Double roller profile rolling machines
Rolling with two (less often three) driven cylindrical rollers has found wide application in machine-building and machine-tool factories in the production of threads and other high-precision profiles.
Advantages of the method: versatility of the process, wide range of rolled thread diameters (2–200 mm) and pitches (0.35–16 mm), no limitation on the length of rolled thread (up to 2000 mm and more), high tensile strength of the workpieces being processed - up to 1500 MPa , high precision rolled thread (tolerance range 4h and above); relative simplicity of equipment design.
The semi-automatic profile-rolling (thread-rolling) machines used for this method are universal machines. They are designed for cold rolling of precise metric, trapezoidal and other types of threads; worms; profiles on lead screws; corrugations; fine-module helical wheels, as well as for straightening and calibrating cylindrical and spherical bodies. The process of rolling a profile on the cylindrical surfaces of workpieces is carried out by rolling a profile applied on cylindrical thread rolling rollers over the surface of the workpieces, with forced rotation of both rollers and radial movement of one roller under the influence of the force developed by the hydraulic feed drive.
A workpiece installed between thread-rollers on a knife support or in the centers of a special device will rotate as a result of the friction forces that arise when the rollers come into contact with the workpiece and increase as the profile of the rollers is introduced into the workpiece and a profile is formed on it that is negative to the profile on the rollers.
Currently, machines with rolling pressure from 5 to 60 tons are mass-produced. Depending on the modification, the machine can be equipped with CNC, instead of electric motors and transmissions, servomotors are used, all commands are given from the control panel, and the results of setting up the machine are entered into memory and can be subsequently shown on the display. The accuracy and reliability of the machines allow them to be used for rolling all types of threads (including tapered threads), worms, fine-module helical wheels, nipples, trunnions, as well as for rolling valves. The machines are easily equipped with automatic mechanisms for loading and unloading parts, which allows them to be widely used in automatic complexes and lines for the production of mass parts. When using automatic loading, the machine rolls up to 1200 parts per hour.
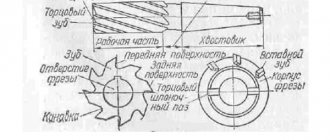
Thread rolling heads
Rolling with a non-driven cylindrical tool is carried out using thread rolling heads and holders mounted on supports of universal equipment. The use of thread-rolling heads and devices expands the scope of application of rolling and ensures that this method produces precise threads on universal metal-cutting machines: lathes, turret lathes, single- and multi-spindle automatic machines. The use of heads and devices makes it possible to obtain finally processed parts that meet the necessary requirements for alignment, runout and stability of thread dimensions, without isolating the production of threads into an independent operation.
Modern thread rolling heads can be divided into three main groups:
- with longitudinal feed by three thread-rollers with annular thread;
- with tangential feed by two thread-rollers with screw threads;
- with radial feed by two or three backed rollers.
Along with the positive properties of thread rolling heads, such as providing a reduction in machine time by 5-7 times compared to cutting with round dies, it can be said that this technology is not intended for large-scale production.
Thread rolling with flat dies
Rolling with flat thread-rolling dies has found wide application in hardware factories in the manufacture of fasteners of normal precision. The accuracy of the rolled thread is no higher than the sixth degree according to GOST 16093-81. This method has the following advantages: relatively high productivity, simplicity of equipment design and fairly high reliability of its operation, simplicity of design and manufacture of tools. Disadvantages limiting the use of this method: narrow range of rolled thread diameters (1.5 - 33 mm), step limit 0.35-3 mm; limiting the length of the rolled thread with the width of the dies up to 100 mm and the tensile strength of the rolled workpieces up to 900 MPa. It is difficult to obtain threads on parts of increased hardness using this method. The use of flat thread rolling dies of a special design makes it possible to roll threads on self-tapping screws in one pass.
Also on topic...
Operating principle, purpose, advantages
Thread cutting is an inseparable operation in metalworking production. Thread cutting is typical for CNC lathes, screw cutting and turning units, and thread processing units. Drilling machines can also cope with the thread-cutting mode during the drilling process.
Thread rolling units are installations used for rolling threaded and screw planes on workpieces - bodies of revolution made from ferrous and non-ferrous metals, as well as mixtures. These alloys give the installation high strength characteristics and long service life. The equipment is convenient to maintain, which allows thread rolling using several methods:
- Radial roller feed. Designed for cultivation of small helical planes.
- Tangential feed of the part. An improved feeding technology than radial feeding of the workpiece, since it is carried out tangentially to the circle in a certain area.
- Method of axial approach of a blank. Designed for processing long-length screw connections.
The most famous and popular method of thread rolling is considered to be a variation when the rollers are fed radially. This procedure is simple. The knurling procedure takes place through two movable rollers, but radial feed is carried out by only one of the shafts.
It is worth noting that in the radial tool feeding method only cylindrical rollers are used that comply with GOST 9539 standards.
All these methods are used in different areas of production. The operating principle of the machine is based on changing the surface of the part and creating a shape with special tools. The formed profile is performed by pressing the part into the plane under a load depending on the equipment. This is how the production of self-tapping screws, screws, and rivets is carried out.
The main positive aspects of the thread rolling device are:
- absence of chips, which increases the usefulness of the device;
- favorable economic indicator in the purchase of expensive consumables;
- increased wear resistance and service life of treated surfaces;
- integrity of the threaded connection of the workpiece;
- high performance of building elements.
These advantages of roller knurling technology have made them popular in large-scale production.
How to create threads using Centertap
Thread rolling with Centertap taps is a chip-free process. A spiral with a uniform pitch is applied to the working area of the tool. The cross-section of the Centertap tap is made in the shape of a polygon. This ensures uniform, gradual pressing of the working area into the workpiece. The material in a plastic state is fed from the base of the spiral of the chipless tap and further, which leads to the formation of grooves of the required depth and frequency on the workpiece (i.e., internal threads).
We offer to buy the Centertap thread rolling tool, which has a wide range of applications. It can be used to form threads in workpieces made of various materials. The Centertap taps themselves are coated with TiN (titanium nitride), which provides them with increased wear resistance and surface hardness, hence durability.
CENTERDRILL (Germany) HOLE FORMING BY FRICTION
| Thread | Punch Ø (mm) | Punch | Chipless tap (roller) | |||||
| steel | Stainless steel | short | extended | short-edging | extended-butting | |||
| METRIC THREAD | ||||||||
| M02 | 1,75 | 1,75 | 63,60 | 68,40 | 105,60 | 108,00 | M02 TiN | 16,56 |
| M03 | 2,70 | 2,70 | 63,60 | 68,40 | 105,60 | 108,00 | M03 TiN | 16,56 |
| M04 | 3,70 | 3,70 | 67,20 | 72,00 | 105,60 | 108,00 | M04 TiN | 17,28 |
| M05 | 4,50 | 4,50 | 72,48 | 73,88 | 100,80 | 108,00 | M05 TiN | 17,52 |
| M06 | 5,40 | 5,40 | 81,60 | 82,78 | 110,40 | 114,00 | M06 TiN | 17,28 |
| M08 | 7,30 | 7,40 | 96,00 | 100,80 | 121,20 | 129,60 | M08 TiN | 21,84 |
| M10 | 9,20 | 9,30 | 122,88 | 127,92 | 148,80 | 160,80 | M10 TiN | 28,80 |
| M12 | 10,90 | 11,00 | 144,00 | 148,80 | 194,88 | 199,68 | M12 TiN | 46,32 |
| M14 | 13,00 | 13,10 | 195,60 | 198,00 | 234,60 | 239,40 | M14 TiN | 93,60 |
| M16 | 14,80 | 14,90 | 216,00 | 223,92 | 266,40 | 268,80 | M16 TiN | 93,60 |
| M18 | 16,70 | 16,80 | 252,00 | 264,00 | 307,20 | 319,20 | M18 TiN | 169,63 |
| M20 | 18,70 | 18,80 | 288,00 | 292,80 | 343,20 | 348,00 | M20 TiN | 197,52 |
| PIPE THREAD | ||||||||
| G 1/8″ | 9,20 | 9,30 | 122,88 | 127,92 | 178,80 | 183,60 | G1/8″ TiN | 80,40 |
| G 1/4″ | 12,40 | 12,50 | 175,92 | 180,72 | 222,00 | 226,80 | G1/4″ TiN | 96,00 |
| G 3/8″ | 15,90 | 16,00 | 235,92 | 240,72 | 291,84 | 296,64 | G3/8″ TiN | 108,00 |
| G 1/2″ | 19,90 | 20,00 | 319,20 | 324,00 | 370,80 | 378,00 | G1/2″ TiN | 148,80 |
| G 3/4″ | 25,40 | 25,50 | 439,20 | 448,80 | 516,00 | 525,60 | G3/4″ TiN | 168,00 |
| G 1″ | 32,00 | 32,10 | 561,60 | 597,60 | 656,64 | 692,64 | G1″ TiN | 393,36 |
TOOL ACCESSORIES
| Collet | Collet | Coolant for punch (250g) | Coolant for tap (0.5 l.) | ||
| Morse Cone 2 (MK2) | 381,60 | 25,20 | for steel (aluminum) | 30,00 | 19,85 |
| Morse Cone 3 (MK3) | 552,00 | 25,20 | for copper | 40,00 | |
Prices are indicated in Euros, payment at the rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, incl. VAT 20%
Thread rolling tool
The main goal of any equipment is to create high-quality products with the highest possible productivity. The use of semi- and automatic equipment models makes it possible to achieve such parameters that are economically feasible, because human participation is practically eliminated.
The main tools for forming threaded connections of future self-tapping screws to give a metal surface a special shape are a die and a roller. For metric, pipe, tapered, thrust, and trapezoidal threads, thread rolling equipment with flat dies is used. These thread rolling heads are excellent at creating screw and ring recesses on flexible workpieces of various grooves, fittings and screw threaded connections.
To create an internal thread, special rolling machines are used, where the thread is already present. They look like metal rods. Taps have a shank, a calibration and a tapping area. The resulting thread comes out similarly to roller processing, that is, due to plastic deformation of the part. Rolling machines are used to work with soft, viscous, ductile metals.
Description and features of the unit
The hydraulic thread rolling machine is in demand in the industrial sector. Its scope of application is the processing of rounded surfaces, for example hairpins. This creates different thread planes. If we go deeper, thread rolling machines are usually used for pipes. Processing (knurling) compares favorably with cutting, since the part has high-quality characteristics and processes the metal economically.
Hydraulic thread rolling systems of the JDY production series have working shafts with a mobile spindle head. They are used for thread rolling and profiles on solid blanks. The knurling pressure in devices of this series varies in the range of 4-40 tons. If the consumer needs a greater load on the product being processed, then upon request the manufacturer will review the maximum possible rolling parameters.
The supporting bed of the JDY thread rolling machine is designed using the finite component method. By combining a cast and welded form, the maximum possible rigidity is achieved, but the work area is free for the equipment operator.
The running spindle assembly of a metalworking machine moves along roller bearings. The installation is designed for rolling a threaded connection using a radial method, called the mortise version. The length of the working rollers is determined by exceeding the length of the created thread by a small distance. Such equipment is effective in several modes: with flat dies, operation without retracting the threading head on the stop, adjustment, semi- and automatic modes.
The technical characteristics of some models of JDY CNC machines are summarized in the table:
| Equipment series | JDY-50 | JDY-30A | JDY-3T |
| Outer thread diameter, mm | 6-80 | 8-40 | 2-12 |
| Threaded connection pitch, mm (per inch) | 1-6 | 0,5 – 2,5 | 0,4 – 1,5 |
| Knurling frequency, rpm | 10-38 | 250-500 | 40 |
| Permissible cross-section of rolling dies: internal external, mm | 180 54 | 80 25,4 | 90 50,4 |
| Number of self-tapping screws and similar materials produced, pcs/min | 4-30 | 4-30 | 24-40 |
| Spindle motor | 10 HP | 2HP | 1HP |
| Machine weight, kg | 2700 | 520 | 280 |
| Device parameters | 1800x1500x1300 | 1150x920x1360 | 800x600x750 |
Requirements for materials for rolling taps
It is recommended to use chip-free taps for processing workpieces made of fairly plastic materials that have:
- relatively low strength (its limit should be σв ≤ 1200 MPa);
- relative elongation at the level of δ ≥ 10%.
In addition, the following requirements are put forward when using a tool for rolling threads through plastic deformation:
- higher hole accuracy (compared to thread cutting technology);
- slightly larger hole diameter than for threading. It should be approximately equal to the average thread diameter. The larger diameter reduces the load on the rolling tool and increases durability.
Thread rolling by plastic deformation may require more powerful (100–150%) equipment than when using unblunted cutting tools. It is also necessary to ensure reliable lubrication of the taps, because it is the coolant that reduces the load that occurs during thread formation and prevents material sticking. For chipless taps, it is recommended to use graphite-containing oily cutting fluids.
Centertap tools are recommended to be used in conjunction with chucks that are designed for both deforming and cutting taps. It is the chuck that provides axial micro-compensation for tool displacements that occur when processing workpieces.
Specialists are ready to advise in more detail on all issues related to the specifics of choosing and using Centertap thread rolling tools and provide all the necessary technical documentation.
Models of thread rolling equipment, main parameters
Let's look at the popular equipment and their descriptions intended for thread rolling:
- "PEE-WEE." Among competitive equipment they stand out for their efficiency and reliability. The components and installation as a whole are made in Germany. The rolling pressure indicators are 5-60 tons. All series of technical equipment are equipped with automatic loading of workpieces that do not require human intervention and can work with long profiles. The equipment passport can be found on the World Wide Web.
- "PROFIROLL". The machines are made in Germany. They are noted for their simplicity in the control system. They are easy to maintain and have a long service life. The passport of any equipment model is presented on the website. A thread rolling machine is used to produce self-tapping screws. The productivity of the device is more than 100 units per minute. The quality of manufactured self-tapping screws is not lost at high production rates. The model is characterized by its simplicity in control and reliability in operation. This type of equipment is not very cheap, but it pays for itself quite quickly, since construction products are in demand. The technical data sheet can be found in electronic form.
- "ARM-40C". A unit for fittings used on construction sites all over the world. Its effectiveness is explained by its compact design parameters and versatility of use. It can be used both directly on construction sites and on the floor slab.
- "KOMAND SNSH 12". A thread rolling machine is used to create threaded rods using the thread rolling method. Productivity for hairpins is 3-120 sec/product and operates in automatic mode. Main advantages: CNC machine with the ability to program up to 40 variations of parts. The setting is carried out by the operator. An important positive side of the unit is adaptation to the technical requirements of the customer.