History of discovery
The incredible qualities of the alloy were discovered in 1903 by an engineer from Germany who worked in the city of Duren. The name “duralumin” comes from this name. Duralumins are alloys that are distinguished by high strength and low weight, as well as other sought-after qualities.
Interesting: In 1911, at the St. Petersburg exhibition, such an alloy was awarded a silver medal in the category of the best materials used in aircraft.
Duralumin brought great benefits during the Great Patriotic War. It was used to make components for weapons, armored vehicles and military aircraft.
Over time, the composition of the material was updated, and new types of alloy were born.
Chemical composition
The composition of duralumin mainly consists of two metals.
The main part of duralumin is aluminum. Its share can be up to 94% of the total weight. The second most important element that is usually available is copper. The mass of other components is small. Additionally, the duralumin formula may contain magnesium, manganese, iron, and other metals. Composition of the popular alloy grade D16T:
- aluminum - 93-94%;
- copper - 3.8-4.9%;
- alloying alloys - 1.5-2%.
Industrial production
For industrial production of the alloy, high-power electricity is used.
To obtain duralumin, a compound (charge) is made - these are particles of different metals; later they will be fused into a homogeneous material. After this, the component is heated to a level of +500 ° C, then sharply cooled with water or nitrate. When the temperature of the duralumin workpiece reaches room temperature, hardening is done.
Interesting: What is a coupling, what does it look like and where is it used?
Following this, the so-called “artificial aging” of the manufactured component is most often used. To do this, the material is additionally kept at high temperature for a long period: about 2 hours at +…+200° C. The process is carried out taking into account the brand of the mixture and the required properties. The aging procedure is carried out in order to obtain high strength duralumin. If this process is not applied, the metal will be soft and pliable.
Once formed, the component is sometimes coated with a protective substance that protects against corrosion.
First alloys
The discovery of copper, as well as alloys containing this metal, occurred after accidental (and then intentional) heating of sulfide ores to a temperature of more than 8000C.
This process has been available to humanity since 4000-3000. BC, then copper alloys were obtained. Since the extraction of copper from copper ores occurred with the inevitable inclusion of associated chemical elements - silicon, tin, iron - in the composition of the final product, then in fact we were talking about obtaining bronze. Bronze is historically the first copper alloy. It is reliably known that bronze was already known in ancient Iran and the Balkans. Thus was born the metallurgy of the Bronze Age of mankind.
Much later, brass was discovered. Brass (later called “fake gold” for its dull yellow luster) was first received by the Romans during the reign of Emperor Octavian Augustus (beginning of our era). To do this, copper was fused with ore containing a large percentage of zinc.
Subsequently, the metallurgy of copper alloys was constantly improved: the amount of foreign impurities decreased, the accuracy of the composition of alloys containing copper increased, and their nomenclature grew.
Brands of duralumin
Depending on the scope of use and the need to impart the required properties to the material, different components are added to duralumin.
To protect against rust, the metal is anodized - coated with special substances.
Duralumin grades are divided into:
- hardened in a natural environment, designated by the letter “T”;
- those who have undergone the artificial aging procedure are designated using the symbols “T1”;
- anodized, that is, treated with special varnishes - with the letter “A” in the name of the material.
Areas of application
The use of duralumin is quite diverse. Plates, rods, sheets and wire are made from it. These materials are used to make various parts.
Duralumin products are used in the following areas:
- Aviation technology. Light alloy is used in the manufacture of aircraft and the creation of bodies of other aircraft - airships or rockets. This component is used to make the casing, power elements, steering rod materials, etc.
- Construction sector. Pipes, angles, sheets, etc. are often used in this area.
- Automotive industry. Bodies, radiators, and other components are made from duralumin substance.
- Production of drills. Drills, circles, etc. are made from metal.
- Dural is often used in everyday life; it is used to make foil used in baking or when wrapping sweets.
Areas of use
Copper alloys play a key role in meeting modern social needs - in the production of renewable energy, healthcare, high-efficiency energy devices, and communications. Here are some examples:
In the manufacture of ventilation, heating and air conditioning systems, copper alloys help reduce the labor intensity of manufacturing and assembling air conditioners, reduce their weight, reduce their size, increase the efficiency of the devices, and reduce refrigerant consumption.
In construction and architecture, copper alloys improve the appearance and expressiveness of buildings, and increase their resistance to floods and flooding. The use of copper alloys meets the important requirements of modern building design, which require the use of recyclable and environmentally friendly materials, thereby effectively protecting the environment.
In the electric power industry, copper alloys are used, ranging from the production technology of high-voltage wires and microcircuits to powerful generators and computers. Their role in matters of optimal distribution and generation of energy, including from renewable sources, is increasing.
The efficiency of using copper-based alloys increases with the introduction of recycling processes for substandard devices that contain parts made from these materials in their design.
Properties and characteristics
Due to the beneficial qualities of duralumin, it is used in manufacturing, in the manufacture of parts, and insulation.
Interesting: DIY cold forging of metal
Characteristics are divided into the following types:
Physical and mechanical
The properties of duralumin are the lightness of the metal and resistance to high temperatures. In addition, the material has increased hardness. The density of duralumin is 2.8 g/m³, for steel this parameter is 8 g/m³. The melting point of duralumin alloy is +500 °C. A negative feature of the material is its susceptibility to corrosion as a result of exposure to high temperatures or heavy load.
Technological
A characteristic property of the metal is its ease of manufacture. The material can be made even at home: in the garage, etc. It does not need to be heated to extreme temperatures. Due to the simple production technology, the alloy is inexpensive to manufacture.
Alloys based on copper and aluminum
Alloys based on copper and aluminum
All alloys based on copper and aluminum, although they have sufficient physical and mechanical strength, do not have the necessary corrosion resistance. Therefore, in orthopedic dentistry they find very limited use (for the manufacture of temporary appliances in maxillofacial orthopedics). Recently, they have been successfully replaced in this section of orthopedic dentistry with stainless steel.
Copper-aluminum alloy (aluminum bronze) consists of 90%. copper and 10% aluminum, golden yellow in color, does not change it when in the oral cavity, despite the oxidation that occurs. Melting point 1030°, hardness 50, tensile strength 40 kg/mm2, elongation 30%, Aluminum bronze is used in the form of wire in orthodontics and maxillofacial orthopedics.
Copper-zinc-nickel alloy - nickel brass. An alloy of copper with zinc, and sometimes with the addition of small quantities of other elements, is called brass. Thus, nickel silver consists of 60-65% copper, 18-23% zinc and 12-22% nickel. The alloy has high strength and toughness, high anti-corrosion properties, and can be easily processed under pressure. In the oral cavity it becomes covered with a thin oxide film.
Duralumin contains, in addition to aluminum, copper 4%, magnesium, manganese, silicon and iron, approximately 0.5% each. The alloy is soft, ductile and easily deformed; at room temperature it strengthens over time. For annealing, they resort to heating at 350-370°.
Tin alloys
In the manufacture of various designs of dentures, it is necessary to obtain metal forms, dies and counter-dies. For this purpose, alloys based on tin and lead are used. These alloys, in addition to having a low melting point (hence the name low-melting alloys), have a relative hardness that ensures the stability of the alloy during operation. These alloys do not shrink very much when cooled.
To reduce shrinkage and slightly increase hardness, up to 50% bismuth is introduced into tin and lead alloys.
These alloys are a mechanical mixture type alloy. They are produced industrially in the form of blocks weighing about 50 g.
When working with alloys, it should be remembered that overheating not only leads to combustion of the metal, but also increases shrinkage and makes the alloy brittle. In addition, the lead and bismuth contained in the alloy easily combine with gold and platinum, causing them to become brittle and crack.
When metal overheats, it releases cadmium vapors, which are toxic to the body.
Types of alloys
Taking into account the manufacturing method and exposure to different temperatures, the parameters of duralumin may change. There are the following types of metal:
- Aluminum with copper, magnesium, addition of manganese. Another name is “duralumin”. It is not hardened during creation. The compounds are used for the production of automobile radiators, hermetically sealed tanks, and pipes for the manufacture of gasoline pipelines. They are used to produce building materials. Alloys are easy to weld and do not rust easily. They are difficult to cut. However, additional coating must be used to protect against rust.
- Aluminum, magnesium or manganese. Another name is “mangaliya”. The material is complex in design. The main element is aluminum, other components are presented to give the alloy useful properties. Used for assembling space objects, aircraft, and high-speed trains. Slightly susceptible to corrosion, easy to weld. However, it does not tolerate exposure to a humid environment.
- Aluminum, magnesium and silicon. Another name for it is “avial”. It is well protected from corrosion and weighs little. It is used in high humidity and when electric current is passing through. During manufacturing, the alloy is hardened at a temperature of 525°C. Then it is sharply cooled with water to 20°C. The procedure lasts 10 days.
Interesting: Table of inch threads: designation in mm
Zinc and its alloys
Zinc is a non-ferrous metal of a gray-bluish hue. In D.I. Mendeleev’s system it is designated by the symbol Zn. It has high viscosity, ductility and corrosion resistance. Important properties of the metal:
- Low melting point - 419 ° C.
- High density - 7.1 g/cm3.
- Low strength - 150 MPa.
In its pure form, zinc is used to galvanize steel to protect against corrosion. Used in printing, printing and electroplating. It is often added to alloys, mainly copper.
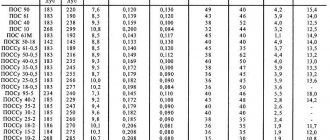
There are the following grades of zinc: TsV00, TsV0, TsV, Ts0A, Ts0, Ts1, Ts2 and Ts3. TsV00 is the purest grade with a zinc content of 99.997%. The lowest percentage of pure substance in the Ts3 brand is 97.5%.
Wrought zinc alloys
Wrought zinc alloys are used to produce parts using drawing, pressing and rolling methods. They are processed hot at temperatures from 200 to 300? C. The alloying elements are copper (up to 5%), aluminum (up to 15%) and magnesium (up to 0.05%).
Wrought zinc alloys are characterized by high mechanical properties, due to which they are often used as substitutes for brass. They have high strength with good ductility. Zinc, aluminum and copper alloys are the most common as they have the highest mechanical properties.
Cast zinc alloys
In cast zinc alloys, alloying elements also include copper, aluminum and magnesium. Alloys are divided into 4 groups:
- For injection molding.
- Anti-friction.
- For centrifugal casting.
- For chill casting.
The ingots are easily polished and accept electroplating. Cast zinc alloys have high fluidity in the liquid state and form dense castings when solidified.
Casting alloys are widely used in the automotive industry: they are used to make housings for pumps, carburetors, speedometers, and radiator grilles. Alloys are also used for the production of certain types of household appliances, fittings, and instrument parts.
In Russia, non-ferrous metallurgy is one of the most competitive industries. Many domestic companies are world leaders in the nickel, titanium, and aluminum sub-sectors. These achievements were made possible thanks to large investments in non-ferrous metallurgy and the use of innovative technologies.
The difference between duralumin and aluminum
Dural and aluminum differ in chemical composition, which affects the specific application. In addition, duralumin has a specific gray color, and the source material has a light shade. However, the main difference between duralumin and aluminum is that it has no ductility, it is hard and fragile. The connection cannot be bent or made a dent. The chips made from it are brittle and brittle. Metal is easily scratched; if you look at the damage, it becomes clear that the material consists of small crystals.
There is an easy way to understand what material is in front of you. Drip sodium hydroxide onto the metal. If the stain darkens after 10 minutes, it is duralumin.