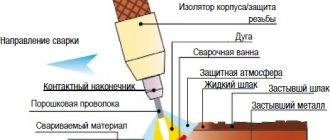
Cold welding of cast iron is carried out without preheating the workpieces in the furnace. This processing method helps preserve carbon and prevents the metal from becoming brittle. To form a seam that is resistant to mechanical stress, it is necessary to properly prepare the workpieces. Following the technology will help avoid the appearance of pores, cracks and other defects.
Cold welding of cast iron is usually called welding without preheating.
Types of cast iron
Cast iron is an alloy of iron and carbon. Depending on the ratio of these main components, the following types of metal are distinguished:
- white;
- grey;
- malleable;
- high strength;
- half, etc.
An alloy often includes a number of impurities that give it specific physical and chemical properties. The material often contains impurities of phosphorus, manganese, copper, chromium, nickel and sulfur. Hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen are present in small quantities in the alloy.
Impurities affect the quality of the weld formed by cold welding. The more impurities, the higher the likelihood that cracks and pockets of porosity will be present in the weld area. To successfully solder parts made of this metal, it is often necessary to use flux.
To create a uniform structure and improve the technical characteristics of the finished seam, it is advisable to use special additives.
Solid white
In solid white cast iron, the carbon is bound. This substance is represented by cementite Fe3C. This chemical composition determines the high wear resistance and strength of the alloy. At the same time, white cast iron does not cut well. With this impact, it becomes brittle, so large fragments may break off. There are 3 subtypes of white cast iron, including:
- hypoeutectic;
- eutectic;
- hypereutectic.
White cast iron contains carbon compounds.
They differ in the content of fixed carbon. The hypoeutectic subtype contains from 2.4% to 4.3% cementite. Eutectic white cast iron contains 4.3% carbon.
In the hypereutectic subtype of the alloy, the presence of cementite ranges from 4.3% to 6.67%.
Gray with a touch of graphite
Gray cast iron contains carbon in the form of flake graphite. The alloy has a multicomponent composition. It includes:
- carbon – 3.2-3.5%;
- manganese – 0.1-0.3%;
- silicon – 0.5-0.8%;
- sulfur and phosphorus – 0.12% each.
Gray cast iron with an admixture of graphite has a multicomponent composition.
To cast gray cast iron products, metal or earthen molds are used. This alloy is characterized by low resistance to mechanical stress, so parts for the least critical purposes are made from it, which will not be subject to shock loads. Often frames of presses and machine tools, covers, etc. are made of gray cast iron.
Malleable alloy
Ductile iron contains 2.4-3.5% carbon in the form of graphite flakes. In addition, the alloy contains:
- manganese – 0.3-01%;
- phosphorus – 0.2%;
- silicon – 0.8-1.4%;
- sulfur – 0.1%.
Ductile iron contains carbon, manganese and phosphorus.
The malleable appearance is obtained by heating and holding white cast iron for a long time. This procedure is called graphitizing annealing.
The alloy is characterized by high strength and resistance to mechanical loads.
Half cast iron
The half-shape look is obtained by alloying white and gray cast iron. Its structure contains carbides. Half cast iron contains both cementite and uncombined carbon. The alloy has a high level of resistance to mechanical wear, high temperatures and frictional effects.
Half cast iron is produced by alloying white and gray cast iron.
High strength nodular graphite
Ductile iron contains 2.4-3.0% carbon in the form of flake graphite. Additionally, it contains the following impurities:
- magnesium -0.6-0.8%;
- silicon – 1.9-2.6%;
- sulfur – 0.3%;
- phosphorus – 0.12%.
Ductile iron contains magnesium, silicon and sulfur.
This type of cast iron is produced by introducing a modifier containing magnesium into the liquid melt. The mechanical properties of this alloy are similar to those of carbon steel, but the casting properties are higher.
High-strength cast iron is used to make parts and products that will be subject to high loads.
Difficult gluing cases
Experienced builders recommend paying attention to the following situations, which are classified as complex and require more thorough preparation:
- connecting parts with different coefficients of linear expansion;
- bonding pieces of metal that are constantly exposed to moisture.
With different linear expansion coefficients
When working with high temperature adhesive, keep in mind that different materials react differently to heat. Therefore, when gluing parts made from heterogeneous materials, it is advisable to mix polyurethane additives into the glue. They will make the seam more elastic and stronger.
Metals exposed to moisture
Metal that has been in a humid environment for a long time begins to oxidize. This negatively affects the strength and durability of the connection. Try to treat the joints with special water-repellent paint, otherwise the work will soon have to be redone.
What difficulties arise when welding cast iron?
Cold welding on cast iron is often fraught with difficulties due to the specific properties of the alloy. Potential problems should be considered before work begins.
Poor connection
Due to its high carbon content, cast iron has a fairly porous structure and low thermal conductivity, which causes its poor jointability. The situation is aggravated by impurities, incl. silicon. This leads to the seam being uneven with unwelded areas.
We recommend reading: How to weld a cast iron vice with your own hands
Cast iron has low thermal conductivity.
Formation of oxides
The melting point of the impurities contained in the alloy differs from the indicators of the main components of the alloy. In addition, they can quickly oxidize in the weld pool. This leads to the formation of oxides that are refractory. An increased content of such compounds during welding causes the appearance of uncooked areas.
Difficult treatment of areas with cementite
Shock cooling leads to the formation of areas with cementite. This substance is characterized by increased strength and hardness. Such areas are poorly machined during welding.
The seam comes out very hard, but if there are any defects in it, it will be extremely difficult to correct them.
Liquid state of the alloy
When exposed to high temperatures, cast iron quickly turns into liquid form. In this state it is characterized by high fluidity. This complicates the process of holding the alloy in the weld pool. Swelling may occur. This makes it extremely difficult to form a seam.
The liquid state of the alloy is characterized by high fluidity.
Tendency to form pores
When heated, the alloy begins to release gases. This contributes to the formation of many micropores. Even with a slight deviation from the technology, the seam turns out to be too porous and fragile.
In addition, cast iron in liquid form absorbs oxygen well. During welding, oxygen reacts, which promotes the formation of internal bubbles filled with water vapor. Subsequently, after the seam cools, the material becomes porous, which creates conditions for the appearance of various defects.
Tips and tricks
Cast iron has high fluidity and is difficult to keep in the bath. Experts recommend placing the parts on the stove so that the cutting is horizontal, at the bottom.
Having made tacks, you should apply short seams up to 25 mm long and immediately hammer them with light blows of a hammer. They should be located at a distance of 150–200 mm. If the connection is short, you should wait for the workpieces to cool. You can check the readiness of the material for welding by hand. She will feel a pleasant, non-burning warmth.
Those who like to do their own repairs can use cold welding at home when repairing cars or household appliances. Small seams on small parts will not overheat the cast iron and will hold up well.
Cold welding technology for cast iron
Before starting work on forming a welding seam, it is necessary to thoroughly clean the cast iron surfaces. In addition, the material is cut and deep cracks are eliminated. Cold welding technology involves heating cast iron to temperatures no higher than +820…+860°C. This is not enough to strongly melt the alloy.
Welding can only be carried out with small diameter electrodes. The process is carried out at low current. If in the future there will not be a large load on the seams, welding can be carried out with steel electrodes. In cases where the connection must be highly durable, it is better to use special copper-nickel rods. It is permissible to use electrodes containing copper and iron.
Often, special fluxes and rods are used during processing. Under the influence of temperature, the additive materials begin to melt. Drops fall on a well-prepared surface, spreading over it. This ensures a tight connection of the parts.
To eliminate casting defects in cast iron products, low-temperature gas welding is often used. In this case, thick-walled rods are used as filler material. This approach helps eliminate existing shortcomings that arise during the casting process.
When welding, the use of lithium carbonate is recommended.
If there is a high risk of oxide formation and when processing old cast iron parts that were operated in unfavorable conditions, it is recommended to use fluxes such as:
- soda ash;
- lithium carbonate;
- fused borax;
- sodium nitrate;
- cobalt oxide;
- potassium fluorozirconate;
- sodium fluoride, etc.
The use of fluxes promotes chemical cleaning of surfaces from fats, oxides and other contaminants. This increases the adhesion strength of the deposited metal to the base, and also protects the surface from nitrogen and oxygen when heated. At the same time, the use of fluxes increases the fluidity of the material. In this case, during welding of workpieces, the strength of the seams increases and the risk of defects decreases.
After welding work, you cannot carry out actions aimed at accelerating the cooling of the surface. A rapid decrease in temperature will cause a white coating to appear around the welded area and will also make the substrate hard but brittle. In addition, it is not recommended to clean it immediately after forming a seam. This will lead to cracks and other defects.
Glue characteristics
Adhesive for joining metals has its own technical characteristics, which differ from one manufacturer to another. When choosing a specific adhesive composition, you need to pay attention to the following properties:
- drying time and conditions - as a rule, this depends on the place where gluing is performed and the specifics of the work itself;
- the maximum temperature at which the beneficial properties of the glue will be preserved - you should choose a composition that can withstand the conditions of use of the assembly or its future processing;
- method of application - some adhesives are recommended for spot treatment, others for complete coverage of the joints of parts;
- gluing technology;
- consistency - these can be tubes with the composition and hardener, as well as plastic sticks. The latter are convenient because you don’t need to knead: being anywhere, you cut off a piece, knead it and use it;
- materials with which gluing is possible - universality is a vague and unreliable concept here; it is better to choose a narrowly targeted adhesive to solve a specific problem. For example, for joining plastic and metal.
Scope of application
Metal adhesive is broadly applicable in many areas of life. Breakdowns often occur in industry and everyday life.
A child’s toy is broken – we are looking for an opportunity to fix it. It is necessary to repair a car, an exhaust pipe, repair any damage - there is also a need to reliably connect metal surfaces to each other. In the aviation, general construction and chemical industries, gluing metal parts is also widespread.
However, the compositions can differ in their narrow purpose and be universal. For example, professional heat-resistant adhesive is often used to repair plumbing, to repair cracks in metal, in the construction of fireplaces and stoves, when installing heated floors and for many other tasks.
Properties of heat-resistant base
If metal components are exposed to elevated temperatures during operation, their integrity will deteriorate over time and their service life will be shortened.
A heat-resistant composition of type “300” based on epoxy resin will be a worthy alternative to welding work.
Even high-temperature operation of the device will not damage the connections of the components. The lower limit of stability of the heat-resistant composition is 300 degrees Celsius. In addition, it is waterproof, thermally conductive and environmentally friendly.
Requirements for adhesives
A high-quality glue for metal after its use must fulfill several conditions:
- the most durable connection, which allows you to use parts without risk;
- preservation of properties over time;
- resistance to temperature changes;
- chemical neutrality, protection of the bonding site from corrosion;
- water resistance;
- minimal shrinkage after curing;
- no pungent odors;
- environmental friendliness.
Preparing metal for exposure
Comprehensive preparation of cast iron for further welding is necessary to obtain a high-quality result. If this process is not performed correctly, the formed seam can become porous and brittle. More pronounced defects may also appear.
As part of the preparation of the cast iron surface, the first step is to saw through the cracks. They are often thin, but they penetrate deep into the structure of the alloy. If the thickness of the part exceeds 4 mm, then applying a seam will lead to melting of the surface. The inner part of the base will remain damaged, which will reduce its resistance to mechanical stress. The crack must be sawed to its full length. To do this, it is most convenient to use a grinder equipped with a thin disk. The thicker the workpiece, the deeper the sawing should be done.
We recommend reading: How to weld cast iron and steel
In some cases, drilling the edges is recommended. This is due to the fact that when examining the damage, it is often not possible to accurately determine the depth of the cracks. Before starting welding, the edges must be drilled at a distance of 5 mm from the end of the fracture. This will ensure that the internal space of the parts is filled with melt during welding. In addition, the procedure will reduce the risk of increasing splitting under mechanical stress.
If the metal is not prepared correctly, the formed seam can become brittle.
Before starting welding, it is necessary to prepare the edges. This is necessary to ensure uniform heating of the parts over the entire length of the connection and to prevent overheating, which can cause brittleness of the section. To connect thick-walled workpieces, it is necessary to bevel the edges at an angle of 45°. At the base there should be a deviation of 3-4 mm. Carrying out cutting of edges increases the wear resistance and strength of the treated area.
If the cast iron part is thin-walled, the risk of the alloy heating up too much and causing it to leak increases. In this case, it is extremely difficult to form a strong seam. To facilitate welding, a graphite spacer is placed under the workpiece. This element will create an obstacle to the spreading of the metal, which has turned into a liquid state under the influence of high temperature. This will help preserve the original appearance of the part.
If work will be carried out outdoors, it is recommended to use screens to protect the welding site from the wind.
Types of cold welding
There are several ways to carry out welding. Most often, procedures are performed using electrodes. To obtain a durable seam without defects, polymer compounds can be used.
Using simple electrodes
Welding cast iron with electrodes can be carried out both in the lower horizontal and vertical positions, but the first option is the best. In this case, direct current is used. It is extremely important to control the speed of work and try to prevent strong penetration of the base.
After applying each seam, it is necessary to allow the surface to cool naturally to +50…+60 °C. There are many brands of electrodes that can be used for welding cast iron products. Graphite and carbon electrodes are rarely used for processing cast iron, because their use reduces the strength of the seam. Such rods are used only when processing thin-walled products, which will not be subjected to heavy loads in the future.
When welding cast iron, electrodes use direct current.
The most commonly used rods are OZCH-2 and OZCH-6. Their base is copper. The outer surface of such electrodes is coated with a special composition containing iron powder.
In addition, iron-nickel and nickel electrodes can be used effectively. If it is necessary to obtain a weld that is resistant to aggressive environments, corrosion and the effects of flammable gases, iron-copper-nickel rods of the MNCh-2 brand are used. Their cost is high, so they are more often used in cases where particularly stringent requirements are imposed on the quality of the seam.
When using polymer compounds
Welding without the use of a machine and electrodes involves the use of special polymer compounds, which, after application, form a strong connection that is resistant to thermal effects. This method of eliminating defects is most often used when repairing plumbing fixtures, automotive parts, racks, etc.
Welding using polymer compounds forms a strong connection.
Polymer compositions include cast iron powder. The product is 2-component. It should be prepared immediately before use. After mixing the ingredients, a thick mass is obtained. The already cut seam is carefully covered with it. After hardening, the adhesive mass is characterized by increased strength and high resistance to heat. You can determine the treatment area by its lighter shade. After sanding, the transition becomes blurry.
This method can only be used to remove small defects.
If there are deep cracks or chips, the use of a polymer composition becomes ineffective.
Manufacturers
Most types of electrodes for cold welding of cast iron are produced in the Russian Federation:
- MNC-2;
- OZZHN-1;
- OZCh-6;
- TsCh-4.
They are used in car repairs, welding of heating radiators, and at large foundries and machine-building enterprises. Popular manufacturers:
- Frunze electrode;
- Aspik;
- Special Electrode.
Of the foreign companies, consumables for welding cold cast iron are produced by German companies:
- CAPILLA;
- UTR SchweiBmaterial.
Other companies limit themselves to the production of electrodes and wire for hot welding of cast iron.
Instructions for cold welding cast iron
To reduce the risk of defects appearing on a finished seam, it is extremely important to follow all instructions for the work. Recommendations vary depending on the specific methods of connecting individual elements.
Using electrodes
Before starting work, you should set up the device and check how well the processing was carried out. If possible, the surfaces to be treated should be horizontal and facing downwards. This will avoid deformation of the product when the material overheats and melts. To obtain a high-quality seam, a paste containing boric acid and iron filings should be applied to the edges. After this, the parts are heated by the burner flame. The current value is determined at the rate of 50-60A per 1 mm of electrode.
It is extremely important to pace yourself. It is necessary to control the welding process to avoid overheating of individual areas above the recommended values. The rod must be guided in transverse movements. If the thickness of the parts is small, flux is used.
We recommend reading: How to cook cast iron yourself using a semi-automatic machine
When welding, you need to evenly distribute copper wire with a diameter of up to 2 mm. Transverse vibrations should not be allowed to avoid the appearance of pores and microcracks. It is best to do the work in small sections. It is necessary to take breaks for more than 30 minutes, and then start forming the seam again.
To obtain a high-quality seam, you need to use electrodes.
This can increase the duration of work when eliminating large defects. However, sudden heating and cooling provoke a change in the crystalline structure of the metal. This increases the fragility of the material in the seam area.
In this case, forging is required. When work on 1 section is completed, you can proceed to the next one.
Welding of cast iron can be carried out in a protective environment. This allows you to obtain a high-quality seam with high strength. In this case, it is necessary to monitor the consumption of the mixture. If you need to brew products thinner than 10 mm, 150 liters is enough for 1 hour of work.
To process thicker workpieces, gas consumption will increase to 200 liters. Welding must be done quickly to avoid cracks and other defects. It is extremely important that the additive melts before the workpiece metal.
If the product is thicker than 10 mm, it is recommended to use 2 burners. In this case, fluxes containing boron should be used.
How to use polymer compounds
When eliminating defects in cast iron products, 2-component compositions based on epoxy resin are more often used. These products have a high initial hardening rate, so you need to work with them quickly.
First, the surface must be cleaned of dust and other contaminants. It is extremely important to degrease to remove any remaining grease and oil. It is recommended to use a solvent for this. It is necessary to prepare the adhesive mass before direct application. The composition should be diluted in a well-ventilated area. This will reduce the risk of irritation to the nasal mucosa and eyes. The composition must be kneaded until a homogeneous mass is obtained.
When eliminating defects by cold welding, polymer compounds are used.
After this, you should begin to eliminate defects in cast iron workpieces. Glue is applied to both surfaces. After this, the surfaces are connected. If the composition is used to repair cracks with chips, the mixture is carefully compacted into the existing cavity. At the same time, you should not put too much pressure on the surface. Excess product must be removed immediately with a dry cloth.
The repaired cast iron product should be left until initial setting. This may take from 5 minutes to 1 hour. Then you need to evaluate the quality. If there are no visible defects, the composition is left for a period of 12 to 24 hours until completely hardened. Once the product has hardened, its surface can be sanded.
Cold welding with linoleum
Adhesive compositions for welding with linoleum include plasticizers, tetrahydrofuran, and polyvinyl chloride. This composition can be effectively used to eliminate defects in cast iron products. Work to restore a damaged element should begin with its careful preparation. The surfaces to be treated must be cleaned of all contaminants and treated with a solvent to remove grease particles.
Adhesive composition.
After this, the adhesive composition is prepared. You can use a spatula to apply it. It is extremely important that it gets to the maximum depth into existing cracks and chips. Remains of the composition must be removed from the surface with a rag. Then you need to let the product harden. After this you will need to sand the surface.
Aluminum bonding
Before choosing a suitable adhesive for aluminum, you should remember that this metal is very difficult to process (including its gluing).
The fact is that in the normal state there is always a hard oxide film on the surface of the metal, which significantly reduces its adhesion to the adhesive mixture. To obtain the required result, you need to take care of the preliminary preparation of aluminum surfaces for gluing. To do this, they should be treated with special chemical compounds, which most often use alkalis and acids.
Sometimes mixtures based on epoxy resins are used for these purposes.
Among the known adhesives for metal, the most preferable is a two-component mixture, made on the basis of epoxy or acrylic components, supplemented with a hardener.
To obtain a high-quality connection, immediately after treatment with chemicals (before gluing), the surfaces are degreased and then covered with a layer of a special primer.
When preparing metal, care must be taken to ensure that the glue and primer do not react when mixed to form an undesirable chemical compound.
In addition to two-component adhesives, another type of heat-resistant adhesives for aluminum processing, colloquially called “cold welding,” has become widespread.
This composition is very convenient to use, but does not allow obtaining the required joint strength. Due to this limitation, its main area of application is sealing minor cracks and cracks.
How to deal with common defects
The most common defects when welding cast iron include cold cracks that occur after the alloy has cooled. To reduce the risk of such a problem, local preheating of the welded surfaces to +250 °C is recommended.
Another common problem is the base melting too much. To prevent this, it is extremely important to control the operating parameters of the welding machine. This will help avoid overheating. Graphite substrates will reduce the risk of deformation of cast iron parts.
In addition, weld decoction is often observed during welding. This is facilitated by the formation of a chain of small pores. Subsequently, microcracks are formed in their place, communicating with each other. To prevent the occurrence of such a defect, it is necessary to avoid the use of high-nickel alloys when welding ferritic cast irons containing flake graphite.