Spring wire GOST 9389-75 is a cold-drawn carbon steel wire used for the manufacture of cold-wound springs that are not subject to hardening.
A spring is an elastic element used to absorb shocks and shocks, vibration isolation, create specified initial forces, and accumulate mechanical energy.
Spring wire GOST 9389-75 is manufactured:
- by mechanical properties: grades A, B, C;
- classes 1, 2, 2A, 3.
- normal accuracy;
Spring wire of classes 1, 2, 3 is manufactured with normal and increased accuracy, class 2A - with increased accuracy.
Types and method of manufacture
In industry and in everyday life, various types of metal have become the most in demand. After heat treatment they acquire powerful spring properties. Such alloys include:
At factories, wire GOST 9389–75 is produced in two types of accuracy:
The cross-section of the spring wire GOST 9389 75 should not exceed the range of 0.2−30 mm. Typically the product has a round cross-section. Sometimes special-purpose parts may have a different geometric appearance:
To manufacture this fastener, the drawing method is used. The workpiece is pulled through holes of different diameters. The diameter of the hole gradually decreases. At the finishing stage there is a calibration die. This technology makes it possible to obtain high accuracy and the size of a given section. The result is a smooth surface without burrs.
Then the product undergoes heat treatment. As a result, spring properties are improved and the tensile strength coefficient increases.
The finished product in the coil is coated with a thick layer of preservative lubricant. It protects the wire from rust and corrosion. The bay is wrapped in moisture-proof paper. The finished coil is additionally covered with plastic film.
Characteristics of spring material
Wire GOST 9389–75 has its own technological features. High precision products are designated 2A. The remaining groups have lower rates. The main parameters that you need to pay attention to are:
- Cross section - 0.14−8 mm.
- The permissible error in diameter is no more than 0.05 mm.
- Each class has a different breaking resistance coefficient. It is subject to regulatory requirements. Its value should be in the range 1030−3090 N/mm2.
- The number of twists depends on the material of manufacture. Typically this number does not exceed 4−35 times.
- The weight of the product depends on its diameter. The calculation is carried out for 1000 meters.
Finished products can be subjected to several technological operations according to individual customer requirements:
Application areas of fasteners
Steel spring wire has become widespread in several industries in the creation of various metal structures.
A large amount of this material is used in the manufacture of springs. Moreover, these products belong to heavily loaded devices. This type of spring is subjected to special tests regarding its wear resistance. After winding, all springs must be hardened. To create a rigid structure, the product was also used in the furniture industry. Finished products are shipped in special coils or coils. Excellent packaging saves the product from corrosion.
Spring wire is constantly used during general construction work as the main material from which the spring is made.
Unlike ordinary wire, spring wire has memory. This property is widely used to create beautiful jewelry.
The composition of this product includes an alloy of neodymium and titanium. The cost of this material is very high. However, this combination gives the product unique properties.
You can purchase such steel wire with memory in a store that sells goods for folk art. It will be possible to make bracelets from it that can retain their shape.
The originality of memory wire is that if it is straightened and then heated after a few hours, it will return to its original appearance. To remember, the product should be given the desired shape - let it lie and then straighten it. After heating, the wire will take its previous appearance.
In stores, such products are sold in the form of beautiful rings. It is in this form that they retain their shape. Rings are available in different diameters.
Various types of springs used in the automotive industry are made from such wire. In almost every modern car you can find a large number of springs of different diameters that perform important work.
Recommendations for the use of spring wire depending on brands and classes
- The relative strength run-up is calculated using the formula:
- K = Δσв / σв
- Where:
- Δσв — run-up of temporary tensile strength in a batch, N/mm2;
- σв is the minimum value of tensile strength in the class, N/mm2.
Diameter and maximum deviations along it of spring wire
1. At the request of the consumer, the supply of wire of intermediate diameters is allowed. In this case, the maximum deviations in diameter must correspond to those established for the nearest larger diameter.
2. The ovality of the wire should not exceed half of the diameter tolerance range.
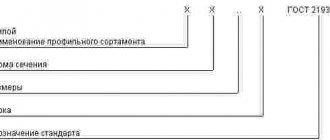
- Examples of symbols:
- Spring wire, grade A, class 1, increased precision, diameter 1.20 mm:
- Wire A-1-P-1.2 GOST 9389-75
- Spring wire grade B, class 3, normal accuracy, diameter 2.0 mm:
- Wire B-3-2 GOST 9389-75
- Spring wire grade B, class 2A, increased precision, diameter 1.20 mm:
- Wire B-2A-1.2 GOST 9389-75
Steel carbon spring wire GOST 9389 is manufactured in accordance with the requirements of the standard according to technological regulations approved in the prescribed manner, from carbon steel in accordance with GOST 1050-88, GOST 14959-79, GOST 1435-90 or according to normative and technical documentation, as well as from steels grades KT-2 and ZK-7, the chemical composition of which is indicated in Table 2, and other special steels manufactured according to regulatory and technical documentation. In this case, class 2A wire must be made of steel with a mass fraction of sulfur not exceeding 0.030% and phosphorus not exceeding 0.035%.
TEST METHODS
4.1. For each type of test, one sample is taken from both ends of the skein for each type of test or one sample from each coil being tested. (Changed edition, Amendment No. 1).
4.2. The diameter and ovality of the wire are measured with micrometers in accordance with GOST 6507 and GOST 4381 in two mutually perpendicular directions of the same section of the wire or with another measuring instrument that provides the necessary measurement accuracy. (Changed edition, Amendment No. 3).
4.3. Inspection of the wire surface is carried out visually, and in controversial cases, using a five-fold magnifying glass. The depth of the wire defect should be determined by removing it by stripping, followed by comparative measurements of the wire in stripped and uncleaned areas. If it is impossible to determine the depth of a defect by cleaning, the depth and nature of the defect is determined by micro-examination.
4.4. Testing of wire for temporary resistance is carried out according to GOST 10446–80.
4.5. The bending test of the wire is carried out around a cylindrical core until the sides are parallel in accordance with the requirements of clause 2.5. (Changed edition, Amendment No. 4).
4.6. The torsion test is carried out in accordance with GOST 1545, with the length of the tested part of the sample being set equal to 100(—wire diameter), but not less than 50 and not more than 500 mm. The non-delamination torsion test is carried out until the sample is completely destroyed. Inspection of fractures is carried out with the naked eye. For wires with a diameter of less than 0.8 mm, a five-fold magnification magnifying glass can be used. Note. Until 01/01/90, testing of wire for non-delamination is carried out by agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer. (Changed edition, Amendment No. 3, 5).
4.7. Determination of the depth of decarburization is carried out according to the M method of GOST 1763.
4.8. The coiling test of the wire is carried out in accordance with GOST 10447. If disagreements arise in assessing the quality of the wire according to clause 2.5, instead of the coiling test, a bending test is carried out.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 3).
4.9. The absence of waviness is ensured by the manufacturing technology.
If disagreements arise in the assessment of waviness, it is determined on samples with a working length of (200 ± 0.5) mm with a micrometer in accordance with GOST 6507, equipped with a special heel (Appendix 2) using 10 measurements in two mutually perpendicular directions along the length of the sample. The samples must be secured in the clamps of a tensile testing machine in accordance with GOST 28840 or another machine in accordance with regulatory and technical documentation that allows the required load to be applied. A wire is considered wavy if the number of deviations from a constant diameter measured in one of the planes is 3 or more measurements. The magnitude of the deviations must be greater than the error of the measuring instrument. (Changed edition, Amendment No. 5).
4.10. To determine mechanical properties, it is allowed to use statistical and non-destructive testing methods according to methods approved in the prescribed manner.
4.9, 4.10. (Introduced additionally, Amendment No. 3).
Spring wire GOST (9389-75)
The requirements for the functional qualities of steel spring wire are determined by the GOST 9389-75 .
As for dividing the product into conditional categories, spring wire is classified according to manufacturing accuracy, grades and classes of mechanical strength, as well as in accordance with the grade of steel used to produce the product. Depending on the manufacturing precision, steel spring wire can be:
- Normal accuracy.
- Increased accuracy (symbol P). This variety is used in the production process of the most critical components of certain devices.
In accordance with the indicators of mechanical strength, carbon steel spring wire is divided into grades (A, B, C), as well as classes (1, 2, 2A and 3).
The diameter of the finished product can range from 0.2 to 8 millimeters. Its final cost depends on this indicator, as well as on the accuracy of manufacturing the spring wire.
Thus, a wire with a smaller diameter will cost more than a thicker analogue.
After manufacturing, the product is in most cases treated with a special preservative oil that protects the wire from the negative effects of corrosion. The coils and skeins in which the finished product is supplied are packaged with polymer film and moisture-proof paper. The surface of the spring wire should not have nicks, cracks, dulls or rust.
PACKAGING, LABELING, TRANSPORTATION AND STORAGE
5.1. Each skein must be firmly tied with soft wire according to regulatory and technical documentation in at least three places evenly spaced around the circumference. Rolls of wire with a diameter of 0.60 mm or less can be tied with the end of a wound wire or twine in accordance with GOST 17308 or other regulatory and technical documentation. Skeins of the same class, group and diameter can be knitted into coils. The end of the upper piece of wire on the reel should be secured to the cheek of the reel. (Changed edition, Amendment No. 3, 5).
5.2. The wire must be coated with preservation oils (lubricants) of type NG-203A or NG-203B according to TU 38−1011331−90 or K-17 according to GOST 10877. It is allowed to use other oils (lubricants) that provide corrosion protection. Wire on spools may be supplied ungreased.
5.2. (Changed edition, Amendment No. 3).
5.3. Reels with wire with a diameter of less than 0.20 mm must be wrapped in a layer of paper and placed in wooden boxes in accordance with GOST 18617 or other normative and technical documentation, or in metal containers made according to normative and technical documentation, lined with waterproof paper on the inside. Hanks, coils of wire with a diameter of 0.20 mm or more must be wrapped in a layer of paper, then in a layer of polymer film or non-woven materials, or fabric made of chemical fibers. For mechanized packaging, coils of wire must be wrapped in a layer of cable crepe paper in accordance with GOST 10396 or KMV-170 grade paper, or other crepe paper with equivalent protective properties, or polymer film with the packaging secured with wire in accordance with GOST 3282 or other wire. By agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, the wire may not be packaged or lubricated. The following packaging materials are used: waxed paper in accordance with GOST 9569 (it is allowed to use two-layer packaging paper in accordance with GOST 8828 or oiled packaging paper in accordance with GOST 8273 grade A, or other paper that provides corrosion protection); polymer film according to GOST 10354, GOST 16272 or other polymer film;
containerized canvas stitched or glued fabric, stitching tape from textile industry waste or fabric from chemical fibers according to regulatory and technical documentation. Wire sent to the Far North and hard-to-reach areas is packaged in accordance with GOST 15846. (Changed edition, Amendment No. 1, 3).
5.3a. The weight of one piece of cargo must be no more than 1500 kg. The consolidation of cargo items into transport packages must be carried out in accordance with GOST 21650, GOST 24597. (Introduced additionally, Amendment No. 3, 5).
5.4. Each coil, coil or coil of wire must have a label firmly attached to it, indicating: the trademark or the name and trademark of the manufacturer; wire symbol; technical control mark; batch number. (Changed edition, Amendment No. 1, 3).
5.5. (Deleted, Amendment No. 2).
5.6. Wire is transported by all types of transport in accordance with the rules for the transportation of goods in force for this type of transport. The placement and securing of cargo in vehicles must comply with the technical conditions for loading and securing cargo. Wire transportation by rail is carried out by carload, small or low-tonnage shipments. It is allowed to transport wire in universal containers in accordance with GOST 15102, GOST 20435, GOST 22225. Transportation conditions must comply with storage conditions 5 GOST 15150. (Changed edition, Amendment No. 3, 5).
5.7. Wire storage is according to storage conditions 3 GOST 15150. (Changed edition, Amendment No. 3).
5.8. Transport marking according to GOST 14192. (Introduced additionally, Amendment No. 3).
technological features of carbon steel spring wire, areas of application
When a part needs to be given elasticity, as well as special spring properties, GOST 9389–75 “Spring carbon steel wire” is used for its manufacture. Such a detail can have a variety of types. Sometimes it is a strong spring, in other cases it is a pin or hook. The most important quality of spring wire is considered to be high strength. It is able to withstand a large number of compressions without destruction due to metal fatigue.
Types and method of manufacture
In industry and in everyday life, various types of metal have become the most in demand. After heat treatment they acquire powerful spring properties. Such alloys include:
At factories, wire GOST 9389–75 is produced in two types of accuracy:
The cross-section of the spring wire GOST 9389 75 should not exceed the range of 0.2−30 mm. Typically the product has a round cross-section. Sometimes special-purpose parts may have a different geometric appearance:
To manufacture this fastener, the drawing method is used. The workpiece is pulled through holes of different diameters. The diameter of the hole gradually decreases. At the finishing stage there is a calibration die. This technology makes it possible to obtain high accuracy and the size of a given section. The result is a smooth surface without burrs.
Then the product undergoes heat treatment. As a result, spring properties are improved and the tensile strength coefficient increases.
The finished product in the coil is coated with a thick layer of preservative lubricant. It protects the wire from rust and corrosion. The bay is wrapped in moisture-proof paper. The finished coil is additionally covered with plastic film.
Characteristics of spring material
Wire GOST 9389–75 has its own technological features. High precision products are designated 2A. The remaining groups have lower rates. The main parameters that you need to pay attention to are:
- Cross section - 0.14−8 mm.
- The permissible error in diameter is no more than 0.05 mm.
- Each class has a different breaking resistance coefficient. It is subject to regulatory requirements. Its value should be in the range 1030−3090 N/mm2.
- The number of twists depends on the material of manufacture. Typically this number does not exceed 4−35 times.
- The weight of the product depends on its diameter. The calculation is carried out for 1000 meters.
Finished products can be subjected to several technological operations according to individual customer requirements:
Application areas of fasteners
Steel spring wire has become widespread in several industries in the creation of various metal structures. A large amount of this material is used in the manufacture of springs. Moreover, these products belong to heavily loaded devices. This type of spring is subjected to special tests regarding its wear resistance. After winding, all springs must be hardened. To create a rigid structure, the product was also used in the furniture industry.
Finished products are shipped in special coils or coils. Excellent packaging saves the product from corrosion.
GOST 9389-75 Carbon steel spring wire. Specifications (with Amendments No. 1-5)
CARBON STEEL SPRING WIRE
Carbon steel spring wire. Specifications
MKS 77.140.65 OKP 12 2100
Date of introduction 1977-01-01
1. DEVELOPED AND INTRODUCED by the USSR Ministry of Ferrous Metallurgy
2. APPROVED AND ENTERED INTO EFFECT by Resolution of the State Committee of Standards of the Council of Ministers of the USSR dated July 17, 1975 N 1830 Change No. 5 was adopted by the Interstate Council for Standardization, Metrology and Certification (Minutes No. 20 dated November 1, 2001) Voted for adoption:
Name of the national standardization body
State Standard of the Republic of Belarus
Gosstandart of the Republic of Kazakhstan
3. INSTEAD GOST 9389-60
4. REFERENCE REGULATIVE AND TECHNICAL DOCUMENTS
5. The validity period was lifted according to Protocol No. 2-92 of the Interstate Council for Standardization, Metrology and Certification (IUS 2-93)
6. EDITION with Amendments No. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, approved in February 1983, December 1984, December 1987, January 1990, March 2002 (IUS 5-83, 3- 85, 3-88, 4-90, 6-2002) Amendments were made, published in IUS N 7 2003, IUS N 6 2007
Amendments made by the database manufacturer
This standard applies to cold-drawn carbon steel wire used for the manufacture of springs that are cold-wound and not subject to hardening. (Modified edition, Amendment No. 3).
TYPES AND MAIN SIZES
1.1. The wire is produced:
a) by mechanical properties: grades A, B, B; classes 1, 2, 2A, 3. Recommendations for the use of spring wire depending on the grades and classes are given in Appendix 3.
b) in terms of manufacturing accuracy: normal accuracy; increased accuracy - P. Wire of classes 1, 2, 3 is manufactured with normal and increased accuracy, class 2A - increased accuracy. (Changed edition, Amendment No. 3, 4).
1.2. The wire diameter and maximum deviations along it must correspond to those indicated in Table 1.
Nominal wire diameter
Maximum deviation for wire diameter
Notes:1. At the customer's request, it is possible to supply wire of intermediate diameters. In this case, the maximum deviations in diameter must correspond to those established for the nearest larger diameter.2. The theoretical mass of the wire is given in the appendix.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 3, 4).
1.3. The ovality of the wire should not exceed half the diameter tolerance range.
Examples of symbols:
Wire grade A, class 1, increased precision, diameter 1.20 mm:
Wire A-1-P-1.2 GOST 9389-75
The same, brand B, class 3, normal accuracy, diameter 2.0 mm:
Wire B-3-2 GOST 9389-75
The same, brand B, class 2A, increased accuracy, diameter 1.20 mm:
Wire B-2A-1.2 GOST 9389-75
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 3, 4).
TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS
2.1. Steel carbon spring wire must be manufactured in accordance with the requirements of this standard according to technological regulations approved in the prescribed manner, from carbon steel in accordance with GOST 1050, GOST 14959, GOST 1435 or according to regulatory and technical documentation, as well as from steel grades KT-2 and 3K -7, the chemical composition of which is indicated in Table 2, and other special smelting steels manufactured according to regulatory and technical documentation. In this case, class 2A wire must be made of steel with a mass fraction of sulfur not exceeding 0.030% and phosphorus not exceeding 0.035%.
At the request of the consumer, the wire is made from a certain grade of steel. (Changed edition, Amendment No. 2, 3).
2.2. On the surface of the wire there should be no cracks, films, sunsets, hairlines, shells and rust. Risks with a depth of no more than half the tolerance field in diameter are allowed, as well as remnants of technological coatings applied to the surface of the wire to prepare the metal for drawing. Class 2A wire for aviation industry must be without traces of technological copper plating of the surface. (Changed edition, Amendment No. 3).
2.3. The mechanical properties of the wire must comply with the standards specified in Table 3.
Wire diameter, mm
Tensile strength, N/mm (kgf/mm)
Dispersion of temporary tensile strength in a batch, no more, N/mm (kgf/mm)
Number of twists, not less
ACCEPTANCE RULES
3.1. Wire is accepted in batches. The batch must consist of coils or coils of wire of the same diameter, the same class and the same manufacturing accuracy and must be documented with a quality document containing: a trademark or the name and trademark of the manufacturer; wire symbol; batch number; number of cargo spaces; net weight; steel grade; acceptance date. (Changed edition, Amendment No. 2).
3.2. Each skein or reel of the batch is checked for size and appearance.
3.3. To check the mechanical properties and waviness, if there is disagreement in the assessment of this indicator, 10% of the skeins or 20% of the coils, but not less than five skeins or spools, are selected, and to check the decarbonization of 2% of the skeins or spools, but not less than three. (Changed edition, Amendment No. 3).
3.4. If unsatisfactory test results are obtained for at least one of the indicators, a repeat test is carried out for this indicator on a double number of skeins (coils) taken from those that did not pass the test. The results of repeated tests apply to the entire batch. If unsatisfactory results of repeated tests are obtained in terms of the “waviness” of the wire, the manufacturer carries out continuous monitoring of this indicator. (Changed edition, Amendment No. 1, 3).
Metaltorg LLC :: Spring wire in Yekaterinburg|metalltorg.su
Good afternoon We offer for delivery from a warehouse in Yekaterinburg wholesale and retail spring wire GOST 9389-75 (patented), (piano), (OVS-especially high resistance, VS-high resistance) steel grades 60,65,70,75,80 ,U8GA,U9A, 1 class, 2 class, 2A class diameters: 0.2 mm; 0.3mm; 0.4mm; 0.5mm; 0.6mm; 0.7mm; 0.8mm; 0.9mm; 1mm; 1.1mm; 1.2mm; 1.4mm; 1.5mm; 1.6mm; 1.8mm; 1.9mm; 2mm; 2.2mm;2.5mm; 3mm; 3.2mm; 3.5mm; 4mm; 4.5mm; 5mm, 6mm; 7mm; 8mm. The wire is used for the manufacture of springs, wound in a cold state and not subjected to hardening, and also, as a wire with elastic and rigid properties, it is used: for pulling cables in pipes, hanging cables, cleaning sewers, for making spring blocks of mattresses, traps, plumbing cables, in modeling, as well as in the production of various household and useful products. The wire is supplied with or without lubricant, in coils: d.0.2mm-0.8mm in coils from 18kg-80kg, d.1mm-4mm from 90-250kg, d.5-8mm from 300kg-1.5t. MetalTorg LLC offers for supply #piano spring wire# GOST 9389-75 wholesale and retail in coils from 1 kg. One of the most frequently asked questions is what grade of wire should I choose?
Wire class 1 according to GOST 9389. High tensile strength. The presence of large residual stresses of the first kind (from drawing and winding) causes the appearance of residual deformations of springs at stresses t 3 > 0.32 Rm. When v max > v k the residual deformations are high, regardless of the application of the captive operation.
Wire of classes 2 and 2A according to GOST 9389. Differs from wire of class 1 in reduced tensile strength and increased ductility. It is used for products operating at low temperatures, as well as for tension springs with complex hook designs. Wire of class 2A differs from wire of class 2 in higher dimensional accuracy, reduction of harmful impurities in the metal and further increase in ductility.
We offer fast delivery of any volume of spring wire to any region of Russia and the CIS along the most optimal route according to the scheme: min. Price - min. Term, with shipment on the day of payment. We will be glad to see you among our beloved clients. Our advantages: any wire GOST 9389-75 in our company is subject to unwinding with subsequent weight control, diameter checking, packaging. We sell any volumes of carbon spring wire, you do not have to buy multi-kilometer skeins if you need, for example, to purchase 10 meters of wire. The goods you paid for are shipped through transport companies of your choice; we provide free delivery to the terminals of transport companies in our city. The most frequently asked question is whether it is necessary to heat treat a spring made from GOST 9389-75 wire? Attention! For information on heat treatment of wire GOST 9389-75 in the manufacture of springs, see below!
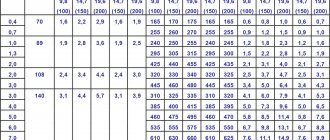
APPENDIX 1 (for reference). Theoretical weight of 1000 m wire
APPENDIX 1 Reference
| Wire diameter, mm | Cross-sectional area, mm | Weight 1000 m, kg |
| 0,14 | 0,0154 | 0,1208 |
| 0,15 | 0,0177 | 0,1387 |
| 0,16 | 0,0201 | 0,1578 |
| 0,18 | 0,0254 | 0,1994 |
| 0,20 | 0,0314 | 0,2465 |
| 0,22 | 0,0380 | 0,298 |
| 0,25 | 0,0491 | 0,385 |
| 0,28 | 0,0616 | 0,484 |
| 0,30 | 0,0707 | 0,555 |
| 0,32 | 0,0804 | 0,631 |
| 0,36 | 0,1018 | 0,80 |
| 0,40 | 0,1257 | 0,99 |
| 0,45 | 0,159 | 1,25 |
| 0,50 | 0,196 | 1,54 |
| 0,56 | 0,246 | 1,93 |
| 0,60 | 0,283 | 2,22 |
| 0,63 | 0,312 | 2,45 |
| 0,70 | 0,385 | 3,02 |
| 0,75 | 0,442 | 3,47 |
| 0,80 | 0,503 | 3,95 |
| 0,85 | 0,567 | 4,45 |
| 0,90 | 0,636 | 4,99 |
| 1,00 | 0,785 | 6,17 |
| 1,10 | 0,950 | 7,46 |
| 1,20 | 1,131 | 8,88 |
| 1,30 | 1,327 | 10,42 |
| 1,40 | 1,539 | 12,08 |
| 1,50 | 1,767 | 13,87 |
| 1,60 | 2,01 | 15,78 |
| 1,70 | 2,27 | 17,82 |
| 1,80 | 2,54 | 19,94 |
| 1,90 | 2,84 | 22,26 |
| 2,00 | 3,14 | 24,65 |
| 2,10 | 3,46 | 27,19 |
| 2,20 | 3,80 | 29,83 |
| 2,30 | 4,15 | 32,58 |
| 2,50 | 4,91 | 38,54 |
| 2,80 | 6,16 | 48,36 |
| 3,00 | 7,07 | 55,50 |
| 3,20 | 8,04 | 63,11 |
| 3,40 | 9,08 | 71,28 |
| 3,50 | 9,62 | 75,52 |
| 3,60 | 10,18 | 79,9 |
| 4,00 | 12,57 | 98,7 |
| 4,20 | 13,85 | 108,7 |
| 4,50 | 15,90 | 124,8 |
| 5,00 | 19,63 | 154,2 |
| 5,60 | 24,63 | 193,3 |
| 6,00 | 28,3 | 221,9 |
| 6,30 | 31,7 | 244,4 |
| 6,50 | 33,2 | 260,5 |
| 6,70 | 35,3 | 276,8 |
| 7,00 | 38,5 | 302,1 |
| 7,50 | 44,2 | 346,8 |
| 8,00 | 50,3 | 394,6 |