07/22/2019 Author: VT-METALL
Issues discussed in the material:
- What are the main advantages and disadvantages of arc welding
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of different arc welding techniques?
- How to minimize the disadvantages of arc welding
One of the widely used methods for joining metal surfaces is arc welding. The essence of this technology is that the thermal energy required to melt the joined edges of metal surfaces using an electrode is obtained through the action of direct or high-frequency current. Let us dwell in more detail on the advantages and disadvantages of arc welding.
What is arc welding?
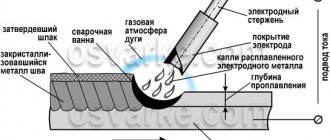
An electric arc (other names: “arc discharge”, “voltaic arc”) is a stable discharge of electricity in gas (air). The voltage between the electrode and the workpiece is 15-20 V, the current density in the channel is 100-1000 A/mm2, the temperature is 6000-25000 K.
The large amount of heat released in the arc combustion zone and the high temperature exceeding the melting point of all known metals have led to the widespread use of arc welding.
The properties of a gas discharge depend on the parameters of the electrical circuit, the electrode material, the parts being connected, and the protective environment. To classify types of arc welding, several characteristics are used.
pros
The main argument, which is understandable even to a person who has absolutely no knowledge of welding, is that people still have not come up with something that has definitely pushed arc welding (MMA) out of the market. But the technology really came into being back in the century before last! Therefore, this is a really good thing, and its main advantages are:
- High practicality. Thanks to replaceable electrodes, any type of steel can be welded using arc welding (MMA), which is very profitable and convenient. For example, Telwin welding machines work with steel, cellulose, aluminum, cast iron, alkali, rutile and stainless steel electrodes. They can also work with both alternating and direct current, which makes them almost universal in welding.
- High efficiency. Such equipment is probably the cheapest to operate - it does not consume too much electricity or a significant number of consumables.
- No gas cylinders. Compared to semi-automatic welding machines, this is very convenient, because there is no need to buy and transport expensive and heavy cylinders, which, among other things, are also explosive.
- Welding in all positions. When using arc welding (MMA), there is no such problem when it is necessary to turn the parts being welded over and secure them at a special angle required by the device - this design works in any position, which means it is applicable in all situations.
- Compactness and low weight - in the case of welding inverters. You can hang the welding inverter on your shoulder and climb with it into places where it is impossible to climb with a large machine, even into remote corners of a construction site. For example, MMA BISON welding inverters weigh from 5 kg and are equipped with a comfortable handle and carrying strap.
- Availability of development. Thanks to the numerous features that manufacturers come up with, even beginners who are not experienced in this matter can easily start working with arc welding. For example, one of the problems that a novice welder encounters is igniting the arc. To solve this problem, Blue Weld welding machines have a quick start function - Hot Start. To solve the problem of arc sticking, Fubag welding machines are equipped with an anti-stick function - Antistick - when when the electrode comes into contact with metal, smart electronics stops the supply of welding current and makes sticking impossible. And to avoid even the possibility of sticking, Resanta arc welding machines are equipped with an arc force function - Arc Force, when the inverter increases the welding current for a very short period of time, which sharply reduces the likelihood of electrode sticking. In fact, many manufacturers equip their devices with similar functions; you just need to carefully study the characteristics of the device or consult the seller.
It looks great, and yet this technique is criticized for something. For what?
Types of Arc Welding
According to the method of action of the arc on the part, they are distinguished:
- Dependent welding - current passes through the product;
- Independent welding - no current passes through the workpiece, heating is carried out by the arc between the electrodes; It is possible to use both types of discharge at the same time.
According to the nature of the influence of the electrode, arc welding can be:
- Using consumable electrodes; the electrode material not only conducts current, but melts, mixes with the metal of the workpiece, and forms a weld;
- Using non-consumable electrodes; electrode material - refractory metal (tungsten), coal; the non-consumable electrode only maintains the arc.
During the welding process, atmospheric oxygen actively interacts with the heated metal. According to the method of protecting the welding zone, there are:
- Open arc - no protection;
- Closed - use flux (vitreous, powdery);
- Protected - the contact zone is surrounded by slag, flux, and inert gas.
Other characteristics are used in the classification: type of mechanization - manual, semi-automatic, automated welding; type of current - DC welding, AC welding, pulse welding.
In each type of welding, subtypes are distinguished depending on the materials used and the features of the technological process.
The main pros and cons of gas-shielded welding
The specific environment has a significant impact on the final result of the work. Thus, the properties of the arc and the characteristics of the seam will differ markedly from those of electric welding. The type of gas used plays a big role.
For example, argon allows you to create a figured seam due to the softness of the arc. And helium is used when it is necessary for the welding site to be practically invisible, as well as when processing thin sheets of metal. However, helium is used less efficiently due to its low weight.
When it is necessary to maintain a balance between efficiency and invisibility of the seam, carbon dioxide is used. By the way, it is almost universal. With its help you can weld products from almost any alloy.
It is worth noting that the type of gas has no effect on the choice of electrode. It may or may not be melting. However, due to the high degree of danger of gases, extra care must be taken during the welding process.
So, the general advantages of this technology:
- high quality seams;
- versatility in terms of processed materials and their thickness;
- independence of the result from spatial position;
- visual inspection of the seam during its formation;
- there is no need to fill up and remove flux and slag;
- efficiency;
- possibility of automation;
- cheapness.
There are also disadvantages of gas shielded welding. Thus, these include the presence of light and thermal radiation from the arc. The operator must be reliably protected from these negative factors, which requires additional financial costs. But the repair of such welding machines is generally no different from others.
is now an authorized LEEK Service Center. We repair voltage stabilizers of any model under warranty and for a fee.
Our service center will soon open in St. Petersburg!
Dear Clients! So we have passed the 40,000 order mark. For more than 6.5 years of daily work, we have repaired a total of about 40,000 units of welding equipment of various types and manufacturers. We are grateful to you for choosing ours. Every day we work fruitfully to provide you with services as efficiently and quickly as possible. We also make mistakes, but we always try to accommodate the client.
Source: welding-zone.ru
Advantages of manual arc welding
The popularity of joining metal workpieces using electric welding is due to a number of factors. Among them:
- Simplicity of technology, accessibility in everyday conditions, minimal initial skills, concepts;
- Availability of simple, cheap machines for manual welding; they are lightweight, compact, reliable; provide current regulation, short circuit protection, ease of operation; comply with safety requirements;
- In most cases, there is no need to additionally surround the arc zone with inert gas or flux; this function is performed by coating the electrodes;
- Ability to work in domestic and field conditions: in the basement, workshop, outdoors, under the sun, in the wind;
- A wide range of welded metals: cast iron, steel (carbon, alloy), copper, aluminum alloys;
- The maximum thickness of workpieces is up to 30 mm.
Effect of welding mode on seam
As for the dimensions of the resulting weld, they do not depend on features such as type:
- angular.
- butt.
- other.
The main characteristic of the seam itself is its shape coefficient during penetration. We are talking about the ratio of seam width to depth. In manual models, it is possible to change this indicator in a wide range. If you reduce the width of the weld, this coefficient will change significantly. In turn, an increase in penetration depth reduces the width, or vice versa.
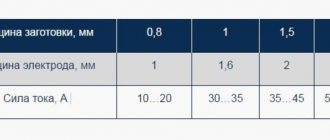
An important welding parameter is the current strength, since increasing it increases the penetration depth, and decreasing it decreases it. You must understand that dense metal blanks give greater performance at a particular current level, but the width of the weld itself remains the same. Also, a special influence is attributed to the type of current. The use of constant electric current technologies narrows the seam. This is especially noticeable when operating at high voltages (from 30 V). It is mentioned that manual welding machines require electrodes with different diameters.
The fewer such elements are used, the lower the mobility of the burning arc, which increases the depth of penetration, but reduces the width of the seam. For this reason, any reduction in the diameter of the electrode leads to an expansion of the depth of the weld.
Another important parameter is arc voltage. And although it does not affect the depth of penetration, the width of the weld seam changes significantly .
As the voltage increases, the total width of the weld seam increases. If the indicator decreases, the width decreases. This approach has found its application in automated solutions where it is necessary to change the width of the weld during the surfacing process. True, during manual welding, the voltage level does not change too much and varies in the range of 18-22 V. In this case, the width of the weld seam practically does not change. To study the basic subtleties and principles of technology, you need to make a lot of effort.
Disadvantages of manual arc welding
Among the negative properties are the following:
- Constant stops during work due to the need to change the electrode; the appearance and quality of the seam deteriorate;
- Slag forms on the surface of the weld; the hardened crust must be removed, and sometimes the seam must be treated with an abrasive tool;
- There is an overuse of electrodes, since replacement is carried out with a remaining length of 5 cm;
- Low productivity, low efficiency;
- The quality of a manual weld is lower than the quality of an automatically produced weld; it greatly depends on the experience and qualifications of the welder;
- The use of a carbon electrode does not allow joining metals with a low melting point (tin, zinc, alloys based on them);
- Manual welding is not intended for joining metals containing active chemical additives (titanium, tantalum);
- The current passes along the entire length of the electrode; at high intensity (cutting with a thin electrode), it becomes hot, the coating cracks and collapses.
Electric welding arc
After carefully studying the pros and cons of manual welding equipment, you can move on to inspecting electrical equipment. Before striking the arc, the welder touches the tip of the electrode to the metal workpiece, retracting its tip by 3 millimeters. Thus, the arc begins to flash, the equidistant length of which is maintained by gradually lowering the electrode itself to the extent of its melting. It is important to have time to cover your face with a shield before forming an arc . Another method of starting an arc is to move the tip of the electrode along the surface of the workpiece, after which it is necessary to move it a short distance.
The arc is maintained as short as possible. It is known that short arcs reduce the number of small drops; moreover, in this case, the electrode melts at a free pace, providing an even beam of sparks. In this case, the penetration depth becomes as large as possible.
If a manual machine is not able to produce a specific depth, then the electrode begins to melt and oxidize, which leads to its extension. Because of this, the seam is uneven and contains a large amount of oxides.
You must understand that the length of the arc is controlled by the sound that occurs when burning. An electric arc of a certain length produces a uniform sound at one tone. If this detail is too long, the tone becomes especially harsh, and sometimes it is accompanied by loud pops. If for some reason the arc breaks, it must be re-excited by carefully welding the hole at the break point. You can then continue welding the seam.
If it is necessary to weld the most important places that will be subject to a certain “fatigue” and variable loads, the arc is lit exclusively outside the zone of the seam itself. If you do not follow this recommendation, the formation of a “burn” on the surface cannot be ruled out, which will lead to further destruction of this area.
The skill level and experience of the welder play a significant role in how skillfully the ignition and subsequent control of the arc length occurs.
After all, the more successfully the length is maintained, the higher the quality of the seams, and, accordingly, the strength of the connection itself. It is important to learn how to correctly manipulate the electrode, moving it along the line of the suture being applied to give it a certain shape.
How to choose a welding machine
The choice of welding equipment is completely determined by the purposes and conditions of use. For household needs, the manufacture of simple structures, and the repair of agricultural machinery, an inexpensive device of medium power is quite sufficient.
Lightweight, efficient inverters have replaced bulky, heavy welding transformers.
When choosing a specific model, pay attention to the following characteristics:
- Device power; the maximum value is not of great importance, since the thickness of the workpieces does not exceed 5 mm; the lower limit should be as small as possible; it allows you to weld very thin sheet metal;
- In terms of functionality, semi-automatic devices and two-in-one devices are approximately the same;
- It is better to choose a model from a well-known brand; the product is more expensive, but it is more reliable and of better quality; well-known manufacturers provide maintenance and repairs;
- The quality of the connection depends on the experience and skill of the welder, and not on the cost of the equipment; You definitely shouldn’t buy the most expensive device.
How to learn the basics of craftsmanship
Learning the basic intricacies of manual welding is not difficult. Currently, you can find a lot of detailed material and video tutorials for this, which are freely available. True, if you intend to comprehend the deeper subtleties, you will have to stock up on serious sources of information, which are available in various manuals and additional guidance.
If you are a beginner and are just beginning to understand the intricacies of this skill, start with electrodes with a diameter of 3 mm, as they are considered the most popular. Thinner models are intended for welding thin metal, while thicker products require a powerful machine. Weak devices simply cannot cope with the task and do not provide the expected performance for successful work.
When purchasing a welding machine, be prepared to spend enough effort and time to learn all the basics of electric or manual welding. In this case, you will discover extensive possibilities for the practical use of equipment in domestic construction, repairing garden accessories, assembling and disassembling metal structures and in many other areas of everyday activity.
If you approach your training correctly, you can quickly and effectively learn a new industry, gaining theoretical and practical skills to work productively with metal workpieces.
Electrode marking
The quality of welds and the strength of the connection are decisively influenced by the correct selection of electrodes. The manufacturer indicates the description, characteristics, and markings on the packaging. From the information posted, you can find out what metals are connected with these electrodes, the preferred spatial arrangement, the diameter of the rods, and the composition of the coating.
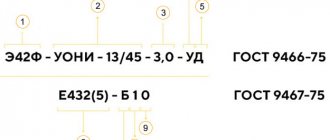
The marking is located after the name, brand in the form of a sequence of letters and numbers. The first letter indicates the purpose of the electrodes:
- U - for connecting parts made of medium-carbon steel with a low content of alloying additives;
- T - for welding heat-resistant alloy steel;
- N - for surfacing;
- A - for welding plastic metal compositions.
The second letter indicates the thickness of the coating: M - thin layer, C - medium layer thickness, D - thick layer, G - very thick coating. The third letter is the rod type; For consumable electrodes, use the letter E.
The numbers after the first three letters indicate the mechanical properties of the connection: tensile strength under tensile load, relative elongation. They are important for specialists performing critical connections.
The properties of the coating are indicated by the following letters:
- A - acid coating;
- B - basic (alkaline) coating (UONI-13/45);
- C—cellulose coating layer;
- R - rutile (ANO-4).
The last digits of the marking indicate the preferred spatial position of the electrodes during the welding process and the characteristics of the welding current.
What is electric arc welding used for?
Features of the technology and equipment operation allow the following processes to be carried out efficiently and efficiently:
- Reliable and durable connection of parts that are made of the same type of metal or metal alloys with similar characteristics. The main task of using electric arc welding in this case is to fasten two structural elements together to create a single surface or give parts a certain shape.
- Creating surfacing on the surface of parts - such processes are necessary to strengthen the load-bearing elements of structures or increase the level of power and endurance by creating special stiffeners from applied molten metal.
- Restoring the integrity and correct condition of components - the surface of the part on which cracks, chips, depressions and other defects have appeared.
- If you use the equipment at some distance from the surface being processed, the welding machine can perform the functions of a cutter.
Despite these shortcomings of the technology, it is actively used for the repair and production of parts in various fields of industry, production and household management.