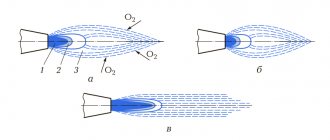
Schematic representation of a gas burner flame
The first step is to figure out what parts the burner flame consists of.
This can be done using the simple diagram below. In this schematic diagram, the following flame areas are indicated by letters:
- O – area of oxidizing flame; here the air-gas mixture burns completely, and an increased oxygen content is observed.
- B – recovery area. Here the gas does not burn completely, since it does not have enough oxygen for this. As a result, it breaks down into molecules that are combustion products. It is they who burn out completely in the oxidizing flame.
- A is the area in which the formation of the air-gas mixture occurs. Here the combustion process does not occur at all.
Gas cylinder burners: flame temperature
Today, burners that are attached directly to a gas cartridge are very popular. Depending on the method of fastening, they are divided into three main types:
- Threaded ones that simply screw onto the cylinder. This method allows for directed combustion and a torch flame structure. To operate such devices, gas with a high propane content is used. The maximum flame temperature of a gas burner is 1800 degrees, but it can be adjusted by reducing or adding gas or oxygen supply using specially designed valves.
- Collet. The most common burners capable of providing a flame temperature of up to 1500 degrees.
- Piezoelectric, which are easy to ignite a flame and use for a variety of purposes. They are not intended for installation on gas canisters, but craftsmen often use just such devices. The flame temperature reaches the same one and a half thousand degrees.
Types of welding flame
A welding flame is formed by the combustion of flammable gas or flammable liquid vapor in oxygen. The flame heats and melts the base and filler metal at the weld site. The oxygen-acetylene flame is most widely used in gas welding, since it has a high temperature (3150°C) and provides concentrated heating. However, due to the scarcity of acetylene, acetylene substitute gases —propane-butane, methane, natural and city gases—have become widespread (especially when cutting metals).
The composition of the combustible mixture, i.e., the ratio of oxygen and combustible gas, determines the appearance, temperature and influence of the welding flame on the molten metal. By changing the composition of the combustible mixture, the welder thereby changes the basic parameters of the welding flame.
To obtain a normal flame, the ratio of oxygen to combustible gas should be 1.1-1.2 for acetylene, 1.5-1.6 for natural gas, and 3.5 for propane.
All flammable gases containing hydrocarbons form a welding flame, which has three clearly distinguishable zones :
- core
- recovery zone
- torch
The hydrogen flame does not have clearly visible zones, which makes it difficult to adjust its appearance.
When the gas jet flowing from the nozzle is ignited, the flame moves in the direction of movement of the gas mixture jet. The flow rate for each gas is selected so that the flame does not penetrate into the burner nozzle and does not come off from it. The gas in the jet must be heated to the ignition temperature, acetylene ignites at a temperature of 450-500°C, and substitute gases - 550-650°C. Therefore, the flame core during the combustion of substitute gases is longer than during the combustion of acetylene.
a - oxidizing, b - normal, c - carburizing; 1 - core, 2 - reduction zone, 3 - torch
Figure 1 - Types of welding flame
The combustion process of acetylene in oxygen can be divided into two stages. First, under the influence of heating, acetylene decomposes into elements: C2H2 = 2C + H2. Then the first stage of acetylene combustion occurs due to the oxygen in the mixture according to the reaction 2C+H2+O2=2CO+H2. The second stage of combustion occurs due to air oxygen: 2CO + H2 + 1.5O2 = 2CO2 + H2O. The process of combustion of flammable gas in oxygen is exothermic, i.e. comes with the release of heat.
The core has a sharply defined shape (close to the shape of a cylinder), smoothly rounded at the end, with a brightly luminous shell. The shell consists of hot carbon particles that burn in the outer layer of the shell. The dimensions of the core depend on the composition of the combustible mixture, its flow rate and flow rate. The diameter of the burner mouthpiece channel determines the diameter of the flame core, and the flow rate of the gas mixture determines its length.
The cross-sectional area of the torch mouthpiece channel is directly proportional to the thickness of the metal being welded. The welding flame should not be too “soft” or “hard”. A soft flame is prone to backfire and popping, while a hard flame is capable of blowing molten metal out of the weld pool. As the oxygen pressure increases, the flow rate of the combustible mixture increases and the core of the welding flame lengthens; when the flow rate decreases, the core shortens. As the number of the mouthpiece increases, the size of the core increases. The core temperature reaches 1000°C.
The recovery (middle) zone is located behind the core and is noticeably different from it in its darker color. Its length depends on the number of the mouthpiece and reaches 20 mm. The zone consists of products of incomplete combustion of acetylene - carbon monoxide and hydrogen. It is called reducing, since carbon monoxide and hydrogen deoxidize the molten metal, removing oxygen from its oxides. If during the welding process the molten metal of the weld pool is in the middle zone, then the weld is obtained without pores of gas and slag inclusions. I perform welding in this flame zone and therefore it is called the working zone. The reduction zone has the highest temperature (3140°C) at a point 3-6 mm from the end of the core.
The complete combustion zone (flare) is located behind the reduction zone. It consists of carbon dioxide, water vapor and gas, which are formed in the flame during the combustion of carbon monoxide and hydrogen of the reduction zone due to the oxygen of the surrounding air. The temperature of this zone is significantly lower than the reduction temperature and ranges from 1200 to 2520°C.
Depending on the ratio between oxygen and acetylene, three main types of welding flame are obtained: normal, oxidizing and carburizing. A normal flame is theoretically obtained when slightly more from 1.1 to 1.3 volumes of acetylene are supplied to the burner per volume of oxygen.
A normal flame is characterized by the absence of free oxygen and carbon in its reduction zone. A little more oxygen is supplied to the burner due to its low contamination and the consumption of hydrogen combustion. In a normal flame, all three zones are clearly visible.
An oxidizing flame is produced when there is an excess of oxygen, when more than 1.3 volumes of oxygen are supplied to the burner per volume of acetylene. In this case, the core acquires a cone-shaped shape, is significantly reduced in length, becomes less sharp in outline and acquires a paler color. The reduction zone and the torch also shorten in length. The entire flame takes on a bluish-violet color. The flame burns with noise, the level of which depends on the oxygen pressure. The temperature of the oxidizing flame is higher than normal, but steel cannot be welded with such a flame due to the presence of excess oxygen in the flame. Excess oxygen leads to oxidation of the weld metal, making the weld porous and brittle. The oxidizing flame can be used in gas welding of brass and brazing.
A carburizing flame is produced when there is an excess of acetylene, when 0.95 or less volumes of oxygen are supplied to the burner per volume of acetylene. The core of such a flame loses the sharpness of its outline, and a green rim appears at its end, which is used to judge the excess of acetylene. The reduction zone is much lighter and almost merges with the core, and the torch becomes yellowish in color. With a large excess of acetylene, the flame begins to smoke, since there is a lack of oxygen necessary for complete combustion of acetylene. Excess carbon in the flame is easily absorbed by the molten metal and deteriorates the quality of the weld metal. The temperature of the carburizing flame is lower than that of the normal and oxidizing flames. By reducing the supply of acetylene to the burner until the green rim at the end of the core completely disappears, the acetylene flame turns into a normal one. A slightly carburizing flame is used for welding cast iron and surfacing with hard alloys.
The welder determines the nature of the welding flame by eye by the shape and color of the flame. When regulating the flame, it is necessary to pay attention to the correct selection of the flow of combustible gas and oxygen.
The flammable mixture flowing from the mouthpiece has a mechanical effect on the molten metal of the weld pool and forms a weld bead. Liquid metal is pressed to the edges of the bath. The nature of metal shaping depends on the angle of inclination of the torch mouthpiece to the surface of the metal being welded.
a - vertical, b - inclined, c - diagram of the movement of liquid metal in the bath
Figure 2 - Scheme of the mechanical effect of a flame on the liquid metal of a weld pool at different positions of the nozzle
Gas pressure affects the liquid metal, moving it to the rear wall of the weld pool, forming weld flakes. With high oxygen pressure, the flammable mixture flows out of the nozzle at high speed, the flame becomes “hard” and blows the molten metal out of the weld pool, thereby making welding difficult.
The quality of the deposited metal and the strength of the weld depend on the composition of the flame, therefore, during gas welding, the welder must monitor its character and regulate its composition throughout the entire welding process. The nature of the flame is selected depending on the metal being welded and its properties. For gas welding of steels, a normal flame is required, for welding cast iron, surfacing hard alloys - a carburizing flame, for welding brass - an oxidizing flame.
Dependence of temperature on fuel type
For domestic needs, two types of gas are used: natural and liquefied. Both of them are a transparent, explosive substance without color or odor. Therefore, to increase safety and the possibility of instant leak detection, ethyl mercaptan is added to the gas - a substance whose tart smell is felt by a person when he opens the gas tap. According to its chemical composition, natural gas consists of 98% methane and 2% of impurities that are represented sulfur, nitrogen and carbon dioxide.
In private homes, dachas and in areas not equipped with a main gas pipeline, liquefied bottled gas is used. For this, two types of mixture are used: propane-butane with a ratio of 65/35 and butane-propane prepared in a ratio of 85/15. The flame temperature of bottled gas is slightly lower than that of natural gas, and never exceeds 1000 degrees.
Due to the difference in temperatures, each gas has its own gas equipment. However, many manufacturers of gas stoves running on natural gas equip them with jets and reducers necessary to convert the stove to bottled gas. If the stove is connected to a cylinder without these important devices, the burner will begin to emit a huge amount of soot and constantly go out.
In this case, you will need to immediately contact the gas service and under no circumstances switch the stove to another type of gas yourself.
Combustible gases can be divided into two groups:
- Compressible or compressed are gases that, under normal storage conditions, do not turn into a liquid state (examples of compressed gases: methane, hydrogen, multicomponent gases)
- Liquefied gases are gases that, under normal storage conditions, have a liquid state (propane, butane and their mixtures)
Liquefied gas has the following advantages over compressed gas:
- in cylinders of the same capacity, liquefied gas can hold approximately 2 times more than compressed gas;
- liquefied gas during combustion emits 3 times more heat than the same volumetric amount of compressed gas;
- liquefied gas is stored in tanks at a pressure more than 10 times lower than compressed gas, which reduces cost
Gas burner flame temperature control
A value of 1800 degrees is ideal, for example, for welding metal workpieces, as well as for calcination, warming up in winter, or burning out individual sections of pipelines. For light alloy wheels and metals, you just need to choose a burner that can provide a directed effect.
But for other purposes this temperature may be excessively high. Therefore, we suggest that you follow the recommendations below:
- For processing wood, a temperature of 700-800 degrees will be sufficient. Such a flame will allow you to successfully cope with wood burning and decorating wood products, kindling wood on a barbecue, in a fireplace or in a stove.
- The maximum flame temperature is not required for working with glass, quartz, porcelain products, as well as with workpieces made of polymer materials. In addition, to process them, the flame must be directed and very thin.
- A minimum temperature of 200-350 degrees is ideal for cooking on a camping trip or in the field. In addition, you need to set it to this value if you want to process poultry carcasses, create some original decoration for desserts, or give a dish a more pleasant color.
The quality and efficiency of the flame depends not only on temperature indicators. In addition, it is very important to achieve proper oxygen distribution. Otherwise, there will be a lack of air, which will ultimately lead to the accumulation of combustion products in the burner. Because of this, soot appears, which then settles on the parts being processed or the dishes being prepared.
The gas burner allows you to perform a different range of work using a controlled flame at elevated temperatures. The device is used to perform soldering, welding, and household tasks. Special models are used for tourism purposes for cooking and lighting a fire. The temperature of the gas burner depends on the type and design features of the product.
Rating of gas burners for soldering and repair
1st place – mini gas burner with soldering attachment
Designed for both heating medium-sized parts and for contact soldering due to the heating of the tip from the flame. A kind of soldering iron without wires. The gas tank capacity is 8ml. The flame temperature when filling with butane reaches 1300 degrees Celsius, and the tip temperature – 450 degrees. The flame length is adjustable from 4 to 6 cm. The burner length is 13 cm and the diameter is 1.5 cm.
small and inexpensive, the refill is enough to solder several medium-sized parts, there is a nozzle for contact soldering, it is easy to refill.
2nd place – gas micro burner
There is nothing in it except a tank with a filling valve and a nozzle with a gas supply regulator. The ZC57100 does not have piezo ignition and it is supplied unfilled, so you will also have to buy a gas cartridge - it will be suitable for lighters. In general, to solder two wires or heat heat shrink without a soldering iron, such a torch is enough. The burner is also about 20 cm long and weighs 43 g.
This is the cheapest burner that can be found and the price of such a micro burner is 200 rubles.
the cheapest, easy to refill.
small flame, the filling runs out quickly, there is no piezo ignition.
3rd place – mini gas soldering iron KVT XZ-1
This remarkable soldering iron from the gas powered brand features piezo ignition and comes in a case with a set of 4 soldering tips, a spool of solder, and a tip cleaning sponge. Thus, the declared power of the soldering iron for contact soldering is 137 W - this is a lot for a soldering iron with a length of 21 cm and a weight of 120 g. Electric soldering irons have never dreamed of such weight and size characteristics. This soldering iron is not positioned as a torch, but it can be used as a torch - the flame is pencil-type.
This soldering iron is good for everyone, except for the price of 2300 rubles, which is why it landed in 3rd place.
burner from a famous brand, easy to solder, set of components, good case, high heat output.
4th place – gas burner IRIS BARCELONA
This torch is not only designed for soldering, welding, repairing electronic devices and jewelry. The flame of this burner is of course adjustable. Can be charged with a standard lighter gas cylinder. The flame length reaches 3 cm. The operating time is about 20 minutes. The flame temperature reaches 1300 degrees Celsius. The length of the burner itself is exactly 20 cm.
small size, piezo ignition, brand.
The length of the flame does not allow heating medium and large parts.
5th place – butane burner KVT X-220
It is positioned as a burner for construction and repair work. She looks very stylish. The knurled handle fits nicely in the hand. Has a piezoelectric flame ignition system. The capacity of the cylinder for highly purified butane is 22 ml. This amount of gas is enough for 110 minutes of continuous operation. The flame length is adjustable from 30 to 80 mm from a sharp wedge-shaped flame to a soft flame with yellow tongues. The weight was only 226 grams with a length of 14 cm.
a good option for desktop work, there is a stand, piezo ignition, and a comfortable handle.
It's bulky, you can't put it in your pocket, you can't fit it into a narrow place.
Goods for tourism and active recreation
It is much more economical than electric stoves or other modern household appliances for the kitchen. How high the temperature will be in the flame of a gas stove directly depends on the quality of the mixture used to operate the device. There are several types of natural fuels.
Among them:. Important: before buying a gas stove, you need to check its equipment, and whether there are special jets that can ensure the correct operation of the nozzle in the desired mode.
If the equipment was initially purchased for one type of gas, but during operation it needs to be changed, then you need to check whether the kit includes additional parts that will help to correctly install the equipment. Violations during installation of even the smallest and seemingly insignificant part can lead to improper operation of the gas stove. For example, it will start to smoke heavily, or the fire will constantly go out.
Rexant GT-19
- Fuel type – propane-butane mixture.
- The connection is collet.
- Flame temperature – 1400 ºС.
- Gas consumption – 80 g/hour.
- Overall dimensions – 153x40x57 mm.
- Weight – 135 g.
Rexant GT-19 is a compact and convenient burner designed for connection to standard gas cylinders using a collet connection. The model can be used for a variety of jobs involving flame processing, including removing old paint, lighting fires, barbecues and stoves, soldering pipe connections, and insulating wires using heat-shrinkable materials. Thanks to the built-in piezoelectric element, ignition is carried out with one touch.
After two minutes of warming up, the burner can be held at any angle, based on the characteristics of the work being performed. The design provides the ability to adjust the flame, which ensures economical fuel consumption. Recommended continuous operation time is no more than 30 minutes. It should be remembered that the burner is a subject of increased fire hazard. It is prohibited to be transported on public transport or left unattended while working. During operation, the device requires minimal human intervention. Maintenance comes down to periodically cleaning the burner from contaminants that could lead to clogging of the nozzle.
Operating principle and features
The user receives an even torch, the power of which is controlled by a special valve. Due to this, the temperature at which it heats up changes depending on the thickness of the material and the tasks being pursued.
The device is more cost-effective for welding and cutting than massive, expensive equipment.
The range of uses is so wide that the product is even used for disinfecting wooden hives, treating animal cages, roofing, and so on..
The burner is ignited with matches, a lighter or an open fire source. This option is cheaper than models with installed piezo ignition. This element leads to combustion after pressing the button, which provokes the appearance of a spark, which ignites the gas jet.
A burner is a popular tool, so developers strive to improve the design and increase functionality. The market offers several types of such equipment:
- Gas soldering iron.
- Cutter.
- Burner for tourism.
- Blowtorch.
Kinds
A burner is a popular tool, so developers strive to improve the design and increase functionality. The market offers several types of such equipment:
- Gas soldering iron.
- Cutter.
- Burner for tourism.
- Blowtorch.
A blowtorch is one of the types of burners . Shows high temperature and is used for processing metal, plastic and other durable materials.
Each type differs in appearance (design, color , packaging) and purpose. These features are taken into account before purchasing, since this directly determines the final result of processing and ease of use.
How is the efficiency obtained from gas combustion?
When choosing a gas boiler, you should pay attention to the technical data sheet. It indicates the efficiency factor, for example, 93 or 91%. But this does not mean that the efficiency will really be that way. In fact, the formed heating system has an efficiency that tends to 0. The faster the heat leaves the room, the faster the indicator will approach 0%. If this is due to the increased thermal conductivity of building structures, then it is possible to insulate them efficiently. You can use mastic, sealing rubber bands, heat-insulating material and double-glazed windows with a standardized distance between the glasses. But it is worth remembering that infiltration cannot be avoided. First of all, it is provoked by a gas boiler, which requires air to burn gas.
What does it depend on?
The burner temperature is determined by the chemical composition of the gas and the power of the product. During the research, it was possible to establish that the temperature parameters of the torch depend on the calorific properties of the gas mixture.
After combining the fuel with air, the gas is consumed critically, so the combustion intensity increases. By using an additional air source, you can increase the temperature you get at the burner. Without blowing, the value reaches 1500 degrees; access to auxiliary air flow gives an increase of up to 2200 degrees. The temperature differs in different parts of the torch :
- Internal . This is a short zone with little heating.
- Average . In this area, the temperature of the flame from the gas burner reaches its limit, but the fire does not open completely, which is due to a lack of oxygen and the release of decay products.
- Bordering . Visually characterized by a bright fire with high efficiency.
Cheap burner models are structurally the same. Expensive ones are equipped with additional elements that increase technical characteristics and ease of use.
To perform welding and cutting, special requirements are placed on the composition of the gas mixture, since the temperature regime of the product depends on it.
Features of application
Thus, pyrolysis gas has a slightly lower degree of heat transfer than natural or liquefied gas. Therefore, for the correct operation of various types of heating and kitchen equipment when using it for proper, more intense combustion, it is necessary to increase its supply.
In kitchen equipment, for example, jets can be drilled out for this purpose. In this case, a furnace using pyrolysis gas will work in the same way as using natural gas. That is, the intensity of fuel combustion will be the same. Also, to transfer various types of equipment to another type of gas, its firmware often changes. In cars that run on this type of fuel, the fuel system is completely replaced.
Temperature conditions of different types of burners per cylinder
You can purchase a burner online or at a hardware store. It is better to give preference to the second option, since the buyer can consult with an experienced seller, he will select the appropriate option depending on the tasks set by the user. The product range includes models that differ in temperature conditions:
- Refillable. They are characterized by small dimensions and thoughtful shape, as well as ease of use and a piezoelectric element. This type does not apply to the cylinder variety of gas burners.
- On a collet can. They are a source of powerful flame with an average outlet temperature of 1500 degrees.
- Threaded. Propane accounts for the lion's share of the fuel, due to which the temperature in the combustion zone is 1800 degrees. Advanced models are equipped with systems for mixing air with a propane mixture.
Some burners are equipped with autonomous heating of the combustible mixture, which increases the angle of use.
Oxygen-propane burners and concentrator
As we already know, there are two types of burners:
– operating on one type of gas – propane (the most popular burner of this class is HotHead – you can read about it in the previous article).
– burners operating on a mixture of two gases – propane and oxygen.
In this article we are talking about burners to which propane and oxygen are supplied separately and mixed into a working mixture directly on the surface of the burner nozzle. There is much more in this class of burners - you have the opportunity to study the characteristics and user reviews and choose the best option for yourself.
What are the advantages of an oxygen-propane burner compared to just a propane burner (hereinafter I call the HotHead propane burner - after the most popular of them)?
- The two-gas burner operates almost silently compared to HotHead. And if you work behind a torch for several hours a day, it really makes a difference!
- Due to the mixture of oxygen and propane, the burner flame has a much higher temperature, which allows you to melt glass faster, as well as work with borosilicate glass (hard glass) - making a bead from this glass on HotHead is very difficult, if not impossible). Using a two-gas burner you can make large beads from soft glass (Moretti, Vetrofond), and in general, many operations are performed faster and easier.
- The nozzle of a two-gas burner has several holes for the flame to exit (from 7 to 63 depending on the type of burner!), which allows you to make the flame more precise - this greatly simplifies the process of decorating the bead. Also, the flame can be easily varied. The nozzle is generally a separate issue - one can argue endlessly about the merits of this part in burners from different companies))
- With a two-gas torch it is much easier to reproduce the reduction and reaction processes that are necessary to create beads using expensive silver-containing glass (such as Double Helix - perhaps no lampworker will deny himself the pleasure of playing with this glass)). If it is possible to easily make a reduction on HotHead, then reaction glass practically does not exhibit its properties, because it needs oxygen to work.
The main disadvantage of a two-gas burner is the need to use oxygen - this gas is more explosive and requires more careful handling than propane. But this problem can be solved by replacing the gas cylinder with a concentrator. And, of course, burners of this class are an order of magnitude more expensive than HotHead.
The most popular entry-level burners in the oxygen-propane class are the Minor Bench Burner and CC Mini Burner.
Minor Bench Burner (manufacturer Nortel - average cost 160-170 dollars) - many craftsmen work on this burner (including me)). It was developed by Peter Norton in the 50s of the last century and still serves lampworkers faithfully. The most affordable burner in its class. It has 7 outlet holes, is quite heavy and stable, it can be easily adjusted and mounted on a table, it is almost silent, and it is very easy to work with the flame. For the lampworker who creates beads for jewelry, this is a great torch option. With 1 oxygen concentrator it creates a base level for work, with 2 concentrators or oxygen from a cylinder it works faster and hotter.
CC Mini Burner (manufacturer Carlisle - average cost $190-220) is also a very popular burner that allows you to work both with oxygen from a cylinder and using an oxygen concentrator. Since I have no experience working with it, I will refer to the opinion of Corina Tettinger, who has tested many burners and claims that the Mini SS has become her favorite among many)) It is silent and the flame that it is capable of producing has greater variability than that of the Minor .
However, some Mini SS users say that with one concentrator the burner works worse than with two (this does not apply to oxygen from a cylinder) and recommend immediately buying 2 concentrators for this burner (or one quite powerful one, which can output about 10 liters of oxygen).
Addition on the Mini SS burner from Yulia (JT-handmade): “The kit included a burner on a stand, two hoses, mounting hardware and a DVD with instructions in English. They talk in great detail about their history and production, about different flame options and, of course, show all sorts of beauties afterwards =) The only negative that I can note for myself, I don’t know how it is with other models, but adjusting the flame on a “heated” burner not so comfortable, in the sense that the regulators also heat up and you can’t just turn them back and forth... but this can be solved with the help of rags =).”
Also in this class of burners are: Bobcat (average cost about $200), Lynx (average cost about $430), Little Dragon (one of the recently developed burners - $200).
Oxygen Concentrator.
This device can serve as a replacement for an explosive oxygen cylinder.
The principle of operation of the concentrator is that the compressor supplies air to special filters through which only oxygen molecules can pass. As a result, the output is 90-98% oxygen.
Adjustment
The cleanliness of the cut depends on the correct flame setting . Oxygen treatment is carried out with a slightly oxidized or normal torch. The carefully adjusted flame of cutters with concentric nozzles is surrounded by a cutting stream of oxygen. The core of the torch in each section should be symmetrical and not differ in brightness.
Cutting with a torch with the mouthpiece moved cannot be carried out, as this will lead to heating of the edge, which will negatively affect the quality of the cut. The use of self-centering mouthpieces increases the ease of use of such equipment, because the device makes the flame symmetrical.
Sometimes the movement of the gas mixture is hampered due to clogging of the channel, which divides the torch into streams and leads to loss of stability. Such a product not only reduces the quality of processing, but also reduces productivity. Flame adjustment is based on creating a symmetrical flame of the required power in relation to the oxygen cutting jet.
A normal flame is ensured with the valves slightly open, which makes it possible to make adjustments during operation. When acetylene and oxygen are fully open, an excessive amount of the former is observed. Smooth closing of the acetylene valve leads to stabilization of the process.
Gas combustion air
If you take air from the common ventilation duct, this will have a bad effect on the operation of the system. This is due to the fact that the ventilation duct has common walls with the bathroom, kitchen or toilet. If the temperature outside is negative, then after a while the temperature in the ventilation duct will be 1 degree, and in the room adjacent to the duct there will be an uncomfortable atmosphere. Agree, it is unpleasant to be in a cold bathroom or cook in a cool kitchen. Therefore, it is not advisable to take air from the general ventilation duct.
Recommendations for work
Gas burners function as an autonomous source of large thermal energy . By regulating power and adjusting temperature conditions, the scope of application of the device is significantly expanded, it includes:
- processing of fusible metals (burning, calcination, heating) - using a directional torch with a temperature of at least 1500 degrees;
- working with wood - creating patterns, firing finished products;
- tourist purposes - you can give preference to compact models with low temperature parameters.
When using a gas burner, it must be taken into account that a lack of oxygen leads to heat losses and the accumulation of decomposition products from the combustion of the gas mixture. These phenomena provoke the appearance of soot and excessive glow, which affects the quality of cutting, welding, and melting.
The table shows the main characteristics of flammable gases
| with air | with oxygen | ||||||||
| Gases | |||||||||
| Acetylene | 3150-3620 | 1,173 | 52,6 | 12600 | 1 | 1,0-1,3 | 2,2-81,0 | 2,3-93,0 | All types of gas flame treatment |
| Butane | 2118-2500 | 2,54 | 116 | 27800 | 0,6 | 4,0 | 1,5-8,5 | 2-45,0 | Oxygen cutting, welding and soldering of non-ferrous metals, welding of steel up to 6 mm thick, metallization, straightening, bending, fire cleaning |
| Hydrogen | 2000-2235 | 0,09 | 10,6 | 2400 | 5,2 | 0,3-0,4 | 3,3-81,5 | 2,6-95,0 | Welding steel up to 2 mm thick, brass, lead, aluminum, cast iron, soldering, oxygen cutting |
| City gas | 2000-2300 | 0,84-1,05 | 18,8-21 | 4400-6500 | 2,5 | 1,5-1,6 | 3,8-24,6 | 10,0-73,6 | Welding of low-melting metals, soldering, oxygen and oxygen-flux cutting |
| Coke gas | 2100-2300 | 0,4-0,55 | 14,7-17,6 | 3520-4215 | 3,2 | 0,6-0,8 | 7,0-21,0 | – | Welding of low-melting metals, soldering, oxygen cutting |
| Methane | 2043-2200 | 0,67 | 33,4 | 8000 | 1,6 | 1,5 | 4,8-16,7 | 5,0-59,2 | Welding of low-melting metals, soldering, oxygen and oxygen-flux cutting |
| Petroleum gas | 2300 | 0,65-1,45 | 40,9-56,4 | 9800-13500 | 1,2 | 1,5-1,6 | 3,5-16,3 | – | Welding of low-melting metals, soldering, oxygen and oxygen-flux cutting |
| Pyrolysis gas | 2300 | 0,65-0,85 | 31,3-33,4 | 7500-8000 | 1,6 | 1,2-1,5 | – | – | Welding steel up to 2 mm thick, welding brass, lead, aluminum, soldering, oxygen cutting |
| Natural gas | 2100-2200 | 0,5-0,7 | 35,4-40 | 8500-9500 | 1,6-1,8 | 1,5-1,6 | 4,8-14,0 | 5,0-59,2 | Welding steel up to 4.5 mm thick, low-melting metals, soldering, oxygen and oxygen-flux cutting |
| Propane | 2110-2500 | 1,88 | 89 | 21200 | 0,6 | 3,5 | 2,0-9,5 | 2,0-48,0 | Oxygen cutting, welding and soldering of non-ferrous metals, welding of steel up to 6 mm thick, metallization, straightening, bending, fire cleaning |
| Propane-butane mixture | 2400-2700 | 1,92 | 89 | 21200 | 0,6 | 3,0-3,5 | – | – | Oxygen cutting, welding and soldering of non-ferrous metals, welding of steel up to 6 mm thick, metallization, straightening, bending, fire cleaning |
| Shale gas | 2000 | 0,7-0,9 | 12,6-14,3 | 3000-3400 | 4,0 | 0,7 | – | – | Welding of low-melting metals, soldering, oxygen cutting |
| Couples | |||||||||
| Petrol | 2500-2600 | 0,7-0,76 | 42-44,5 | 10000-10600 | 1,4 | 1,1-1,4 | 0,7-6,0 | 2,1-28,4 | Oxygen cutting of steel, welding, soldering of low-melting metals, underwater cutting |
| Kerosene | 2400-2450 | 0,8-0,84 | 42-42,8 | 10000-10200 | 1,0-1,3 | 1,7-2,4 | 1,4-5,5 | 2,0-28,0 | Oxygen cutting of steel, welding, soldering of low-melting metals, underwater cutting |