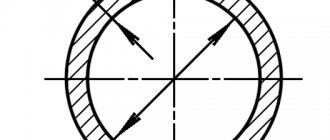
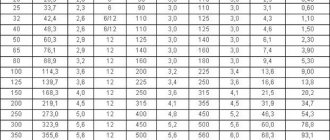
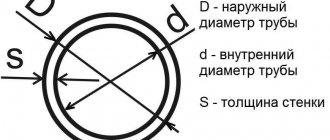
The main types of diameters of galvanized pipes are: external electric welded according to GOST 10704 and internal water and gas pipes according to GOST 3262. The main dimensions of the diameter of a galvanized pipe are the nominal diameter (DN) in inches and millimeters and the external diameter in millimeters. The diameters of galvanized steel pipes are presented in the table below:
| internal diameter of galvanized pipe, mm | internal diameter of galvanized pipe in inches | external, outer diameter of galvanized pipes, mm | wall thickness | weight of a meter, kg per 1 mp |
| DN Ø 6 | ¼″ | Ø 10.2 mm | 1.8, 2.0, 2.5 | 0,37, 0,40, 0.47 |
| DN Ø 8 | ⅓″ | Ø 13.5 mm | 2.0, 2.2, 2.8 | 0,57, 0.61, 0.74 |
| DN Ø 10 | 2/5″ | Ø 17 mm | 2.0, 2.8 | 0.74, 0.98 |
| DN Ø 15 | ½″ | Ø 21.3 mm | 2.5, 2.8, 3.2 | 1.16, 1.28, 1.43 |
| DN Ø 20 | ¾″ | Ø 26.8 mm | 2.5, 2.8, 3.2 | 1.50, 1,66, 1.86 |
| DN Ø 25 | 1″ | Ø 33.5 mm | 2.8, 3.2, 4.0 | 2.12, 2.39, 2.91 |
| DN Ø 32 | 1 ¼″ | Ø 42.3 mm | 2.8, 3.2, 4.0 | 2,73, 3,09, 3.78 |
| DN Ø 40 | 1 ½″ | Ø 48 mm | 3.0, 3.5 | 3,33, 3,84 |
| DN Ø 50 | 2″ | Ø 60 mm | 3.0, 3.5, 4.5 | 4.22, 4,88, 6.16 |
| DN Ø 65 | 2 ½″ | Ø 75.5 mm | 3.2, 4.0, 4.5 | 5.71, 7,05, 7.88 |
| DN Ø 80 | 3″ | Ø 88.5 mm | 3.5, 4.0, 4.5 | 7.34, 8,34, 9.32 |
| DN Ø 90 | 3 ½″ | Ø 101.3 mm | 3.5, 4.0, 4.5 | 8.44, 9.6, 10.74 |
| DN Ø 100 | 4″ | Ø 114 mm | 4.0, 4.5, 5.0 | 10.85, 12,15, 13.44 |
| DN Ø 125 | 5″ | Ø 140 mm | 4.0, 4.5, 5.5 | 13.42, 15.04, 18.24 |
| DN Ø 150 | 6″ | Ø 165 mm | 4.0, 4.5,5.5 | 15.88, 17.81, 21.63 |
Diameters of galvanized steel pipes
Galvanized pipes are produced in accordance with GOST 3262-75 and GOST 10704-91.
Length from 6 to 12 meters. According to GOST 3262, pipes are called galvanized water and gas pipes. Measured by internal diameter in inches and millimeters. Example of designation: VGP galvanized pipe 50x3.5 st3sp dl6m GOST 3262-75.
According to GOST 10704, pipes are called galvanized round electric-welded longitudinal pipes. Measured by outer diameter in millimeters. Designation example: Galvanized pipe 89x4 st3sp dl12m GOST 10704-91.
Our table shows the main diameters of electric-welded galvanized steel pipes.
Galvanized pipe
Galvanized steel water and gas pipes (WGP) are widely used in construction. Due to the galvanized coating, a galvanized water and gas pipe (WGP) acquires anti-corrosion properties. Galvanized water pipes are used for water supply in construction, which is why they are called galvanized water pipes. The dimensions of galvanized steel VGP pipe are the same as those of ordinary black VGP pipe. The indicator is the nominal diameter (DN), but although the wall thickness may be different, only the outer diameter of the galvanized steel water and gas pipe remains unchanged. Due to the great popularity and widespread use of galvanized VGP pipes, manufacturing plants began to produce VGP pipes with zinc coating in accordance with GOST 3262-75.
Galvanized pipes
Steel pipes are durable and reliable, but they have a significant drawback - a high corrosion rate under the influence of water (up to 0.18-1.0 mm per year).
Galvanized pipes - metal products of round cross-section with surfaces coated with a zinc compound - do not have this drawback. Despite the fact that the coating thickness usually does not exceed 30 microns, it significantly reduces the corrosion rate (up to 0.015-0.020 mm per year) and increases the overall service life of the entire pipeline (up to 25 years).
The quality of galvanized pipes is determined by the nature of the surfaces (traces of technical processing and minor dents are acceptable, while scratches, cracks and swelling indicate a violation of the technology) and the degree of processing of the cuts (threads may be absent, but if there are any, they must be smooth, accurate, without burrs).
VGP pipes
Water and gas pipes are a complex category, including metal pipes made of carbon steel (St1, St2, St3), as well as steel grades 08, 10, 20. In this case, the selection of material and production of VGP pipes is carried out in accordance with regulatory documents (GOST 3265-75 , GOST 380, GOST 1050, GOST 3262-75).
Galvanizing is one of the modern and advanced types of anti-corrosion coating, which greatly increases the service life of the metal: galvanized pipes. Galvanized pipes are widely used in road construction: guides and pillars, water outlet and drainage pipes, lighting masts, supports for road signs. Galvanized pipes are also widely used in urban infrastructure: flagpoles, elements of advertising structures, bus stops, sports and playgrounds. Plumbing work, the production of metal structures, laying channels for cables and wires are also areas where galvanized pipe is used.
Areas of use of steel pipes
The use of galvanized pipes is in demand in the public sector, in the construction of industrial and residential buildings. Galvanized pipes are installed in heating systems, water supply systems, pumping gas and oil products.
A galvanized product is recommended for outdoor lighting. Products with strong seams, galvanized on the inside and outside, are used in plumbing, fire pipe lines, and smoke exhaust systems.
- Galvanized rolled metal is used in the construction of highways.
- Pipes are used to make supports for road signs, traffic lights, and to create fences for bridges.
- The galvanized ball is 30 microns thick – provides resistance to corrosive chemicals and high humidity.
Galvanized products are used in the construction of trade pavilions, repair shops, hanging structures, gyms, warehouses, and car parks.
In private buildings it is used for ventilation systems, air ducts, fence supports, and outbuildings. In agriculture it is used to create greenhouses and conservatories.
Which is better: stainless steel or galvanized?
The formulation “Which is better?” - fundamentally not true. First of all, stainless (alloy) and galvanized steel are produced using completely different technologies, which ultimately determine their physical characteristics, scope and cost.
- The corrosion resistance coefficient of both materials is quite high and largely depends on the characteristics of production and the quality of the raw materials.
- Stainless steel is in many ways more resistant to extremely high temperatures than galvanized steel, which should be taken into account when installing, for example, chimneys.
- The price of galvanizing is usually 20-25% lower.
Advantages and disadvantages of galvanized steel pipes
Compared to polymer pipes, galvanized pipes have a number of advantages:
- High index of strength and resistance to intra-circuit pressure and mechanical damage.
- Dimensional stability over a wide range of operating temperatures: no cracking in frost and no expansion under high temperatures.
- High level of heat and energy conductivity.
Non-galvanized steel analogues are inferior to galvanized ones in a number of characteristics:
Resistance of the external and internal circuit to corrosive processes.
- The smooth inner surface of the pipes is not prone to the formation of internal build-up, which narrows the passage opening. In addition, this feature allows the use of galvanized pipelines for organizing drinking water supply.
- The antiseptic properties of zinc disinfect water transported through pipes.
Among the disadvantages it should be noted:
- Unpresentable appearance.
- Reduced anti-corrosion resistance when the galvanized layer is damaged.
- Higher cost compared to plastic and conventional metal pipes.
Labeling, packaging, transportation and storage
The marking for VGP bends with a cross-section of up to 159 mm is placed on the label. It includes the standard sizes of the VGP product, alloy grade, and manufacturer’s trademark. The label is attached to the product packaging.
During transportation, products are securely secured with various devices to prevent their arbitrary movement.
Store galvanized pipes on racks and platforms in the open air. They are laid in groups according to standardization and steel grades to eliminate the possibility of mixing.
Advantages and disadvantages
The considered galvanized VGP bends have the following advantages:
- Higher anti-corrosion resistance.
- Extended service life (up to 25 years).
- Blockages inside form much slower than with non-galvanized bends.
- Withstands operating temperatures of 140 degrees.
Experts include the following disadvantages:
- Rapid appearance of rust in welding areas.
- High cost compared to black pipe.
Flaring of steel VGP pipes
The need for flaring arises when it is not possible to butt weld the VGP pipes. For example, when they are closely located near walls.
Moreover, SNiP indicates that the connection of steel bends (both non-galvanized and galvanized) with a nominal diameter of up to 25 mm should be carried out by socket welding.
For flaring, various types of cone-shaped nozzles are used, which, with the help of mechanical forces, expand the end of the pipe, giving it the shape of a bell. To speed up the process, the VGP outlet is heated with a gas burner.
Average price per meter and per ton
The cost of galvanized structures is approximately one and a half times higher than the cost of black bends. Prices are set based on the standard sizes of products.
For example, the retail price of a galvanized bend with a DN of 20 mm and a wall of 2.8 mm will be 121 rubles per meter.
A similar galvanized pipe, but with a DN of 40 mm and a wall of 3.5 mm, will cost 257 rubles.
In the case of wholesale sales, goods are sold by weight, prices are determined per ton. The above-mentioned VGP outlet DU 20×2.8 will cost 66.9 thousand rubles per ton.
Installation features
The assembly of pipelines from galvanized steel pipes is carried out:
- Welding connection.
- Using threads and fittings.
Given the difficulties with welding pipes, they often turn to the threaded method on fittings. I recommend using either galvanized or stainless steel connectors. This will help avoid problems with corrosion from contact of galvanized bends with simple steel parts.
Galvanized elbows with quick-release connections have appeared on sale. They are used in many industrial areas, including the laying of communications with drinking water.
As for welding, here you can use one of the options:
- Thoroughly clean the joint area from the zinc coating.
- Carry out the welding connection as usual.
- Apply a spray containing zinc to the area.
Galvanizing process
Galvanizing technology involves coating steel pipes with a thin layer of zinc, both inside and outside. The resulting zinc coating has a characteristic light shade, for which it is called “white rust.” The service life of the pipeline depends on its thickness and quality of application.
There are 5 technologies for galvanizing pipes, of which the first 3 are the main ones:
- Electrogalvanic.
- Thermal diffuse.
- Hot.
- Cold.
- Gas thermal.
Electrogalvanics (galvanostegy)
Electrogalvanics, or more precisely, its subsection - electroplating - is the most common method of galvanizing metal pipes. Through electrolysis (exposure to electric current passing through cyanide, non-cyanide or acidic electrolytes), zinc electrodes are dissolved, followed by the deposition of zinc on the pipes. Production processes are regulated by GOST 9.301-86.
The thickness of the zinc coating applied by electroplating varies in the range of 10-30 microns and depends on the technical parameters of production: current strength, heating temperature, etc.
Advantages of electrogalvanic galvanizing:
- Integrity, uniformity and high density of the zinc layer.
- Attractive glossy appearance, thanks to which these products are widely used as stair railings, in the manufacture of furniture and stand equipment.
- Low price category.
Connection methods
Pipe joining is done in two ways:
- Threaded connection through a fitting.
- Welding.
Most connections of galvanized pipes are made using threaded fittings. The joints are sealed using plumbing flax, which has been tested for decades. Only instead of the outdated red lead, they coat it with ordinary silicone sealant.
Welding leads to damage to the zinc coating and further corrosion of the metal in this area. To reduce the negative aspects of this operation, various welding methods are used.
Installation rules
Couplings, tees and other fittings used in assembling a galvanized pipeline must be made of galvanized steel.
First, mark the joints. Take into account that when joining with a coupling, the ends of the pipes should be at a distance of 3-4 mm from each other.
Lay out the tools prepared in advance and the purchased connecting fittings.
Welding connection
To obtain a high-quality weld, first clean the joint from the galvanized layer and carry out welding work as usual. After welding, a spray containing zinc is applied to the unprotected area.
An option is to use special fluxes. During welding, flux draws off excess heat and prevents the zinc layer from evaporating from the edges of the outlet.
When using manual electric arc welding, it is better to use rutile-coated electrodes.
Threaded assembly
Prepare the bends: cut them to the required size, file the edges.
Install the desired die into the tool and prepare the thread.
Optimally, you need to make 7 turns.
A similar operation is performed with another pipe.
Strands of flax are wound outside the turns and the elements are connected using a coupling. The connecting element is secured with a locknut.
No welding or threading
A coupling can be installed. One such design is the Gebo coupling, which is actively used for joining polyethylene pipes.
Here, also, a nut and compression rings with a seal are put on the ends of the pipes in a certain sequence. Next, the nut is tightened and a long-term and reliable connection is obtained.
Galvanized pipes with quick-release connections have appeared on the market, which can be used in many areas, including the installation of drinking water pipelines.
Types of galvanized pipes (range) and their technical characteristics (dimensions and weight)
Based on wall thickness, pipes are divided into:
- Lungs (wall thickness - from 1.8 to 4 mm).
- Standard or ordinary (2 - 4.5 mm).
- Reinforced (2.5 - 5.5 mm).
Galvanized pipes are produced in a wide range of diameters in lengths of 4-12 meters. The outer diameter of the most popular models ranges from 10.2 to 165 mm, conventional - from 6 to 150 mm.
Gas and water
The main purpose is the arrangement of internal water supply and gas communications. The requirements of GOST 3262-75 require the use of only high-quality steel with a density of 7.85 g/cm³ and a zinc coating thickness of up to 0.03 mm for the manufacture of water and gas shut-off pipes (VGP pipes).
The mass of VGP pipes is usually taken from the corresponding tables:
Electric welded
They are used primarily in construction, the agricultural sector and mechanical engineering. Their production is regulated by GOSTs 10704-91 and 10705-80. They are produced mainly in round sections.
Round (seamless)
They are considered universal, because the scope of their use is not limited in any way. Manufactured from high-quality alloy or carbon steel, they are characterized by a long service life and ease of installation. Depending on the forming method, manufacturing technologies are regulated by GOSTs 8734-75 and 8732-78.
Profile
Profile are pipes that have a cross-section different from round - square, rectangular, triangular, etc. The main GOST is 13663-86; separate GOSTs have been developed for each type of configuration: 8639-62 (square), 8645-68 (rectangular), etc.
Sandwich pipes
Sandwich pipes are a double-circuit structure of pipes of different diameters inserted into one another, usually with a layer of thermal insulation material.
Approximate prices
The cost of galvanized pipelines depends on a number of factors (steel grade, galvanizing method, standard size). The price is usually indicated per linear meter or ton (relevant for large-diameter pipes).
| Pipe type | Diameter, mm | steel grade | Length | Price |
| Electric welded VGP | 15 | st3ps-5 | 6 m.; 12 m. | 88 rub./l.m. |
| Electric welded (ESW) | 25 | st3ps-5 | 6 m.; 12 m. | 160 rub./l.m. |
| Electric welded VGP | 159 | st3ps-5 | 6 m.; 12 m. | 890 rub./l.m. |
| Electric welded (ESW) | 820 | 12Х18Н10Т | 6 m. | 27,000 rub./t. |
| Electric welded VGP | 15 | Art.1-3 | 7.8 m. | 56,000 rub./t. |
| Electric welded (ESW) | 133 | Art.1-3 | 7.8 m. | 54,500 rub./t. |
Where are galvanized pipes used?
In addition to the above-mentioned water and gas supply systems, steel pipes coated with a layer of galvanization are actively used in a variety of industries, agriculture, utilities, and construction:
- Arrangement of heating circuits, sewerage systems and chimneys.
- Laying a protective circuit for electrical cables and other wires.
- Construction of building frames, fences, gazebos, benches.
- Arrangement of playgrounds, public transport stops, road signs.
- Creation of advertising and lighting structures.
On a note! The opinion that the use of galvanization for drinking water supply is dangerous to human health is a prejudice. Provided that uninterrupted supply is ensured, the zinc content in water (5 mg/l) does not exceed standard values (10-15 mg).
What is galvanizing
The main disadvantage of iron bends is their rapid rusting. To protect the metal from rust, it is galvanized. The steel surface is coated with a layer of zinc, resulting in the formation of a protective film that does not allow oxygen to reach the metal and prevents the corrosion process.
The thicker and more durable the coating, the longer the galvanized product will last.
Production technology
Galvanizing is carried out on a ready-made steel water pipe, produced in accordance with the requirements of the relevant GOST. The coating can be applied to both suture and seamless products; the technology is the same in any case.
The process includes the following steps:
- Cleaning the surface from scale.
- Heating the workpiece until the metal reaches the required conditions.
- Direct galvanizing process.
- Removing excess zinc using a centrifuge.
- Product cooling.
Galvanizing methods
Three galvanizing methods are used:
- Hot-dip galvanizing is performed by placing the workpiece in a container with zinc melted to 450°.
- Galvanic - during the electrolysis process, zinc from the electrolyte is evenly deposited on the surface of the product and forms a thin protective layer.
- Diffuse galvanizing is the treatment of the workpiece with zinc vapor at temperatures up to 450 degrees in special closed containers. Zinc particles penetrate the steel structure and form a durable coating with a thickness of up to 50 microns. As a result, the galvanized product, in addition to anti-corrosion properties, also receives electrochemical protection.
The first method is the most common, the latter gives the highest quality coverage.
Technical characteristics and properties
Metal pipes are distinguished by high strength. They are able to withstand maximum loads, are resistant to mechanical stress, and have long-term wear resistance.
Galvanizing significantly improves their characteristics and gives the products additional qualities:
- Corrosion resistance.
- Increased throughput by reducing the roughness of the conductive surface.
- Extends service life.
The zinc layer must be uniform throughout the workpiece and its thickness cannot be less than 30 microns.
The coating should not peel off from the workpiece or have foreign inclusions.
Food grade galvanization of water pipes is safe for human health. The maximum permissible concentration of zinc in them does not exceed 5 mg/l (with the daily norm of zinc for people being 10-15 mg).
Important! Galvanization increases the weight of a metal pipe by 3%.
Is it possible to use galvanized chimney?
Galvanized steel is successfully used for arranging chimney circuits. However, some properties of galvanizing, namely toxicity when heated and instability to extremely high temperatures, somewhat limit the scope of its use as a chimney.
It is important to remember that when heated above 419.5⁰C, zinc begins to release metal oxide fumes that are toxic to humans. The greatest danger is posed by the so-called technical zinc, during the production of which even more harmful lead, arsenic and antimony are added to the composition.
Therefore, galvanized chimneys are prohibited from being installed in systems with a heating temperature of more than 350⁰C, which means they are not suitable for heat generators running on coal or wood. But in symbiosis with a heating unit running on gas or diesel fuel, galvanized chimneys are quite safe.
Life time
The “life” period of a galvanized chimney depends on a number of factors:
Wall thickness, which must be at least 1 mm. At lower rates, the pipe burns out already in the first or second heating season.
Buildings. Single-walled ones, as a rule, require replacement after a couple of years, while double-walled (double-circuit) ones can last about 45 years.
The presence of a thermal insulation circuit. Without insulation, harmful condensation forms in the pipe and soot begins to accumulate, which increases the risk of a chimney fire and reduces its service life by at least 3 times.
Types of chimney pipes
Galvanized chimneys and components for them are classified into:
- Single-walled (single-circuit).
- Insulated sandwich chimneys (double-circuit), which in turn are also divided into:
- Mono-structures in which both metal contours are made of galvanized steel;
- Combo designs in which the outer contour is galvanized and the inner contour is made of stainless steel.
Combined chimneys have the best technical characteristics, because... Stainless steel is more resistant to burnout and the influence of an acidic environment, and its lower cost compared to chimney pipes made entirely of stainless steel allows you to significantly save your budget.
Galvanized mono-structures minimize the production of condensate, but cannot withstand heating above 450⁰C. Most often used for lining brick chimneys.
Is it possible to paint galvanized steel?
Not only is it possible, but it is necessary! Painting gives products a presentable appearance and extends their service life by an average of 10-30 years. However, there are several nuances in the matter of painting galvanized steel:
- The zinc coating must age. Those. Before painting, galvanizing is aged for about 1-2 years under natural conditions. During this time, oxidation products disappear, a durable zinc patina (“white rust”) and some roughness are formed, due to which the adhesion to the paint will be stronger.
- For painting galvanized steel, only special paint compositions that are characterized by a high level of adhesion, hardness and elasticity are suitable. These include:
- Polymer powder paints based on resins and hardeners. When heated, the composition polymerizes, thereby providing strong adhesion to the zinc coating.
- Alkyd, plastisol, polyester and aluminum enamels, characterized by resistance to ultraviolet radiation, moisture, temperature changes and seasonal changes.
On a note! Oil paints are not suitable for painting galvanized steel because... Over time, they oxidize, reacting with zinc, which reduces their adhesive properties.
High-quality coloring is difficult to do on your own without the appropriate skills. Therefore, painting of galvanized steel is most often done in factories or specialized workshops.
How water and gas pipes are made
VGP pipes are welded structures. They are made by folding a metal sheet and then welding its side edges together. Most often, VGP electric-welded steel pipes are manufactured in a straight-seam design. For their production, furnace welding, electric welding and inert gas welding are used.
Manufacturing technology and standards
Furnace welding is carried out in a special tunnel furnace.
Metal strips cut to size—strips—are placed in an oven with a temperature of 1300 °C. There they are heated and cleaned of scale with hot air.
The sheets are then passed through a forming-welding device, where they are welded with a straight seam.
Next, the finished workpiece is pulled through a sizing mill, which compacts and makes the seam stronger.
The quality of the seam is subjected to comprehensive testing using radiographic and mechanical methods.
Galvanization is carried out on finished VGP products.
The essence of the process is to apply a protective layer of zinc to both sides of the surface of the VGP pipe. This is done in one of three ways:
- Electrochemical - immersion in a bath with a zinc electrolyte solution.
- Hot-dip galvanizing - soaking in molten zinc.
- Diffuse galvanizing - treatment with zinc vapor at high temperature in a closed container.
Based on the results of the operations, the thickness of the zinc coating of the VGP outlet should be at least 30 microns.
When the VGP pipe is already galvanized, a thread is applied to it, if necessary, and verification tests are carried out.