Welding thin metal with an inverter can be a real problem not only for an inexperienced welder, but also for some craftsmen with decent experience in this field. When performing a welding operation, you have to adhere to different rules than when welding thick-walled structures, which complicates the selection of the mode and type of electrodes. But if you do not take into account the specifics of welding thin sheet metal when working, you will not be able to obtain high-quality seams.
Problems of thin-walled products
The technology of welding thin metal with coated electrodes requires attention to detail and precision in work from the performer .
Beginners should not start joining thin-sheet products without sufficient experience in welding elements of medium thickness. Training centers produce specialized literature that can facilitate this task. Difficulties in work are caused by the following reasons:
- Danger of burns . This is the most common mistake made by novice welders who cannot select the optimal operating parameters and speed of the electrode.
- Poor welding of the seam . Another problem for inexperienced specialists, the reason for which follows from the first. Trying to avoid burns, the operator chooses the electric arc speed too high. This leads to the fact that the melt zone does not have time to warm up properly. As a result, the connection does not have the necessary strength and tightness.
- Swells . They appear on the reverse side of the connection. It is noteworthy that on the outside of the seam there may be no visual defects, while on the opposite part of the product numerous protrusions may form, which are caused by subsidence of the molten metal under the influence of gravity.
- Surface deformation. The metal has high thermal conductivity. The thin-sheet surface heats up very quickly, and overheating is fraught with a change in the structure at the molecular level: around the contact zone, the metal expands under the influence of temperature, while in other areas the surface is cold. As a result, the surface of the workpiece is deformed.
When doing work at home, it is possible to straighten the surface with hammers with a rubber striking part. Otherwise, welding is not performed in a continuous strip, but alternating in a certain sequence of places where the seam is applied.
Selection of modes and electrodes
When welding thin-walled structures, we recommend using inverter-type devices . Compared to transformer-type units, inverters create a more stable arc, and the range of adjustment of the welding current is much higher. Additional functions, such as “anti-stick electrode”, can make work easier.
Operating parameters are set based on the thickness of the product, and the relationship is direct - the thinner the workpiece, the lower the welding current should be.
Technical reference books indicate that a thin-walled product is considered to be one whose wall thickness does not exceed 5 mm. Practice shows that certain problems begin when working with metal less than 3 mm thick.
As an example, we give the recommended cross-section of the electrode and the strength of the welding current, depending on the thickness of the workpiece:
As you can see, the ampere characteristics cannot be specified accurately, due to the differences in the characteristics of different types of metal. The optimal parameters are selected experimentally.
The function of adjusting the arc ignition mode will help to avoid burnouts in the starting area . This will allow you to start working directly in the docking area. Otherwise, we recommend igniting on a thick section and then transferring the arc to the work area.
It should be remembered that thin electrodes melt much faster than regular ones. When welding sections of equal length, the consumption of thin rods will be higher. The requirements for materials for the manufacture of electrodes do not differ from the standard requirements when performing welding work - the base of the electrode must correspond to the base surface of the product.
Some units have the function of performing work in pulse mode, which copes well with thin metal - the intermittent arc prevents the surface from overheating.
Practical advice
Before the process, experienced welders recommend familiarizing yourself with useful tips:
- Initially, you should train on excess residues and defective products.
- With the inverter method, a small power is selected, because it is forbidden to break the work between the electrode and the iron sheet.
- For any operation, it is necessary to wear protective clothing and additional accessories, for example, heat-resistant gloves, a flame retardant jacket, a durable helmet, and goggles.
- A special lining reduces the likelihood of burning holes, making it easier to weld thin metal.
- A smaller arc prevents overheating of the treated area.
High-quality welding of thin sheet metal is carried out using specialized equipment. The main thing is to prepare the products, remove excess temperature, and set the current.
The right technology
To understand how to properly weld thin iron with inverters, you need to carefully study the technological chain. Its stages do not differ from the welding scheme for standard products:
- Preliminary surface preparation.
- Duty cycle.
- Finishing the seam.
Let's look at each stage in more detail.
Preparation
At this stage, it is necessary to clean the connection area from traces of old paint and pockets of corrosion. After this, the surface is degreased using any available solvent. Particular attention must be paid to the installation location of the welding unit mass. Poor processing of the attachment point may disrupt contact.
Welding
The procedure for performing electric welding work is as follows:
- Prepare the electrodes based on the thickness of the workpiece. The tip should be cleared of the flux coating to a length of 5-6 mm to facilitate ignition of the arc.
- We recommend making point clamps along the line of the future seam at intervals of 100-120 mm. This will avoid displacement of structural elements during the work process.
- The arc ignition process is carried out in two ways. In the first case, you need to run the rod along the surface. The movement should resemble lighting a match. An alternative is to tap the electrode on the surface. This method is used when working in hard-to-reach areas. The length of the welding arc should not exceed the cross-sectional diameter of the electrode. In this case, it will have sufficient density and stability.
- The speed of movement of the electrode is selected individually, based on the current operating conditions. The melt zone should have a slightly elongated shape - this indicates that the metal is heated to the required depth.
- Make sure the arc moves smoothly and avoid sudden movements. Despite the fact that modern models of welding machines are equipped with auxiliary functions, arc fluctuations can lead to weld defects.
Additional features that simplify the connection process are:
- Arc Force . As the discharge lengthens, the operating parameters automatically increase, stabilizing the arc.
- Anti-stick electrode . When the electrode comes into contact with the surface, the automation releases the voltage, preventing the rod from sticking.
During the work process, it is important to ensure visual control of the weld pool. In this case, the angle of inclination of the electrode should be in the range of 60-90º. As the angle of inclination decreases, the seam will have external bulges, indicating that the metal has not warmed up only on the surface.
Experts recommend using a zigzag direction of movement of the filler material to obtain the best results.
After crystallization of the compound, it is cleaned of slag and an initial inspection is carried out for defects.
How to choose the right inverter
When choosing a device, you need to follow the rules:
- the inverter must produce a stable welding current and not be afraid of power surges, which often happen outside the city;
- It is not recommended to use old devices (“variables”): they consume more energy and are more difficult to work with. Modern welding equipment produces direct current at the output;
- adjustment should be made smoothly ; precise selection of parameters will facilitate the process.
Approximate cost of inverters for welding on Yandex.market
Inverters often have the “Arc Force” option. When you turn on the appropriate toggle switch, welding is facilitated by automatically increasing and decreasing the current value, which is important when working at its minimum values. As a result, the electrode will “stick” less.
“Hot start” makes it easier to ignite the arc: the current increases briefly at the moment the electrode touches the workpiece. After this, the parameter automatically returns to its original value.
Techniques
To obtain a high-quality permanent connection, the following techniques are used:
- Overlapping. If there is a reserve length of the products to be connected, this method will allow you to reliably connect them, due to the larger contact area. In this case, it is necessary to carefully monitor the heating of the surface to avoid burns.
- Dots. The method avoids overheating of the surface. Used when joining particularly thin sheets. The recommended point step is three sizes of the electrode cross-section.
- With additional electrode. In this case, it is necessary to clean the anode from the flux coating and lay it along the welding line. Places of installation are thoroughly boiled. The technology is suitable for sealing single holes.
- Reverse polarity. The application of the method involves connecting the holder to the plus, and the mass to the minus. In this case, the surface heats up faster than the electrode, which reduces the risk of burn-through.
- When welding metals of different thicknesses, the following method is used: the arc is ignited on a thicker element, and then it is transferred to a thinner part.
Butt welding of sheet metal is carried out in two ways:
- with flanged edges;
- lined.
In addition, it is recommended to place a copper plate to remove heat from the steel, due to its greater thermal conductivity. This allows you to avoid burn-through of products.
Overlap welding
If you need to connect two thin sheets, it is recommended (if possible) to overlap one another. This connection will avoid burns and achieve a beautiful seam.
The process looks like this:
- Cleaning parts.
- Installation with minimal gaps - it is recommended to use clamps or special clamps.
- Ignition of an arc on one of the sheets.
- The electrode should be guided along the edges with minimal transverse vibrations.
- The electrode holding angle is 45 degrees or less.
During the process, longitudinal vibrations can be made, this will reduce the risk of burns. If welding is carried out in a vertical position, then the “tear-off” method of the electrode is recommended.
Basic connection methods
The technique for performing the work depends on the welding equipment and consumables used . Let us consider the features of the connection depending on the technology, with the exception of welding with consumable electrodes, which was discussed above.
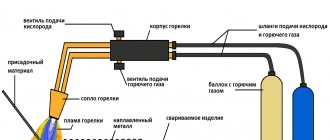
Non-consumable graphite electrodes
This method has become especially widespread when working with thin-walled products by professional welders. There are two ways to achieve the goal:
- Use of filler wire;
- Melting method followed by joining.
The second method is used more often, since reflow eliminates the use of additional filler materials, which affects the cost of work. The essence of the method is to heat treat the edges being joined until the aggregate state of the surface changes. This creates conditions for joining the material. With certain skills, you can create a tight connection without burning out individual sections.
Wire is used as a filler for various cavities and voids. The size of the cross-section of the manufacturing material must correspond to the characteristics of the workpiece.
Very thin metal
This problem is most often encountered by service station workers when repairing car body parts. Modern transport manufacturers use sheets whose thickness does not exceed 0.8 mm. Thus, the use of inverter welding machines is not possible, except in emergency cases.
The main way to solve the problem is to use overlays made of thicker material, which plays the role of a frame for the future connection..
Features of working with galvanized steel
When working with galvanization, we recommend removing the protective coating manually or mechanically . Otherwise, the zinc will burn out during the joining process, which can lead to worker poisoning from its fumes.
In industrial enterprises, a directed flame is used to prepare the product, burning out the zinc layer.
Due to the insignificant thickness, experts recommend using the point connection method.
Alternative Methods
A reliable alternative to an inverter is the use of semi-automatic devices for connecting thin metal elements . The use of wire allows you to increase productivity due to the absence of pauses for replacing electrodes. The range of consumables allows you to choose the ideal option for a particular case.
The disadvantage of a semi-automatic machine is the increased requirements for the qualifications of the worker - a novice welder is not able to master all the skills of working with this equipment in a short period of time.