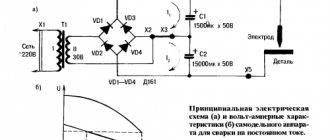
Direct current (or simply “constant”) is widely used in amateur and professional welding. With its help, you can get high-quality and durable welded joints, even if you do not have enough skills. For this you will need a good welding machine and DC electrodes.
Peculiarities
Modern manufacturers offer universal electrodes that can operate at both alternating and direct current. This is a good option if the seam does not have high quality and durability requirements. But, as you understand, in order to weld a truly reliable seam, you will still need specialized electrodes for working with direct current. When using them, the metal practically does not splash and the seam turns out smooth.
The electrodes you purchase must be of high quality and manufactured in accordance with GOST. Do not save money and do not buy rods from unknown manufacturers. After all, low-quality electrodes can ruin not only the seam, but also the surface being welded. Externally, permanent electrodes do not differ from any other rods; their differences begin to appear during operation. When working with DC, the composition of the electrode is not as important as the quality of its manufacture, so make sure that the materials you choose are suitable for welding the necessary parts and feel free to get to work.
Briefly about coverage problems
The coating serves to protect the bath and, of course, to stabilize the arc. The coating also determines the degree of ionization and is responsible for the occurrence of physical and chemical processes in the weld pool. It follows from this that the required mechanical properties of the weld metal and the joint as a whole are largely ensured by electrode coating.
So, for welding especially critical structures operating at subzero temperatures and static loads, where increased strength and ductility are required, direct current is required, and therefore welding materials, in particular electrodes, must be selected taking into account these requirements.
Advantages and disadvantages
Special permanent electrodes have many advantages compared to universal rods, here are some of them:
- Highest seam quality.
- The metal does not splash, so electrodes for DC welding can be used when working in any spatial position.
- Large selection of diameters and coatings.
- Even novice welders can do the welding process.
- The welded joint will be reliable and smooth even without the use of flux.
But there are also disadvantages:
- They are not cheap, but they only allow you to work with direct current.
- It is necessary to take into account all the features of the metal in order to choose the right electrode and not spoil the work.
Welding electrodes for alternating current for RDS
The manual arc welding process using a welding transformer is carried out using alternating current. The electrodes used must be suitable and intended specifically for these purposes.
The practice of using these materials shows a significant decrease in their popularity due to the emergence of modern sources of welding current - inverters. Welding here is carried out with direct current.
Cons when using
We can highlight the following disadvantages of using electrodes during recess, which relegated them to the background:
- reduced stability and behavior of the welding arc. Associated with the changing polarity and characteristics of alternating current;
- low quality weld;
- significant splashing of metal with the formation of “drops”;
- significant energy consumption during welding due to the high power consumption of the transformer, which cannot but affect the cost of the final product.
Designation and marking
To decide on the choice of electrodes, you need to understand their labeling and classification. The last digit in the designation serves as an indicator for the type and polarity used.
All options are presented in table form:
Analyzing these data, we can conclude that most electrodes are universal in relation to the type of current. There are requirements for the use of a certain cold voltage. transformer for alternating current electrodes.
Attention ! The use of rods with the number “0” at the end is not recommended in this case - it is used only for permanent use, for example, “SSSI”.
Stamps
The correct selection of electrodes will depend not only on the current parameters, but also on the type of metal being welded. If we consider standard tasks for welding low-carbon steels, it is worth taking a closer look at the following brands:
- OK 46.00;
- MP-3;
- ANO -4, 6, 21;
- OZS - 4, 6, 12.
These are rutile-coated electrodes, which have proven themselves and cope with the assigned tasks perfectly. It is definitely impossible to put any of them in the best category, because these are all brands, and the manufacturer may be different. Accordingly, he can apply his technical conditions during production and change the composition of the coating, which differs from GOST. When choosing, you should focus on proven brands - ESAB, LEZ.
We recommend! Types of electrodes for cast iron. How to make it yourself
Basic modes
It will be possible to achieve a good result when welding in any spatial position by setting the correct modes depending on the thickness of the metal.
| Diameter size, mm | Welding current range, A | ||
| Down position | Vertical seam | Ceiling seam | |
| 2 | 40 — 80 | 40 — 60 | 50 — 70 |
| 2,5 | 60 — 120 | 60 — 95 | 60 — 100 |
| 3 | 75 — 150 | 75 — 140 | 75 — 170 |
| 4 | 110 — 220 | 110 — 210 | 100 — 190 |
| 5 | 160 — 310 | 150 — 290 | 150 — 280 |
svarkagid.ru
Stamps
We have collected several brands that are popular among beginners and experienced craftsmen. All of them have been tested more than once and have shown their best performance:
- SSSI 13/45. This is perhaps the most popular brand. Excellent for welding low alloy and carbon steel. Provides high seam tightness, therefore it is widely used when welding parts that must in the future work under pressure. Suitable for welding complex metal structures. Such electrodes are produced with a basic coating. Before going on sale, they undergo a sanitary and epidemiological inspection. We recommend this brand to more experienced craftsmen who have already dealt with direct current.
- OZS 12. Another popular brand. It is also used to weld complex metal structures, which are subject to increased demands on quality and durability. Suitable for welding low carbon steel. Can be cooked in any position except vertical.
- OZS 4. A brand that will save you in poor welding conditions. Such electrodes work perfectly even on uncleaned surfaces covered with corrosion. Suitable for welding low alloy and carbon steels.
- MP 3C. A good choice for the beginner or home welder. Surfacing is carried out easily and quickly, the seam is smooth and beautiful. Also suitable for low alloy and carbon steels.
DC electrodes for welding: brands, which ones are better, markings, features of constant current
Home page » About welding » DC electrodes
Welding with direct current has a wider range of applications than welding using alternating voltage. This is due to several undeniable advantages of this type of welding. Therefore, electrodes for DC welding are more in demand. It is the permanent materials that we will consider in the article.
It should be noted that not all equipment has the ability to provide constant voltage. If the welder has a transformer without a rectifier or an alternating current generator, then it is necessary to use consumables for alternating current.
Features of DC welding
The welding process using constant voltage has a number of distinctive properties. Some characteristics can be considered as advantages, others as disadvantages.
Pros:
- the almost complete absence of metal spattering ensures a reduction in electrode costs;
- the constant makes the welder’s work easier;
- high productivity and labor efficiency;
- stability and stability of the arc even when exposed to negative influences: gusts of wind, voltage fluctuations and others;
- high-quality and neat seam;
- the ability to connect thin metal products;
- absence of uncooked areas.
Minuses:
- welding using direct current is carried out using inverter machines. This equipment is highly expensive;
- “magnetic blast” creates problems with an unstable arc in difficult places (eg corners).
Forward or reverse polarity
A welder needs to know! Connecting metals with direct current can be carried out in two modes: with direct and reverse polarity. First mode: a minus is connected to the electrode, and a plus to the metal product. When welding, reverse polarity is the opposite: positive to the electrode, negative to the workpiece.
Welding with direct polarity forms a cathode spot at the tip of the electrode, and reverse polarity creates an anodic spot. In the area of the anode spot the temperature reaches 3900°C, in the area of the cathode spot - up to 3200°C. During straight polarity welding, heat is concentrated on the workpiece, which causes the root of the weld to deepen.
Therefore, it is better to use straight polarity voltage when welding thick-walled products and in cases where high temperatures are required.
Reverse polarity current is used to work with the following materials:
- structures made of thin sheet steel;
- fusible metals;
- steels sensitive to overheating: stainless, alloyed and high-carbon.
Features of welding with direct polarity:
- large spattering and high penetration coefficient are due to the fact that the metal from the materials is transferred into the weld pool in large drops;
- the electric arc is unstable;
- correct heating of the product;
- some welding consumables show an increase in deposition rate;
- the weld seam has a non-standard material composition: no carbon, a large amount of silicon and manganese.
- less heating of the rod allows the specialist to use currents with a higher value.
Features of connection with reverse polarity:
- the need to reduce the current potential to reduce the temperature of the product;
- It is recommended to weld with an intermittent seam;
- very thin parts are welded with periodic interruption of the arc;
Flanging (see features of welding thin metal) - When joining with an overlap, the workpieces must be pressed tightly against each other. Failure to comply with this condition may result in burning of the upper part.
- the butt connection should be made with a minimum gap or, best of all, no gap at all;
- When welding thin products with uneven edges, a copper or steel plate should be placed under the joint. Such an auxiliary layer will take away some of the heat from the welding process;
- You can flange the edges to be joined, the angle is 90°.
Useful video
Watch the video, which clearly explains the difference in the use of polarities.
Electrode marking for DC current
Different types of welding materials have their own markings. The marking contains basic information about the electrode. The format of this information includes 12 digital combinations, each of which has its own meaning. The main feature of markings for DC consumables is the number “0” located at the end of the entry. It is she who indicates that a certain brand is designed only for direct current.
The number “0” in the line “E 513 B20” indicates that these electrodes are used for DC welding of reverse polarity.
How to choose
How to choose DC electrodes. There are a large number of manufacturers and suppliers of electrodes on the welding materials market. Next, we will look at factors that can help determine which electrodes are best for direct current.
When choosing consumables, first of all, you need to pay attention to the brand of welding materials. From a positive point of view, the following brands have proven themselves: ESAB, LEZ, Resanta, Lincoln Electric, Kobelco. You can find out which are the most popular by looking at the survey results in the ranking.
The following components are determined in accordance with the task at hand.
When choosing the diameter of the electrode, you should take into account the type of steel to be welded. Each brand of materials has a specific purpose.
It is also necessary to take into account the specifics of welding: household, production or industrial.
The following parameters need to be defined:
The coating of welding materials is important. It is better for beginners and inexperienced craftsmen to use electrodes with rutile coating. However, this type of coating is not suitable for connecting critical structures.
Having familiarized yourself with the above characteristics, you can easily determine which electrodes are better to choose for constant voltage.
The best brands
Let's look at the best brands of DC electrodes according to welders.
Welding electrodes "UONI-13/55" in packaging.
1. UONI-13/55 electrodes are one of the most popular welding materials for constant voltage. They are used for connecting critical parts and structures made of low-alloy and carbon steels.
Advantages: the weld has sufficient ductility and impact strength; coating of the electrodes ensures a low content of gases and various undesirable impurities in the weld metal; wire Sv-08 or Sv-08A, which is the base material for the rod, guarantees the durability of the seam; easy arc ignition.
2. UONI-13/45 are intended for welding carbon and low-alloy steels. Advantages: resistance of the weld to the formation of hot and cold cracks; plasticity and good impact strength of the connection; high tightness allows these electrodes to be used to weld containers operating under pressure; seams are less prone to aging compared to seams made with materials from other brands. 3. OZL-6 - electrodes used for welding heat-resistant steels. Advantages: the seam is not subject to the formation of pores and cracks, as well as corrosion; the weld metal is heat resistant; This brand is suitable for working with metals of different structures.
4. OZS-12 is used for welding low-alloy and carbon steels. Advantages of using this brand: the welding process can be carried out in all positions; welding of edges with a small rust content is possible; the weld is characterized by strength and durability; stable arc; During work, virtually no toxic substances are released. 5. TsL-11 are designed for welding corrosion-resistant and chromium-nickel steels. Advantages: the welded joint is characterized by increased resistance to corrosion; low splashing; stable arc; slag is separated at a satisfactory level.
6. ANO-21 are used for working with carbon and low-alloy steels. This brand is in particular demand among professionals and novice craftsmen. This is due to several reasons: stability, softness and easy arc ignitability; low metal spattering; The weld metal has a fine-scale structure.
7. LB-52U are used for welding carbon and low alloy steels. Advantages: high performance; stable arc; minimal splashing; welding can be carried out in any spatial position; high resistance to cracking.
8. MP-3 for working with critical elements made of carbon and low-alloy steels. Advantages: high resistance of the seam to the formation of hot cracks and pores; stable and powerful welding arc; metal spattering is at a minimum level; the slag crust is easily separated. 9. OZCH-2 - electrodes intended for welding and surfacing of cast iron. Pros: the versatility of this brand; ease of use; stable arc burning; low level of splashing; the weld is characterized by plasticity, which prevents the appearance of cracks; easy slag separation.
More information:
Electrode brands are selected by polarity and more information on welding current is given on this page:
Where to buy electrodes for direct current.
weldelec.com
Selecting Electrodes
Many novice welders often ask: “Which electrodes are best for DC welding?” There is already an error in this question. There are no better or worse electrodes; each brand has its own characteristics and purpose. The master decides for himself which electrodes are preferable to perform his specific tasks. But there are still some things worth considering when choosing rods.
First, look at what the electrodes you choose are made of and what they are intended for. Some brands may be designed to work with only one type of metal. This needs to be taken into account. Most holding rods are made to weld steels, so you'll have to do some research to know the properties of the part and the electrode. There is no need to weld a low-alloy part with a carbon steel electrode. It would also be a good idea to ask the seller for quality certificates. Some stores are not shy about selling counterfeit products, the quality of which leaves much to be desired. Secondly, decide on the diameter of the electrode and the thickness of the metal. Remember the golden rule: the thicker the part, the larger the diameter of the rod. If you do not follow this recommendation, the metal will either not be welded or will be deformed. Deviations of no more than one millimeter are allowed.
Note! 50% of the result is the correct choice of operating mode. You can choose the desired diameter and composition of the electrode, but set the wrong current mode, and all the work will go down the drain. Take this seriously.
Welding rods: types and characteristics
To work with reinforced products, you need rods coded “E” and hardness codes indicated by numbers: 38, 42, 46, 50, 55, 60, 70, 85, 100, 125, 150; 42A, 46A, 50A.
In the case when it is necessary to connect types of steel products that are resistant to thermal effects, consumables coded E-09 and E-10 are used. Many types of electrodes are suitable for welding high-alloy metal, their number is more than 40. The most commonly chosen electrodes are: E-12X13, E-06X13N, E-10X17T, E-12X11NMF, E-12X11NMF.
To connect materials with previously known characteristics, the following electrodes are used: E-10G2, E-12G4, E-10G3, E-16G2KhM, E-15G5, E-30G2KhM, the total number of types is 38.
Operating modes
So, how to choose the right mode to ensure high-quality and durable work? First, pay attention to the spatial position. When welding, the metal flows down one way or another, so in a vertical position it is better to set the minimum current to control the rate of metal melting. Using the same logic, select the current mode for other positions. Below you can see a table in which we have collected the main operating modes.
Type of rods and explanation of electrode markings
Any container in which welding rods are packaged has an alphanumeric coding, for example: E50A-UONI – 13/55 – 5.0 – UD / E514 (4) – B20
Marking of rods Source bsm21.ru
Electrodes, their markings
The first digits of the designation in our illustrative example indicate the type of rod. E50A - consumables that can be used for welding steel reinforced and non-reinforced metal. To make the abbreviation easier to understand, it is recommended to break it down into its components:
- E - rod is used for welding on an arc machine.
- 50 is the maximum value of the connection strength.
In our sample, this parameter is 50 kgf per 1 sq. mm.
- A – the joint has load toughness and good flexibility.
From this sample it is clear that it is possible to understand the decoding of the electrodes; it cannot be considered a difficult task. If you have an explanation at hand of what the digital and alphabetic signs mean, any beginner will understand.