If a car's radiator leaks, most of us resort to replacing it. However, in most cases, the radiator can be repaired rather than replaced. Sometimes no skills are required, but sometimes you cannot do without knowledge in the field of welding or soldering. We learn to determine the condition and try to restore the radiator with our own hands.
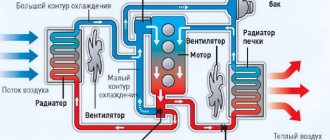
There is a constant circulation of liquid in the radiator, which takes the heat generated in the engine and releases it to the environment. To make this process more efficient, a cooling radiator is installed that has a sufficiently large contact area with air. Antifreeze, antifreeze or plain water can be poured into the system itself - depending on the desires of the motorist. It should be remembered that when using water, operating the car becomes impossible in subzero temperatures.
The most common problem is when the radiator leaks due to age. Coolant runs out from the junction of metal and plastic, which automatically leads to engine overheating. It is not always possible to find a replacement radiator, and repairs will cost at least 2 times less than a new one.
Further discussion will be about car radiators in general, and it doesn’t matter whether it’s repairing a heating radiator, an air conditioner radiator or an engine cooling system radiator.
What is a radiator in a car
As a rule, a radiator is a device consisting of tubes and thin plates in which any liquid circulates, which, passing through the radiator tubes, is cooled and then continues its path into special cavities of the car engine, thereby cooling it and removing excess heat.
Having passed a certain distance in the engine, the heated liquid, which has taken on excess heat from the engine, is returned to the radiator, which is usually blown by outside street air or additionally by a car fan for more efficient cooling. Because of this, it has a lower temperature than the hot liquid that came into it. And thus it takes away excess heat and dissipates it through street airflow or forced airflow, this happens as long as the car engine is running.
Car radiator design
The working part consists of flat metal plates or ribbons bent into an accordion, which pierce the hollow tubes connecting the upper and lower tanks. Thus, the liquid passes through the working part in multiple flows, resulting in an increase in the area and intensity of cooling.
Radiator pipes connect the tanks directly to the engine water jacket, and liquid is poured into the cooling system through a neck located on the upper radiator tank, or through an expansion tank connected to the radiator with a steam exhaust hose. The operating principle of a liquid cooling system is as follows. The water pump provides a system of continuous circulation of fluid, due to which the cylinder walls and cylinder heads are washed, removing excess heat.
The principle of operation of a radiator in a car
The heated liquid is directed through pipes to the radiator, which ensures heat dissipation into the environment. After this, the cooled liquid returns to the motor cooling water jacket and the cycle repeats.
As a rule, in order to increase the efficiency of the cooling system, a fan is installed in front of the radiator, which forces air onto its surface and speeds up the heat transfer process. Typically the fan has an electric drive that starts automatically based on a signal from the coolant temperature sensor.
Soldering
To carry out the operation efficiently, you need to acquire solder, flux, a powerful soldering iron and patience. After cleaning the leakage area from dirt and drying it, apply flux, soldering acid or rosin. The best results are achieved by using soldering acid. It is applied to a heated surface. To be able to heat the soldering area to the required temperature, you must use a powerful soldering iron, at least about one hundred watts. You can also use a mini gas burner. After applying the acid, tin is applied to the damaged area and distributed evenly over the surface with a soldering iron. It is best to carry out this operation several times. If you don’t have enough experience, then it’s best to literally try to pour a large amount of tin into the leak area. Drained coolant can only be used after it has been thoroughly filtered.
Types and types of radiators
Types of radiators that differ in purpose
- Cooling radiators are designed to heat exchange coolant with ambient air and maintain optimal engine temperature
- Heating radiators are designed to heat exchange the coolant with the air inside the cabin and maintain a comfortable temperature for passengers
- Air conditioning radiators provide heat exchange of the refrigerant of the air conditioning system with the environment
- Intercooler radiators provide intermediate cooling of inflatable air on turbo engines, thereby increasing its density
- Evaporator radiators are part of the air conditioning system; they are needed to expand the refrigerant and, accordingly, release cold into the car interior
- Oil coolers provide cooling of engine and/or transmission oil (in order to reduce its fluidity). There are water-oil and air-oil - depending on the principle of heat removal
Radiators by design type
- Aluminum tubular-plate prefabricated ones, in which the working part consists of round tubes strung on cooling plates, and the tanks are made of plastic
- Aluminum tubular-tape brazed, in which the working part consists of flat-oval tubes and a tape folded like an accordion between them, and the tanks are made of plastic or aluminum
- Copper-brass tubular-tape soldered, which differ from the previous type by using copper instead of aluminum, and the tanks are made of brass or plastic
Leaking car radiator symptoms
The most common cooling system problems that car owners have to deal with are two:
- Constant coolant and radiator leaks
- Coking of the radiator, which leads to difficulty circulating fluid throughout the cooling system
The fact that the cooling system is not working correctly can be judged by the constant overheating of the engine, even after a very short period of use of the car. This is fraught with the occurrence of quite serious problems with the power unit and the need for expensive repair work on it.
The most common cause of damage to the integrity of the radiator housing is strong mechanical impact. The relatively thin walls of the radiator can be damaged during repair work or when foreign objects get into it when the car is moving. Quite often, leaks are also observed at the places where the pipes exit the radiator. Whatever the reason for the leak, it must be repaired immediately, since operating a car with a faulty radiator is simply dangerous.
How and with what to seal plastic parts of a radiator in a car
Let's return to the removed radiator. If a leak has formed in the plastic part, then consider half the job done. All that remains is to prepare the surface, run to the store for special glue or cold welding.
Surface preparation
There is no need to use any space technology here. You just need to remove all the dirt and wipe the top with alcohol. Vodka will also work. The main thing you need to remember is that the plastic here is very thin and you shouldn’t apply a lot of force, otherwise the crack may go further.
Use of adhesive
There are a great variety of substances for working with plastic in stores. They are all approximately the same, so you don’t need to bother with the choice, the only thing you should pay attention to is that it says on it that the glue is resistant to aggressive chemical compounds.
The operating technology is also described in the instructions for the product in as much detail as possible. However, it is worth noting that if the hole is large enough or a piece of the body is lost somewhere, additional manipulations will be needed. For example, some apply glue in several stages, gradually building up the lost part.
Most experts do not recommend doing this. It’s better to find a piece of soft plastic and try to stick it inside the crack or put it on top and then glue it on all sides. A kind of patch.
Typically, such compositions cost at least 1,000 rubles, so it’s worth considering whether such repairs are advisable or whether it’s easier to replace the part completely.
How to use cold welding
Most often, of course, cold welding is used for these purposes. It’s much easier to work with and the result looks more confidence-inspiring.
It is enough to squeeze the thick paste onto the crack and spread it evenly with any flat object (some use cotton swabs).
In case the crack is large. It is better to first apply the adhesive base, built up in stages, and secure the result on top with cold welding.
What are the dangers of a car radiator leak?
Among the most common dangers that are fraught with constant leaks of coolant from the radiator include, first of all, engine overheating, caused by the inability of the cooling system to effectively remove the heat generated in the engine.
It is worth knowing that overheating of the cylinder head leads to a rapid change in its configuration and damage to the integrity of the gasket. In addition, if the temperature sensor signals are ignored and the car continues to be driven, the engine may simply seize - this always results in very expensive repairs.
Consequences of poor performance of a car's cooling radiator
A leak from the radiator can have unpleasant consequences not only for the car itself, but also for humans. This is due to the fact that during operation of the power unit a fairly high pressure is formed in the cooling system, and the temperature of the liquid circulating in it cannot be called low.
In the event that the driver opens the hood in an attempt to find out why the engine overheated, a small crack in the radiator, under the influence of hot liquid and high pressure, can suddenly increase, causing a kind of geyser of boiling water. If it comes into contact with the skin, it will cause very serious thermal burns requiring medical attention.
Radiator sealants
In order not to worry on a long journey, you must always prepare for it in advance. Of course, it’s impossible to be prepared for everything, but it’s better to be prepared for a problem such as a radiator leak. Before your trip, it’s enough to purchase and put in the trunk a couple of jars of a special solution for emergency repair of leaks.
How to fix a leak in a radiator yourself
Radiator sealants can eliminate leaks within ten to fifteen minutes. But you should always look at the characteristics of the sealant; most of them cope with holes of no more than two square millimeters. While the sealant is in the coolant itself (the product is poured into the reservoir), it is also in a liquid state. And only after it is exposed to air, it quickly hardens, forming a sealed polymer-metal film at the leak site.
Important nuance! The sealant seals small cracks well, but it can also reliably clog the cooling system lines. Remember that the sealant is a temporary measure, and immediately after arriving home, you should flush the cooling system, then take the car to a car service center for real repairs.
Quickly eliminate car radiator leaks
The occurrence of a sudden leak from the cooling system is the most common problem faced by owners of cars with high mileage. What to do if the radiator leaks while traveling?
The problem can be solved using special liquid sealants. The principle of their operation is as follows. The sealant is poured into the radiator or into the expansion tank, where it is mixed with antifreeze. It flows out through cracks and hardens in air, turning into a durable polymer film.
However, sealants are far from an ideal option for repairing a leaking radiator: they can only be used to repair small cracks with an area of no more than 2 square meters. mm. In addition, experts say that after some time the sealant can cause clogging of the cooling system, so after using this product it must be completely flushed. Otherwise, there is a high probability that the radiator will become unusable and will need to be replaced.
Car radiator repair methods
If you notice that your car’s radiator has become faulty, you need to take care of its speedy restoration. Otherwise, you will have to invest in more expensive engine repairs. In order to properly solder the radiator, you will need to decide on the most suitable method for this matter. The most popular methods for restoring the integrity of this spare part are:
- Soldering. Plastic housings of spare parts are always made of material resistant to high temperatures. This means that the product can be soldered with the most ordinary soldering iron. This way you can achieve a fairly long-term effect.
- Cold welding. This name refers to a special mass of plastic resins, iron and chemical additives. The cold welding method allows you to quickly cope with the restoration of a part from damage. In addition, this method makes it possible to quickly connect two surfaces and form a high-quality, durable seam between them.
- Gluing. This method is most optimal for eliminating minor damage. It is important that not every adhesive is suitable for these purposes: its characteristics must be ideal for working with heat exchanger materials.
How to determine the location of a radiator leak
Typically, the location of the leak is determined as follows. On the removed radiator, all holes for the pipes are sealed, and by placing it in a container with water, excess pressure is pumped up with a pump or compressor. The location of the leak will make itself known by the appearance of air bubbles.
If it is not possible to determine exactly where the radiator is leaking, you need to use special devices. The kit includes a fluorescent additive, a gun for introducing it into the cooling system and an ultraviolet lamp, in the light of which the leaking antifreeze will glow. The problem is that this set is quite expensive and it doesn't make sense to buy it for yourself. It is much cheaper to go to a car repair shop.
How to find a crack or faulty radiator
When the crack is very small, you can detect the location of the antifreeze leak with a simple inspection to determine the source of the leaks. Severe damage is also easily detected by eye.
If the initial inspection fails to identify the location of the leak, experienced technicians do the following:
If the leak is very small, it is better to additionally mark it with a marker. After this, remove the rags and drain the water. All that remains is to decide on the repair method.
Can all car radiator breakdowns be repaired with your own hands?
If the cooling radiator leaks, but the crack is not large, you can fix it yourself. But not in the case when it is located at the junction of the radiator itself and the plastic pipe - such a malfunction is considered irreparable. As a temporary measure, for example, on the road, or if it is impossible to immediately purchase a new one, it is permissible to use epoxy glue or sealant.
If there are one or more small cracks through which antifreeze escapes drop by drop, a special sealant that is added to the cooling system will help achieve an optimal and quick result. Its composition includes special components that tighten small cracks, completely sealing the radiator. After adding the sealant, you can continue to use the car, since the sealant takes a relatively short time to start working and the leakage stops.
Many motorists do not know what to do when the radiator leaks due to corrosion. In this case, no sealant will help, and the radiator can only be repaired by soldering. This procedure is complex, and is performed only with sufficient experience and appropriate equipment. It is equally difficult to restore the functionality of the radiator if it has serious mechanical damage, for example, after an accident. In some cases, it may be necessary to use argon welding.
When carrying out repair work on a radiator yourself, and especially for the first time, you should be prepared for the fact that the work done will have to be redone. It is visually impossible to determine whether all the cracks are repaired on the removed radiator - this becomes obvious only after installing it and starting the engine. If, after half an hour of the car idling, the leak does not manifest itself, then the result has been achieved. If the leak continues, work will have to start all over again.
Cold welding for radiator
If the crack in the radiator exceeds the maximum that can be repaired with a liquid sealant, then you can use another means - a heat-resistant adhesive sealant or cold welding (the composition of such glue has metal powder). Such products are sold in car dealerships in ready-made paste form or in the form of two components that must be mixed before use.
Quick-drying putties contain titanium and steel powder fillers; they set within a few minutes and reach final hardening in fifteen. Such a patch can be subjected to mechanical stress within an hour. Such sealants glue metal, rubber and plastic, as well as glass. As the glue hardens, it expands, giving a cork effect, which helps with fairly large cracks. This plasticine is applied around the damage, having previously cleaned and degreased the area. Cold welding holds up well, and the same coefficient of expansion when heated makes this a reusable patch that can last for several months or longer.
How to find a leak in a radiator
The history of the creation of a car radiator, as well as its development and evolution
During the development of the automotive industry, many new components appeared. But some details were present in the design of “self-propelled carts” almost from the beginning of their operation. One of these components is a car radiator, the history of which dates back to the end of the 19th and beginning of the 20th centuries.
Coils
As long as the engines were of low power, excess heat was dissipated directly from the engine and its components. With an increase in power, the first radiators began to be used - in the form of a smooth-walled copper pipe, bent in the form of a coil. In 1900, external fins for this coil were used.
Honeycomb radiators
In 1913, the first plate brazed copper-brass radiator appeared. In parallel, a radiator design appeared in which the air passed through horizontal air tubes inside the tank; the number of these tubes grew larger over time until a honeycomb radiator was created, which was common until the mid-30s.
Tubular-plate and tubular-tape radiators
Honeycomb radiators are quite labor-intensive to produce, bulky and heavy. The main incentive for the development of automotive heat exchangers - an increase in engine power and a reduction in engine compartment space - forced the development of more complex designs. Radiators have brass bottoms where copper tubes surrounded by steel plates are sealed (tubular-plate copper-steel radiators). Due to the use of steel plates in the production of tubular-plate radiators, many disadvantages of this design arise - high weight, minimal heat transfer rates, low corrosion resistance of the core, low vibration resistance.
In their further development, such radiators receive copper tape instead of steel plates (tubular-plate copper-steel radiators), which can significantly increase their heat transfer. Such a radiator weighs much less with a significant improvement in thermal performance.
Prefabricated aluminum radiators
Prefabricated aluminum radiators began to be developed in the USSR during the Cold War. Since copper was a strategic raw material, researchers began to try to create aluminum radiators of brazed and prefabricated construction. Prefabricated radiators have lower heat output, but are cheaper to manufacture.
The first attempts to create aluminum prefabricated radiators were made at the Mariupol (Zhdanovsky) radiator plant for the ZiS-120 car, but they were not very successful, since the design with flat-oval tubes was taken as a basis. The flat-oval tubes were incredibly difficult to seal at the ends where they met the bottoms, making the project very expensive and soon abandoned. About 2 thousand radiators of this type were made.
Brazed non-assembled aluminum radiators
The first steps towards the most modern heat exchangers - aluminum brazed radiators - were made in the 70s of the 20th century. The first radiators of this design were originally developed for GAZ 3102 cars. Unfortunately, the first experiment was unsuccessful - the brazed aluminum radiator could not cope with heat transfer, especially in urban mode, and therefore was soon replaced by a copper-brass one. However, the reason for its poor heat transfer was the design of the aluminum tape - its pitch was approximately 8mm. The reason for such a large-cell core design is trivial - at the plant that produced these radiators, there was no technological opportunity to make a smaller pitch of the cooling tape.
Interesting developments in the field of car radiators
The entire development of automotive heat exchangers has strived to increase heat transfer while maintaining dimensions and simultaneously reducing cost. The pace of development of automobile radiators was determined by the rapid pace of development of automobile engines - engine power grew very quickly, and it became increasingly difficult to cool it.
In attempts to achieve results, various interesting types of radiators were created, which for some reason were not included in the series. The most interesting samples are presented below:
Automotive radiator
Of interest is the method of securing the tank lids - using bolts. This radiator is repairable, which is especially important for rural areas.
“Waste-free” aluminum radiator
Developed by V.V. Burkov. for the KamAZ vehicle. It is a rather original design; Instead of cooling plates, aluminum production waste (actually sawdust) was used. Such a radiator turned out to be quite difficult to manufacture and therefore did not become widespread.
Aluminum Brazed Heater Core
Used for LiAZ buses. This radiator is of particular interest due to the use of removable radiator pipes. This decision was most likely made to unify the product - given the impossibility of accurately specifying the angle at which the pipes need to be fixed, a variable angle is required.
Aluminum Assembled Flat Oval Tube Cooling Radiator
Designed for PORSCHE cars. While the traditional aluminum prefabricated radiator has round cooling tubes, the flat oval tube radiator takes us back to the first attempts at a prefabricated radiator. Why create a radiator with flat oval tubes? The contact area of the incoming air flow with such a tube is 30% larger than with a round one - accordingly, the heat transfer is greater.
Combined cooling and heating radiators
When creating such radiators, combinations of traditional materials were used - copper, brass, aluminum, steel. The most striking example is a prefabricated radiator with round aluminum cooling tubes and copper plates.
Improving the design of Luzar car radiators
The development of automotive heat exchangers does not stop. The emergence of new types of radiators, which have their own advantages and disadvantages, is accompanied by numerous and sometimes unnoticeable design improvements, which are of great importance for increasing the efficiency of a given vehicle component.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with some of the innovations developed and introduced into the production of Luzar automobile radiators.
Improving heat transfer is the use of plastic turbulators inside the radiator.
This design improvement made it possible to improve heat transfer performance. The turbulator creates turbulence in the flow of coolant in the radiator - due to this, the liquid releases heat faster.
Universal radiators - use a heat-resistant sealed plug at the location where the fan switch sensor is mounted.
Cars of the LADA Samara and LADA Ten family with a carburetor engine are equipped with a fan activation sensor, for which a threaded hole is provided in the radiator tank. Cars of this family with an injection engine are not equipped with a fan switch sensor. The cooling radiator for this engine modification does not have a hole for the sensor.
In addition, VAZ-2105 cars have a forced constant fan drive (the fan does not have an electric motor and rotates along with the crankshaft speed) - the sensor is also not used in radiators on such cars. A similar radiator for VAZ-2104 and VAZ-2107 cars has an electric fan; The radiator for such a car requires the installation of a fan switch sensor.
The use of a heat-resistant plug at the sensor mounting location made it possible to unify six models of radiators.
Universal radiators - double mounting points for the radiator deflector (casing)
These radiators have universal mounting points for the fan deflector (casing), suitable for VAZ-2105 and VAZ-2107 modifications. For VAZ-2105 cars, the upper and lower mounting points of the radiator deflector (casing) are used; for VAZ-2107 and VAZ-2104 cars – the middle location for attaching the deflector.
Both aluminum and copper-brass radiators Luzar received this improvement.
Universal radiators - use a heat-resistant sealed plug at the mounting locations of the fan switch sensor and overheating sensor. Used on aluminum and copper-brass radiators for Volga and GAZelle cars - they unify the use of such a radiator on cars with ZMZ-402 and ZMZ-406 engines.
Construction of aluminum radiators
First, let's look at the design of aluminum radiators and what composite materials are used during their production. The first type is a traditional aluminum radiator with plastic tanks ; depending on the model, it may differ in the way the tanks are clamped and the core is made.
As a rule, the tanks are clamped with wave rolling or teeth. Sometimes it may seem that the only difference is in the rolling method, but this is not true. Without going into details, we note that the type of gasket used between the bottom of the radiator and the tank imposes certain restrictions, or, in other words, entails the use of a specific type of rolling. Now let's look at the types of cores.
typesetting
Stacked cores are divided into:
- all-soldered;
- typesetting (or prefabricated).
Solid soldered
These radiators are more complex to produce, and, accordingly, they cost much more than prefabricated ones. The meaning of the core is that it is collected, like copper, but then sent to a special furnace with an inert gas environment and a strictly defined temperature for sintering. Then, when the core is ready, plastic tanks are connected to it using wave rolling. Naturally, in nature there are combinations of the above methods.
Prefabricated
As a rule, prefabricated models are based on round tubes with a cross-section of 7-11 millimeters, and stacked heat sink plates; they are not welded to the tubes, but simply tightly placed on them. The advantage of this design is its low cost, since almost all work is carried out mechanically, without the help of welding. But there is still one type of prefabricated radiators, where the tubes are not rolled through silicone gaskets to a metal mesh, but are soldered to an aluminum one. In 99 percent of cases, the tanks are connected to these radiators using a certain type of gear rolling.
A little different are all-aluminum radiators, in which both the cores and tanks are made of aluminum. The cores of these radiators are always made using solid-soldered technology .
But, surprisingly, not a single cooling radiator from a large manufacturer uses this technology, since the tanks may require the same amount of material as the core itself. The only exceptions are exclusive American radiators; they are produced to order by the capricious owner of a “drag” or a restored “classic”.
In our country, this technology is found either in stove radiators from some manufacturers (for example, Daewoo Nubira, Lanos), or in models from a frankly Chinese or domestic manufacturer. But these two described options, although cheaper than a copper-brass radiator, the quality of their assembly and design is completely copied from brass models, and inherits all the “innate” shortcomings. In addition to the above, it must be said about aluminum stoves, their tanks are not welded to the mesh, as they should be, but glued, and even with glue, which is dangerous to use even with a garden watering can, let alone a heating radiator.
That is, in order to produce a high-quality aluminum radiator, which, in addition to good heat dissipation, can also withstand mechanical and hydrodynamic loads for a long time, requires careful design and the use of complex equipment during production. And this increases the cost of the final product, which will immediately transfer it from the category of leaders, in comparison with the “copper” product, to the level of expensive outsiders.
Since, for example, in a GAZelle, on our roads, a brass radiator rarely travels 40,000 km without breakdowns, and this is about a year with a daily load of 100 km. After overhauling the radiator with our own hands, we can double its lifespan, unlike the factory one, but doing this with an aluminum analogue is quite difficult, and most importantly, not very profitable financially. Here is a reason to think about whether you need to save money when buying between an aluminum and a brass radiator?
"Exotic"
As a rule, craftsmen call stoves and radiators exotic, which can be found very rarely. 1992 Opel Omega heater ; it is made of a completely plastic mesh (bottom) and tanks, made monolithically, and connected to a stacked core, which has oval tubes, with a welded turbulator.
Besides this example, there are also a number of rarely seen varieties, but again, these are rare. It should be noted that the more exotic the radiator is on your car, the more difficult it is for car mechanics to repair it, and not only because of the complexity of combining different materials, but also because the experience of many craftsmen simply does not make it possible to use a tried and true one the first time. repair option. That is, an inexperienced technician will carry out repairs at random, while simultaneously learning the intricacies, so to speak, practicing with his own hands on your radiator, gaining experience.
Plastic tanks
As mentioned above, plastic tanks lighten the weight and reduce the cost of construction.
But we need to make a reservation, the term “plastic” when considering tanks is not very correct, since they are based on polypropylene, and no one will disclose other additives and impurities; survival in a competitive environment depends on this. Here you can find fiberglass reinforcement, fillers, and other tricks. After a certain time, plastic tanks dry out, the base of the plastic changes under the influence of a constant temperature difference and they become brittle and form a leak. In this case, the best option would be to replace the radiator with a new one, because replacing the tank is not always cost-effective. But sometimes, if we consider exclusive models, there is nothing you can do to repair cracks in the tank with your own hands, but here the second question arises - which repair option is better?
There are three main repair options:
- replacing the tank with a metal one, which is welded or soldered in place of the plastic one;
- soldering the tank with plastic;
- use of special polymers.
The first method is the most reliable, but also the most expensive, and the problem with the second tank remains (since there are two of them in the radiator). If you replace two tanks, the cost will be such that it is easier to order a new, original radiator, and all the assurances of the craftsmen, such as the radiator will last forever, must be ignored, since the aluminum part also has a certain resource, and it decreases simultaneously with the service life of the plastic ones tanks. The high price of these tanks is explained by the fact that they are not made by the master himself, but by an industrial plant, like an aviation plant (Antonov Design Bureau or KhAZ), and the master only welds it in with his own hands using argon welding.
The next two methods are more accessible, since the use of polymers and soldering plastic is cheaper and faster, and when using a very old radiator, it will give you the opportunity to “turn around” before purchasing a new one, without large investments. But it must be said that soldering a complex polypropylene composition is sometimes even dangerous; you can make it even more fragile in the soldering area.
Conclusion
We hope you now have a good understanding of what a radiator is, what functions it performs, and how you can quickly and efficiently repair a car radiator on the road and in stationary conditions.
We recommend articles on this topic:
- How to do car tinting yourself -...
- How to repair a speedometer with your own hands if it is broken
- How to tint a car with your own hands
- How to maintain good condition of a MTZ diesel engine
- Repair of truck engines: stages of work
- Automatic transmission repair
- How is LG TV repair performed?
- Bus repair. What breaks most often?
- Choosing a good oil for a car
- What you need to know before installing amplifiers to...
- How to choose a trailer for a car
- Covering a car with car film
- Car diagnostics
- Useful car accessories
- What is the difference between a simple car wash and a detailing car wash?
- How to quickly remove the front seat of your car
- Stingray - rubber floor mats for the interior of your car.
- Heated car seats
- Car condition assessment
- Advantageous purchase of a car in Kazakhstan
- Popular accessories for the car interior
- Car detailing: what is it?
- What to do after buying a car?
- Why choosing a car should be trusted...
- Armor film for a car: how it works...
What to do if your car radiator is leaking
Let's move on to the most interesting part - how to fix a leak in a car radiator. The radiator can leak in different places. Some leaks can be eliminated with your own hands, while others cannot always be dealt with without serious repairs.
Unfortunately, it can be difficult to determine whether the leak has been eliminated. This becomes visible only after installing the radiator on the car and filling it with antifreeze. The engine must be started and allowed to run for 30 minutes. Only then will you be able to see the result of your work.
In the process of repairing the radiator, attention should be paid to external cleaning of the heat exchanger, because the larger the area of contact of the air masses with the surface of the radiator, the more efficient the cooling of the antifreeze will be. And creating a favorable temperature regime for engine operation will subsequently pay off in the trouble-free and long-lasting operation of the car.