Metal corrosion is a common problem that every car owner faces. The car body is a sheet metal structure with a large number of welded joints that constantly conducts current. Iron and steel oxidize over time when exposed to water and oxygen, forming rust. Galvanization is considered the most effective method.
What is galvanizing
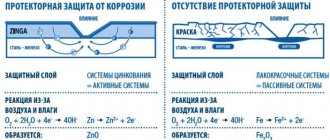
In case of severe damage, after an impact or chipping, the iron is exposed and interacts with air and moisture. This is how the initial source of corrosion is formed: as it spreads, it leads to the destruction of the metal. Galvanizing, or galvanizing, is the coating of a flat metal surface with zinc protection. The zinc layer also oxidizes in air, but at the same time forms a dense protective film that does not allow oxygen to react with the metal.
An alternative option is tinning and tin coating. This method is more expensive. In cases of serious body restoration, both tin and zinc are used: the first layer of tin smoothes out roughness on the metal coating, which is necessary when unevenness is formed when cleaning the body from a layer of rust.
Pros and cons of galvanizing methods
Each of the described methods of applying zinc protection has its own pros and cons.
- Hot-dip galvanizing provides excellent protection, but an even layer cannot be achieved. Also, the color of the coating is gray and matte. You can see zinc crystals.
- The galvanic processing method protects a little less well, but the part turns out shiny and smooth. It is also beneficial from an economic point of view.
- The only advantage of the cold processing method is that it is cheap, but this is only good for manufacturers, although it allows the price of the car to be reduced.
How profitable is galvanization?
Yes, the difference in price between a galvanized and non-galvanized body will be significant. Galvanized models are always much more expensive. And when you take out a car with a car loan, every thousand rubles matters.
However, you should understand that the savings at this stage will begin to resonate in the first months of owning a brand new car. A small scratch, a chip from a flying pebble, and you have a ready-made source of corrosion. Constantly treating and touching up such lesions is a waste of time, money and nerves. Just remember that for painting (!) one (!) element in workshops they charge from 5,000 rubles.
If you want your car to serve you for over 5 years and at the same time maintain its external presentability, do not neglect galvanizing. It’s better to overpay once than to suffer all these years.
But galvanization is different from galvanization, and this needs to be understood.
Approximate prices
In Russia, you can galvanize a body for 500-30,000 rubles . Prices depending on the volume of work are shown in the table.
| Area to be processed | Approximate cost in rubles |
| Door bottom/wheel arch/sill | 1500-3000 |
| Frame | 5000-8000 |
| Bottom | 10000-15000 |
| Small section of part | 500-700 |
| Whole body | 20000-30000 |
The cost of galvanizing at different service stations in the country is given below.
| Company name | City of location | Price for work in rubles |
| Ecoblasting | Moscow | 15000-30000 |
| Bitumenkom | Nizhny Novgorod | 1500-20000 |
| Body galvanization | Belovo | 1200-20000 |
| MDN-PROM | Kazan | 1200-25000 |
The services of private craftsmen are cheaper. On average, such specialists perform processing of body parts for 1,200 rubles .
If you plan to galvanize the body yourself, then the costs will only relate to the purchase of a special spray with zinc. In Russia, such a product costs on average 150-1200 rubles per cylinder.
Advantages and disadvantages
Galvanizing, despite its simplicity and reliability, has both advantages and disadvantages. Advantages:
- the machine is reliably protected from rust;
- The zinc layer is resistant to any weather conditions and can withstand significant
- mechanical damage;
- The corrosion protection time, based on the galvanizing method and operating conditions, is from 5 to 30 years.
Flaws:
- a very expensive procedure that requires certain skills and special equipment;
- galvanized body parts should not be harshly processed and cleaned;
- Even under ideal operating conditions of the machine, the zinc layer is gradually destroyed.
Partial galvanization of cars or simply a publicity stunt
In conclusion, we should consider those brands that use only partial treatment of the body of their cars, passing it off as full galvanization. What brands use this advertising ploy? Here you can find brands of Korean, Chinese and even domestic production.
For example, as for the domestic automotive industry, the latest Lada models are subject to partial processing. These include Kalina and Granta, which recently, according to the manufacturer, are coated with a protective layer of zinc by almost 40%. In these cars, only the bottom, sills and arches are completely galvanized.
In this case, only one-sided galvanization of some body parts is used. The second side is simply primed and painted in the traditional way. Such protection is designed to ensure that the part of the body hidden from view will be reliably protected from unnoticed rotting.
This approach allows you to significantly save money on production lines and make good advertising for your products. And although corrosion protection is still present on such cars, its capabilities are often exaggerated for advertising purposes, passing it off as full-fledged galvanization with the help of competent text. Such manufacturers also include Hyundai, Chery, Geely and Kia. Moreover, the latter brand often uses conventional cataphoretic priming with the addition of zinc particles. Such protection is also very effective, but it cannot be compared with the treatment that cars of European brands are subjected to.
Japanese automobile products have been showing good results lately. Here the Honda brand is considered the leader. It is also worth noting some successes in this area among new Toyota cars. Their technology, of course, is far inferior to the European giants of the automotive industry. However, cars of these brands also have a long warranty on the body and show good protective properties when tested in a salt tunnel.
The only drawback of such manufacturers is that they are overly loud about the protective properties of their products. In order not to fall for the bait of advertisers, it is necessary first of all to pay attention not to the words with galvanization, but to the length of the warranty period for the body. This indicator is more reliable and truthful than any general statements about high-tech metal galvanization.
Types of body galvanization
Surveys show that an extremely small proportion of drivers know that galvanizing the body is done using different technologies, in different volumes, and therefore provides the car with different protection against rust. And manufacturers are happy to take advantage of this.
For example, there is full and partial galvanization.
Full is when all elements of the body are coated with zinc, on both sides.
And partial – when galvanizing is carried out only on those areas that are most susceptible to chipping. As a rule, these are the front bumper, hood and front fenders of the car. What about the bottom, doors and sills? After all, they are the ones who suffer from rust if the car has been around for more than a year and is often parked on the street.
A favorite trick of advertisers is to call any type of galvanized bodywork galvanized. Thus, they sell us fake confidence in the complete security of our car. And under this sauce, sometimes we are ready to pay an extra 30 - 100 thousand rubles for something completely different from what we expected to get in the end.
Factors that determine cost
Galvanizing a body cannot be called a cheap procedure. The cost of the service is influenced by the following factors:
- Processing technology.
- Workload.
- Composition used.
- Thickness of the zinc layer.
- Difficulty of work.
- Equipment used.
- Class, make of car.
- Dimensions of the structure.
- Rating and pricing policy of the service company.
- Availability of current discounts.
- The city where the service is provided and the level of competition there.
Types of car body galvanizing
In mechanical engineering, when processing a body, in addition to full or partial galvanization, there are other types and types of galvanizing of the car body.
There is a huge difference in how one or another car body was galvanized, even within the same brand.
1. Hot galvanized
The best type of galvanizing. This thermal technology is most resistant to corrosion during operation of a machine with such galvanization.
A pre-prepared and dry body is lowered into a bath of molten zinc, the temperature of which is from 500 to 4000 degrees C.
The manufacturer's warranty for a car body with this type of treatment starts from 15 years and above.
High resistance to corrosion even after body damage. With minor damage to the body, the place where the chip has formed may, over time, become covered with a thin layer of zinc deposits (a self-healing process).
The procedure is expensive, which significantly increases the price of the car and manufacturers use it mainly for premium and business class cars. Hot-dip galvanizing provides a zinc coating thickness in the range of 2-15 microns.
Test results of cars that came off the assembly line with the same damage (a cross) on the lower part of the front right door.
Tests were carried out in the laboratory. Conditions in a chamber with hot salt fog for 40 days correspond to 5 years of normal operation. Hot-dip galvanized vehicle
(layer thickness 12-15 microns)
2. Galvanic galvanizing
The body is bathed in a bath with a zinc-containing electrolyte, where, under the influence of an electric current, zinc is deposited on the metal surface.
This treatment is less resistant to corrosion, but ensures uniform coating, a shiny, decorative surface with unchanged dimensions.
Galvanic galvanizing ensures the thickness of the zinc coating in the range of 5-20 microns. The manufacturer's warranty for the car body of such treatment starts from 10 years.
Almost all manufacturers who use one of the above methods note the presence of a zinc coating in the technical characteristics of their vehicles and provide a separate guarantee for the body against through corrosion.
Vehicle with galvanic galvanization
(layer thickness 5-10 microns)
3. Cold galvanizing
In recent years, this method has become widespread among inexpensive brands. Galvanizing occurs by painting the body with anaphoretic primers with a high content of highly dispersed zinc powder (zinc content in the finished coating is 89-93%).
Cold galvanizing is a mixture of galvanizing and painting. When using such a body, very poor resistance to corrosion is noted.
Manufacturers of budget car models often use such galvanizing during production so as not to inflate the final cost of the product.
Often the manufacturer is disingenuous, calling the body of such a car galvanized, which is actively used for advertising purposes. Cold galvanized vehicle
(layer thickness 10 microns)
4. Zinc metal
The method consists of coating steel at the rolling stage with a primer consisting of a sublayer of oxides containing zinc particles and a zinc-rich organic top layer.
A body can be made from such metal without any problems. The material is easy to weld, form, paint and is compatible with commonly used adhesives. The coating does not lose its protective properties.
Zinc metal is good where there is no high humidity, but when used on cars in the realities of our country, very low protection against corrosion is noted, especially in places of damage.
This type of galvanizing is common only among a few inexpensive brands. Car with zinc metal
Car without galvanization
Determining the type of galvanization
When buying a used car, the presence of so-called galvanization can be proven or disproved only with the help of expensive tests and special equipment.
Zinc metal
This technology involves processing not the finished product, but the metal itself during its manufacturing process. To do this, inorganic and organic polymer impurities with a high content of Fn, as well as its oxides, are added to the steel. After metal production is completed, it is molded, stamped, welded, etc. All this does not affect the quality of protection in any way.
However, zinc metal is significantly inferior to thermal and galvanic treatment. Therefore, it is more often used in the production of cars in the low-cost segment. For example, the KIA concern is a big “fan” of zinc metal.
In connection with all of the above, galvanizing can really significantly improve the characteristics of a car body. However, high-quality processing affects the final cost of the machine. Therefore, a natural question arises.
Machines with hot-dip galvanized body
It’s worth starting with cars with galvanized bodies using hot technology. The procedure itself is considered quite complex and expensive. This requires the use of expensive equipment. This cannot but affect the cost of the cars themselves.
Not all car companies are interested in providing the highest level of anti-corrosion protection. Explain this with a banal desire to increase your sales. Galvanized vehicles of lesser quality quickly become unusable. This forces you to sell your old car and buy a new car. Because of this, manufacturers do not want to spend money on making the body durable.
That is why the final list of brands and direct models that have a hot-dip galvanized car body is not so long.
The main list consists of the following brands:
- Volkswagen.
- Audi.
- Skoda
- Porsche.
- Seat.
In fact, these are companies of the VAG concern.
But here it is worth adding some car models under the brands of General Motors, Volvo and Ford. In some plants they also use hot-dip galvanizing.
Factory processing of the car body
These machines have proven their high level of rust resistance through natural and laboratory tests. Cars were placed in special salt chambers.
It is believed that the ancestor of hot zinc is the Audi company. But even now they pay special attention to protecting the body of their models. Audi even patented a special technology for double-sided coating of all body elements. Weld seams are subjected to similar treatment.
Recently, aluminum has been actively used, which helps reduce the weight of cars, as well as reduce the cost of hot-dip galvanizing.
There are several modern car models from different brands, the development of which uses the most effective method of zinc coating the body:
- The entire current range of Audi cars.
- Opel Vectra C.
- Opel Astra G.
- Ford Escort.
- Ford Sierra.
- Chevrolet Lacetti.
- Chevrolet Epica.
- Buick.
- Cadillac.
- Fiat Albea.
These cars were produced with a completely hot-dip galvanized body. The switch to aluminum made it possible to switch to partial processing.
List of cars that can last up to 30 years without corrosion
We have prepared a rating of cars whose owners need not be afraid of corrosion.
Audi A6 C4
The model was produced from 1994 to 1997. Thus, the “youngest” Audi A6 C4 is now 24 years old. Despite this, cars are still actively sold on the secondary market, and one of the main reasons for this is the almost “eternal” body, completely hot-dip galvanized.
New Audi A6 C4
A major overhaul of the engine, suspension, and brake system may be required, but nothing will happen to the body parts.
Ford Focus
The model has been produced from 1998 to the present. Perhaps the only representative of budget cars on the list treated with hot-dip galvanizing. It is extremely popular in the secondary market; many cars of the first generations are still “on the move”.
These achievements would not have been possible without the full hot-dip galvanization that Ford generously bestows on its vehicles.
Porsche Cayenne 955
The model was produced from 2002 to 2010. A premium crossover with permanent all-wheel drive, excellent interior trim, powerful engines and a body that will never rot.
Machines with galvanic processing method
Next, we will consider a list of cars with galvanized bodies that are presented on the Russian market.
This is also a thermal processing method, but it requires fewer resources and financial costs for implementation. Therefore, the method has become very widespread, and it is much easier to find cars with such a body.
Mostly Japanese and American automakers have switched to galvanic processing. They are noticeably less common among European companies. Considering the low efficiency compared to hot-dip galvanizing, leading automakers are developing improved methods for applying zinc, thereby modernizing the galvanic principle. In particular, these are companies such as Mercedes and BMW.
In order to improve the quality and efficiency of galvanizing, the following steps are used:
- In the production of the body parts themselves, high-alloy steel grades are used. Their advantage is that the amount of impurities in such steel is minimal.
- A thicker layer of zinc itself is applied. The thickness can range from 9 to 15 microns.
- In addition to galvanizing, the body is additionally primed with a thick layer and the layer of paintwork applied on top of the zinc is thicker.
- The adhesive properties of surfaces increase, providing a stronger and more durable bond between all layers.
Before publishing a list of brands and models of cars that have galvanized car bodies using galvanic technology, it is worth noting one pattern. Japanese cars were initially inferior to European ones in the quality of galvanization and durability of the body. But then the situation began to change, and they reached approximately the same level. This was due to the fact that the Japanese began to use zinc somewhat later to make cars.
Toyota and Lexus brands are considered to be of the highest quality. They demonstrate excellent corrosion resistance. Largely thanks to a fairly thick layer of protective coating.
The galvanic method of galvanizing car bodies was used in the production of the following cars:
- Alfa Romeo (only after 1993).
- Audi A4.
- Mitsubishi Lancer 9.
- Mercedes W124.
- Mercedes W201.
- Lexus (all models).
- Volkswagen (all cars after 2000).
- Toyota model range (after 1991).
- Skoda Fabia
- Skoda Octavia.
- Peugeot.
- Honda Legend.
- Renault Espace 3rd generation.
- Renaul Logan.
- Chrysler 300M.
The same Renault Logan has far from exemplary paint quality. But due to a good level of protection through galvanic galvanizing, their body can be under attack from moisture and chemicals for a long time, preventing pockets of corrosion from appearing.
List of cars that do not rust
In the history of the global automotive industry, much attention has been paid to the level of rusting of cars of different brands and models. But it is important to understand that even those machines that are traditionally resistant to metal corrosion in one operating region can behave completely differently in another. And here the quality of materials and protective coatings, operating conditions and the manufacturer’s work on additional anti-corrosion protection are of great importance.
We bring to your attention a list of cars, which was compiled on the basis of the opinions of car designers, body shop technicians and even resellers who have their own “types” of optimally reliable brands/models of vehicles.
Oddly enough, the leaders of this rating are foreign cars that behave better in the conditions of the Russian climate and the poor condition of domestic roads than Russian-made cars.
What kind of galvanization do Russian models have?
Unfortunately, the domestic auto industry has not yet realized the importance of galvanizing. We are very far behind the West in terms of mechanical engineering.
The old Soviet models were strong because they were made from imported parts. At domestic enterprises until 1999, galvanizing as such was not carried out at all. And only ten years ago our factories began to massively introduce galvanization of the body of their models. However, not completely and not using the hot method.
Galvanizing the body on Russian models is usually done using galvanic or cold methods. In addition, no more than a third of the body is covered with zinc: these are mainly the parts most susceptible to chipping.
For example, about 30% is galvanized in the VAZ 2110 and Lada Priora (produced in 2008). Since 2009, Priora began to be completely galvanized. XRAY does not treat the roof, Vesta does not treat the bottom and sills.
The advertised Lada 4×4 has not been galvanized at all; its body is simply coated with a cataphoresis primer. Grant's sedan was also left without galvanization.
The quality of the galvanized body of Russian models leaves much to be desired; after any chip, the paintwork in the area of the defect will have to be corrected, otherwise rust will quickly develop.
Volkswagen Passat
Any Passat stood out among other cars for its reliability and body resistance to rotting. And why? Yes, because the body was galvanized during production. Therefore, if you manage to find an undamaged Passat, even if its year of manufacture is 1990, then we can say that you hit the jackpot. Although it’s unlikely that anyone will sell an unbeaten Passat, because you need “such a cow” yourself.
True, it is worth recognizing that over the years, galvanization has become worse, cars began to rot faster, which means they also began to be sold more often.
Galvanizing the body at home
It is possible to galvanize a car at home. This will save you money, but not time. All parts that you plan to process will have to be removed and cleaned of paintwork.
As you already understood, the most affordable method is cold galvanizing using a zinc-containing primer. And this method is the most unreliable, so don’t even waste your energy!
But the galvanic method is worth taking a closer look at. Of course, it will require a more complex process, the purchase of a large container and special solutions, but in general it is possible.
How to galvanize a body yourself
At home, do-it-yourself galvanizing is possible in two ways: cold and galvanic. Technologies are different, the main attention is given to safety. The car or the selected part of the body will be processed quickly and efficiently if you adhere to certain rules:
- All galvanizing operations should be carried out in rooms with good ventilation, preferably outside.
- Use personal safety measures: protective suit, gloves, goggles, respirator.
- Remember about the environment, because the material used is heavy metal and aggressive chemicals.
The galvanizing process begins with preparing the vehicle.
- Removing the primary paintwork.
- If there is corrosion under the paintwork layer, remove rust using polyrite.
- Alignment and straightening of the body.
- Alcohol degreasing of the surface.
Do not use chemicals to remove dirt, paint or rust.
Within 10 minutes after degreasing, galvanizing is carried out using one of the methods.
How to choose a car with the right galvanization: 5 rules
You already know which body galvanization is better. But how to choose a car? How not to fall for the false promises of sellers and spend money on a truly worthy model?
Rule No. 1: If the advertising offer and documents do not contain the word “galvanized,” the body is definitely not galvanized. The seller will never ignore the opportunity to trump such an important advantage of the car.
Rule #2: Ask for documentation. Managers can embellish and promise you anything, but the documents always contain the truth.
Rule No. 3: Do not believe in 100% galvanization of a car if the documents do not indicate “full galvanization.” When there is no “full” prefix, and you are lured by galvanizing, it means that only some parts have been processed.
Rule #4: Check what type of galvanizing was used. And remember that Western methods are always better than domestic, Chinese and Korean ones.
Rule #5: Check the warranty period for the body. Manufacturers always indicate this characteristic. If it is 3–5 years old, either there was no galvanizing, or it was done using the cold method. A mark within 6 - 10 years indicates a galvanic processing method, and 10 - 15 or more indicates high-quality hot processing.
Sometimes the presence of galvanization is visible to the naked eye. If there is a small scratch somewhere on the body (and this occurs even on new copies), and you see that the material is not rusty, but darkened, this means that the surface is galvanized.
Peugeot 307
Peugeot makes truly interesting cars: out of the frying pan and into the fire. Either their cars can turn out great, or they fall apart with every sneeze. Fortunately, the Peugeot 307 belongs to the first group, and therefore you can safely purchase it.
The car model was produced since 2001, and production ended in 2007. From the very first year, the car body was completely hot-dip galvanized. There was probably not a single detail that did not undergo processing.
Hot-dip galvanizing is the best body treatment option in the world because it maximizes the life of the body, even when the metal is starting to wear out.
How to find out if a car has undergone anti-corrosion zinc treatment
Information about this can be found in the technical documentation for the vehicle. If you couldn’t find the word “zinc” in the papers, the body is unlikely to be protected from corrosion in any way.
To determine the presence of galvanized car body without papers, you will have to spend a lot of money. In particular, seek a service from a specialized center or trust the information provided on the Internet.
Partial protection or its complete absence can be judged by the cost of the car. Budget models are rarely galvanized, especially using one of the high-quality methods. They are simply treated with inexpensive paints and materials. These cars include Asian economy class cars.
How to determine whether a body is galvanized or not
Most modern car manufacturers - 98% - try to galvanize the car. The type of galvanization and the degree of coating are displayed in the technical passport of the vehicle. If you purchase a car from the secondary market with significant mileage, it is almost impossible to find out whether the body is galvanized or not.
To clarify this issue, an expensive operation is needed: testing the metal using special equipment, which is only available in specialized services.
How to prevent rust on metal
Additional anti-corrosion treatment will help protect the car from rust, especially if these are inexpensive foreign cars or domestic cars - usually their protection leaves much to be desired from the factory. Therefore, inhibitors should be applied to the surface of the body as soon as you bought the car.
Inhibitor compounds cover unpainted metal with a thin film that does not allow air and moisture to pass through, prevents rust from forming and stops the spread of small pockets of corrosion. They should also be updated regularly.
If you have lost sight of the corrosion process, you will need drastic protective measures and stronger anticorrosion agents:
- phosphoric acid - not only kills rust, but also penetrates the metal structure, strengthening its resistance to rust;
- rust converters – simplify cleaning of rusted surfaces and create a protective film;
- powerful inhibitors - cover iron with a waterproof film and protect it from adverse weather conditions for a long time.
Sandblasting also effectively removes rust and cleans metal without reducing its thickness, but after using it, surface treatment with anticorrosive agents will be required.
Attention! It is better not to use folk remedies - Coca-Cola, kerosene-paraffin solution or Cillit cleaning agent - metal and paintwork behave under their influence in a unpredictable manner, and they are questionable as rust removers.
In conclusion, it should be noted that any car is iron, which spends its entire life in extreme climatic and technical operating conditions, is subjected to severe mechanical and chemical loads, freezes, heats up, gets wet and dries in the fresh air. The appearance of corrosion on a car body is more likely a normal phenomenon than an exceptional one.
Your task is to choose a car whose manufacturer cares about its customers and works on anti-corrosion protection and strives to maximize the service life of the vehicle.
Much also depends on you - how carefully you behave on the road, take care of the car, monitor its condition, clean and wash it in a timely manner, promptly detect and competently eliminate any corrosion stains that have appeared.
Opel Astra G
Admittedly, the Opel Astra F was relatively good, but it could rust faster than any tin can hidden in the ground, water and the like. The company's engineers decided to eliminate this drawback on the new G series model, so they decided to make it completely galvanized. As a result, the Opel Astra G truly became one of the best in terms of body reliability and durability.
Production began back in 1998, and ended 10 years later. Today you can buy it for only 150 thousand rubles, and at the same time its body will not be easy to “live”, and even without a single trace of rust, although until 2007 only partial galvanic galvanization was used.