04/30/2021 Author: VT-METALL
Issues discussed in the material:
- Operating principle of semi-automatic machine
- Pros and cons of semi-automatic welding
- Equipment for semi-automatic welding
- Semi-automatic welding without gas
- Semi-automatic gas welding
- Which semi-automatic welding method is better?
- Criteria for selecting a welding machine
Which semi-automatic welding is better - with or without gas? It is quite difficult to answer these questions. Each technology has its own advantages and disadvantages, so one or another method is better to use depending on the specific situation.
In general, semi-automatic welding, using any of the methods, is today one of the most popular types of metalworking. But in order to properly take advantage of its benefits, you need to have an idea of the technological nuances of each method.
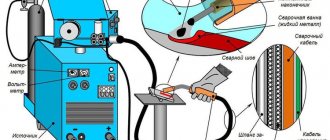
Operating principle of semi-automatic machine
A semi-automatic machine is an inverter machine that is used for TIG and MIG/MAG welding. Sometimes an additional mode is suggested for MMA welding. Compared to a conventional inverter, a semi-automatic machine provides a wider range of capabilities. The inverter works in tandem with an electrode and is necessary for manual arc welding. Whereas a semi-automatic machine is used with an electrode, wire, gas, which means that many more different operations are available with it. It is also possible to work in a protective gas environment. The result is very high quality and reliable seams.
The name of the semi-automatic machine is explained by the principle of operation of the mechanism responsible for feeding the wire into the working area. In other words, it works in semi-automatic mode.
VT-metall offers services:
Before talking about which semi-automatic welding is better, you need to imagine the operation of the device. Everything is simple here: a spool of wire is mounted in the feeding mechanism, the latter is fed into the metal processing zone during the welding process. Thanks to this feature, it is not necessary to frequently change electrodes, as is done during manual arc welding. In parallel with the feeding of the electrode wire, protective gas enters the cutting zone. The electrode and the product are energized, a discharge occurs in the gas cloud, resulting in an arc that melts the metal. Thanks to all these processes, welding is possible.
How to cook semi-automatically without gas
Semi-automatic welding without gas using regular flux wire is performed according to the following algorithm:
- metal parts must be pre-prepared; to do this, clean the joint and degrease the edges;
- on the mechanism with wire, a low feed speed is set, as well as minimum voltage values;
- It is recommended to run the torch at an angle forward, the arc is intermittent;
- the equipment is set to the correct polarity for welding with flux-cored wire without gas;
- the movement rollers and the tip on the head are selected according to the diameter of the filler material;
- the end is treated to prevent the adhesion of metal splashes;
- the welding movement begins from the top of the seam, evenly without jerking;
- flux cored wire is fed to the leading edge;
- For novice welders, it is recommended to initially perform a test weld.
Joining metal by welding is a complex technological process that requires compliance with the necessary safety measures, as well as the availability of protective equipment.
Pros and cons of semi-automatic welding
This type of welding is gradually gaining popularity among professionals and amateurs. Working with a semi-automatic machine has its advantages and disadvantages, which are important to understand before using the equipment.
Among the advantages of the technology are the following:
- formation of a permanent connection on galvanized products without damaging the coating through the use of copper wire;
- processing not only structural steel, but also other metals, such as aluminum, cast iron;
- the ability to weld thin steel sheets, the thickness of which is 0.5 mm;
- no impact on the result from contamination or rust on the base material;
- the ability to evaluate the seam during operation, since the slag does not block the operator’s view;
- low cost compared to other technologies that allow the creation of permanent connections.
The disadvantages of working with a semi-automatic machine are fewer than the advantages, but it is also important to remember them:
- hot iron spatters more when welding without a gas environment;
- more intense arc radiation is observed, so the welder requires a protective uniform and a face mask.
We recommend articles on metalworking
- Steel grades: classification and interpretation
- Aluminum grades and areas of their application
- Defects in metal products: causes and search methods
Despite these disadvantages, semi-automatic welding is actively used in many industries. It is most widely used in the automotive industry and vehicle repair.
Table of technical characteristics of wire for aluminum parts
| Base metal to be welded | Filler material (welding wire) universal | Filler material (welding wire) special to ensure special weld properties | |||
| Resistance to hot cracks | Tensile strength | Relative extension | Corrosion resistance | ||
| A99, A97, A95 | A99 | A99 | SvA85T | A99 | A99 |
| AD0, AD1 | SvA5 | SvA5 | SvA5 | SvA97 | SvA97 |
| Amts | SwAMts | SwAMts | SwAMts | SwAMts | SwAMts |
| AMg3 | SvAMg3 | SvAMg5 | SvAMg5 | Avch | Avch |
| AMg5 | SvAMg5 | SvAMg6z | SvAMg6 | SvAMg5 | Sv1557 |
| AMg6 | SvAMg6 | SvAMg6z | SvAMg6 | SvAMg6z | Sv1557 |
| AB, AD31, AD33 | SvAK5 | SvAK5 | Sv1557 | Sv1557 | Avch |
| 1915 | Sv1557 | SvAMg5 | SvAMg6 | SvAMg5 | Sv1557 |
Equipment for semi-automatic welding
There is a large selection of devices operating on the basis of this technology, so it is important to understand which semi-automatic welding is better. Various classifications are used among specialists.
According to the method of protecting the material during welding, the following types of semi-automatic welding are distinguished:
- Under the flux layer, where the flux is a powder located in the core of the working wire. In terms of chemical characteristics, it is close to the coating composition for the electrode.
- Using inert and active mixtures of gases.
Depending on the wire feeding method, the equipment can be:
- stationary, that is, the device is mounted on a stand or a special console;
- mobile - with a special trolley for moving within the premises;
- portable – the equipment is made in the form of a portable cabinet.
Semi-automatic welding units can be single-phase or three-phase. Single-phase devices are powered from a 220 V household outlet. If the network does not match the power of the unit, it is impossible to obtain a stable arc, and this is fraught with seam defects. For a three-phase device it is not always easy to find a suitable power source, but it provides high quality work regardless of the load.
State standards of technical process and equipment used
The technology and process parameters are regulated by the USSR state standard of 1977, extended in 1991, GOST 11533-75 “Automatic and semi-automatic submerged arc welding. Welded joints at acute and obtuse angles.” GOST introduces designations for subtypes of the method:
- Ac – automatic submerged arc welding on a steel backing;
- Apsh – automatic submerged arc welding with preliminary application of a backing seam;
- P - semi-automatic submerged arc welding;
- PS – semi-automatic submerged arc welding on a steel backing;
- PPsh – semi-automatic submerged arc welding with preliminary application of a backing seam.
The necessary parameters of the equipment are contained in GOST 18130-79 “Semi-automatic machines for consumable electrode arc welding”, created in 1980, extended in 2015. It contains requirements for rated voltage, electrical circuits, total cable cross-section, operating conditions and other process characteristics.
Semi-automatic welding without gas
We often hear the question of which semi-automatic welding is better: with or without gas. At the moment, experts consider the most promising and in demand technology without the use of gas.
In this case, welding is done using flux-cored wire, also known as flux-cored wire. We are talking about a steel tube, inside of which there is a special powder. This is a welding flux, reminiscent of coating electrodes.
Flux burns under the influence of high temperature, due to which a protective gas cloud is formed in the metal processing zone. According to its operating principle, the process differs little from conventional electrode welding.
The main advantage of this approach is the wide choice of materials with different chemical compositions. This allows you to provide the arc properties required in a particular situation and change the characteristics of the seam.
Since we are interested in which semi-automatic welding is better, it is worth dwelling on a number of advantages of gasless technology. This:
- simplicity;
- refusal to use and transport a gas cylinder;
- fast work.
This method is very similar to conventional electrode welding; for example, here it is also not possible to completely protect the seam from the ingress of slag from burnt flux. This means that it is important to ensure the sealing of the welding surface by placing several additional seams on top of the finished seam.
Flux-cored wire is characterized by low rigidity; therefore, it is fed to the metal processing zone with slight increased pressure. Any bends in the semi-automatic welding hose are unacceptable.
Features of the method
Additives that are used when welding without gas make it possible to reduce the diameter of the wire to 0.8-2 mm, and at low currents to obtain the required degree of metal melting.
Using this method, it is possible to obtain high-quality and reliable seams when fusing products of any thickness, as well as significantly increase the efficiency of the semi-automatic machine.
Semi-automatic welding of metal workpieces without shielding gas provides a number of advantages, the main of which are:
- eliminating the need to carry heavy cylinders;
- significant savings on gas mixtures, the refilling of which costs a lot of money;
- a variety of methods for forming additive compositions (using flux, powder and similar fillers);
- the ability to control the location of the welding cut directly through the mask.
When welding metals semi-automatically without gas mixtures, some professionals manage to produce from 20 to 40 meters of connecting “threads” per hour.
Features of semi-automatic welding include the use of gas-replacing attributes such as wire consumables.
The wire is produced in the form of a thin steel tube, the diameter of which is selected to be about 0.8 mm (similar to welding in a gas environment). Its internal cavities are filled with a special powder flux, its composition reminiscent of the coating of standard electrodes.
During the welding process using a semi-automatic machine and with strong heating, the filling composition completely burns out. As a result, a cloud of gas appears in the resulting bath, which reliably protects against the access of oxygen.
Semi-automatic gas welding
A semi-automatic welding machine for working in a protective gas environment is considered a new type of welding, which is just beginning to gain popularity today. However, over the past 20 years he has earned the trust of experts. The method allows for two types of work:
- MIG (Metal Insert Gas), where the connection of metal elements is carried out under the influence of an inert gas. The latter can be argon or other gas mixtures.
- MAG (Metal Active Gas) involves welding using an active gas such as carbon dioxide.
Due to the large and heavy gas cylinders, this technology cannot be used in all conditions; the equipment lacks mobility. Whereas for stationary work this type of welding is indispensable.
The composition of the electrode wire used includes silicon and manganese. By feeding the wire into the welding zone along with carbon dioxide, an environment is formed that protects the electrode and welding surface from environmental influences.
What is the main advantage of this type of semi-automatic welding? This method of joining metal makes it possible to better monitor the process. In addition, the use of a gas environment allows you to complete the job faster, since gasless welding requires changing electrodes and removing slag from weld seams.
In a protective gas environment, a weld is obtained that is significantly superior in quality to the result of gasless welding. True, there are some subtleties here. Thus, the choice of gas mixture plays a key role. If active CO2 gas is used, the seam will be scaly, with burrs, that is, with the effect of stuck balls. Whereas, due to a mixture of 80% argon and 20% carbon dioxide, a smooth and even seam is formed that does not require additional processing.
Serious disadvantages of the technology are the need to provide protection when working in open areas and additional costs associated with the supply of gases.
Welding technique
The technique has much in common both with the work of the MMA method with discrete electrodes, and with the work of a gas semi-automatic MIG/MAG .
Before starting welding, you should clean the seam area using an angle grinder to clean the workpiece from mechanical impurities, traces of rust, and remnants of old paint coatings. Next, it is necessary to thoroughly degrease the seam area and the adjacent area no less than 10 cm in order to wash off all oil and fat contaminants.
The seam edges are cut without any special features.
The burner must be moved along the seam smoothly, without jerking. The electrode should be pulled off and the arc extinguished at the end of the seam smoothly so as not to disperse the protective cloud of carbon dioxide on the cooling weld pool.
Welders who know how to weld parts with flux-cored wire without gas pay attention to the following nuance. During welding, there is still a risk that slag from the burning flux powder will unexpectedly flow into the weld pool . In this case, both the strength and durability of the seam in this area may suffer.
In this case, you should interrupt the work, clean the seam area from slag and re-weld it.
Which semi-automatic welding method is better?
When working without gas, the welding zone is completely closed from external influences due to flux. It is lighter than metal, so it is able to form a protective surface.
If you plan to work without gas, the use of ordinary wire is unacceptable. Otherwise, you will end up with an uneven, low-quality seam with shells. Also, such a solution will lead to a significant increase in wire consumption, because part of it will evaporate during the welding process. And most importantly, a reaction with oxygen will occur in the weld pool, which will cause oxides and cavities to appear in the weld.
If you follow gas-free technology and all the rules, you can form a neat seam.
Then which semi-automatic welding is better: with or without gas? Due to the gaseous environment, it is possible to prevent oxygen from entering the immediate work area. Therefore, you don’t have to worry about the appearance of defects caused by carbon content - the seam is of really high quality. However, the use of this technology is associated with serious physical and financial costs. Thus, moving large gas cylinders, without which welding is impossible, is impractical for the sake of several seams. Charging cylinders is considered unprofitable if the work is carried out quite rarely. In this case, it is much more profitable, for example, to weld aluminum semi-automatically without gas.
However, when using a gaseous medium, for example, with carbon dioxide, more favorable conditions are formed. In addition, metal cooling is ensured in the processing zone. This method is used more often, since a simple rule applies here: you can talk about economic benefits only if the device is used on an ongoing basis.
It is difficult to say exactly which semi-automatic welding is better, since often the choice of one of the methods depends on a specific situation.
It’s up to you to decide which technology to choose, especially since all the necessary equipment today can be easily found in specialized stores.
Possible seam defects during semi-automatic welding and how to prevent them
VIEW Welding machine on AliExpress →
Seam defects occur if welding is carried out in violation of the technology and the selection of consumables is carried out incorrectly. In this case, cracks, undercuts, pores in the weld metal, unevenness in width and length, as well as burns, sagging and other defects cannot be avoided. Incorrectly selected following values affect the following factors:
- Wire diameter: with a smaller one, the seam width will be insufficient; with a larger one, it will increase, which will affect the penetration depth.
- Current strength. It will also affect the depth of welding: the larger the value, the deeper the seam, which leads to burns, especially if you are welding thin-walled metal.
- The arc voltage will increase the width of the weld.
- Welding speed. If the value is large, the depth of welding decreases, the seam becomes narrow; if the value is insufficient, burns will occur, the seam will be uneven, and in some cases this will lead to warping of the product.
Figure 5 - Defective seam
Figure 4 - Defective seam
Most often, defects occur when welding is done by a person who does not have the skills to conduct the welding process. Share your experience of semi-automatic welding in the comments to the article.
Criteria for selecting a welding machine
When purchasing a machine, you need not only to understand which semi-automatic welding is better, but also to evaluate specific technical characteristics.
The key indicator is the operating current at which welding occurs. The thickness of the metal available for processing depends on this figure. It is recommended to select a device so that the maximum current is 20–30% higher than required. Having such a reserve, you don’t have to worry about the reliability and operating time of the device.
Another important characteristic is the duration of activation. It is recorded as a percentage and allows you to understand what part of the 10-minute period the semi-automatic device is in operation. According to this parameter, welding equipment is divided into professional and amateur. In addition, the cost of the device largely depends on this indicator.
Seam technology and characteristics
Welding with self-shielding wire is performed at a minimum voltage and feed speed. For metal 1.2 mm thick, a voltage of 14V and a speed of 2m/min are suitable. Sutures can be placed by moving the torch at an angle forward or backward. All this is done with an intermittent arc.
A slag crust forms on the joint surface. It is impossible to separate it with a hammer after waiting for the metal to cool. For multi-pass seams, this action is necessary for good adhesion of the next layer.
Seams using flux-cored wire turn out to be rough, with large scales, and characteristic sagging when working with an intermittent arc. A common defect is lack of penetration. Molten metal splashes are moderate. After completing the weld and removing the slag, the joint is cleaned with a metal brush.
The use of flux-cored wire allows welding work to be carried out in hard-to-reach places. Although the quality of the seam is inferior to welding in an inert gas environment, other positive aspects of this method greatly facilitate installation and construction processes.