Home |Blocks and floors |Overlap on metal beams
Date: January 22, 2018
Comments: 0
To install durable floors in buildings being constructed, builders use proven methods that involve the use of various building materials. An increased margin of safety is provided by profiles made of rolled steel. Floors constructed on their basis on metal beams ensure the reliability of the structures being erected and a long service life. They are superior to structures based on wooden beams in terms of performance and are able to withstand significant loads. Let's look at them in detail.
Structural options for flooring on metal beams
Based on a steel profile, you can make a durable floor using various options:
- The ceiling is monolithic on metal beams. It is formed by pouring concrete into the formwork, and is additionally reinforced with reinforcing mesh. This is a practice-tested option with a range of advantages. The main advantages that attract developers are the increased strength of the seamless surface and the absence of irregularities;
- monolithic prefabricated structure. For its arrangement, blocks of cellular concrete manufactured at industrial enterprises are used. They are laid with their edges on the surface of the steel profile. Thermally insulated formwork is constructed, reinforcement is made and the joint areas are filled with concrete mortar;
- composite structure made of various materials. Standard panels, wooden boards, and slabs can be used. The base elements are installed on load-bearing steel beams. To ensure comfortable operating conditions, it is important to insulate and soundproof the formed surface, as well as seal the gaps between the elements.
Depending on financial capabilities and availability of materials, developers equally use these options.
Particularly stringent requirements are imposed on the quality and strength of floors in a building of any design.
Varieties
Metal structures differ in many ways. It is recommended to take this into account when choosing a product.
By purpose
Using metal beams, you can create a high-quality durable floor by choosing one of the options.
Monolithic . Concrete is poured into the formwork and reinforced with a grid of reinforcement. The surface is seamless and highly durable.- Monolithic-prefabricated . In this case, in addition to metal beams, concrete blocks are used, which are laid on a steel profile. The joint areas are filled with concrete.
- Composite . A combination of materials is used, that is, slabs, boards, and panels are laid on load-bearing metal products. This option involves the creation of additional insulation and sound insulation of the surface.
By material: steel and aluminum
Metal structures can be made from different materials. The most popular are steel and aluminum floor beams.
- Steel products are made from steel alloy by cold or hot rolling.
Steel structures come in several types: angle, channel, I-beam. The advantages of steel beams include fire resistance, resistance to rotting and external factors, and high strength. The main disadvantages are: high cost, low heat and sound insulation, risk of corrosion. Installation of steel structures cannot be carried out without the use of special equipment. - Aluminum beams . In their manufacture, not just aluminum is used, but its alloys. In construction, such products are used less frequently than their steel counterparts, since they are inferior in terms of stability under heavy loads. Most often, aluminum beams are used in the construction of small-sized buildings. When constructing industrial facilities, products made from this metal are used only in combination with steel structures.
By design
In modern construction, several types of metal beams are used, varying in design.
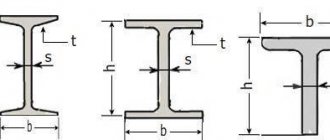
T-bars . The main section consists of a wall and a shelf in the shape of the letter “T”.- I-beam. The cross-section of rolled metal looks like the letter “H”. The product is more rigid than a T-bar due to the fact that it has an additional shelf on the opposite side.
I-beam elements are divided into several types, each of which is marked:- B – standard I-beams.
Ш – product with wide brim.
- U - narrow-flange structures.
- D – mid-shelf products.
- K – column beams. The width of the shelf of such an element can be equal to the height of the product.
- Channel . The cross section of the element is the letter “P”. These beams are considered universal and are used in all areas of industry.
There are I-beams not with parallel, but with inclined shelves. They are classified into special and ordinary. Their characteristics are regulated by GOST 19425-74.
Materials and equipment used
Various types of rolled metal are used as load-bearing beams:
- I-beam number 16 or 20;
- channel up to 20 cm high;
- corner welded into a load-bearing frame.
To form the selected design option, in addition to load-bearing elements, the following materials will be required:
- concrete mixture to form a solid base;
- standard blocks made of cellular concrete for a prefabricated monolithic version;
- planed boards or ready-made concrete panels for a composite structure.
For reinforcement, reinforcing bars are used, the diameter of which corresponds to the results of the calculations performed.
The construction of formwork will require the use of the following building materials:
- wooden panels or moisture-resistant plywood with a thickness of 2 cm or more;
- polyethylene film for waterproofing concrete mass;
- supports made of metal or wood to ensure the stability of the formwork.
For different types of houses, they use both metal and wooden beams, as well as reinforced concrete
You should also prepare the equipment:
- concrete mixer, which speeds up the process of preparing the working mixture;
- a welding machine designed for welding reinforcement cages.
No special tools are required for construction activities. A set of tools available in the arsenal of every home craftsman is used.
What is it and what sizes do they come in?
The beam is one of the main elements of any structure; its function is to increase the stability of the structure and strengthen it. A beam (or transom) consists of flanges and walls of various sizes, connected by butt seams using welding. Elements are manufactured at equipped factories using special machines.
The manufacturing procedure is carried out in several stages, after which the finished product is checked for compliance with GOST standards.
Metal structures vary in size; for convenience, they have numbers , with which you can select the necessary material for construction.
“10” is a small product, used as a ceiling to strengthen moving elements in construction. Can be used as a guide for small lifts.- “12” is a slightly larger structure size that can withstand a larger load. Used as a basis for frames, used in mechanisms.
- “14” - products of this size can be used in industrial production for installation in reinforced concrete structures.
- “16” is a durable structure that acts as a full-fledged support and can be used to move vehicles around the workshop.
- “18” is a reliable supporting element, used in the construction of buildings, it will ensure the stability of a large area.
- “20” is a large element that can serve as the basis for a column or frame. Often used in mechanical engineering.
- “25” - the product can serve as a support for large cranes and large-sized lifting mechanisms.
- “30” is the largest structure not used in residential construction. It is the basis for lifting mechanisms.
Scope of application
Metal floor beams have found their application in various fields. Can be used for :
- Roof strengthening in residential and industrial construction.
- Creation of interfloor ceilings.
- Construction of supports and various columns in industrial structures and architectural buildings.
- Installation of hangar frames.
- Mine shafts.
- Creation of various railway cars.
- Construction of bridges, overpasses.
- Construction of metal trusses.
Note : metal floor beams can also be used in the construction of low-rise private houses.
Advantages and disadvantages of flooring on metal beams
The design with load-bearing elements made of rolled steel has a number of advantages:
- increased reliability;
- high safety margin;
- long service life;
- increased load-bearing capacity.
By using metal structures made from steel profiles, it is possible to cover spans of increased dimensions by correctly selecting the number of rolled products used.
[testimonial_view id=”19″]
Along with the advantages, there are also weaknesses:
- the complexity of installation work associated with the increased weight of metal structures and the need to transport them using special devices;
- the need to perform complex engineering calculations confirming the load capacity of foundations being constructed based on steel profiles.
Disadvantages also include the metal's susceptibility to corrosion processes, which reduce the strength of structures. However, with the help of special coatings it is possible to reliably protect the metal and ensure the durability of metal structures throughout the entire period of operation of the building.
Metal beam ceilings are very durable and reliable
Requirements for concrete
Table of concrete grades.
The brand and class of concrete that will be used to pour the floor are selected at the project creation stage. The most commonly used brands are B15, B20, B25. The class of concrete used depends on the distance between the beams inside the floor. The larger the step, the higher the concrete class should be. The quality of concrete also depends on moisture permeability and frost resistance. In a private house, concrete with frost resistance class F50 is used for flooring. In places of high humidity (on open terraces, balconies), frost resistance grade F75 and moisture permeability grade W2 are used.
The cross-sectional profile of the metal rods and the grade of steel used are calculated at the design stage. Since concrete reinforcement protects large spans from stretching, the diameter of the bottom layer of reinforcement is larger than the top layer. Additional reinforcement is required at the junctions of the slabs with the supports.
Calculation of floors using metal beams
It is necessary to take a responsible approach to performing calculations when deciding to make a floor or ceiling based on steel profiles.
In this case, it is necessary to take into account a number of factors:
- total weight;
- load capacity;
- area of the formed surface;
- distance between beams;
- span width.
The selection of a suitable number of rolled metal products corresponding to the profile height is carried out taking into account the perceived load.
Load bearing capacity is:
- 0.075 t/m2 – for attic floors;
- 0.150 t/m2 – for the basement base and interfloor foundations.
As the span width increases, the height of the steel beams increases:
- strength over a six-meter span is provided by I-beam No. 20 with a profile height of 200 mm;
- when the distance between the walls is reduced to 4 m, I-beam No. 16 with a height of 160 mm can be used.
Knowing the area of the monolithic surface, it is easy to calculate the need for concrete. To do this, multiply the area by the height of the concrete mass. Having a drawing of the reinforcing lattice, you can calculate the need for steel rods to strengthen the base. All calculations are made on the basis of pre-developed design documentation or a working sketch.
However, they also have a drawback - they are susceptible to corrosion.
Wooden floors
The ceiling is a set of wooden beams made of timber and plank flooring made over these beams. For beams, timber 150 by 100 mm, 200 by 100 mm, 200 by 200 mm, sewn boards or other sections suitable for the calculation are used. Glued laminated timber is also used. It is more expensive, but preferable due to the higher strength and absence of defects of natural wood. The plank flooring is made of boards 40 or 50 mm thick.
The advantage of a wooden floor is the ability to make it manually without lifting mechanisms. Another possible advantage is low cost in regions where wood is cheap.
- Large deflections and vibration;
- Fire hazard;
- High labor intensity;
- Susceptibility to rot and insect attack. Especially in wet areas where there are bathtubs, showers or water supply risers.
Technology
Sockets are left in the wall structure for supports of floor beams. In this case, after installing the beam in the design position, there should be space left at the end to ensure ventilation. Over time, moisture escapes through the pores of the wood at the cut site. It must be removed to avoid rotting of the beam. At the point of contact between the beam and the wall, it is wrapped in waterproofing material, such as roofing felt or glassine. But the end of the beam must remain uncovered.
After installing the beams, the boardwalk is laid. A gap of at least 20 mm is left along the walls in case of wood swelling. Otherwise, the flooring may push the wall outward.
Soundproofing material is fixed into the space between the small parts. After this, the ceiling is lined from below with boards 20 mm thick.
Thus, the ceiling is ready with a rough floor on top and a rough ceiling below. Next, the floor is made on wooden planks using joists or using building mixtures. The ceiling can be made, for example, from plasterboard, attaching the hangers of its frame to the lower plank flooring.
Flooring on I-beams - preparatory work
At the preparatory stage, perform the following activities:
- Decide on the material that is supposed to be used to make the ceiling of the room, and also study the sequence of actions.
- Develop a working drawing that provides complete information about the design features of the ceiling and the range of materials used.
- Perform calculations confirming the strength characteristics of the building structure and the safety margin necessary for long-term operation.
- Calculate the need for building materials, estimate the amount of expenses, and prepare tools.
- Mount the I-beams, maintaining an interval between the supporting elements of 1–2 m and check the correct installation using a level.
- Assemble panel collapsible formwork along the lower level of the I-beam using laminated plywood or planed boards, provide a flange 15–20 cm high.
- Anchor wooden beams or steel spacers to ensure the formwork structure remains stationary and must support the mass of concrete.
When installing supports, install one wooden beam for each square meter of area, and metal elements 2 times less often. The use of telescopic racks will significantly facilitate the work of fixing the formwork structure. Having completed the preparatory activities, proceed to the main work.
Correct calculation of flooring on metal beams is very important
Prices for all types
In construction, I-beams are most often used. The average cost of production is presented in the table.
| Beam name | Length | Price |
| I-beam No. 10 | 12 m | 880 |
| I-beam No. 10 B-1 | 12 m | 780 |
| I-beam No. 12 | 12 m | 900 |
| I-beam No. 12 B-1 | 12 m | 660 |
| I-beam No. 14 | 12 m | 1050 |
| I-beam No. 14 B-1 | 12 m | 740 |
| I-beam No. 16 | 12 m | 1300 |
| I-beam No. 16 B-1 | 12 m | 980 |
| I-beam No. 18 | 12 m | 1280 |
| I-beam No. 18 B-1 | 12 m | 1150 |
| I-beam No. 20 | 12 m | 1560 |
| I-beam No. 25 B-1 | 12 m | 2150 |
| I-beam No. 25 Ш-1 | 12 m | 3500 |
| I-beam No. 30 | 12 m | 2600 |
| I-beam No. 35 | 12 m | 3300 |
| I-beam No. 40 | 12 m | 3500 |
| I-beam No. 45 B-1 | 12 m | 5200 |
We install a monolithic ceiling on metal beams
Developers are attracted by the solid structure, made of concrete reinforced with reinforcing lattice.
After installing the metal beams, constructing the formwork and ensuring its stability, carry out work on forming a monolithic reinforced concrete slab according to the following algorithm:
- Check for any gaps in the wooden formwork and, if necessary, seal them.
- Assemble the reinforcement frame using metal rods with a section size of 10–12 mm.
- Place the frame in the formwork, ensuring a constant interval of 4–5 cm to the surface of the future concrete slab.
- Pour the concrete mixture into the formwork and thoroughly compact the concrete mass using a vibrator.
- Do not expose the hardening mortar to loads for 4 weeks and then dismantle the formwork.
Pay attention to the size of the supporting surface around the perimeter of the slab, which should be more than 150 mm.
Calculation
When planning the installation of a ceiling or floor using metal beams, it is recommended to correctly perform the necessary calculations.
What indicators to consider?
When carrying out calculations, a number of factors are taken into account simultaneously:
- surface area under construction;
- total weight;
- distance between metal beams;
- maximum possible load;
- span width.
The greater the span width, the greater the height of the metal products.
Formulas
The calculation is made based on the strength and rigidity of the product . By calculating the values in the GOST tables, you can find the required rental number.
Linear load is calculated using the formula q = Q * p and is used in subsequent calculations.
The deflection calculation is calculated using the formula My = (q * L2) / 8 , where:
- q – linear load value;
- p – beam laying step;
- L is the length of the overlapped span.
The maximum moment of resistance of a beam section (Wy) is found by dividing the bending moment by the design resistance of the material.
Stiffness calculations are carried out using the formula f = 5 * q * L4 / (384 * E * Jy) , where:
- q – linear load on the beam;
- L – span length;
- E – elastic modulus of the material
- Jy is the minimum moment of inertia.
Installation work
Floor slab installation diagram
After the calculation is completed and work on creating a metal frame has been completed, they begin to form a monolithic reinforced concrete floor slab. We must immediately warn you that these works are performed exclusively by the hands of professionals, as they require certain skills.
If the design estimate was carried out by professionals, then they make an accurate calculation of the quantity and determine the grade of concrete and the thickness of the floor. Construction companies will not only prepare a project and calculations, but will also provide a team of builders for installation work. When choosing a performing company, it is best to focus on experience and positive feedback from clients.
Concrete interfloor slabs of large sizes must exactly correspond to the design design. The ability to work not only with building materials, but also with technical documentation indicates the high professionalism of the workers. You should not trust builders who claim that design documents for roofing are unnecessary and work based solely on their experience. Monolithic concrete floors must be completely safe.
Don’t forget to ask if builders are familiar with the technological process of creating a monolithic floor. After all, it is not enough to simply dilute concrete mixtures, pour them and wait until they dry completely. Good specialists are familiar with a number of professional nuances in ceiling installation. A professional should be familiar with the terms “thickness of the protective layer”, “fastening of reinforced rods”, “installation of a support for a monolith”, “location of seams”, “concrete vibration” and others. Only strict adherence to all points of the project will allow you to obtain a high-quality and reliable overlap.
Errors and difficulties with the device
Risks when installing a monolithic floor are associated with some disadvantages of the profiled sheet. List of unforeseen moments that you may encounter during the work process:
- the need to increase the amount of concrete solution;
- reduction of structural rigidity;
- shifting construction deadlines;
- exceeding the estimated cost.
What to pay attention to:
- Calculation quality. You should not skimp on designer services. If the calculation is carried out incorrectly, then the load-bearing profiled sheets may not withstand the increased mass of concrete.
- Quality of tools and components. The tool must be convenient and highly durable.
- Speed of work. The corrugated sheet heats up very quickly and dries the concrete. If delayed, this will complicate the work.
If you follow the recommendations and technology, the strength of the structure will correspond to the required values.
Reliability of different supports
Floors are divided into beam, slab and monolithic. The design depends on their properties.
Beam
In beam floors, the load-bearing elements are strong beams: wooden, metal, reinforced concrete.
Wooden beams
Wooden beams are found in old low-rise buildings. The gaps between the beams are covered with wooden bevels. The “black” layer is performed on logs that are laid across the beams. The ceiling of the apartment below is sewn onto the beams from below. Unfortunately, it is impossible to repair wooden beams without disturbing the ceiling of the lower neighbors.
Metal and reinforced concrete beams
Metal and reinforced concrete beams of T- or I-section were used in Soviet-built houses until the seventies of the twentieth century. Flooring in the form of solid gypsum or hollow concrete liners, or precast reinforced concrete slabs could be placed on the lower flanges of the beams. In this case, the “black” floor can be made on a lathing or on a screed. And since it is not always possible to purchase prefabricated slabs during renovations, they are replaced with a monolithic reinforced concrete slab for the entire room, cast on site on top of the beams. High-profile steel sheets are sometimes used as formwork and reinforcement.
In houses built in the seventies and eighties, the well-known series II-29, P-3, P-44, P-46, P-55 with their modifications, slab reinforced concrete floors are used. They can have a width from 1.2 to 3.6 m, a nominal length from 2.4 to 6.6 mm. They can be used to create “black” floors on joists or screeds. Hollow-core slabs with a thickness of 220 mm are less common. They are in old series, for example, II-68, and in new ones: I-155. Provide better sound insulation than solid slabs.
Reconstruction of old housing stock
Wooden floors deteriorate over time: they become damp from high humidity and are susceptible to fungi, insects and microorganisms. Wooden beams in an old house are replaced with monolithic floors of large spans. This allows you to extend the service life of the housing stock. Reconstruction and complete replacement of the interfloor ceiling requires preparation. It is necessary to clear the adjacent floors of the house from furniture and residents. On the lower floor, racks and beams are installed under the ceiling. Only after appropriate strengthening can dismantling work begin: the floor covering is removed, wooden logs, insulating backfill, and rough ceiling boards are removed, electrical wiring is dismantled, window frames and heating systems are protected from accidental damage, and then the old wooden floors are dismantled.