When developing a new car model, each manufacturer strives to increase the dynamics of its products, but at the same time not to deprive the car of safety. Although the dynamic characteristics largely depend on the type of engine, the car body plays a significant role. The heavier it is, the more effort the internal combustion engine will exert in order to accelerate the vehicle. But making the car too light often has a negative impact on downforce.
By making their products lighter, manufacturers strive to improve the aerodynamic properties of the body (what aerodynamics is is discussed in another review ). The weight of the vehicle is reduced not only through the installation of units made of light alloy materials, but also thanks to lightweight body parts. Let's look at what materials are used to make car bodies, as well as the pros and cons of each of them.
Background of automobile bodies
The body of a modern car is given no less attention than its mechanisms. Here are the parameters it must meet:
- Lasting. In the event of a collision, it should not injure people in the cabin. Torsional rigidity should ensure that the car maintains its shape when driving over uneven terrain. The smaller this parameter is, the greater the likelihood that the car frame will deform and the vehicle will be unsuitable for further use. Particular attention is paid to the strength of the front part of the roof. The so-called "moose" test helps the automaker determine how safe the car will be in a collision with a tall animal, such as a deer or elk (the entire mass of the carcass is located on the windshield and the roof crossbar above it).
- Modern design. First of all, sophisticated motorists pay attention to the shape of the body, and not just to the technical part of the car.
- Safety. Everyone inside the car must be protected from external influences, including in the event of a side collision.
- Versatility. The material from which the car body is made must withstand different weather conditions. In addition to aesthetics, paint coating is used to protect materials that are susceptible to aggressive moisture.
- Durability. There are often cases when the creator skimps on body material, which is why the car becomes unusable after just a few years of use.
- Maintainability. To avoid having to throw away the car after a minor accident, the production of modern body types involves modular assembly. This means that the damaged part can be replaced with a similar new one.
- Affordable price. If the car body is made of expensive materials, a huge number of unclaimed models will accumulate on the sites of automakers. This often happens not because of poor quality, but because of the high cost of vehicles.
In order for the body model to meet all these parameters, manufacturers have to take into account the characteristics of the materials from which the frame and outer body panels are made.
To ensure that car production does not require a lot of resources, company engineers develop body models that allow them to combine their main function with additional ones. For example, the main units and interior parts are attached to the car structure.
Initially, the design of cars was based on a frame to which the remaining components of the car were attached. This type is still present in some car models. An example of this is full-fledged SUVs (most jeeps simply have a reinforced body structure, but no frame; this type of SUV is called a crossover ) and trucks. On the first cars, each panel attached to the frame structure could be made not only of metal, but also of wood.
The first model with a supporting structure without a frame was the Lancia Lambda, which rolled off the assembly line in 1921. The European model Citroen B10, which went on sale in 1924, received a solid steel body structure.
Lancia Lambda Citroen B10
This development turned out to be so popular that most manufacturers of those times rarely deviated from the concept of an all-steel monocoque body. These cars were safe. Some companies refused steel for two reasons. Firstly, this material was not available in all countries, especially during the war years. Secondly, the steel body is very heavy, so some people made compromises in body materials in order to install an internal combustion engine with less power.
During the Second World War, steel was in short supply throughout the world, since this metal was entirely used for military needs. Out of a desire to stay afloat, some companies decided to produce the bodies of their models from alternative materials. So, in those years, cars with aluminum bodies first appeared. An example of such models is the Land Rover 1-Series (the body consisted of aluminum panels).
Another alternative is a wooden frame. An example of such cars is the Willys Jeep Stations Wagon modification Woodie.
Since the wooden body is not durable and needed serious care, this idea was soon abandoned, but as for aluminum structures, manufacturers seriously thought about introducing this technology into modern production. Although the main apparent reason was a steel shortage, this was not actually the motivating factor that led automakers to look for alternative options.
- Since the global fuel crisis, most car brands have had to reconsider their production technology. First of all, the audience requiring powerful and high-capacity engines has sharply decreased due to the high cost of fuel. Motorists began to look for less power-hungry cars. And in order for transport with a smaller engine to be sufficiently dynamic, a lightweight, but at the same time sufficiently durable material was required.
- Over time, environmental standards for vehicle emissions have become increasingly stringent throughout the world. For this reason, technology began to be introduced to reduce fuel consumption, improve the quality of combustion of the air-fuel mixture and increase the efficiency of the power unit. To do this, you need to reduce the weight of the entire car.
Over time, developments from composite materials appeared, which made it possible to further reduce the weight of vehicles. Let's consider what is special about each material that is used to make car bodies.
Features of the automotive industry in Russia
The Russian automobile industry is considered an important sector of the Russian economy. As of 2022, Russia ranked 15th among all countries in the world in terms of the number of vehicles produced. By 2022, the number of domestic cars has reached 15% of total production.
The total number of cars that are imported is 48%. This indicator depends on the models produced and the segment occupied.
Cars
Russia ranks second among European countries in terms of the number of passenger cars produced. Germany is in first place. If we take official data from OICA statistics, Russian automobile manufacturers produced 1,919,636 passenger cars in 2013. At the same time, the total number of cars that EU countries produced in the same year was 11,341,479. Between 2001 and 2008, Russia operated factories that could produce 422,920 passenger cars per year.
Vintage passenger car (Photo: Instagram / givievechy)
Trucks and special equipment
Russia holds second place in the production of trucks and special equipment. Germany takes first place. It is impossible to know the exact statistics, since OICA data regarding trucks has been closed since 2010.
The main factories for the production of special equipment and trucks were introduced in several stages:
- from 1991 to 1999;
- from 2001 to 2008;
- from 2005 to 2007 (the most powerful production facilities were involved).
If we compare the statistics of trucks produced in 2016 and 2017, in 2022 production increased by 50.4%.
Buses
Russia is the absolute leader in bus production. According to OICA statistics, 23,107 heavy buses were produced and put into service in 2013. At the same time, all EU countries over the same period of time were able to produce only 12,460 vehicles of this type.
The main plants were introduced from 2001 to 2008.
Steel body: advantages and disadvantages
Most body elements of a modern car are made of rolled steel. The thickness of the metal in some sections reaches 2.5 millimeters. Moreover, low-carbon sheet material is used predominantly in the load-bearing part. Thanks to this, the car is quite light and at the same time durable.
Today steel is not in short supply. This metal has high strength; elements of various shapes can be stamped from it, and parts can be easily fastened together using spot welding. When manufacturing a car, engineers pay attention to passive safety, and technologists pay attention to the ease of processing the material, so that the cost of transport is as low as possible.
And for metallurgy, the most difficult task is to please both engineers and technologists. Taking into account the desired properties, a special grade of steel was developed that has the ideal combination of drawability and sufficient strength of the finished product. This simplifies the production of body panels and increases the reliability of the car frame.
Here are some more advantages of a steel body:
- Repairing steel products is the easiest - just buy a new element, for example, a wing, and replace it;
- It is easy to recycle - steel is highly recyclable, so the manufacturer always has the opportunity to obtain cheap raw materials;
- The technology for manufacturing rolled steel is simpler than processing light-alloy analogues, so the raw materials are cheaper.
Despite these advantages, steel products have several significant disadvantages:
- Finished products are the heaviest;
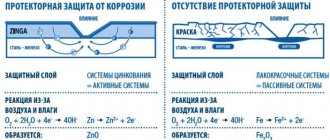
- Rust quickly appears on unprotected parts. If the element is not protected with a paint coating, the damage will quickly render the body unusable;
- In order for sheet steel to have increased rigidity, the part must be stamped many times;
- The resource of steel products is the smallest compared to non-ferrous metals.
Today, the properties of steel are improved by adding certain chemical elements to the composition that increase its strength, oxidation resistance and ductility characteristics (TWIP grade steel can stretch up to 70%, and its maximum strength is 1300 MPa).
What material is used to make a car?
For the manufacture of cases and main parts for cars, different materials can be used (titanium, carbon fiber, gold, etc.), but the most popular are aluminum, steel and plastic.
Gold bars (Photo: Instagram / gold_officiel)
Steel
Among all types of automotive metal, low-carbon sheet steel is considered the most popular. Suitable sheet thickness is from 0.65 to 2 mm.
Advantages of steel for car body assembly:
- High strength, rigidity.
- Low price.
- Easy to repair.
Since the technology has long been proven, most technological operations can be performed by robots.
- Large mass of finished products.
- Short service life.
- The need to make a large number of stamps.
To prevent steel surfaces from rusting, they must be coated with a special anti-corrosion compound.
The car body is manufactured in several stages. Initially, individual parts are produced from steel sheets of different thicknesses. They are then welded to form large assemblies. The last stage of assembly is connecting the individual parts into a single structure.
Aluminum
Aluminum alloys began to be used in the automotive industry quite recently. The material is suitable for the manufacture of the entire body or its individual parts.
More often, parts made of aluminum and steel are combined with each other to achieve the optimal weight of the car. Assembling a case from aluminum parts is practically no different from working with steel. The exception is the welding of individual parts. It is carried out in an argon environment. Individual parts are fixed with rivets.
- Aluminum alloys are lighter and stronger than steel.
- Damaged parts can be easily recycled.
- Finished products are immune to rust formation.
- The parts can be given any shape.
- To work with parts made of aluminum alloys, you need to use special equipment.
- To make a high-quality connection of parts, you need to use expensive equipment.
- Parts are difficult to repair.
Aluminum (Photo: Instagram / tipichnyiizolirovshchik)
Polymers
Since metal makes the structure heavier, most manufacturers use polymers in the manufacture of the body. On plastic cars it is easy to squeeze out maximum power and achieve maximum speed
Different types of polymers are used in production:
- ABS plastic.
- Polypropylene.
- Fiberglass.
- Polyurethane.
- Polyvinyl chloride.
- Polyamide.
- Polyethylene.
- Polycarbonate.
- Polyacrylate.
Fiberglass is most often used. Its advantages:
- light weight;
- high strength;
- ease of manufacturing parts of various shapes.
- Long production times for parts.
- Difficulty in repairing damage.
- High price for fillers.
Plastic is cheaper than other materials.
Aluminum body: advantages and disadvantages
Previously, aluminum was only used to make panels that were attached to a steel structure. Modern developments in aluminum production make it possible to use the material also to create frame elements.
Although this metal is less susceptible to moisture compared to steel, it has less strength and mechanical elasticity. For this reason, to reduce the weight of a car, this metal is used to create doors, trunks, and hoods. To use aluminum in the frame, the manufacturer has to increase the thickness of the products, which often works against ease of transport.
The density of aluminum alloys is much less than that of steel, so the sound insulation in a car with such a body is much worse. To ensure that a minimum of external noise enters the interior of such a car, the manufacturer uses special noise reduction technologies, which is why the car will cost more than a similar option with a steel body.
The production of an aluminum body in the early stages is similar to the process of creating steel structures. The raw materials are broken into sheets, then they are stamped into the desired design. The parts are assembled into a common structure. Argon welding is used only for this purpose. More expensive models use laser spot welding, special glue or rivets.
Arguments in favor of an aluminum body:
- Sheet material is easier to stamp, so the panel manufacturing process requires equipment that is not as powerful as for stamping steel;
- Compared to steel bodies, an identical shape made of aluminum will be lighter, while at the same time the strength remains at the same level;
- The parts are easy to process and can be recycled;
- The material is more durable compared to steel - it is not afraid of moisture;
- The cost of the manufacturing process is lower compared to the previous version.
Not all motorists agree to buy a car with an aluminum body. The reason is that even in the case of a minor accident, car repairs will be expensive. The raw materials themselves cost more than steel, and if a part needs to be replaced, the car owner will have to look for a specialist who has special equipment for high-quality connection of elements.
What metal is used in assembling and repairing machines?
In the production of cars, different types of metals and polymers can be used. They are used in the manufacture of bodywork and individual spare parts. Each manufacturer uses different material. This is especially noticeable when comparing cars of domestic and foreign brands. If you know what metal the car is made of, you can independently repair the body if corrosion occurs or after an accident.
Automobile
Plastic body: advantages and disadvantages
The second half of the twentieth century was marked by the emergence of plastic. The popularity of this material is explained by the fact that any structure can be made from it, which will be much lighter than even aluminum.
Plastic does not require paint coating. It is enough to add the necessary dyes to the raw materials, and the product acquires the desired shade. In addition, it does not fade and does not need to be repainted when scratches appear on it. Compared to metal, plastic is more durable; it does not react with water at all, so it does not rust.
The Khadi model has a plastic body
The cost of manufacturing plastic panels is much lower, since powerful presses are not needed for embossing. The heated raw material is fluid, thanks to which the shape of body parts can be absolutely any, which is difficult to achieve when using metal.
Despite these obvious advantages, plastic has a very big drawback - its strength is directly related to operating conditions. So, if the air temperature outside drops below zero, the parts become fragile. Even a small load can cause the material to burst or break into pieces. On the other hand, as the temperature increases, its elasticity increases. Some types of plastics warp when heated in the sun.
Here are some other reasons why plastic bodies are less practical:
- Damaged parts can be recycled, but this process requires special, expensive equipment. The same goes for plastic production.
- During the manufacture of plastic products, large amounts of harmful substances are released into the atmosphere;
- Load-bearing parts of the body cannot be made from plastic, since even a large piece of material is not as strong as thin metal;
- If a plastic panel is damaged, it can be easily and quickly replaced with a new one, but this is much more expensive than welding a metal patch to the metal.
Although these days there are various developments that eliminate most of the listed problems, it has still not been possible to bring the technology to ideal. For this reason, bumpers, decorative inserts, moldings are mainly made from plastic, and only in some car models - fenders.
Results
Having understood the reasons why modern cars have thin bodies, we note that you should not be afraid of changes. Not all of them imply a deterioration in certain qualities. In particular, this applies to the thickness of the car body.
As we found out, this does not make traveling in your favorite car any less safe. On the contrary, driving becomes safer. Plus, motorists receive pleasant bonuses in the form of savings on fuel, maneuverability and improved aerodynamics.
Do you agree that thin metal cars are safer?
Source: mycary.ru
Body made of composite materials: advantages and disadvantages
The term composite means a material that contains more than two components. During the process of creating the material, the composite acquires a homogeneous structure, due to which the final product will have the properties of two (or more) substances that make up the raw material.
Often, a composite will be obtained by gluing or sintering layers of different materials. Often, to increase the strength of a part, each individual layer is reinforced so that the material does not peel off during operation.
Monocoque body
The most common composite used in the automotive industry is fiberglass. The material is obtained by adding a polymer filler to fiberglass. External body elements are made from this material, for example, bumpers, radiator grilles, and sometimes head optics (more often they are made of glass, and lightweight versions are made of polypropylene). The installation of such parts allows the manufacturer to use steel in the design of the load-bearing parts of the body, but at the same time keep the model quite light.
In addition to the advantages listed above, polymer material occupies a worthy place in the automotive industry for the following reasons:
- The weight of the parts is minimal, but at the same time they have decent strength;
- The finished product is not afraid of the aggressive effects of moisture and sun;
- Thanks to elasticity at the raw material stage, the manufacturer can create completely different shapes of parts, including the most complex ones;
- Finished products look aesthetically pleasing;
- You can create huge body parts, and in some cases even the entire body, as is the case with kit cars (read more about such cars in a separate review ).
However, innovative technology cannot be a complete alternative to metal. Here are some reasons for this:
- The cost of polymer fillers is very high;
- The mold for making the part must be perfect. Otherwise, the element will turn out ugly;
- During the manufacturing process, it is extremely important to keep the workplace clean;
- Creating durable panels takes a long time, since the composite takes a long time to dry, and some body parts are multi-layered. Often solid bodies are made from this material. The popular term “monocoque” is used to designate them. The technology for creating monocoque body types is as follows. The carbon fiber layer is glued with a polymer. Another layer of material is laid on top of it, only so that the fibers are located in a different direction, most often at a right angle. After the product is ready, it is placed in a special oven and kept for a certain time at high temperature so that the material bakes and takes on a monolithic shape;
- When a part made of composite material breaks, it is extremely difficult to repair (an example of how car bumpers are repaired is described here );
- Composite parts are not recycled, but only destroyed.
Due to the high cost and complexity of manufacturing, conventional road cars have a minimal number of parts made of fiberglass or other composite analogues. Most often, such elements are installed on a supercar. An example of such a car is the Ferrari Enzo.
2002 Ferrari Enzo
True, some exclusive models of the civilian series receive dimensional parts made of composite. An example of this is the BMW M3. This car has a roof made of carbon fiber. The material has the required strength, but at the same time allows you to move the center of gravity closer to the ground, which increases downforce when entering corners.
Another original solution in the use of lightweight materials in the car body is demonstrated by the manufacturer of the famous Corvette supercar. For almost half a century, the company has been using a spatial metal frame in its model, onto which panels made of composites are attached.
Popular automotive companies in Russia and the USSR
Companies that made the greatest contribution to the development of the automotive industry:
- AvtoVAZ - Volzhsky Automobile Plant. Was founded in 1966. Now about 20% of all cars in Russia are manufactured by this company.
- KamAZ - Kama Automobile Plant. It is considered the best manufacturer of trucks in Russia.
- UAZ - Ulyanovsk Automobile Plant. Founded in 1941. In recent years, the company has modernized equipment for car production and increased sales.
- GAZ - Gorky Automobile Plant. The oldest automobile manufacturer in Russia. The company was founded in 1932. The pedigree begins with the legendary representatives of the Ford company.
Less well-known manufacturers are LiAZ, PAZ, GolAZ, BAZ.
Carbon body: advantages and disadvantages
With the advent of another material, the safety and at the same time lightness of cars has reached a new level. In fact, carbon is the same composite material, only a new generation of equipment makes it possible to create more durable structures than in the manufacture of monocoques. This material is used in the bodies of such famous models as the BMW i8 and i3. If carbon fiber in other cars was previously used only as decoration, these are the world's first production cars, the body of which is made entirely of carbon fiber.
Both models have a similar design: the base is a modular platform made of aluminum. All the components and mechanisms of the car are attached to it. The car body consists of two halves, which already have some interior parts. They are connected to each other during the assembly process using bolt clamps. The peculiarity of these models is that they are built on the same principle as the first cars - a frame structure (only as lightweight as possible), on which all other features are attached.
During the manufacturing process, the parts are connected to each other using a special glue. This simulates welding of metal parts. The advantage of this material is its high strength. When a car overcomes large bumps, the torsional rigidity of the body prevents it from deforming.
Another advantage of carbon fiber is that the manufacture of parts requires a minimum of workers, since high-tech equipment is controlled by electronics. The carbon body is made from individual parts that are formed in special shapes. A polymer of a special composition is pumped into the mold under high pressure. Thanks to this, the panels are stronger than if the fibers were lubricated by hand. In addition, smaller ovens are needed to bake small items.
The disadvantages of such products primarily include high cost, because expensive equipment is used that requires high-quality maintenance. Also, the price of polymers is much higher than that of aluminum. And if a part breaks, it is impossible to repair it yourself.
Here is a short video - an example of how the carbon fiber bodies of the BMW i8 are assembled:
This is how your BMW i8 is assembled. Assembling Your car BMW i8
How to carry out body repair?
If the car body is made of steel, you can repair it yourself. You don't need to learn automotive engineering to do this. It is enough to be able to handle the tool, to know the technology of machine production in theory.
Body repair (Photo: Instagram / skr53b)
Material selection
To repair the body, you need to buy a sheet of low-carbon steel. To do this, you can visit a construction market or a car dismantling center. With the second option, you can find a whole replacement part at a low price.
Equipment
To carry out the work you will need a grinder, an argon cutter, a welding machine, metal scissors, and accessories for power tools. To completely hide the damage, you need a primer, putty, paint, brushes, a spray bottle, and an anti-corrosion compound. If the damage site is difficult to reach, you will need a jack or hole.
For the production of machines, metal is used that meets certain requirements. Recently, plastic has been gradually replacing steel and aluminum-based alloys, but the production of metal cars continues.
Source
Determining the size of paintwork on a passenger vehicle
Different types of cars have more or less the same level of paintwork. Standards from the factory suggest a level of 100-140 microns.
However, during body modifications and further painting of the car, in some places there is a deviation of the cover from this norm.
Due to the increased presence of putty. In these places, the coating thickness can increase to 200 microns.
For body parts where it is difficult to determine this indicator with the eye, a special tool is used to identify this thickness - a thickness gauge.
If on one car you observe a spread of coating from 110 to 310 microns. Most likely, such a car was undergoing repairs and was repainted.
This device is present in all major auto repair shops. Therefore, if you need a detailed assessment of your car, you always have a chance to contact specialists in this profile.
The most expensive high-level thickness gauges can determine the thickness of paint on individual parts: aluminum or plastic.
Don’t forget that American cars usually have a thicker factory coating layer than Russian or Japanese ones.
The device determines the length of the interval from the sensor to the base of the car body. The closer the thickness gauge magnet is to the metal body, the greater the angle the needle moves.
To accurately determine the thickness of the paint layer, there is a special table of factory indicators. Which must be followed for an accurate conclusion.
Tips for using a thickness gauge
There are simple recommendations for effective use of the thickness gauge. Which experts of this profile give:
- You should purchase a device depending on your situation and the surfaces you intend to inspect. If you need to evaluate the quality of coating on steel. Then an expensive thickness gauge for ceramics is not so relevant for you. You can also rent equipment to reduce costs. Or use the metering service at a service station.
- After purchasing a device, you need to take time to calibrate it. There are special samples made of plastic and steel, on which a layer of paint is applied. Check your measurement data with the readings on the samples and, if necessary, adjust the device.
- For each individual measurement plane, it is better to make separate settings for the thickness gauge. And your measurements will be more accurate.
- Slight differences in values are acceptable. Even in the field of one body component, the values are variable: for example, the roof can show 80 microns, and the doors 140 microns.
- Each body element must be measured in at least five places: in the corners and in the middle. This way your measurements will be as effective as possible.
Body metal thickness by car brand
For accurate measurements, you need to attach the device to the car body. Smoothly move it along the surface, starting from the front edge. To ensure accurate results, measurements must be repeated 3-5 times.
Then calculate the average, taking into account all measurements. And then be sure to compare your measurement options with the indicators in the factory table.
Metal thickness on cars table
| Automobile | Model | Paintwork thickness (µm) |
| Audi | A1, A3, A4, A5, A7, A8 Q3, Q5, Q7 | 80-100 110-165 |
| BMW | 1-series, 2-series, 3-series, 5-series, 7 series X1, X3 X5, X6 | 100-165 90-110 120-165 |
| BYD | F3 | 75-100 |
| Cadillac | Escalade,CTS | 120-150 |
| Chery | Amulet, Tiggo | 100-120 |
| Citroen | C5, C-Elysse C4, C3, Picasso, Berlingo DS4 | 110-140 75-125 205-230 |
| Daewoo | Nexia, Matiz | 90-120 |
| Fiat | Albea, Punto | 100-140 |
| Ford | Focus Explorer, Kuga Mondeo | 150-165 135-145 115-130 |
| Hyindai | Accent, IX35, I30, I40, SantaFe, Elantra Tucson, Solaris, Sonata | 70-110 90-130 |
| Honda | Accord Civic Fit, CR-V | 130-150 100-135 80-100 |
| KIA | Sportage, Sorento, Cerato, Cee'd, Picanto Soul, Rio, Venga, Optima Quoris | 100-140 120-140 150-180 |
| Lexus | RX, ES, LX CT, GX, LS IS | 140-150 120-150 110-140 |
| Mazda | CX-7, CX-5 3.6 | 85-120 110-130 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C, E, S GL, ML | 165-180 90-140 |
| Mitsubishi | Lancer, Pajero L200, Outlander XL, ASX | 90-125 55-75 |
| Nissan | X-trail, Patrol, Juke, Qashqai, Murano, Tiida, Pathfinder lmera, Teana | 80-120 130-150 |
| Opel | Astra, Corsa, Mocca, Zafira, Insignia, Vectra | 110-160 |
| Peugeot | 208, 308, 508, 3008 4008 | 100-120 60-80 |
| Renault | Logan, Koleos Fluence, Duster, Megane, Sandero | 180-230 100-140 |
| Skoda | Octavia, Yeti, Superb, Fabia, Roomster | 100-140 |
| Subaru | Forester, Impreza, Outback, Lagacy, Tribeca | 100-140 |
| Suzuki | Grand Vitara SX4, Swift, Splash | 70-100 90-120 |
| Toyota | LC200, Camry, Highlander, Auris, Verso Avensis, Corolla, Prado, Prius, RAV4 | 110-130 80-110 |
| Volkswagen | Polo, Golf Tiguan, Passat, Caddy, Multivan, Amarok Touareg, Jetta | 80-110 110-140 140-180 |
| Lada, VAZ | Kalina, Priora Granta, Niva Largus | 60-100 110-140 180-230 |