- home
- Information
- Articles
- Drill chucks: quick-release and keyed
Back to list
Cam drill chucks for machine tools and hand tools are the same in design - both use a jaw clamp to secure the drill shank. The chuck is attached to the spindle using a threaded connection, an external or internal Morse taper, a Weldon adapter and other methods. In our catalog you can choose and buy quick-release and key drill chucks for the desired shank diameter, adapters for different mounting options to the spindle, equipment for specific equipment and universal models for machine tools, drills, and screwdrivers.
Description and use of cartridges
The drill chuck is used for drilling both with hand tools (this includes a drill or screwdriver and hammer drill), and on various machines. These cartridges are produced according to European and domestic standards. The devices must meet the requirements of fastening rigidity, radial runout of the standard size required for drilling, depending on the size of the drill, as well as the density of the material. The stiffer it is, the greater the load on the drill will be. And if the chuck is selected incorrectly, the drill will break.
Drilling machine chucks are divided into 2 large groups according to the type of fastening:
- Chucks that match the mounting hole in the lathe for taper fastenings.
- Chucks that have a threaded connection to the machine.
Types of tool fixation
There are several main types of tool holders for drilling machines:
- Three-jaw chuck for clamping a cylindrical shank.
- Double jaw chuck. Used for light loads and small diameter tools.
- Quick change devices with tapered shank.
- Self-aligning locking devices. Used for boring pre-drilled holes.
- Safety clamps are used to work with taps when preparing threads.
- Reversible chucks for drilling machines. Used when cutting threads on equipment without spindle rotation.
Fast-acting self-clamping drill chuck
The mechanism of standard chucks does not guarantee good centering and strong fastening of the clamped cutting device, which, of course, costs time when the tool is frequently changed during operation.
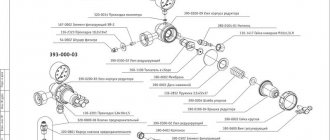
The drill chuck consists of the following elements: a housing, in which, thanks to the nut, there is a cage, as well as a screw shank with a left-hand thread. There is a ball bearing between the nut and the shank. In the frame, 3 grooves are milled at equal intervals from each other, and cams are placed in them. There are 3 radial L-shaped grooves cut on the top of the screw, provided for a movable radial connection of the cams with the screw.
When the shank rotates relative to the chuck body, the screw is unscrewed or screwed in and transmits axial as well as radial movement to the cams, forcing them to slide both inside the body cone and along the side of the holder. This method carries out combined axial and radial movement of the cams and clamps or releases the device.
When drilling, the shank rotates clockwise in the drill chuck body and unscrews the screw, which displaces the cams and strengthens the clamping of the drill. When changing the drill, you need to support the shank and rotate the core counterclockwise, while the screw moves the cams and opens them. Using a ball bearing, you can quickly release the part, even when the part is tightly tightened.
General operating rules
To ensure accuracy when performing work, durability of equipment, tools and equipment, it is recommended to follow the rules of safe operation:
- Select the chuck based on the minimum and maximum diameter of the tool shank.
- When choosing a chuck, take into account its design, pay special attention to the methods of connection to the spindle (cone number) and fixation of the tool.
- Use a variety of adapter bushings to secure the chuck and tools. When installing, make sure the surface of the cone is clean.
- Before drilling, mark the center of the future hole with a core.
- When selecting a drill, take into account the vibration of the chuck, which increases the resulting diameter by 0.05 - 0.3 mm. For high-precision drilling, use precision chucks.
- Use vices, prisms and other clamps for workpieces.
- Use coolant to cool the tool and extend its life.
- When drilling large diameter holes, use a smaller tool and then drill out.
Purpose of these cartridges
Drill chucks are divided into several types. They come with a mechanical clamp or self-clamping, in addition, they differ depending on the cutting device being fixed:
- A drill chuck with a cone is divided into several types: B16, B18, B24, B32, etc. And if it is necessary to interact the cone with the spindle (first it must fit exactly to the inner hole of the latter), this chuck is already combined with it. In addition, some self-clamping drill chucks with a cone in the tail were specially produced for precise connections.
- A self-clamping drill chuck is a very precise device that can spontaneously clamp a cutting device with a cone-shaped shank. These chucks are also used on numerically controlled machines, as well as on jig boring and vertical drilling machines.
- Chucks that interact with core drills. They are used to secure core drills. Compared to spiral ones, these drill holes of large diameter in a very short time. The process is not only fast, but also very accurate.
Disassembling and assembling cartridges
There are times when a cartridge requires detailed cleaning to continue its normal service life. Almost anything can be taken apart, but not put back together. A quick-release fastener often has a casing under which its components are hidden. In this case, disassembly or surface cleaning of the parts will have to be determined by removing the plastic casing.
Most often, you can disassemble it using brute physical force, holding it in a vice and tapping it on the back with a hammer. This method is applicable for prefabricated structures, the parts of which are made of thick metal, but not from a single piece of metal.
It will not be possible to disassemble a cam quick-clamp, where the crown and the holder form a monolith, using force alone. Due to its design, a heating tool may be required. For example, a construction hair dryer can heat the metal up to 250 ⁰ C. Before inserting the cartridge with a rotating ring into a vice, you need to hide its jaws inside. Heating of the rotating ring must be done from the outside, cooling it from the inside with the help of a cotton material inserted inside, which is periodically poured with cold water while the part is heating.
After sufficient heating temperature, you can knock the base out of the ring, which will remain in the vice. During assembly, the part will also need to be heated.
Features and description of the 16 mm cartridge
Let’s take a separate look at the 16 mm quick-release drill chuck. It is specially designed for high-precision machines operating at high speeds. The inner cone of this cartridge has a diameter of 16 mm.
Its peculiarity is that, thanks to additional mandrels designed for placement on drill chucks, it makes it possible to install a chuck with a cone inside on a chuck with a cone outside.
Classification
- The quick change drill chuck is used with a replaceable sleeve for taper shank drills;
- The safety chuck for cutting threads in blind and through holes has a more complex structure. It consists of clutch cams, driven coupling halves, main clutch cam, spring and adjusting nut. It is used as a holder for notes.
- A collet drill chuck consists of a shank connected to a cylindrical part. There is a split sleeve between the clamp and the shank inside the chuck.
- The double-jaw drill chuck clamps the drill using internal hooks at the top of the chuck, secured by a spring. This explains its peculiarity of use for thin drills and use with low loads on the drill.
Only drill chucks with a key that have a Morse taper have the corresponding requirements in accordance with GOST 8522-79; having met the GOST indication, the compliance with the size of the Morse taper used for a given size can be determined from the table. The quick-clamp does not have a cone, but unlike its counterpart with a key, it has an internal thread, the range of which must be indicated in the marking.
Three-jaw
The marking most often looks like this (on products from Russian manufacturers):
- PSK 3-16 indicates the range of drill diameters in mm;
- KM B12; B16; B18 – which indicates the Morse cone of the connecting hole;
- GOST 8522-79 - this designation in the marking clearly indicates compliance with all parameters in the table compiled in 1979.
Download GOST 8522-79 “Three-jaw drill chucks”
The marking on the quick-clamping tool only indicates the size of the internal thread and the range of diameters of the clamped drills.
A three-jaw chuck for a drilling machine, with a key to fix the drill, complies not only with GOST 8522-79, but its Morse taper meets the CMEA 148-75 standards. What makes drill chucks manufactured in Russia in accordance with GOST 8522-79 suitable for drilling machines from foreign manufacturers working according to international standards.
Dimensions according to GOST 8522-79 are a strict indication of compliance with the standard size in terms of clamping range and permissible radial runout. At the same time, compliance with the basic parameters is not an indication of a specific design. Drill chucks can look different:
- according to the shape and length of the working part;
- the presence or absence of a plastic protective casing;
- the method of attaching the main parts of the cartridge to each other,
- alloy color.
The Morse taper changes upward as the size number increases. The radial runout tolerances change with the size.
For example, Morse taper B16 has drill chucks of sizes 10 and 13. These numbers correspond to the upper parameter of the drill clamp, the lower one is set by GOST 8522-79. With a Morse taper B18, cartridge No. 16 is made according to the same table. Its minimum clamp is 3 mm, maximum - 16 mm.
The keyless chuck must be selected in accordance with the dimensions of the mounting hole and thread of the machine. Key cartridges, thanks to the Morse taper, have an advantage. Cone adapters allow you to install chucks with a smaller or larger Morse taper on the machine, expanding the capabilities of the machine.
The most durable keyless chuck, but also the most expensive, is the precision quick-change chuck. It is ideal for a machine operating at high speeds. Tapered shanks make the precision keyless chuck versatile.
For what purposes are cartridges used?
Drill chucks are intended for clamping and fastening asymmetrical complex workpieces of cylindrical and non-cylindrical shape. In this case, self-centering chucks are distinguished for parts that have an axisymmetric shape, as well as chucks with independent jaws for asymmetrical ones.
Collet drills are used for fastening small-diameter drills with a cylinder-shaped shank.
Adapter cone-shaped bushings are used to secure a device with a cone-shaped shank if the cone number of the device shank does not correspond to the cone number in the spindle of the unit.
Quick-change – used to instantly change the cutting mechanism during processing, this reduces time and increases productivity when making holes.
Self-aligning - used in the manufacture of pre-made holes, they provide the ability to center the unit along the axis of the turning hole.
Possible applications
Drill chucks are used to fix metal-cutting tools with a shank with a diameter of up to 20 mm. The design and variety of equipment options allows it to be used for a number of technological operations:
- Drilling holes in parts. It is possible to cut both through holes and blind holes to the required length.
- Drilling pre-drilled holes to a larger diameter.
- Reducing the roughness of the inner surface of a hole by countersinking.
- Reaming conical and cylindrical holes.
- Preparation of chamfers and recesses for washers and countersunk heads by countersinking.
- Rolling out holes using a mandrel and hardened rolling elements (balls and rollers) to obtain a dense and smooth surface with low roughness.
- Cutting threads with a tap to the entire depth or part of it.
- Trimming the ends to obtain a flat surface at right angles to the axis of the hole.
Flaring of hollow rivets and many other metal-cutting operations are also possible.
Standard sizes of conventional and quick-release drill chucks
According to GOST, there are 6 standard sizes for clamping drills with a shank diameter from 0.2 to 16 mm, but universal models with an extended range are usually used:
- 1.5-13 mm. Smaller diameter shanks are used in highly specialized equipment and usually use collet clamps for drilling.
- 3-16 mm. To securely fix larger diameter shanks, collets or another fastening method are also used.
The clamp of a classic chuck is tightened and loosened with a key, which is used to rotate a ring with a serrated surface. To tighten the shank evenly, distribute the force and turn the ring, resting against the recesses on different sides. Keyless chucks operate without a key - the ring is turned manually. This is more convenient and faster, which is why such models are used when it is necessary to speed up tool replacement. To loosen the tightening, some models have key grooves.
How to buy a keyless drill chuck
The catalog of the Kerner online store presents several models of chucks: quick-release chucks and toothed chucks (key), with thread and cone, adapter to SDS-plus, as well as any adapter options for machine tools, rotary hammers, drills and other equipment. If you need expert help, call the number or send a request by email [email protected] or write to the chat and our manager will select the appropriate model for a specific operation.
Back to list
How to choose a drill key or keyless chuck
Tool shank diameter and design. The jaws clamp without distortion only on tools with a cylindrical shank. The range of working diameters is indicated in the card of each model. Type of fixation on the spindle. Make sure the shank fits your equipment model. If the machine or tool has a different system, a mandrel or adapter will be required. Replacement speed. If the tool is changed frequently, quick-release chucks are better suited (for example, for a drill, screwdriver or machine that performs several operations). Anti-rotation protection. The cams of high-quality models have longitudinal teeth that better fix the shank. Positioning accuracy. Depends on the quality of workmanship - if the seating surfaces and clamping mechanism are made correctly, the tool will have minimal runout. The number of connections also affects the runout - if adapters are used in the work, the error increases. Materials. Drill chucks are made with metal and plastic clamping rings. Plastic ones are better suited for drills, hammer drills and screwdrivers, metal ones are better for machine tools and stationary equipment. Versatility. Some models are produced specifically for specific equipment: keyless chucks from Bosch, Makita, Metabo and other brands. But most designs are interchangeable; the main thing is to choose a model with a suitable landing system.