When it is necessary to reliably fasten various solid connections together, soldering is most often chosen for this. This process is widespread in many industries. Home craftsmen also have to solder.
This operation helps not only when the TV or computer has failed, and to restore it it is necessary to replace the burnt microcircuit or chip. Using this process, refrigeration equipment and industrial systems are restored. Soldering helps if you need to get a tight connection. In addition, some materials simply cannot be combined in any other way.
Aluminum, copper, and brass cannot be joined by welding. In order to obtain a high-quality and reliable, as well as hermetically sealed connection, you need to have not only good equipment and special skills, but also suitable consumables - solders and fluxes for soldering.
Solder alloys and types of flux are selected depending on the materials with which you will have to work. For example, when working with aluminum products, a different flux is needed than what is suitable for copper or silver. Below we will look at the main characteristics of each of them and choose the best option for the job.
Wettability
First of all, any type of solder must have excellent wettability. Without this characteristic, the parts being soldered simply will not be able to reliably contact each other. What is wettability? This is such an interesting phenomenon when the strength of the bonds between the particles of a solid and a liquid is higher than that of the molecules of the liquid. If there is wettability, then the liquid will spread over the surface and enter all cavities. So, if solder solder does not wet copper, for example, then it cannot be used on that metal. Pure lead is not used for soldering. Its wetting characteristics are very poor and high quality joints cannot be counted on.
Preparation of material
To achieve a good quality connection, you need to use not only the right technologies, but also be able to properly prepare the surface to be treated . All dirt and oxide films must be removed. Mechanical processing is carried out using sandpaper or a metal brush, and sometimes a stainless steel mesh and a grinding machine are used. You can also use different acid solutions.
The surface must be degreased using solvent, acetone or gasoline. When an aluminum surface is cleaned, an oxide film immediately forms. However, its thickness will be lower than the original one, and therefore the soldering process will be easier.
Melting temperature
Whatever the type of solder, the temperature at which it begins to melt must necessarily be below the melting point of the materials being soldered. It should also be higher than the operating temperatures of the parts.
When we talk about melting point, we mean two points. This is the value at which low-melting components will begin the melting process, and the minimum at which the alloy will turn into a liquid. The difference between these two temperatures is called the crystallization interval. If the soldering site is within this difference, then even small mechanical loads on the part can completely destroy the structure of the solder. Such a connection will exhibit high fragility and resistance. Remember the main thing: you should not influence the connection in any way until the solder solder has completely crystallized.
Important properties of solders
Whatever the type and type of alloy, whatever material it is used with, it should not contain heavy metals or any other toxic substances above the established norm. The composition of the solder matches the material of the parts as closely as possible. Otherwise, you will not be able to get a reliable connection. There will be excessive fragility.
Any solder, regardless of type and purpose, must be heat-stable. Also, solder for soldering must be electrically stable. The coefficients of thermal expansion and thermal conductivity should be taken into account. They should not differ significantly from those values that apply to soldered products.
Why is aluminum difficult to solder?
Anyone who has tried to solder aluminum knows that ordinary solder does not stick to it at all. This is all due to a stable film of aluminum oxide, which has poor adhesion to solder. Moreover, this film covers aluminum and its alloys very quickly. Before you have time to clean it, the light metal has already oxidized. Therefore, all methods of aluminum soldering first deal with the film, and then take care of adhesion.
Aluminum oxide (Al2O3) in mineralogy is called corundum. Large transparent corundum crystals are gemstones. Due to impurities, corundum comes in different colors: red corundum (containing chromium impurities) is called ruby, and blue corundum is called sapphire. Now it is clear why the oxide film does not solder at all.
Soft solders
Tin-lead alloys with different contents of components are considered one of the most popular and widespread. In order to give the material the necessary characteristics, various additional ingredients can be added to the solder composition. For example, bismuth and cadmium are used to lower the melting point. The addition of antimony increases the strength of the solder joint.
Lead and tin alloys have a low melting point and low strength. They should not be used for parts whose operation involves heavy load. These solders are also not recommended if the operating temperatures of the parts are above 100 °C. If you have to solder loaded parts with soft solders, you should try to increase the contact area of the two products.
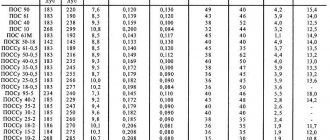
Among the most popular soft materials are POS-18, POS-30, POS-40, POS-61, POS-90. The numbers are shown here for a reason. This is the percentage of tin in the alloy. In industry, it is more often used in the production of electronics and instrument making. In everyday life, they can connect a variety of parts: circuits for televisions, microwaves, electric kettles and other small appliances.
Purpose of soft solders
POS-90 is designed to work with parts that will then be processed using galvanic technology. POS-61 can be used to repair high-precision equipment. The alloy is also ideal for joining high-demand parts made from a wide variety of materials. POS-61 has proven itself as a solder for soldering copper and brass. Solder is suitable when it is necessary to achieve strong connections with a high degree of electrical conductivity.
POS-40 is widely used for operations with non-critical and imprecise parts. In this case, the working area can heat up to high temperatures. POS-30 is suitable for soldering copper or brass, steel alloys and iron.
How to remove oxide film?
The aluminum oxide film is removed in two ways: mechanical and chemical. Both methods remove aluminum oxide in an airless environment, that is, without access to oxygen. Let's start with the most difficult, but most correct and reliable method of removal - chemical.
Precipitate copper or zinc
The chemical soldering method is based on the preliminary deposition of copper or zinc onto aluminum by electrolysis. To do this, apply a concentrated solution of copper sulfate to the desired location and connect the negative of the battery or laboratory power source in a free place. Then take a piece of copper (zinc) wire, connect a plus to it and immerse it in the solution.
Through the process of electrolysis, copper (zinc) is deposited onto the aluminum and adheres to it at a molecular level. Then aluminum is soldered on top of the copper. True, it is not clear how all this passes through the oxide barrier. I think that this instruction skips the step of scratching aluminum under a film of copper sulfate or other chemical exposure. Although the practice from the video below shows that you don’t have to scratch.
Use oil without water
The second most difficult method is to remove the aluminum oxide under the oil film. In this case, the oil should contain a minimum of water - transformer or synthetic oil will do. You can hold the oil at a temperature of 150 - 200 degrees for several minutes so that the water evaporates from it and it does not splash when heated.
Under the oil film, you also need to remove the oxide. You can rub it with sandpaper, scratch it with a scalpel, or use a serrated tip. When I needed to solder the engine cooling radiator, I used the chip method. We take a nail, saw it with a file to get steel shavings.
Next, apply oil to the soldering area and sprinkle chips. Using a soldering iron with a wide tip, we try to rub the soldering area so that there are shavings between the tip and the aluminum. In the case of a massive radiator, I additionally heated the tinning area with a hot air soldering station.
Then we take a drop of solder onto the tip, immerse it in oil at the soldering site and rub it again. For better tinning, you can add rosin or other flux. The so-called surfacing under a layer of flux occurs. The video shows a good example of soldering aluminum with oil.
Solder with active flux
There are separately developed active fluxes for soldering aluminum. They usually contain acids (orthophosphoric acid, acetylsalicylic acid) and salts (sodium salt of boric acid). Strictly speaking, rosin also consists of organic acids, but in practice it gives a weak result on aluminum.
Due to their activity, acid fluxes must be washed off after soldering. After the first wash, you can additionally neutralize the acid with alkali (soda solution) and wash it a second time.
Active fluxes give good and quick results, but inhaling the vapors of this flux is strictly prohibited. Vapors irritate mucous membranes, damage them, or can enter the bloodstream through the respiratory tract.
Solid
Among refractory alloys, only two groups are distinguished and widely used. These are mainly copper or silver alloys.
The first group includes solders made of copper and zinc. They are well suited for those connections that will only be subject to static loads. The fragility of these alloys does not allow their use in components that will experience shock or any vibration.
Copper solders or zinc-based compounds include PMC-36 and PMC-54. The first is an ideal solder for soldering brass and any other copper joints. The second is suitable for working on copper, bronze or steel parts.
If you need to connect two steel parts together, then you can use pure copper, brass grades L-62, L-62, L-68. These brass-based solders create stronger, more ductile joints. Copper alloys do not have these characteristics.
Silver alloys are considered the highest quality. The composition may also contain zinc and copper. PSR-70 – solder for soldering copper, for working with brass or silver parts. This element is suitable if the connection point must conduct electricity. PSR-65 is used in the production of jewelry, fittings, and water pipes. PSR-45 is necessary for connecting those parts that operate under vibration and shock loads.
Tools
If you need to connect aluminum products at home, then it is advisable to use an electric soldering iron. This is a universal device that very conveniently allows you to solder wires, repair small tubes and other elements. The adaptation requires a minimum amount of space. There must also be electricity in the house. If you need to repair a large-sized device, then use a gas torch for soldering aluminum, which uses butane, argon and propane. To solder objects at home, a standard blowtorch is suitable.
If gas burners are used, then it is necessary to constantly monitor the flame, which represents a balanced supply of gases and oxygen. If the correct gas mixture is present, the flame will be bright blue. A dim hue will indicate that there is excess oxygen.
Features of aluminum soldering
Connecting aluminum parts by soldering is used in industry and in everyday life. For example, modern bicycle frames are made of aluminum alloys - they often break during extreme riding. The question arises: which solder should I choose?
It is believed that soldering aluminum is a very complex process. But in fact, this is true if the process uses materials for stainless steel or brass, steel, and copper. The reason for this is the oxide film. It is this that does not provide the required level of wettability, and the base metal does not dissolve.
Features and principles of the process
The technological process of soldering is complicated by the low temperature value of the material melting . Parts will very quickly lose strength when heated, and the design will reduce stability when the temperature reaches 300 degrees. If you use low-melting solders, which consist of cadmium, bismuth, indium, tin, then they will be very difficult to come into contact with aluminum, and good strength will not be provided.
Metals that combine zinc have very good solubility . In this case, the soldered materials will be highly reliable. Before starting soldering, the material should be cleaned of oxides and dirt. For this purpose mechanical action is used. You can use a brush or use special fluxes that have a strong composition. Before starting the procedure, it is necessary to tin the areas that will be treated. If the coating is tin, the part will be protected from the formation of oxides.
To reliably solder aluminum products, you need to select the right heating tool. And the reliability of the connection also depends on the choice of alloy and flux for soldering aluminum.
How to solder aluminum and aluminum-based alloys
In order for the work to be carried out at the proper level, the solder for soldering aluminum must contain silicon, aluminum, as well as copper, zinc and silver. Today you can find formulations on sale where all these components are in different proportions.
When choosing reliable solder, it is important to consider the following. The maximum resistance to corrosion and high strength will have the connection that was made with solder, which contains a lot of zinc.
Also for aluminum you can use compounds based on tin and lead. But it is important to properly prepare the work surface, clean it with a stainless steel brush and use active fluxes. But experts do not recommend using such an element.
Any solder for soldering aluminum is high-temperature. The most optimal ones, which allow you to obtain a reliable connection, are aluminum-silicon and aluminum-copper-silicon.
Kastolin
Imported castolin consists only of aluminum and zinc. It has good fluidity, penetrating ability, and electrical conductivity.
Some inconvenience is caused by the impossibility of using this solder for parts with a magnesium content of more than 1.5% and products that are subsequently planned to be anodized.
Castolin sells a range of solders with a varied combination of components. After consultation, you can choose a remedy for specific conditions.
How to solder copper?
As noted above, you can work with most compositions. Both low-temperature fusible and hard solders can be used. Compositions based on tin with lead, tin, silver, copper with silver and zinc are also used.
If you need to repair a computer motherboard or repair a TV in the country, any fusible elements will do. If you need to solder fittings on pipes or repair a plumbing system or refrigerator, then only hard solder for soldering copper will do. This is how you can get high-quality results.
Stainless steel
If you need to connect stainless steel parts, then professionals recommend using rods made of tin and lead. Materials containing cadmium also work well. Low-melting alloys based on zinc can be used. However, they should not be used together with carbon or low-alloy steels. The best solder for soldering stainless steel is a composition based on pure tin. In addition, only tin is allowed if the soldering area will be in contact with food.
If the work will be carried out in a dry or furnace atmosphere, then silver with manganese, chromium-nickel solders or pure copper (or even better, brass) should be used. When soldering has to be done in corrosive conditions, silver tinols with a small part of nickel are used.
Soldering fluxes
During the operation, flux plays no less a role than solder. It is a chemical solvent and oxide absorber. It also protects metals from oxidation and increases wetting.
To work with elements based on lead and tin, hydrochloric acid and zinc chloride can be used as a flux. Borax and ammonium chloride are also suitable. These are active fluxes. Inactive substances include rosin, petroleum jelly, olive oil and many other substances.
For example, hydrochloric acid solutions can be used with soft solders. Zinc chloride is used with brass, copper, and steel. Ammonia sleeps perfectly dilutes and dissolves fatty substances. For aluminum, a composition of tung oil, rosin, and calcined zinc chloride is used. You can also use concentrated phosphoric acid.
So, we found out what solders exist, and which one is better to use in different cases.
Safety precautions
Before you start working with a soldering iron, you should always first study the safety rules.
- You only need to work with the window open. Because you can get poisoned due to secretions during work.
- There should be nothing flammable around. If a soldering iron is dropped onto paper, for example, it can cause a fire.
- The device should be held exclusively by the special handle, since during operation it becomes very hot, which can lead to burns.
- Children should not be allowed near the soldering iron. The device should always be kept in a place that is difficult for the baby to reach.
- The device can only be lowered on a special stand during breaks between soldering. If the soldering iron is placed on a table, a fire may occur.
Follow these simple rules, and no problems will arise during operation.
To perform high-quality soldering of aluminum materials at home, it is necessary to fully comply with the technology. If you choose high-quality methods, solders, fluxes and materials, then the result will be positive.