Currently, there are a lot of welding devices, the operation of which is based on different principles. Each technology has its own advantages and disadvantages. In addition, sometimes situations arise when a certain type of welding is suitable. The most popular is powder welding with a special wire.
Flux cored wire welding
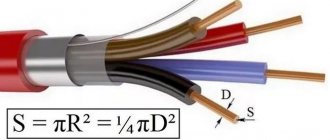
The cored wire used for arc welding is a tube where the inside is filled with metal powder and flux. The material is based on a metal strip processed using cold forming technology and filled with a mixture of flux and powder. At the final stage of production, the cored wire is stretched to the required parameters.
Flux-cored wire used for welding without gas, the price of which is affordable, is classified according to its purpose, the method of protection used, the technology of welding with flux-cored wire in different spatial positions and mechanical properties. Flux-cored wire welding is used in the installation of low-alloy and low-carbon steel. The material can also be divided according to the conditions of use (for simple or special welding - under water, with forced welding, installation of reinforcement, etc.).
Manufacturers
Quite a lot of enterprises that produce consumables specialize in the production of stainless steel welding wire, some of them.
ESAB is a Swedish company whose activities are based on innovative solutions in all areas of welding technology. Over the 110 years of its activity, it has become a world leader in the welding industry, producing not only stainless, but also polished, copper-plated, aluminum and other types of wire.
Stainless steel welding wire ESAB OK Autrod 316LSi, 0.8mm., 5.0kg. Photo Welding Technologies
OLIVER has been on the welding technology market since 1993. The company has kept pace with evolving trends and continues to strive to look into the future.
LINCOLN ELECTRIC is an American company founded in 1895, which released the world's first single-user welding machine in 1911. Has its own separate enterprise for the production of welding wires.
DEKA is a Chinese manufacturer offering a wide selection of stainless steel wires at affordable prices.
Requirements for consumables and their advantages
Flux-cored wire used for arc welding is produced in accordance with the basic requirements:
- With the creation of uniform melting of the material without large splashes;
- Stable heating and easy arc initiation;
- The result should be a neat seam, without defects (pores and cracks);
- The slag formed during melting should be evenly distributed along the seam and separated upon cooling.
Such requirements are the main parameters for welding materials and determine the use of flux-cored wire when welding steel under different conditions.
Welding of powder steel helps solve construction and production problems, increases the productivity of the process, and reduces the labor intensity of manual cleaning of products from splashes. Depending on the type of use and protection from external factors, the wire can be gas-protective or self-protective.
Welding with self-shielded flux-cored wire
Gas-shielded wire is used in semi-automatic and automatic flux-cored welding to join low-alloy and carbon steels in carbon dioxide or its combination with argon. This material is characterized by powder welding with high penetration, which ensures its use in the production of overlaps, joints and corners in 1 or several approaches in automatic or semi-automatic mode. Welding with flux-cored wire in a gas environment is characterized by low spatter, stable jet transfer, rapid peeling, and resistance to the appearance of slag and pores.
Conventionally, wires are divided into the following types
:
- To connect low-carbon steels with a high level of surfacing, wire with a flux core is used;
- Flux-cored wire is used to join low-carbon steels in different positions;
- For installation of low-alloy steels, wire with a core of metal powder is used;
- For installation of low-alloy steels, wire with a flux core is used;
- For welding low-carbon steels, wire with a core of metal powder is used.
Flux-cored welding with a gas-shielded wire produces a good weld shape and low spatter. Also, the consumable material differs from other types in its high deposition rate, efficiency of welding and low smoke.
Self-shielding flux-cored wire is an inverted electrode. Self-shielded cored wire welding can be done in windy conditions, extreme temperatures, or outdoors. The core composition includes dioxidizing, slag-forming and protective additives, which eliminates the use of flux and gas. Thus, welding is carried out with flux-cored wire without gas.
The advantages of self-shielding wire include the following:
- Carrying out welding in different positions;
- Accurate movement of the deposited metal due to the open arc;
- Carrying out strict control of the chemical composition allows you to obtain the exact composition of the slag;
- There is no additional device for the supply of gas and flux;
- The special coating on the wire is resistant to high pressure from the rollers.
Wires are classified according to general purpose; they can be used for connecting pipes or metal structures, etc.
Welder tasks when working with aluminum
Taking into account the peculiarities of the behavior of aluminum alloys during welding, you must solve the main tasks during the work: get rid of the oxide film, ensure a stable arc during welding and timely supply of welding wire so that the aluminum welding process is continuous, otherwise it will have to start again.
The welder must:
- get rid of the oxide film at the seam: pierce it with an electrical impulse or mechanically clean the surface using a metal brush or by chemical etching. To pierce the film, a special pulse operating mode of the equipment is used;
- when choosing a welding mode, avoid burning through the metal due to the increased thermal conductivity and low melting threshold of aluminum, leading to a rapid loss of strength when heated. To do this, he must ensure the required process temperature and an arc of 12 to 15 mm in length, select the correct electrodes and filler wire size suitable for the thickness of the aluminum parts being connected and the torch nozzle;
- take into account the tendency of aluminum to significant linear shrinkage (almost twice as much as steel) upon rapid cooling after heating, since this leads to the creation of internal stress with the formation of deformation cracks or craters in the weld area. To prevent this, you need to start the welding process with a high welding current in order to break through the oxide film, and finish it by gradually reducing it towards the end of the process, this will soften the sudden change in temperature and prevent the formation of a crater.
Flux cored wire production technology
In flux-cored wire, the inner core - the charge - must be made of certain components, selected according to granulation and chemical composition. Some materials (alumina, starch, fluorite concentrate, rutile concentrate, iron powder, sodium fluoride, etc.) are supplied in powders, which must be sifted and dried. The finished composition is sent to the wire filling area.
Flux-cored wire consists of an outer coating and a core. For the outer layer, unpolished cold-rolled strip made of low-carbon steel is used. In the production technology of wire of the specified diameter, the width and thickness of the tape are determined. The tape with special lubricant is sold in the form of circles or rolls with an internal diameter of 15 cm, and is cleaned of dirt and oils before use. Chemical and mechanical ultrasound is used to clean the tape. During mechanical cleaning, the tape passes through drums with Vienna lime, degreasing.
Flux-cored wire is often used in the creation of metallurgical complexes, reactor vessels at nuclear power plants, in the manufacture of large tanks, heavy cranes, coal combines, construction and agricultural equipment. The production of solid wire of alloyed and high-alloy types is a costly process, so it is carried out at large hardware enterprises.
The production of high-alloy electrodes for mechanized surfacing is carried out from flux-cored wire, consisting of a coating and a powder core (a mixture of carbides, metals, borides, iron alloys). To make self-shielding wire, slag and gas-forming compounds are added to the core, after which welding is carried out with flux-cored wire without gas.
Often people decide to buy flux-cored wire, which is used for welding with the following characteristics: 3.6 mm in diameter (for flux-cored welding) and 0.2-0.3 cm in size (for open-arc joining).
Other types of welding wires
For welding most non-ferrous metals and their alloys, welding wires of various diameters made of aluminum, copper and brass are used.
For aluminum wire and wire made of aluminum alloys there is a domestic GOST 7871-75, which specifies its dimensions (from 0.8 to 12.5 mm) and chemical. compound. GOST 16130-72 applies to wire made of copper and copper-based alloys. Copper wire is available in Ø from 0.8 to 8 mm.
The diameters of welding wire produced in accordance with GOST in our country differ from foreign analogues. And since automatic and semi-automatic welding machines are mostly foreign-made, there is a need to know analogues of wire produced abroad. For example, an analogue of the most used brand Sv08G2S is copper-plated wire ER-70S-6, manufactured by the well-known manufacturer FARINA from China. Supplied with row wound spools. Foreign wire is marked according to AWS standards.
Welding wire can be supplied:
- in coils (Ø 830 ÷ 850 mm, height 700 ÷ 1000 mm, weight up to 1.3 t);
- skeins (Ø 220 ÷ 730 mm, thickness 60 ÷ 180 mm, weight 15 ÷ 120 kg);
- on cassettes and reels weighing 5, 15 and 18 kg.
Coils, skeins, cassettes and reels can be supplied unpackaged and packed in polyethylene or special boxes. If the wire is supplied unpackaged, then before use it must be dried at a temperature of at least 200 0C for half an hour
Features of arc welding
The flux-cored arc welding technique is often used because it has many advantages. For example, welding with flux can be complicated by accurately directing the electrode to the required point. It is also necessary to control the formation of the seam. Such difficulties often arise if semi-automatic powder welding is carried out. But welding with flux-cored wire in shielding gas will be difficult, since the protection may be compromised due to drafts or the nozzles supplying gas may become clogged.
In this case, the best option is welding powder steel without gas and flux, where a cylinder, gearboxes, hoses, and flux fittings are not needed. All that is required is to direct the electrode into the groove and control the formation of the weld seam.
Melting of the flux-cored wire will occur in the same way as it was intended during its manufacture. The design of the material is a fundamental factor when it is melted by an arc. Inside the metal shell there is about 70% non-metallic materials, which is why the core's resistance to current will be much higher than that of the outer layer. Because of this, the metal coating melts faster. The core melts as a result of thermal radiation from the arc and heat transfer from the heated metal. As a result, during welding operations, the internal material will come into contact with the pool of molten metal and enter it unmelted.
Welding technology using flux-cored wire
Basically, welding with GOST flux-cored wire is performed using a semi-automatic hose machine. Therefore, a person must constantly monitor the quality of the weld. The technology for welding powder metals and joining corners and joints is almost no different from joining parts in shielding gas.
But flux-cored wire welding has some peculiarities - slag appears on the surface of the weld, which can get into the gap between a pair of edges in front of the weld pool.
If the work is carried out in stages, then before each start of welding it is necessary to clean the resulting seam from slag. But a process such as flux-cored wire welding has some disadvantages in user reviews. The material itself does not have very high strength, which is why automatic wire feeding with limited compression by feed rollers is required.
When using conventional flux-cored wire with a diameter of 2.6 mm or more, you need to use an arc with high current (for constant burning). Therefore, the material can be used in a lower position and sometimes in a vertical position. This limitation can be explained by the large volume of the weld pool and the formation of flowing slag on the surface.
The next disadvantage of the method is based on the likelihood of pores appearing in the weld (due to the presence of uneven filling and voids in the space of the metal shell)
. In this case, it is necessary to select welding modes with flux-cored wire in carbon dioxide. This will significantly reduce the risk of porosity in welds. It should be taken into account that the composition of the filler in the base material will determine the choice of several parameters (type and polarity of flux-cored wire welding).
When using flux-cored wire in arc welding, the price of which is optimal, you can use high-density current (200 A/mm2). This allows you to melt a lot of metal and helps to increase productivity (up to 10-11 kg/hour) at a current strength of 400-500 A. This produces materials whose chemical composition cannot be replicated in conventional industry.
General information
Flux-cored wire for welding without gas looks like a metal hollow tube. Inside it is a filler, which is simply flux or flux mixed with metal powder. Sheath steel refers to cold-rolled strip made from mild steel containing a small amount of carbon. The dimensions of the tape are selected depending on the diameter of the shell.
This type of wire is used in semi-automatic welding, during which gas protection is not required. Self-shielding welding wire can be used without the use of a gas cylinder, which is a definite advantage. This is ensured by the presence of flux inside the steel sheath, which, when the wire begins to melt, is gradually released outward and forms a kind of cloud that has the same protective properties as gas.
The tube contains small fractions of elements such as iron, phosphorus, and chromium. This guarantees the following circumstances:
- achieving a suitable temperature near the arc and bath and stabilizing it;
- increased mixing of molten metal;
- uniform seam coverage;
- no metal spattering;
- uniform boiling of the molten metal.
There is also an increase in the speed of the process. It is possible to carry out not only welding, but also surfacing of metals. Flux-cored wire for semi-automatic welding is widely used in the automotive industry and the repair of various metal products. Of particular note is the possibility of ceiling-type welding work.