Which GOSTs regulate
High-alloy steel 12x18n9t is produced in accordance with GOST 5632-72, which contains all the necessary information about the percentage of different compounds and manufacturing technology.
The chemical composition of steel includes the following elements:
- carbon – 0.12%;
- silicon – 0.8%;
- manganese – 2%;
- sulfur – 0.02%;
- phosphorus – 0.035%;
- chromium – 19%;
- nickel – 9.5%;
- titanium – 0.8%.
Depending on the manufacturer, the composition of the alloy may vary slightly, but these changes should not exceed the specified content of certain elements in the composition.
Since metal blanks are produced in different forms, depending on the category, one of the following GOSTs is used:
- long products - GOST 5949-75;
- forgings – GOST 25054-81;
- thick sheet - GOST 7350-77;
- wire – GOST 18143-72;
- rods - GOST 189087-73.
The main area of use of 12x18n9t steel according to GOST is the production of various parts, therefore, the most convenient type of workpiece is selected for each production task. For example, in the manufacture of pipes, a metal sheet is used, and depending on the category of the pipe itself, the raw material has different thicknesses and surface types.
Designations
| Name | Meaning |
| Designation GOST Cyrillic | 12Х18Н9 |
| Designation GOST Latin | 12X18H9 |
| Translit | 12H18N9 |
| By chemical elements | 12Cr18H9 |
| Name | Meaning |
| Designation GOST Cyrillic | Х18Н9 |
| Designation GOST Latin | X18H9 |
| Translit | H18N9 |
| By chemical elements | Cr18H9 |
Characteristics and properties
Corrosion-resistant steel is used for the manufacture of parts that are used in complex and aggressive environments, so the metal has the following characteristics:
- Mechanical strength. Steel grade 12x18n9t is used to produce elements of machinery that remain operational under prolonged shock and vibration loads.
- Heat resistance. Metal products can operate in temperatures from – 196 degrees to +600 degrees Celsius.
- Corrosion resistance. The alloy retains its crystalline structure while being exposed to high temperatures and aggressive acidic environments.
Steel does not oxidize when directly exposed to atmospheric factors and when there is a sudden change in temperature.
The main advantage of this alloy is its excellent manufacturability. Metal products can be produced by hot plastic deformation. Deep-drawn steel 12x18n9t retains high ductility during cold deformation, which makes it possible to manufacture parts with complex configurations. Manufacturability parameters are also expressed in the ability to accept welding well by any means. To connect metal elements, manual and automatic welding is used, the seam is smooth and airtight.
Description of mechanical symbols
| Name | Description |
| Section | Section |
| sT|s0.2 | Yield strength or proportional limit with tolerance for permanent deformation - 0.2% |
| σB | Short-term strength limit |
| d5 | Elongation after break |
| d4 | Elongation after break |
| d10 | Elongation after break |
| y | Relative narrowing |
Scope of application of stainless steel 12x18n9t
Steel 12x18n9t according to GOST 5632-72 is used in the manufacturing industry and construction. This alloy is used to produce the following products:
- welded structures of any type;
- metal products that come into contact with nitric acid;
- parts of equipment operating under increased exposure to atmospheric factors;
- cryogenic technology;
- capacitive and heat exchange equipment.
The main advantage of this alloy is that the workpieces are easy to process. To preserve the characteristic characteristics of the metal, there is no need to resort to special metalworking technologies. Steel retains high strength, corrosion resistance and ductility both during mechanical and thermal processing.
The main area of application is related to mechanical engineering, which specializes in the creation of heavy equipment. Units that are operated in extreme conditions, exposed to heat and in contact with acid-containing environments necessarily consist of metal parts of this category.
Description
Steel 12Х18Н9 is used : for the manufacture of chemical equipment; various parts and structures made of sheet and tape, welded by spot welding, pipes and parts made from them; aircraft manufacturing parts; products subjected to heat treatment (hardening); wire woven mesh with square cells of micron sizes, used for control and separation of materials by particle size, filtration of liquids, gases and other purposes.
Note
The steel is corrosion-resistant and heat-resistant. Unstabilized chromium-nickel steel of austenitic class. Recommended maximum long-term operating temperature is +800 °C. The temperature of intensive scaling in air is +850 °C. The steel is unstable in sulfur-containing environments and is used when nickel-free steels cannot be used.
Stainless steel products 12x18n9t
Corrosion-resistant steel is prepared in arc furnaces, and to strengthen the crystalline structure, the workpiece goes through a stage of hardening and gradual cooling.
The company complies with all established standards and requirements, closely monitors product quality and can produce any type of assortment.
The company’s catalog presents all types of assortment of alloys of this brand:
- metal sheets of different thicknesses and overall dimensions;
- pipes of different diameters with machined and rough surfaces:
- steel flanges;
- wire;
- rods, circles and hexagons.
To select and purchase products made of stainless steel 12x18n9t, go to the catalog.
Chemical composition
| Standard | C | S | P | Mn | Cr | Si | Ni | Fe | Cu | V | Ti | Mo | W |
| TU 108-930-80 | ≤0.12 | ≤0.02 | ≤0.035 | ≤2 | 17-19 | ≤0.8 | 8-10 | Remainder | ≤0.5 | ≤0.2 | ≤1 | ≤0.5 | ≤0.2 |
| GOST 5632-72 | ≤0.12 | ≤0.02 | ≤0.035 | ≤2 | 17-19 | ≤0.8 | 8-10 | Remainder | ≤0.4 | ≤0.2 | ≤0.5 | ≤0.5 | ≤0.2 |
Fe is the basis. For aircraft parts, Mo% content ≤ 0.30%.
Steel grade X12M
| Chemical composition in % of steel X12M | ||
| C | 1,45 — 1,65 | |
| Si | 0,15 — 0,35 | |
| Mn | 0,15 — 0,4 | |
| S | up to 0.03 | |
| P | up to 0.03 | |
| Cr | 11 — 12,5 | |
| Mo | 0,4 — 0,6 | |
| V | 0,15 — 0,3 | |
| Fe | ~85 | |
| Properties and useful information: |
| Material hardness: HB 10 -1 = 255 MPa | |
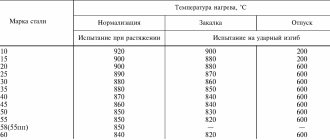
| Critical point temperature: Ac1 = 830, Ac3(Acm) = 855, Ar1 = 750, Mn = 230 |
| Physical properties of X12M steel | ||||||
| T (Grad) | E 10— 5 (MPa) | a 10 6 (1/Deg) | l (W/(m deg)) | r (kg/m3) | C (J/(kg deg)) | R 10 9 (Ohm m) |
| 20 | 7700 | 580 | ||||
| 100 | 10.9 | |||||
Explanation of steel grade X12M: the letter X indicates that this is an alloy tool steel with a chromium content of about 12% and a small manganese content.
Application of X12M steel and heat treatment of products: for the manufacture of cold stamping dies the following grades of steel are used: carbon and alloyed X12, X12M, X, KhG, KhVG, 9ХС, Х09, 5ХВГ, 5ХВ2С, 6ХВ2С.
Dies for cold stamping must be of high hardness and sufficient viscosity.
Annealing of forgings is carried out according to the same conditions as annealing of forgings for hot stamping dies.
When hardening dies, cracks most often form along the auxiliary holes. Commonly used measures in the form of filling holes with clay and asbestos do not completely protect against the formation of cracks. Much more effective is intermittent cooling, carried out as follows: a stamp, heated for hardening 20-30° above normal temperature, is lowered into water with one side until the auxiliary holes darken, and then the other side, after which the stamp is completely cooled in water to a temperature of 150- 180° and transfer to oil. The auxiliary holes are cooled intermittently. With this method, “dangerous” places are not subjected to hardening, which eliminates the appearance of cracks.
When hardening upsetting and other dies, where the working part is a hole, cooling is carried out under running water in a special device that allows only the working part to be cooled. Once the entire die has darkened, it is immediately transferred to a preheated tempering oven.
Some authors, in order to obtain deeper hardenability, recommend raising the heating temperature for hardening of dies made of steels for cold stamping to 900°. This high temperature will cause overheating, especially for coarse natural grain steels, and reduce toughness. The limit to which dies made of U10 steel can be heated without fear of overheating is a temperature of 820-830°.
Dies of large sizes, as well as complex shapes and working in difficult conditions, are made of alloy steel. The best alloy steel for cold dies is X12M steel. To reduce deformation during hardening, dies made of this steel are annealed in molten salt or in a stream of dry air. The hardness of the dies should be within the range Rc = 56-60.
The use of HVG steel for the manufacture of dies should be limited due to its low viscosity. In the case of using HVG steel, the hardness of the dies should be within the range Rc = 53-55.
Punches for punching holes must have a high hardness Rc = 54-58 only on the cutting part. The rest should be more viscous to prevent breakage during operation. Therefore, heat treatment of punches should be done as follows:
1. Carbon steel punches with a diameter of up to 15 mm:
a) heat the entire punch to the quenching temperature; b) soak the cutting part in water to 150-200°; c) transfer the punch to the oil and cool it completely; d) loosen the fastening part in a salt or lead bath.
2. Carbon steel punches with a diameter of more than 15 mm and alloy steel punches:
a) heat and completely harden the entire punch; b) to release the transition part, place the punch in a heated environment and keep it in it until a dark yellow tarnish appears on the cleaned end of the punch; the heating medium can be a salt or lead bath, a tempering plate with sand, a spectacle furnace, etc.; c) release the fastening part.
The temperature of the tempering furnace must be set based on the grade of steel and the required hardness, for example, with the required hardness of the transition part of the punch Rc = 48-55, the temperature of the tempering bath for steel U10 will be 300-370°, for steel X12M 500-600°.
In addition, broaches are made from steel; consider the technological process of heat treatment of broaches made from X12M steel:
1) annealing after machining in cast iron shavings or coal to relieve internal stresses;
2) checking for runout and straightening (if necessary);
3) heating with intermediate heating to a temperature of 980-1020°;
4) cooling in oil to a temperature of 150-200°;
5) straightening under a press in a hot state and cooling in air;
6) tempering in an oil bath at a temperature of 160-190° for 1-1.5 hours;
7) incomplete hardening of the shank;
tempering in an oil bath at a temperature of 160-190° after grinding to relieve internal stress.
Published:
2010.11.08
| Brand: X12M | |
| Class: Die tool steel | |
| Use in industry: for the manufacture of rolling rollers, drawing boards and dies, eyes for metal calibration; dies and punches of cutting dies; punches and cold extrusion dies operated with operating pressures up to 1400-1600 mPa |
The closest equivalents (analogues) of steel 10Х17Н13М2Т
| USA (ASTM/AISI) | 316H, 316Ti, 316, S31635 |
| Germany (DIN, WNr) | 1.4571, 1.4583, X10CrNiMoNb18-12, X10CrNiMoTi17-10, X10CrNiMoTi18-10, X6CrNiMo17-12-2 |
| Japan (JIS) | SUS316Ti |
| France (AFNOR) | Z6CNDT17-12B, Z6CNDT17-12, Z6CNDT17-13, Z6NDT17-12 |
| England (BS) | 320S17, 320S18, 320S31, 321S12 |
| Euronorms (EN) | 1.4571, X6CrNiMo17-12-2 |
| Italy (UNI) | X6CrNiMoTi17-12-2 |
| Spain (UNE) | F.3535, X6Cr18NiMoTi17-12-2 |
| China (GB) | 0Cr18Ni12Mo2Ti |
| Sweden (SS) | 2350, 2353 |
| Poland (PN) | H17N13M2T, H18N10MT |
| Czech Republic (CSN) | 17348 |
| Austria (ONORM) | X2CrNiMo18-14-3KW |