General issues
Argon arc welding is called welding with the formation of an electric arc in an argon environment. One of the electrodes is the surface of the part. The second electrode may be consumable or non-consumable. The non-consumable electrode is usually made of tungsten. In regulatory documents, argon arc welding can be designated by the following abbreviations:
- RAD – manual argon arc welding. In this case, a non-consumable electrode is used.
- AMA is argon arc welding, carried out with non-consumable electrodes, but in automatic mode.
- AADP – automatic welding with consumable electrodes.
In the international classification, this type of welding is defined as TIG - Tungsten Inert Gas or GTAW - Gas Tungsten Arc Welding, which translated means “welding in an inert gas environment”. Often this gas is argon.
An inert gas was chosen to create a protective environment due to the lack of chemical interaction with metal and other gases. Since argon is heavier than air, it displaces atmospheric oxygen and hydrogen from the weld formation zone, which eliminates the appearance of pores and cracks in the metal, and also prevents the formation of a layer of oxide film.
Welding technology boils down to the formation of an arc between a tungsten electrode and the surface. Gas enters the welding zone through a special torch nozzle. Unlike welding with a consumable electrode, here the additive is excluded from the electrical circuit, and is supplied to the bath area separately in the form of a rod. Manual welding differs from automatic welding in that in the first case the welder himself holds the torch and adds the additive, and in the second the process is automated. The technology also differs in the method of arc formation.
For a number of reasons, the arc cannot be formed by simply touching the electrode, so the installation provides for parallel operation of the oscillator. It is necessary to understand that welding can be carried out with both direct and alternating current. According to the method of connecting the electrode, direct and reverse polarity are distinguished. Before carrying out preparatory work, it is necessary to select the necessary parameters for each specific metal.
The main issues were discussed above, since many parameters are subject to standardization. GOST for argon arc welding is not limited to just one document. Standards have been determined for burners, processing and size of seams, working with aluminum, for filler wire, for equipment and electrodes. But, before presenting a list of these documents, let’s look at the issue of standardization.
What electrodes should be used to cook steel 12x18n10t.
Nowadays, almost all people have access to all brands and types of electrodes. Electrodes are divided into different classes according to their characteristics, for example they can be divided into electrodes for welding high-alloy and low-alloy steels. Electrodes are also divided into classes based on coating material: basic, acidic and regular. The list of classes into which electrodes are divided is very large, so there is no point in listing it completely. One of the types of electrodes are electrodes for welding steel 12x18n10t , that is, they are intended for welding chromium-nickel steels. This type of steel is used in cases where the product must be as resistant to corrosion as possible and not succumb to other environmental factors. Also, products that are welded with electrodes for welding steel 12x18n10t are subject to increased requirements for resistance to intercrystalline corrosion.
Stainless steel products are highly valued all over the world, so the popularity of electrodes for welding steel 12x18n10t continues to grow every day. However, many people are also attracted to these electrodes by their excellent combination of price and quality. Truly, such a combination is extremely rare, so this is precisely one of the most important advantages of these particular electrodes.
Now let's talk about the process of welding with electrodes for welding chromium-nickel steels. Welding with these electrodes is carried out in all spatial positions using direct current of reverse polarity. Also, these electrodes also have such qualities, for example, stable arc burning, low metal spattering, excellent seam formation and easy separation of slag from the surface of the product.
Immediately before starting welding, you need to calcinate the electrodes for welding 12x18n10t steel in a special furnace for calcining electrodes at a temperature of 300 to 350 degrees Celsius for one hour. After complete cooling, the electrodes are ready for use. Seams welded with these electrodes can be exposed to temperatures up to 350 degrees. Welding with electrodes for welding chrome-plated steel can be done either manually or with an inert gas arc.
Also, for welding with these electrodes, such types of welding as plasma welding, pulsed-arc welding, spot and roller welding, welding in an active gas environment, submerged arc welding are also used, and resistance welding is also possible. During welding, a porous oxide layer is formed, which contains chromium. This leads to a decrease in corrosion resistance, so if you need high corrosion resistance, then you need to subject the material to subsequent processing so that the product remains the same after several decades.
For a long time now, many economical people have continued to weld chrome-plated steel products for their homes. They order them without any problems through the “Contacts” menu item and remain satisfied.
- Decoding the electrodes
- Electrodes by Brand
Electrodes Uoni 13 45 Electrodes ANZHR Electrodes ProfHelper
Specifications and standards
Some types of work, goods and services are controlled by the state in terms of quality. The reason for such control was the inter-industry significance. State standards (GOST) contain a list of requirements for each product, for each result of activity that is subject to standardization. This is a document based on international standards and taking into account best practices, as well as all the achievements of science and technology. Standardization was introduced during the existence of the USSR. Standards cannot be static, so they change over time.
GOSTs in Russia are mandatory only for defense products, but in construction they are of great practical importance, because the main design indicators are safety and reliability. Some people confuse the state standard with technical specifications. In fact, specifications regulate the production of those goods that are not subject to standardization according to GOST. We can say that technical specifications are the result of the development of entrepreneurs who are producers. Although the TU is not a guest document, they do not contradict the state document, but, on the contrary, complement it.
In some sources, upon request, you can find only one document. However, it does not fully reflect all the standards relating to argon arc welding, its preparation and implementation. The list of all regulatory documents contains GOSTs adopted at different times. To date, there are 9 documents.
- GOST 5.917-71 defines the requirements for hand-held burners RGA-150 and RGA-400.
- GOST 14806-80 contains information on the parameters of argon arc welding of alloys containing aluminum.
- GOST 14771-76 is similar in structure to the previous document. Only here we are talking about gas-shielded arc welding as a generalized process.
- GOST 7871-75 defines the parameters of aluminum welding wire for TIG welding.
- GOST 2246-70 is a document that specifies the requirements for steel wire.
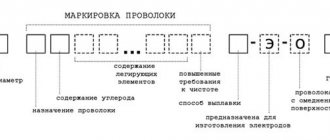
- GOST 23949-80 is a standard applied to tungsten electrodes for argon arc welding.
- GOST 18130-79 and GOST 13821-77 regulate the operation of equipment, including semi-automatic devices and rectifiers.
- GOST 10157-79 defines the standard for the most inert gas (argon).
Stainless steel welding options, GOSTs, methods
GOST 14771-76 Arc welding in shielding gas. This standard establishes the basic types, structural elements and dimensions of welded joints made of steels, as well as alloys on iron-nickel and nickel bases, performed by gas-shielded arc welding.
It should also be noted such welding methods as: spot, roller, laser, high-frequency, resistance welding and others.
So, the next stage is processing the welds. The surface of a stainless steel weld joint forms a porous oxide layer, which contains chromium. This layer contributes to a significant weakening of corrosion resistance. The surface of the oxide layer arises from the steel, after which a so-called steel is formed under the oxide layer. low chromium content. When there is a need to increase the corrosion resistance of a welded joint, the oxide layer and the layer with low chromium content must be removed. This process is carried out using heat treatment, in this case heat treatment is capable of dissolving inside the steel structure, thanks to this process all possible differences in filler materials are smoothed out. You need to know that you are allowed to use only those accessories that are intended for processing stainless steel, these can be: belts and wheels for grinding, brushes for processing stainless steel, stainless steel shot.
Weld processing
An effective method for treating weld seams is etching. If the etching method is performed correctly, this will qualitatively remove the oxide layer and the zone with a low chromium content. The processing of this method is carried out by coating, dipping or external application of paste, all depending on the conditions. Basically, mixed acids (nitric acid/hydrofluoric acid) are used for etching in proportions of 8 - 20% nitric acid and 0.5 - 5% hydrofluoric acid, with the addition of H2O (water). The etching time depends not only on the concentration of acids, but also on temperature, type of rolled product and thickness of scale (acid-resistant rolled steel, compared to stainless steel, requires long-term processing). After the etching method, the structure becomes resistant to corrosion.
We have become familiar with the basic methods of welding stainless steel and now we can safely talk about the special requirements for welding in the manufacture of stainless steel. When preparing the above alloys and steels, special requirements and main features must be taken into account:
5.917-71
This document was published on May 13, 1971 in accordance with the decree of the State Committee of Standards of the USSR. The given limits apply only to burners of the RGA-150 and RGA-400 types. They are used in argon arc welding with a tungsten electrode of aluminum, its alloys and stainless steel. Products that comply with GOST received a quality mark.
Expert opinion
Bagrov Viktor Sergeevich
Welder of the highest 6th category. He is considered a master of his craft, knows the intricacies and nuances of the profession.
Today, manufacturers of welding inverters operating in TIG mode do not adhere to these standards, however, thanks to modern technologies, the quality of the devices remains high.
Using auxiliary signs
Additional clarifications on the implementation of welded joints in accordance with GOST are indicated on the drawings using auxiliary signs:
Modern computer-aided design (CAD) systems are complex software products designed to assist engineers. Among the most well-known are AutoCad (on its basis, Autodesk Building Systems was developed for internal engineering networks), construction Allplan, and ATHENA for facade and metal structures. Of the Russian CAD systems, Compass and Monomakh have proven themselves well.
Auxiliary symbols for designating welds
14806-80 and 14771-76
Standardization of direct welding technology for aluminum and aluminum products is reflected in the corresponding regulatory document. This includes connections of parts with edge thicknesses from 0.8 to 60 mm. Pipeline welding has slightly different requirements, so this standard does not apply to them.
GOST 14771-76, as stated earlier, has the same structure. The only difference is that the first document is defined specifically for aluminum-containing materials, and the second - for steels and alloys based on nickel and iron-nickel.
Which GOST standards are developed for argon arc welding
Welding is usually understood as a type of joining of parts in which interatomic bonds are formed. This effect can be achieved by partial heating of the surfaces to be welded or by their plastic deformation. The energy source can be an electric arc or a gas flame. Technologies are known that convert the energy of friction, ultrasound, and laser radiation.
7871-75 and 2246-70
The introduced GOST concerns wire made of aluminum or alloys. Manufacturers use it, since the document regulates the possible values of wire diameter. Among all other requirements, standards for the chemical composition of consumables have been determined.
There are several types of wire, differing from each other in the quantitative content of elements (magnesium, manganese, aluminum, iron, silicon, titanium, beryllium, zirconium). Most popular brands:
- SvA99;
- SvA97;
- SvA85T;
- SvA5;
- SvAMts;
- SwAMg3;
- SvAK5.
The presence of impurities is allowed. The manufactured wire is tested, including for strength. The table shows the values of the maximum loads at which rupture occurs. Acceptance of materials is carried out in batches. One batch must contain wire with the same parameters. The appendix to the document specifies the conditions for storing and transporting the wire. Since it is supplied in coils, the dimensions of the coils are also subject to normalization.
Steel wire must meet the requirements of GOST 2246-70. Popular types:
- Sv-08;
- Sv-08A;
- Sv-10GA;
- Sv-08GSMT.
This is not a complete list of wire brands. They are divided not only by characteristics, but also by applicability. There are materials for the manufacture of electrodes, wires for welding copper-plated surfaces, and wires for surfacing.
18130-79 and 13821-77
Currently, GOST standards adopted back in 1977 remain relevant. They prescribe the functional features of welding equipment, in particular, semi-automatic machines for argon arc welding. The list of requirements includes such as functionality, resistance to external factors, welding current values, availability of measuring and control instruments.
Such a variety of requirements does not allow us to formulate all the standards in one document, therefore this GOST refers to a number of minor regulatory documents. Thus, standardization of the argon arc welding process has a comprehensive approach. The total number of major and minor standards amounts to several dozen approved and adopted documents that are still in force at the present time, with the exception of some minor changes.