Classification
Employees of production and construction facilities controlled by Rostekhnadzor are subject to certification by the National Welding Control Agency. The certificate confirms that the certified person has the necessary knowledge and skills to perform a certain type of work - welding building structures or equipment (boiler, mining, metallurgical, etc.).
Main NAKS levels:
- Welder.
- Foreman – certification of a person responsible for managing a specific production area.
- Process engineer – employees responsible for the development of technological documentation, its approval and control of welding operations are certified.
- Chief welder - certification is carried out by the heads of the welding service, leading engineers who are authorized to approve technical documentation and other documents regulating welding operations.
The question often arises: NAKS electric gas welder - what is it? Based on the above, this is a person who has a qualification certificate with permission to perform electric and gas welding work. Level 2 can be obtained by employees applying for the position of foreman or supervisor of the welding and assembly section of critical metal structures or equipment.
Examination tickets for the profession “Electric welder 3-4 categories”
EXAMINATION TICKETS
by profession "Electric welder 3-4 categories"
Electric welders 3-4 categories.
TICKET No. 1.
1. Classification of fusion welding processes.
2. Basic physical, chemical and technological properties of metals.
3. Tension. Electricity. Conductors, semiconductors, dielectrics.
4. Welding technology for low-carbon steels. Welding materials. Selection of welding modes. Features of welding seams with symmetrical cutting of edges.
5. Basic requirements for personnel allowed to perform electric welding work.
6. Task. Determine the strength of the welding current using the formula for 4 mm electrodes of grade UONII 13/55 when welding in a vertical position, if: k - coefficient is 30-45 A/mm2.
TICKET No. 2.
1. The essence of the fusion welding process.
2. Classification of steels according to: chemical composition, purpose, carbon content and alloying elements.
3. Thermal effect of electric current.
4. Welding technology for low-alloy silicon-manganese steels with a thickness of more than 30 mm. Welding materials. Thermal rest of welded joints. Welding designation on drawings.
5. Safety requirements for equipment that is a source of electric current for welding work.
6. Task. Determine the mass of deposited metal for 1 m of a single-pass weld with a cross-section of 0.6 cm2, if g = 7.8 g/cm3 (density of deposited metal).
TICKET No. 3.
1. Welding arc, its characteristics.
2. Classification of steels by weldability.
3. Short circuit. Alternating current.
4. Welding technology for high-carbon steels. Welding materials. The essence of heat treatment is “tempering”. Designation on the drawings of welded joints made along a closed contour and seams made in a checkerboard pattern.
5. Safety requirements for the organization of permanent workplaces for electrical welding work.
6. Task. Determine the consumption of UONII 13/55 electrodes for welding a single-pass weld with a cross-section of 0.6 cm3 and a length of 10.5 m, if g = 7.8 g/cm3 (density of the deposited metal), the coefficient taking into account the consumption of electrodes is k = 1.6.
TICKET No. 4.
1. Conditions for a stable arc burning process.
2. Carbon structural steels of ordinary quality and quality steels. Designation.
3. Measuring instruments for measuring: current, voltage, resistance, power.
4. Welding technology for high-alloy austenitic steels. Material for welding. The essence of heat treatment is “hardening”. Decipher the designation of welding
GOST S17
2№1
Methods for quality control of welded joints.
5. Specify the length of the primary circuit between the power source and the mobile welding unit. What can and cannot be used as a return wire?
6. Task. Determine the strength of the welding current using the formula for 4 mm electrodes of grade UONII 13/55 when welding in a vertical position, if: k - coefficient is 30-45 A/mm2.
TICKET No. 5.
1. The type of current used to power the welding arc. Current polarity when feeding the arc with direct current.
2. Alloy steels, their classification according to the content of alloying elements.
3. Welding arc power sources, requirements for them.
4. Welding technology of two-layer steels. Material for welding. Types of preparation of edges for welding. The essence of the ultrasonic method for quality control of welds.
5. Safety measures when performing welding work inside closed containers and pits.
6. Task. Determine the mass of deposited metal for 1 m of a single-pass weld with a cross-section of 0.6 cm2, if g = 7.8 g/cm3 (density of deposited metal).
TICKET No. 6.
1. The influence of the magnetic field and ferromagnetic masses on the welding arc.
2. Determination of mechanical properties of metals and alloys.
3. Welding transformers, welding rectifiers. Device. Methods for adjusting welding current.
4. Welding technology for heat-resistant steels grade 12ХМ. Material for welding. The essence of heat treatment is “annealing”. GOST for pipe welding. The procedure for welding I-beams. Defects in welded joints.
5. Safety measures when performing electric welding work in fire hazardous areas.
6. Task. Determine the consumption of UONII 13/55 electrodes for welding a single-pass weld with a cross-section of 0.6 cm3 and a length of 10.5 m, if g = 7.8 g/cm3 “density of the deposited metal”, the coefficient taking into account the consumption of electrodes is k = 1.6.
TICKET No. 7.
1. The mechanism of formation of cold and hot cracks.
2. Welding materials used for welding.
3. External characteristics of welding arc power sources.
4. Welding technology for chromium-silicon-manganese steels 20KhGSA; 30ХГСА. What is the difference in the welding symbol on the drawing? :
GOST S-21
GOST S21
How are seams of different lengths and thicknesses welded?
5. Selection of light filters, their classification.
6. Task. Determine the strength of the welding current using the formula for 4 mm electrodes of grade UONII 13/55 when welding in a vertical position, if: k - coefficient is 30-45 A/mm2.
TICKET No. 8.
1. The influence of harmful impurities and alloying elements on the weldability of steels.
2. Rules for storage and release of welding materials into production.
3. What external characteristic of the power source is most suitable for manual arc welding?
4. Welding technology for medium-carbon steels. Material for welding. Welding modes depending on the electrode diameter, steel grade, thickness, spatial position. The essence of heat treatment is “Normalization”. Procedure for correcting cracks in welds.
5. Types of personal protective equipment for electric welders, used depending on specific working conditions.
6. Task. Determine the mass of deposited metal for 1 m of a single-pass weld with a cross-section of 0.6 cm2, if g = 7.8 g/cm3 (density of deposited metal).
TICKET No. 9.
1. Air-arc gouging of metals, scope.
2. Decipher the welding materials as directed by the examination committee: 3sv08G2S; 2sv08A; 4sv10X16N25AM6, etc.
3.Why is the open-circuit voltage and short-circuit current of the power supply limited?
4. Preheating before welding, purpose. Reasons for the formation of cold and hot cracks in the metal of a welded joint. Features of welding technology for high-chromium martensitic steels with chromium content in steel up to 12-13%. Measures to combat stress and deformation during welding.
5. The effect of electric current on the human body, basic measures to protect against its damage.
6. Task. Determine the consumption of UONII 13/55 electrodes for welding a single-pass weld with a cross-section of 0.6 cm3 and a length of 10.5 m, if g = 7.8 g/cm3 “density of the deposited metal”, the coefficient taking into account the consumption of electrodes is k = 1.6.
TICKET No. 10.
1. Factors on which the performance of the welding process depends.
2. What components are included in the electrode coating?
3. Design and principle of operation of the welding converter.
4. Technology of welding combined welded joints from steels of various structural classes (Vst3ps4+12Х18Н10Т). Material for welding. Decipher the welding symbol in the drawing as directed by a specialist. Purpose of electrodes E - 10Х25Н13Г2 - OZL-6 Æ3 VD.
E -2975 - B20
Welding procedure for long welds.
5. Procedure for providing first aid for burns, fractures, dislocations and sprains.
6. Task. Determine the strength of the welding current using the formula for 4 mm electrodes of grade UONII 13/55 when welding in a vertical position, if: k - coefficient is 30-45 A/mm2.
EXAMINATION TICKETS
by profession "Electric welder 5-6 categories"
Electric welders 5-6 categories.
TICKET No. 1.
1. Electric welding arc.
2. Methods of steel production.
3. Types and purposes of electrodes for electric arc welding. Welding wires, non-consumable electrodes, shielding gases, welding fluxes.
4. External characteristics of power supplies. Purpose and principle of operation of ballast rheostats. Types of welded joints and seams.
5. Welding of low-alloy steels. Welding materials. Select the welding mode with an E-46A Æ4 mm electrode in a vertical position. Specify the sequence of welding a seam with an X-shaped groove, 4 m long.
6. Basic requirements for personnel allowed to perform electric welding work.
7. Task. Determine the amount of heat input of bead surfacing in the following mode:
Ist = 220 A; Ud = 22 V; welding speed Vw = 0.36 cm/sec; coefficient h=0.8.
Answer: qn = 2,582 cal/cm.
TICKET No. 2.
1. Welding arc zones and its characteristics.
2. Classification of steels according to carbon content in steel.
3. Classification of electrodes: for welding and surfacing; by appointment; technological features; type and thickness of coating; chemical composition of the rod and coating; the nature of the slag; mechanical properties of the weld metal; welding wires; fluxes.
4. Welding transformers. Ohm's law. Structural elements of the form for preparing edges for welding, their role.
5. Welding of low-alloy silicon-manganese steels with a thickness of 32 mm, material for welding. Heating before welding and during welding, its role. Sequence of crack welding.
6. Safety requirements for equipment that is a source of electric current for welding work.
7. Task. Determine the mass of deposited metal using UONII 13/55 electrodes for welding a single-pass weld with a cross section of F=0.6 cm3 and a length of 10 m; specific gravity of metal g=7.8 g/cm2.
Answer: ~4.7 kg.
TICKET No. 3.
1. Conditions for stable arc burning.
2. Chemical composition and marking of carbon steels.
3. Purpose of electrodes. Types of electrode coatings.
4. Welding converters, device, operating principle. Decipher VDU-1201. Requirements for the assembly of welded joints.
5. Steel welding technology 35. Material for welding. Reasons for the formation of hot cracks in steels. Sequence of welding seams of a box-section beam 8 m long.
6. Safety requirements for the organization of permanent workplaces for electrical welding work.
7. Task. Determine the amount of deposited metal if welding is carried out with UONII 13/55 electrodes at a current Iw=160 A, welding time t=0.32 hours and del=8.5 g/A. h.
Answer: 0.435 kg.
TICKET No. 4.
1. Effects of ferromagnetic masses on the welding arc.
2. Classification of steels according to the content of alloying elements.
3. Classification of electrodes by type according to GOST 9467; GOST;
GOST.
4. Single-point and multi-point rectifiers. Decipher TDM-250. The drawing indicates: the welded connection is made in accordance with GOST C-15, what is the welding method and type of connection?
5. Welding technology for steel 10Х17Н13М3Т, material for welding, type of heat treatment. Methods for determining weld defects.
6. Specify the length of the primary circuit between the power source and the mobile welding unit. What can and cannot be used as a return wire?
7. Task. Determine the amount of heat input of bead surfacing in the following mode:
Ist = 220 A; Ud = 22 V; welding speed Vw = 0.36 cm/sec; coefficient h=0.8.
Answer: qn = 2,582 cal/cm.
TICKET No. 5.
1. Mechanism of pore formation.
2. Chemical composition and marking of alloy steels.
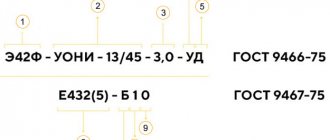
3. Marking of welding wires and electrodes. Decipher:
4. Lenz-Joule law, its practical application. Decipher if there is a designation on the drawing
GOST 5264-80 T3 10 RZ40.
5. It is necessary to weld two-layer steel 09G2S+12Х18Н10Т, 14 mm thick, type of edge cutting, material for welding, welding procedure for this steel. The essence of the ultrasonic method of weld inspection.
6. Safety measures when performing welding work inside closed containers and pits.
7. Task. Determine the mass of deposited metal using UONII 13/55 electrodes for welding a single-pass weld with a cross section of F=0.6 cm3 and a length of 10 m; specific gravity of metal g=7.8 g/cm2.
Answer: ~4.7 kg.
TICKET No. 6.
1. Formation of hot and cold cracks.
2. Mechanical properties of steels.
3. Ways to increase labor productivity using various welding methods, give examples. What type of electrode coating if the electrode brand designation includes: - B...?
4. The type of external characteristic is most suitable for fusion welding, why? What device measures the current and its inclusion in the welding circuit. Decipher if there is a designation on the drawing
GOST R-S-17- — RZ40
5. Welding technology of heat-resistant steel grade 12ХМ, material for welding. Methods for reducing welding stresses and deformations of welded joints.
6. Safety measures when performing electric welding work in fire hazardous areas.
7. Task. Determine the amount of deposited metal if welding is carried out with UONII 13/55 electrodes at a current Iw=160 A, welding time t=0.32 hours and del=8.5 g/A. h.
Answer: 0.435 kg.
TICKET No. 7.
1. Characteristic zones of the welded joint.
2. The influence of harmful impurities and alloying elements on the weldability of steels.
3. Rules for storing and issuing welding materials. Storing them at the workplace. What type of electrode coating if the designation of the electrode brand includes: - P...?
4. Types of electric welding stations. Direct and alternating current. There is a designation on the drawing: - what does this mean?
№ 5
2 №19
5. Welding technology for steel 12Х18Н10Т, material for welding. Select the welding mode with an electrode of type E -08Х20Н9Г12Б in the lower position. Internal defects in welds, reasons for their formation. Measures to reduce deformations when welding a seam with a V-shaped groove of edges 400 mm long.
6. Selection of light filters, their classification.
7. Task. Determine the amount of heat input of bead surfacing in the following mode:
Ist = 220 A; Ud = 22 V; welding speed Vw = 0.36 cm/sec; coefficient h=0.8.
Answer: qn = 2,582 cal/cm.
TICKET No. 8.
1. The influence of oxygen, nitrogen, hydrogen in the air on the quality of the weld metal.
2. Carbon equivalent of steels as an indicator of the weldability of steels.
3. Preparation of welding materials for welding. Decipher 3sv10X16N25AM6; 1.6sv08G2S,
GOST; GOST 9466-75.
4. External characteristics of power supplies. Purpose and principle of operation of ballast rheostats. Decipher if there is a designation on the drawing
GOST T3 10 RZ40
5. Welding technology for medium-carbon steels. Material for welding. The essence of quality control of welds using color flaw detection. Describe the procedure for welding a butt joint of a pipe Æ180x12 consisting of 2 equal parts, each 1 m long.
6. Types of personal protective equipment for electric welders, used depending on specific working conditions.
7. Task. Determine the mass of deposited metal using UONII 13/55 electrodes for welding a single-pass weld with a cross section of F=0.6 cm3 and a length of 10 m; specific gravity of metal g=7.8 g/cm2.
Answer: ~4.7 kg.
TICKET No. 9.
1. Dependence of the metal melting rate on the polarity of the electric arc current.
2. Heat treatment of steels and welded joints, its essence and purpose.
3. Electrode coatings, composition and purpose. The role of alloying components and stabilizing components.
4. Welding converters, device, operating principle. Decipher VDU-1201. Decipher if there is a designation on the drawing
GOST R-S-17 RZ40
5. Thermal rest of welded joints, when it is performed, an example of welding of this grade of steel. Specify the electrodes for welding joint 09G2S+12Х18Н10Т. Reasons for the formation of pores in welds.
6. The effect of electric current on the human body, basic measures to protect against its damage.
7. Task. Determine the amount of deposited metal if welding is carried out with UONII 13/55 electrodes at a current Iw=160 A, welding time t=0.32 hours and del=8.5 g/A. h.
Answer: 0.435 kg.
TICKET No. 10.
1. Alloying of molten metal.
2. The influence of heat treatment on the structure and properties of steels and welded joints.
3. Conditions for selecting welding materials depending on the grade of steel being welded and operating conditions of the product. Determine welding materials for welding VSt3kp4 steel; 08Х18Н10Т; 20X13.
4. The type of external characteristic most used for fusion welding, why? What device measures the current and its inclusion in the welding circuit. There is a designation on the drawing: - decipher
№5
2 №19
5. Welding technology for steels with a chromium content of 12-13% (martensitic class), materials for welding. Reasons for the formation of cold cracks in seams. Welding sequence for an I-beam with a seam length of 12 m.
6. Procedure for providing first aid for burns, fractures, dislocations and sprains.
7. Task. Determine the amount of heat input of bead surfacing in the following mode:
Ist = 220 A; Ud = 22 V; welding speed Vw = 0.36 cm/sec; coefficient h=0.8.
Answer: qn = 2,582 cal/cm.
EXAMINATION
TICKETS
for the profession “Electric welder 1-2 categories”
TICKET No. 1.
1. Classification of welding methods.
2. Which external characteristic is most acceptable for manual arc welding and why?
3. Measures to combat angular deformations when welding butt and fillet welds.
4. Composition and properties of low-carbon structural steels. Welding features.
5. Basic techniques for providing first aid in case of poisoning.
TICKET No. 2.
1. Classification of seams of welded joints.
2. Why is the open circuit voltage of power supplies limited?
3. Main defects of the seam and welded joint.
4. The relationship between the size, shape of the seam and modes in manual electric arc welding.
5. Safety rules for welding in open areas.
TICKET No. 3.
1. Types of welding stations used in industry and construction.
2. What external characteristics may power supplies have?
3. How is good penetration of the root of the weld ensured during welding?
4. Technology for manufacturing combined welded structures from steels of various structural classes.
5. Safety precautions when welding vertical seams.
TICKET No. 4.
1. Welding converter device.
2. General information about edge preparation and weld assembly.
3. Features of welding two-layer steels.
4. Defects in seam formation. What conditions are required to obtain a high quality weld?
5. Safety measures in workshops.
TICKET No. 5.
1. Main types of welding converters used in industry.
2. What parameters set the welding mode?
3. The influence of carbon and silicon on the properties of steel.
4. Features of welding high-alloy chromium-nickel corrosion-resistant steels.
5. Electrical safety rules when operating welding transformers.
TICKET No. 6.
1. What main components does the welding converter consist of?
2. What properties of high-carbon steel make welding difficult?
3. What is an electric arc?
4. Measures to relieve welding stresses and eliminate residual deformations.
5. Safety measures when working at height.
TICKET No. 7.
1. The essence of air-arc gouging of metals and areas of application.
2. How are seams of various lengths and thicknesses welded?
3. How is welding indicated on the drawings?
4. Features of welding medium-carbon steels?
5. Industrial sanitation and occupational hygiene.
TICKET No. 8.
1. The operating principle of the welding rectifier and its design features.
2. Main types of heat treatment. Their purpose.
3. Welding arc.
4. How are defective areas with cracks cut and welded?
5. Personal protective equipment for welders.
TICKET No. 9.
1. How can the weld metal be alloyed?
2. Types of electrode coatings?
3. How are steels and welding wires designated?
4. Talk about measures to combat deformation during welding.
5. Self-help and first aid in case of accidents.
TICKET No. 10.
1. Who is the founder of electric welding?
2. Methods for testing welds.
3. Where is the letter “A” placed in the designations of steels and welding wires and for what purpose?
4. How can you explain the reasons for the formation of cold and hot cracks in the metal of a welded joint?
5. Fire prevention measures.
How is certification carried out?
An employee of an enterprise or a person who wishes to obtain a 2nd degree certificate must successfully pass 2 exams in accordance with the selected welding methods and production industry:
- Theoretical.
- Practical.
The tests are carried out under the supervision of a commission - certified welding production employees with a certificate of at least level 2 and representatives of Rostechnadzor.
You can learn in detail about how to obtain a NAKS certificate at the certification center. Information about the person being certified is provided in the application. After successfully passing the qualification tests, the person is issued an appropriate certificate and protocol. Subsequently, the master confirms his qualifications every 3 years and undergoes periodic certification.