Mass production requires the rapid production of large quantities of parts. Productivity can be increased by welding cast iron using semi-automatic welding machines in a shielded gas environment. Seams of any length can be created in one installation. Saves time on changing consumables. Cast iron is welded using different technologies using the same equipment. Only the fixtures, wire and welding modes change.
Semi-automatic welding
Welding cast iron with a semi-automatic machine: how to weld metal
Cast iron is used to produce manifolds, pulleys and pipes. The material is characterized by good casting qualities, which helps to produce products of various configurations. However, the alloy has a significant drawback - fragility. When struck, damage occurs, to eliminate which semi-automatic welding of cast iron is used. There are several ways to use such equipment.
Welding work on cast iron is quite complex technologically.
The problem of welding cast iron with a semi-automatic machine
It is difficult to weld cracks in parts made of such an alloy. During the work process, the welder faces the following difficulties:
- The increased fluidity of cast iron prevents the formation of a strong seam. Excessive dilution of the weld pool does not allow a thorough assessment of the quality of the joint. When welding thin plates, burns occur and drops of the melt flow out. The use of fire-resistant substrates helps prevent the development of such a situation. You can learn how to form seams under conditions of increased metal fluidity by regularly practicing on unnecessary workpieces made of a similar alloy.
- Another difficulty is the low melting point. The electric arc heats the welding site to extreme temperatures. Cast iron quickly overheats, which causes gaps to form between the edges and the filler material during the solidification process. If cast iron contains silicon or magnesium additives, hard inclusions appear in the structure of the welded joint, making grinding of the weld more difficult. Slow heating of the workpiece before welding and gradual cooling of the structure after completing the work help to avoid the formation of defects.
- It is also difficult to brew cast iron due to the presence of many pores that arise when carbon is released. Even careful processing of the seam does not improve its aesthetic qualities or increase its resistance to mechanical stress. Copper-plated welding wire is used to protect the connection. The process takes place in a protective gas environment. The filler material used must contain flux.
Cast iron has a low melting point.
Types of welding methods available
The method is chosen taking into account the purpose of the parts being connected. The methods differ in the speed of connection formation and the cost of work.
Cold welding method
This is the simplest method of joining workpieces made of an alloy with a high carbon content. The material is not heated before starting work; it must be at room temperature. The cold method is intended for welding structures subject to minimal loads. It can be used to restore worn surfaces of cast iron products.
Continuous supply of filler material helps to quickly form a seam and carry out large repair work in a short period of time. The connection obtained by the cold method has average performance qualities.
Cold welding is a simple joining method.
Semi-hot method
Before cooking cast iron semi-automatically using this method, the workpieces are heated to +350 °C. To do this, heat from coals is used to create the necessary conditions. Preparatory work prevents changes in the structure of cast iron during welding. In this case, under the influence of an electric arc, fewer cracks appear.
The technology is used in the assembly of structures subject to medium loads.
Hot welding method
This method is used when it is necessary to obtain a strong welded joint. Before starting work, the workpieces are heated to +600 °C. For this purpose, installations that generate inductive currents are used. Cables are connected to the part, and a measuring device monitors the temperature. After reaching the required values, an electric arc is excited, with the help of which a seam is formed.
The hot welding method is used to obtain a strong connection.
Leaving the structure in the ash until completely cooled helps reduce the likelihood of cracks. The duration of the cooling period depends on the thickness of the workpiece.
The hot method helps to obtain a strong, reliable seam, but it is associated with significant time and material costs.
Features of semi-automatic welding of cast iron
With the help of such equipment you can restore metal yourself. In this case, any welding mode is selected: MIG welding (using a chemically inactive gas) or MAG welding (surfacing using carbon dioxide).
When using these technologies, the filler material is distributed evenly, and the wire is fed into the weld pool automatically. The use of spot welding on cast iron is not recommended. Due to the limited contact area, thorough heating of the part becomes impossible.
Preparing cast iron for work
The strength of the connection depends on the quality of the edges. Cracks are cut to their full depth before welding. The corners are leveled and polished. The cutting should exceed the width of the defect by 1-2 cm, the depth by 1-2 mm.
The locking points are drilled, which increases the reliability of the connection. The cutting is performed at an angle of 45°. Oil stains are removed with a degreasing agent or burned. A graphite stand is placed under thin workpieces. In this case, the metal will not spread.
The edges are cleaned of chips and dust, which reduce the strength of the joint.
Before welding, cast iron must be leveled and ground.
Filler wire selection
Consumable electrodes are used for welding in a carbon dioxide environment. You cannot use regular wire on steel. This contributes to the appearance of a large number of cracks during the cooling process. The choice of wire for cast iron is determined by the welding mode:
- when working with the cold method, consumable electrodes PP ANCh-1 are used;
- the semi-hot method involves the use of the additive PP ANCh-2;
- when welding with heating up to +600 °C, use PP ANCH-3.
The “PP” symbols in the marking indicate the presence of a powder-filled core.
The material contains all the filler components necessary for welding (silicon, iron, copper, nickel). They make the seam stable and durable.
Necessary equipment
Semi-automatic welding is carried out using a machine that continuously supplies filler material into the weld pool. The work area must also be protected with gas or flux.
Simple semi-automatic machines are represented by a single module that combines a gearbox, an engine, a feed mechanism, and a gas exhaust system. For large volumes of work, composite equipment is used.
The gas burner and the wire feeder of such a unit are enclosed in separate housings. Taking into account the design of electrical circuits, devices are divided into:
- Single-phase semiautomatic devices. They are characterized by compact size and ease of connection to the network. The devices operate from household 220 V sockets.
- Three-phase units. Powered by industrial electrical network 380 V.
Welding is carried out using a semi-automatic machine.
When choosing a device, take into account the type of feeding mechanism, which can be:
- Pushing, located within the body. The device delivers the additive into the sleeve. If you use thin wire, the material may get stuck.
- Pull, built into the burner handle. It draws in the additive, feeding it evenly into the weld pool. The disadvantage is the possibility of excessive thinning of the wire.
- Combined, combining 2 types of mechanisms. The nodes work synchronously, ensuring a stable supply of consumables.
Welding process
The connection of cast iron blanks is performed as follows:
- Prepare the edges of the parts and install a backing if necessary.
- When using the semi-hot or hot method, the parts are heated to the desired temperature. When working with the cold method, this step is skipped.
- Fix the workpieces in the correct position. Start the gas supply, after 10 seconds the electric arc is ignited.
- Slowly move the torch along the seam, holding the tool at an angle.
- The seam is welded again (depending on the thickness of the metal, the action is performed 2-5 times). At this stage, transverse guidance of the electrode is allowed.
- They break the arc and turn off the gas after 30 seconds.
- Clean the seams and leave them under an asbestos or coal layer to cool slowly.
- Perform final connection processing.
The parts are heated to the required temperature.
How to cook malleable and high-strength cast iron
Work with these types of alloy is carried out in a carbon dioxide environment using Np-30GHSA, Sv-08G2S or Sv-08GS wire. Preheating of the workpieces is not required. During the welding process, the following rules are observed:
- To reduce the volume of additive in the weld, welding is carried out by covering 1/3 of the width of the bead. The arc should be directed towards the melt. To preserve the structure of cast iron, a method of cascade formation of a joint using annealing rollers is used.
- The use of Np-30GHSA wire promotes the appearance of inclusions in the joint, increasing the strength of the deposited layers.
- Primary welding of especially strong cast iron with steel is performed using consumable material grade Sv-08G2S. The last layer is fused using Np-30GHSA wire.
Correction of welding defects
The method of elimination depends on the type of deficiency:
- A crater, which is a depression at the end point, reduces the strength of the joint. It is welded again, breaking the arc at the finished section of the seam.
- Undercut - local thinning of the metal is eliminated by fusing a new layer. If the depth of the defect is small, mechanical cleaning is used.
- Lack of penetration occurs when the welding process is interrupted and resumed incorrectly. Such defects negatively affect the resistance of the connection to impacts. To eliminate lack of penetration, increase the current strength.
- Sagging is formed when the melt hits the surface of the part. To prevent its occurrence, increase the arc voltage and reduce additive consumption. Eliminate the defect mechanically.
- A burn-through is a through hole formed when the melt flows out. To eliminate the defect, the damaged areas are re-cleaned and boiled.
The strength of the finished structure depends on the quality of welding. Therefore, after completing the work, carefully inspect the seam.
Types of welding methods available
The method is chosen taking into account the purpose of the parts being connected. The methods differ in the speed of connection formation and the cost of work.
Cold welding method
This is the simplest method of joining workpieces made of an alloy with a high carbon content. The material is not heated before starting work; it must be at room temperature. The cold method is intended for welding structures subject to minimal loads. It can be used to restore worn surfaces of cast iron products.
We recommend reading: How to weld cast iron and steel
Continuous supply of filler material helps to quickly form a seam and carry out large repair work in a short period of time. The connection obtained by the cold method has average performance qualities.
Cold welding is a simple joining method.
Semi-hot method
Before cooking cast iron semi-automatically using this method, the workpieces are heated to +350 °C. To do this, heat from coals is used to create the necessary conditions. Preparatory work prevents changes in the structure of cast iron during welding. In this case, under the influence of an electric arc, fewer cracks appear.
The technology is used in the assembly of structures subject to medium loads.
Hot welding method
This method is used when it is necessary to obtain a strong welded joint. Before starting work, the workpieces are heated to +600 °C. For this purpose, installations that generate inductive currents are used. Cables are connected to the part, and a measuring device monitors the temperature. After reaching the required values, an electric arc is excited, with the help of which a seam is formed.
The hot welding method is used to obtain a strong connection.
Leaving the structure in the ash until completely cooled helps reduce the likelihood of cracks. The duration of the cooling period depends on the thickness of the workpiece.
The hot method helps to obtain a strong, reliable seam, but it is associated with significant time and material costs.
Principles of semi-automatic welding of cast iron
Mass production requires the rapid production of large quantities of parts. Productivity can be increased by welding cast iron using semi-automatic welding machines in a shielded gas environment.
Seams of any length can be created in one installation. Saves time on changing consumables. Cast iron is welded using different technologies using the same equipment.
Only the fixtures, wire and welding modes change.
Semi-automatic welding (Instagram / umkural)
Why is it difficult to cook cast iron?
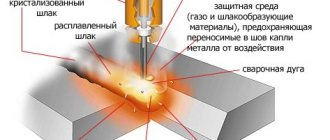
Cast iron contains a large amount of carbon, which, when heated, begins to interact with oxygen and turns into a gaseous state. This leads to the formation of gas pockets inside the seam.
The structure of the metal is coarse-grained with graphite inclusions along the crystal boundaries. As a result, cast iron is brittle and has low thermal conductivity. With sudden heating, cracks form along the temperature boundary.
The low melting point and high fluidity of high-carbon metal leads to the fact that during welding the base metal goes into a liquid state before the electrode and filler wire. At the same time, it is difficult to keep it in the bath; it flows out through the slightest cracks and gaps.
Welding methods
You can cook cast iron semi-automatically in different temperature conditions, with the appropriate wire:
- cold without heating parts;
- warm or semi-hot with heating up to 300⁰;
- hot - the part is heated to 600⁰.
The technological process of semi-automatic welding is different in each case. The seam is obtained with different performance characteristics.
Heating the part before welding (Instagram / svarka70)
Cold method
Cold cast iron parts are welded with short seams, almost spot welds. The metal should not have time to warm up and crack. The wire base is steel coated with copper.
The seams are plastic, soft, with high tensile and bending strength. They cannot withstand high dynamic loads and temperature changes.
Hot method
Warming up cast iron before welding allows you to create strong connections between parts of any size. An inert gas, mainly argon, is used as a flux.
The root seam is welded by passing the wire straight without swinging to the sides. To prevent metal leakage from below, copper or graphite pads are installed.
Subsequent passes are cooked in a zigzag manner, with an arc moving from one end to the other.
Strong connections are practically no different from the base metal. Due to heating and isothermal tempering, there is no transition zone.
Weld seam (Instagram / argon4yk)
How to cook cast iron semi-automatically
The semi-automatic machine is used for repairing parts when cracks and holes form during operation and for assembling and creating cast iron products. Technologies used for welding:
- MAG for surfacing and crack sealing;
- MIG in the manufacture of cast iron parts from several elements, surface surfacing.
At home, preference is given to cold spot welding.
Preparatory work
When preparing parts, the edges are cut at an angle of 60⁰ on a machine. Small cracks are selected with a grinder. It is not recommended to use chisels or other tools with dynamic loads. The brittle metal will break.
Surfaces should be cleaned of dirt and oils using solvents and purified gasoline. The workpieces are laid out and tacked. After this, welding is carried out. Horizontal position, floor.
Preparation of materials (Instagram / kievwelding)
Selecting wire for cast iron
The brand of consumables is selected depending on the temperature conditions. The wire mainly used in production is:
- PP ANCH-1 - cold welding;
- PP ANCH-2 - mode with heating of the part;
- PP ANCH-3 - heating up to 600⁰.
The rod contains copper, nickel, iron and silicon.
What is semi-automatic welding
Before starting practical classes on mastering the technology of working with semi-automatic stations, you should study the theory in detail. The equipment consists of the following main components:
- the main block through which filler wire and power are supplied;
- a burner with a wire located inside it;
- welding sleeve;
- shielding gas supply system;
- conductive tip.
Large enterprises often use stationary semi-automatic installations for welding parts on assembly lines. Such equipment ensures good quality of the welded joint, uniform distribution of weld deposits along the entire length of the seam, high speed of work and low energy consumption. Depending on the principle of operation, semi-automatic models are divided into several groups:
- for welding edges in a protective environment;
- performing work using flux;
- welding with flux-cored wire;
- universal automatic devices.
Without exception, all installations do an excellent job of joining workpieces made of non-ferrous or ferrous metals. Depending on the type of filler wire feeding, semi-automatic machines are:
- stationary. The housing is installed on a special console or other base and is rigidly fixed;
- portable. The device has relatively small dimensions and weight. Can be moved effortlessly by one person;
- mobile. The unit is mounted on a trolley and moved within one room - usually a workshop or assembly area.
There is also a classification of equipment depending on the type of feed rollers: pulling, pushing or push-pull.
This is interesting: How to change the chuck on a drill with your own hands
Semi-automatic welding of cast iron with conventional wire
Cast iron is widely used for the manufacture of pulleys, blocks, and commutators. It has good casting properties, which makes it possible to produce products of various shapes from it. But this material also has disadvantages - it is quite fragile.
Impacts often cause chipping of sides on pulleys or cracks in pipes. To correct the situation and restore the product, they resort to various methods of joining metals. One of them is semi-automatic welding of cast iron.
What are the features of this method? How many options are there for using a semi-automatic machine? What supplies are suitable?
Equipment and consumables
To obtain good joints from difficult-to-weld alloys, any semi-automatic machines are used. The main criteria are compliance with the maximum current of the device required to penetrate a specific thickness of metal. The adjustable current and wire feed speed parameters are similar to welding conventional steel.
Wire is used with specialized markings: PP ANCH-1, as well as with numbers 2 and 3. Each number is intended for a specific method (cold, semi-hot, hot).
The wire has a tubular structure and contains flux powder inside, which protects the weld pool from exposure to oxygen. Enrichment of the applied metal with special impurities promotes high tensile strength of the seam and tensile strength.
Thanks to Anch wire, it is possible not only to eliminate minor defects in cast iron, but also to produce full-fledged seams that firmly connect this specific metal.
To weld cast iron, a gas supply is used, which additionally protects the weld pool. Depending on the purpose of the product and the amount of impurities in the alloy, you can use carbon dioxide in its pure form or its mixture with argon, where the latter will be 80%. The flow rate from the pressure gauge to the burner should be 6-11 liters. This will optimally protect the molten metal from displacing carbon.
Semi-automatic welding technology
When welding cast iron with a semi-automatic machine, regardless of the temperature conditions, it is necessary to properly prepare the material. If you need to weld a crack, it is important to make a preliminary cut with a grinder along the entire split line. This will allow the filler material to be fused deeper. It is recommended to drill the edges of the cracks to limit its continuation.
If the thickness of the plates is more than 5 mm, then cutting the edges at 45-60 degrees is necessary. When working with thin sheets (up to 3 mm), graphite preforming is used to prevent burns.
The first seam is made with a smooth pass without oscillatory movements. The burner can be operated from top to bottom or from right to left, tilted 50 degrees. The distance between the nozzle and the surface is maintained within 6-8 mm.
Horizontal seam
Semi-automatic welding makes it possible to produce horizontal seams of the highest quality, regardless of the direction of movement. To obtain a high-quality seam, you need to take into account some features:
- it is necessary to balance the gravity of drops of molten metal and the burning force of the electric arc;
- it is important to choose the optimal speed of moving the electrode along the joint;
- To control the melt, welding work should be carried out continuously.
In some cases, it is not possible to complete the seam in one pass. Then you can resort to a technique that involves periodically extinguishing the arc. Various welding patterns can be used on workpieces with edges up to 4 mm. In all other respects, the quality of the seam will depend on the experience and skill of the welder.
A horizontal weld is created in four stages:
- Formation of the root roll. It is performed with a short electric arc. The electrode is held at an angle of 80 degrees in relation to the working surface. The primary roller is formed, as a rule, at maximum current.
- Secondary roller application. Before starting the process, the average current strength is set. The roller is performed in one pass using an electrode of the largest possible diameter. When forming a roller, the forward angle technology is used.
- Creating the third roller. Depending on the previously obtained results, one of two methods is used to form the third roller. The area of the secondary roller is large - the third one lies in the center. When the dimensions of the secondary correspond to the norm, then the third stage is performed in two approaches.
- Checking the quality of work.
Welding defects most often form in the upper part of the seam. Therefore, you should carefully monitor the quality of work at this stage.
Semi-automatic welding of cast iron - features and specifics, selection of wire for high-quality results
An alloy of iron and carbon, when the amount of the latter is more than 2.14 weight percent, is called cast iron. Thanks to its excellent casting qualities, it is widely used in various industries and heavy engineering.
When casting massive castings, surface casting defects may appear. One of the most common is the sink. Remelting a large mass of metal due to a minor notch on the surface is not justified.
Welding comes to the aid of production workers in such a situation, as it can cope with minor defects.
Using a semi-automatic machine for cast iron
Among the various types of welding, special attention is paid to semi-automatic welding. A conglomerate of gas argon and arc welding in one device allows you to weld cast iron parts and eliminate casting defects.
Semi-automatic surfacing of cast iron makes it possible to restore a worn layer of almost any thickness while maintaining its properties. Let us remind you that semi-automatic welding (MIG/MAG method) involves melting a special wire using an electric arc in a protective gas environment.
The semi-automatic machine, using automation, feeds the wire into the welded area at a speed previously set by the welder. The protective gas environment avoids contact of oxygen from the environment and the metal molten bath.
Reducing the amount of slag and gas bubbles in the thickness of the frozen metal leads to an improvement in the quality and mechanical characteristics of the joint.
Semi-automatic welding allows you to cope with the assigned tasks of welding cast iron, regardless of its metal matrix structure, content and shape of carbon inclusions. These parameters divide cast iron into
- ferritic,
- pearlite,
- grey,
- malleable,
- high-strength with spherical graphite inclusions and others.
This fact requires a special calculation and approach when choosing semi-automatic welding modes, taking into account the different physical properties of the alloys.
Correction of welding defects
The method of elimination depends on the type of deficiency:
- A crater, which is a depression at the end point, reduces the strength of the joint. It is welded again, breaking the arc at the finished section of the seam.
- Undercut - local thinning of the metal is eliminated by fusing a new layer. If the depth of the defect is small, mechanical cleaning is used.
- Lack of penetration occurs when the welding process is interrupted and resumed incorrectly. Such defects negatively affect the resistance of the connection to impacts. To eliminate lack of penetration, increase the current strength.
- Sagging is formed when the melt hits the surface of the part. To prevent its occurrence, increase the arc voltage and reduce additive consumption. Eliminate the defect mechanically.
- A burn-through is a through hole formed when the melt flows out. To eliminate the defect, the damaged areas are re-cleaned and boiled.
The strength of the finished structure depends on the quality of welding. Therefore, after completing the work, carefully inspect the seam.
Connecting cast iron workpieces with a semi-automatic welding machine: hot and cold methods
Cast iron, despite its relative fragility, remains one of the most popular structural metals. This is facilitated by the hardness of the material, resistance to alternating and fatigue loads, and high heat capacity.
Features of technical equipment for the process of semi-automatic welding of cast iron
Welding cast iron is difficult due to the metal's tendency to develop defects and reduce performance characteristics when exposed to high temperatures.
To connect cast iron workpieces and eliminate faults in finished products (cracks, chips, etc.), a simple and fast method of semi-automatic welding is most often used, which, however, requires special equipment. MIG and MAG technologies are acceptable, which involve the supply of inert and active gases, respectively.
Basic equipment
For semi-automatic welding, specialized electromechanical devices are used, which provide a continuous supply of a consumable electrode to the weld pool, as well as protection of the seam from the harmful effects of atmospheric air using flux or gas. Simple “semi-automatic machines” have a single-body design, when the following are combined in a single module:
- welding power source;
- motor, gearbox and passive wire feed units;
- shielding gas injection system;
- device operation control system.
The external elements of such a device include primary and secondary cables, a gas cylinder with a pressure-reducing unit and a discharge hose, and a burner.
For large production volumes, as well as complex welding work, it is advisable to use modular semi-automatic machines.
Their feed mechanism and gas system are located in a separate housing, and the welding power source with the control unit is located in the main module.
If the device is designed for intensive use, the burner can be supplemented with a forced liquid cooling system.
Depending on the design of the primary power circuits, single-phase and three-phase “semi-automatic machines” are distinguished.
The former are attractive due to their compactness and ease of connection to the network, as they operate on 220 V alternating current.
The latter are used in industrial cycles; they are powered by a 380-volt network. An equally important factor is the type of wire feeding mechanism. He can be:
- pushing – located inside the body of the device, pushes the welding wire into the sleeve, which in some cases (for example, when using thin or excessively soft material) can lead to jamming;
- pulling - located inside the torch handle, tightens the wire, ensuring its uniform feeding, which can sometimes lead to unwanted thinning of the material;
- combined - has both pushing and pulling units that act synchronously, and is characterized by stable and uninterrupted operation.
For hose lengths less than 4 meters, feed mechanisms with one pair of support rollers are usually used; for hoses longer than 4 meters, two pairs are used. If the hose length exceeds 8 meters, the only possible feed mechanism is a combination with two pairs of rollers.
Optional equipment
In addition to a semi-automatic machine, for welding cast iron you will need standard tools and materials for surface preparation and personal protection. These include:
- grinding machine (grinder);
- metal brushes;
- degreasing solution;
- dry clean rags;
- welding gloves;
- protective mask.
When welding with gas weld protection, you will need a cylinder with carbon dioxide, argon, helium or a mixture of gases. In some cases (for example, when welding cracks in cast iron crankcases), a hand drill with metal drills and other power tools can be used to pre-process the workpieces.
Filler wire
Semi-automatic welding of cast iron is carried out using a wire-type consumable electrode. The use of electrodes on steel is unacceptable, since in any case this will lead to cracking of the seam when it hardens. The choice of filler wire grade for cast iron depends on the welding mode:
- welding without heating (cold) – PP ANCH-1;
- welding with heating up to 350℃ (semi-hot) – PP ANCH-2;
- welding with heating up to 600℃ (hot) – PP ANCH-3.
The abbreviation “PP” in the wire marking indicates its powder type. This means that the material contains the necessary filler elements (Fe, Ni, Cu, Si, etc.) that provide the necessary strength and stability of the weld.
Approximate cost of cored wire on Yandex.market
Semi-automatic cast iron welding technology
When choosing a welding mode for cast iron, it is important to take into account a number of its physical and chemical features, which make it difficult to work with the material using classical methods. First of all, these include:
- low metal melting point;
- change in the structure of a substance under the influence of high temperatures (“bleaching”);
- high fluidity of cast iron , which increases the risk of burn-through and deformation of workpieces;
- the appearance of pores in the material under the influence of atmospheric oxygen.
This necessitated the use of gentle welding modes with constant protection of the seam by active or inert gas media. Cold and hot technologies for semi-automatic welding of cast iron have become widespread.
Cold way
Cold technology is used mainly in domestic conditions to create seams that do not withstand direct mechanical loads. It is simpler and cheaper, however, it does not provide a sufficiently high-quality connection of the workpieces. The algorithm of actions includes the following:
- Joint processing , edging if necessary.
- Fastening workpieces to the supporting surface with a gap of 1.5-2 mm.
- Setting the semi-automatic CA to low DC mode with reverse polarity.
- Ensuring the supply of shielding gas to the welding zone and ignition of the arc.
- Welding the seam at an angle forward (the slope is 50-60°, which is enough for visual inspection).
- The arc breaks and the supply of shielding gas stops (after 15-30 seconds).
- Cleaning the seam from slag and mechanical treatment.
Unlike MIG and MAG welding of steel, working with cast iron does not require oscillatory and transverse movements of the electrode.
In addition, cold technology allows the application of a single-layer seam at the joints of parts up to 4 mm thick.
Hot way
The best quality of welds in cast iron is ensured by the hot method of semi-automatic welding, which is widely used in repair shops and sometimes in industrial complexes. It requires the following sequence of actions:
- Joint processing , edging if necessary.
- Preparing the supporting surface , installing a graphite lining on it.
- Heating the workpieces in the oven to a temperature of about 600℃.
- Fast fixation of workpieces to the backing and early start of welding with low direct current with reverse polarity in a protective gas environment.
- Welding the seam at an angle forward (the slope is 50-60°, which is enough for visual inspection).
- Repeated welding of the seam (depending on the thickness of the metal, from 2 to 5 layers are applied), during which the method of transverse guiding of the electrode is acceptable.
- The arc breaks and the supply of shielding gas stops (after 15-30 seconds).
- Cleaning the seam from slag , ensuring a slow decrease in the temperature of the part under a layer of asbestos, charcoal or other non-combustible material.
- Final cleaning and mechanical treatment of the seam.
It is important to remember that the speed of semi-automatic welding is much higher than manual welding. If you have not worked with a semi-automatic machine before, practice on scrap cast iron before starting to weld critical joints.
What is cored wire
How to brew cast iron and how to melt cast iron?
Flux-cored wire is the best option for solving these problems associated with low productivity, optimal heating conditions for workpieces and ensuring proper process performance. Self-protecting flux-cored wires coated with a layer of flux are known. When it burns out from the heat of the arc, a protective screen is formed, which limits the temperature gradient on the surface to 500...700 °C. As a result, working conditions are improved and the risk of cast iron cracking is reduced.
Flux-cored wire in the form of a continuously supplied consumable material was invented by scientists at the All-Union Institute of Electric Welding named after. Paton in the middle of the last century.
It is a hollow steel shell of round cross-section, inside of which a charge of a certain chemical composition is contained.
The use of consumables continuously supplied to the welding zone provides the following advantages:
• Eliminates the need for preheating of workpieces;
• More components can be added to the charge;
• Burnout of the steel shell of the hollow wire is minimized;
• You can regulate the composition of the components located in the internal cavity;
• For welding cast iron with flux-cored wire, no external shielding gas is required to protect the weld from atmospheric influences.
The basic constituents of flux-cored wire have been developed to achieve properties not achievable with solid wire welding. Since all protection is provided by shielding gas, core components must be carefully selected to increase welding performance in a specific area, for example to achieve smooth spray transfer. In this case, the actual welding speed is approximately two times higher than when welding cast iron with electrodes with an external flux coating.
Flux-cored wire, developed by specialists from the Paton Institute, despite the increased labor intensity of its production, can be used both for permanent connection of cast iron parts and for repair and restoration operations.
Welding cast iron semi-automatically
Cast iron is widely used for the manufacture of pulleys, blocks, and commutators. It has good casting properties, which makes it possible to produce products of various shapes from it. But this material also has disadvantages - it is quite fragile.
Impacts often cause chipping of sides on pulleys or cracks in pipes. To correct the situation and restore the product, they resort to various methods of joining metals. One of them is semi-automatic welding of cast iron.
What are the features of this method? How many options are there for using a semi-automatic machine? What supplies are suitable?
How to cook malleable and high-strength cast iron
Work with these types of alloy is carried out in a carbon dioxide environment using Np-30GHSA, Sv-08G2S or Sv-08GS wire. Preheating of the workpieces is not required. During the welding process, the following rules are observed:
- To reduce the volume of additive in the weld, welding is carried out by covering 1/3 of the width of the bead. The arc should be directed towards the melt. To preserve the structure of cast iron, a method of cascade formation of a joint using annealing rollers is used.
- The use of Np-30GHSA wire promotes the appearance of inclusions in the joint, increasing the strength of the deposited layers.
- Primary welding of especially strong cast iron with steel is performed using consumable material grade Sv-08G2S. The last layer is fused using Np-30GHSA wire.
How to weld with electric welding
Before you start welding using electrodes, you must carefully study the features of welding cast iron of this type. First of all, you need to select the right electrodes and special equipment. The main feature of this method is that the degree of fragility of the metal increases in the area of the weld.
The increase in fragility is due to the fact that during welding work the alloy on the cast iron alloy is highly hardened. For this reason, electrode welding of a cast iron boiler and other parts in an industrial environment has significant differences compared to the conventional processing of other products. During it, it is necessary to heat the material to a temperature of almost 600-650 degrees Celsius.
Typically, two types of electrodes are used in electric welding:
- OZCH-2. The electrodes of this model have a copper metal rod, which is coated with a special composition containing graphite;
- MNC-2. For the rod of this type of electrode, different types of metals are used - nickel, copper, manganese and iron. This model is the most suitable option for electric welding of cast iron, but it has a high cost.
Features of welding cast iron parts using electrodes:
- during cold electric welding, it is necessary to maintain a certain pace of sutures;
- control of the welding process is required, this will help to avoid overheating of the surface above the established values;
- The welder must carry out work “randomly”, in small parts. In this case, forging must be performed and breaks must be taken;
- due to the fact that the main feature of cast iron is that it cools quite slowly, so welding a cast iron part may require some period of time;
- if small defects are being restored, then an additional graphite substrate may be required; this will prevent metal leakage.