severe fires, it is necessary to extinguish the fire from a distance and be sure to use a special protective suit.
To prevent accidents, gas cylinders must be checked regularly. They must be sealed. You can recognize a gas leak by smell and characteristic noise.
Acetylene combustion
Acetylene combustion occurs according to the reaction: C2H2 + 2.5O2 = 2CO2 + H2O + Q1
For complete combustion of 1 m3 of acetylene according to the above reaction, 2.5 m3 of oxygen or = 11.905 m3 of air is theoretically required. In this case, heat is released Q1? 312 kcal/mol. Higher calorific value 1 m3 C2H2 at 0°C and 760 mm Hg. Art., determined in a gas calorimeter, is QB = 14000 kcal/m3 (58660 kJ/m3), which corresponds to the calculated:
312?1.1709?1000/26.036 = 14000 kcal/m3
The lower calorific value under the same conditions can be taken as QH = 13500 kcal/m3 (55890 kJ/m3).
Storage and transportation of acetylene
Acetylene is produced in accordance with GOST 5457 dissolved and gaseous. It is stored and transported in a dissolved state in special steel cylinders in accordance with GOST 949, filled with a porous mass impregnated with acetone. Acetylene dissolved in acetone is not prone to explosive decomposition.
The cylinders are painted gray with the inscription “ACETYLENE” in red letters on the top cylindrical part.
The maximum pressure of acetylene when filling the cylinder is 2.5 MPa (25 kgf/cm2); when the cylinder settles and cools to 20°C, it decreases to 1.9 MPa (19 kgf/cm2). At this pressure, a 40-liter cylinder holds 5-5.8 kg of C2H2 by mass (4.6-5.3 m3 of gas at 20°C and 760 mm Hg).
The pressure of acetylene in a fully filled cylinder changes with temperature as follows:
| Temperature, °C | -5 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 30 | 40 | |
| Pressure, MPa | 1,3 | 1,4 | 14 | 1,7 | 1,8 | 12 | 2,4 | 3,0 |
Other safety requirements can be found in the article on the hazard class and safety measures when working with acetylene