Chemical composition
The steel composition includes:
The rest of the chemical composition of 60S2A steel is represented by iron. Steel is an alloy of Fe and C with the latter content being less than 2.06%. As the percentage of carbon in the composition increases, the material becomes more sensitive to heat treatment, hardenable, durable and hard. Negative consequences include decreased ductility, toughness, and increased brittleness.
To improve the properties of the metal, alloying additives are introduced. The result is an alloy that is hard and tough, strong and resistant to corrosion.
Silicon Si is used as a deoxidizer, replacing oxygen molecules in 60C2A steel. This makes the steel stronger and more resilient. Manganese Mn is introduced for the same purpose; it prevents the formation of iron sulfides. As a result, the number of cracks during hardening of products is reduced. When the manganese content is more than 1%, grain growth occurs, which leads to a decrease in the uniformity of structure and strength.
Chromium Cr is used as an alloying component due to its ability to displace oxygen. It forms iron carbides, prevents corrosion of the alloy, and improves hardenability. Nickel Ni also increases the anti-corrosion properties of spring steel 60C2A and reduces red brittleness. Copper Cu has similar properties. When its content in the composition increases to more than 1%, intermetallic compounds are released, which reduce the processability of the metal during tempering.
A carefully calibrated composition ensures such properties of steel as strength, elasticity, impact strength, and anti-corrosion qualities.
Decoding the brand
The steel grade designation contains a set of letters and numbers, each of which indicates the percentage of elements and their name:
- The mass of carbon, which is expressed in hundredths of a percent;
- One or more letters express the alloying element;
- A fraction of a percent, rounded to the nearest whole number.
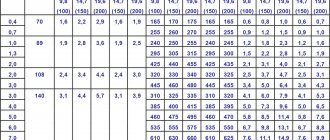
Content of elements in steel 60С2А, %:
| WITH | Si | Mn | S | P | Cr | Ni | Cu |
| 0.58−0.63 | 1.6−2.0 | 0.6−0.9 | <0.025 | <0.025 | <0.3 | <0.25 | <0.2 |
When choosing a material such as spring steel, it is very important to choose the right chemical composition and mechanical properties. GOST for products made of spring steel is determined by the assortment and a number of other parameters. The chemical composition and properties are influenced by the content of incoming elements:
C-carbon determines the structure and characteristics; increased carbon content leads to cold brittleness and reduces viscosity. Plasticity and strength decrease when the carbon content is more than 1%. Carbon influences mechanical properties such as ductility, weldability, and machinability.- Si-silicon is a deoxidizing agent and one of the main alloying elements, which promotes wear resistance, thermal hardening, and plays a role in increasing elasticity and fluidity. Affects hardenability.
- Mn-manganese affects quality by being a deoxidizing agent that is used to remove sulfur, phosphorus and oxygen. It has a beneficial effect on the metal structure and mechanical properties: weldability, malleability.
- Cr-chrome is an alloying element. Chromium increases resistance to oxidation and corrosion, increases strength at high temperatures, and also increases resistance to abrasive wear.
- Ni-nickel is an element that increases strength. Nickel increases corrosion resistance, increases the ability to be thermally hardened, and helps increase toughness and strength.
- Cu-copper increases corrosion resistance and increases strength properties. As the copper content increases, the quality of the surface during hot working deteriorates.
- S-sulfur is an undesirable element; increasing the sulfur content increases red brittleness and negatively affects ductility, weldability and toughness.
- P-phosphorus impairs plasticity and viscosity, increases the tendency to cold brittleness. However, increased phosphorus content improves mechanical processing.
Material properties
Based on the type of temperature treatment, the strength parameters and hardness of the product are determined. The characteristics of spring steel 60C2A in castings, circles and strips are different. In this case, the qualities of the alloy are considered using the last two examples.
The wheels are characterized by a strength of 129 MPa and a yield strength of 117 MPa. This ensures their elasticity. For comparison: the tensile strength of ST3 is 370 MPa. Tensile endurance is 490 MPa, torsional endurance is 295 MPa.
Hardening is most often used as a heat treatment method. It is carried out by cooling in oil, after which tempering is carried out to eliminate residual stresses.
Application of grade 60С2А
The scope of use of steel is determined by its properties. Steel 60S2A is widely used for the manufacture of heavily loaded structural elements experiencing alternating loads.
These are various springs, friction discs, Grover washers, spring rings, collets, torsion bars - elastic rods that work in torsion. The latter are found in suspensions of heavy tracked and wheeled vehicles, elastic shafts of multi-threaded gearboxes that transmit high power.
Specifications
The main characteristics of 60S2A steel include:
Fragility
| lack of fragility after tempering; | |
| Flock sensitivity | lack of flake sensitivity; |
| Short-term strength limit | 780-1180 MPa; |
| Density | 7590 kg/m 3 |
| Proportionality limit | 1375 MPa; |
| elongation at break | 8%; |
| Weldability | impossibility of creating a welded joint. |
The price of 60S2A steel varies around 50 rubles. per kilogram. It varies based on the quantity of steel, timing and delivery method.
Heat treatment
Hardening is carried out at 870 degrees, the product cools in an oil bath. Tempering is carried out at 470 degrees, which makes it possible to obtain troostite (ferrite-cementite structure). It maintains a hardness of 35-45 HRC.
Temperature treatment is:
- initial – annealing;
- final – hardening;
- middle - vacation.
Tempering increases the hardness of 60S2A steel to 365-445 HB. If the coiling of the spring is carried out with a single heating, then the next stage is heat treatment.
Hardening
Hardening is carried out in a shot blasting machine, in which each point is exposed to shot for 20-30 seconds. Feeding is carried out at a speed of 70-100 kg/minute, the diameter of the elements is 0.8-1.2 mm. This treatment creates an even silver color.
The second treatment option is captivity. The spring is kept in a compressed state for 20-40 hours. The procedure is carried out after heat treatment of steel 60C2A. Repeated compression (5-10 times) and shot peening are also used.
Physical and mechanical properties of steel 60S2A
Alloy grade 60C2A has high hardness , which is calculated as follows: HB 10-1 = 269 MPa. If you take a closer and more careful look at the composition of such a brand, then in addition to carbon, you can identify other chemical elements in its composition that affect what properties it will have.
Of course, the highest proportion in the composition is carbon. But, besides it, the composition of the 60C2a alloy may include the following elements:
- from 1, 6 and to 2 percent silicon;
- from 0.60 to 0.90 percent manganese;
- from 0 to 0.30 percent chromium;
- from 0 to 0.25 percent nickel;
- from 0 to 0.20 percent copper;
- from 0 to 0.025 percent phosphorus;
- from 0 to 0.025 sulfur.
Typically, an alloy such as grade 60C2A is produced in the form of long shaped rolled products. These can be calibrated rods, strips, tapes, forged blanks and forgings, as well as ground rods in the form of finished wire. Currently, the production of alloys has stepped forward so far and progressively that you can already find 60C2A grade sheets on sale - even hot-rolled sheets.
Analogs of steel 60S2A
The following can be used as analogues of the material:
- Japanese SUP6, SUP7;
- German 60MnSiCr4, 60SiCr7, 65Si7;
- Chinese 0Si2Mn;
- French 61SiCr7;
- American steels 9260, G92600.
quote: Originally posted by TENCH:
As I understand it, its properties are closer to ShKh15 than to 65G?
| TENCH | posted 24-6-2012 17:24 |
quote: Originally posted by GAU-8A:
Why did it happen? 60С2А spring-spring class, Lord, is it really so difficult to google?!
Those. closer to 65G? Is there any point in making “metal”?
| GAU-8A | posted 24-6-2012 18:03 Yes. |
| TENCH | posted 25-6-2012 21:23 Thank you. |
| SENSXUP | posted 25-6-2012 22:12 There is a knife made of this steel, now it’s my favorite. He's hungry, yes. But it cuts very well. |
| TOPIC Minsk | posted 26-6-2012 18:52 Yep. |
| grafolog | posted 30-6-2012 13:38
What do you recommend? The fish is getting darker “before our eyes”. I will look for a more resistant material. |
| TENCH | posted 3-7-2012 21:53 Will chrome plating help? There has been no rye on my chrome-plated quick cutter for ten years. cutting edge only. |
| HarryA | posted 4-7-2012 00:17
|
knives made of steel 65G
Structural spring steel 65G, produced in accordance with GOST 14959 and is characterized by high elasticity and wear resistance. It is not for nothing that this steel is used for the manufacture of springs, bearing housings and springs, etc. for knives. Of course, this is not the best option for kitchen, hunting, tourist and similar knives, but there are two groups of bladed weapons for which 65 G is the best option. Did you guess it? Of course, these are throwing knives and tournament swords.
The photo shows a throwing knife “Twist” with an all-metal blade made of 65G steel
Decoding steel
Characteristics of steel (briefly)
- Wear resistance
- Viscosity
- Strength
- Elasticity
- Tear resistance
- Impact resistance
- The knives show a good cut (although this is of no use for throwing knives)
- Relatively low cost
Steel for tournament weapons
All of the above is relevant not only for the manufacture of throwing knives, but also for the production of tournament weapons (swords, checkers, etc.).
In the photo: Tournament weapons for the “Heroic Fun” festival in the Oruzheynik park (Zlatoust) were made from 65G steel.
Minuses
As noted above, steel belongs to the carbon group and is susceptible to corrosion. Therefore, do not forget two important rules: keep the blades dry and clean and periodically lubricate them with castor oil. Caring for knives made from 65G steel is comparable to caring for knives made from Damascus steel.
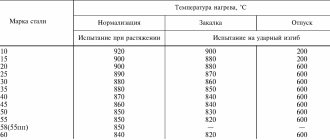
Chemical composition
| steel grade | C | Si | Mn | Cr | Mo | V | H.R.C. |
| 65G | 0.62-0.7 | 0.17-0.37 | 0.9-1.2 | 0.25 | – | – | 45-47 |
Heat treatment modes
The temperature range for hardening steel 65G is in the range of 800-830 °C. Subsequent high tempering at 160-200 °C with further cooling in still air makes it possible to obtain a steel hardness of 45-47 HRC. This grade of steel is not afraid of overheating, however, when hardened at high temperatures, the impact strength of the steel begins to decrease.
Application of steel 60S2A
The use of steel 60s2a means operation under conditions of severe deformation and cyclic loads. For this reason, spring steel is subject to requirements for ductility, elasticity, endurance, and abrasion. Mechanical properties are used in the production of springs, friction shafts, springs, rods and other products. 60S2A according to GOST 14959–79 is classified as highly loaded. Wire 60C2A has good deforming properties.
The characteristics of steel 60C2A are similar to structural steel 60, from which parts with increased requirements for high strength, wear resistance, and elasticity are made (shafts of metal rolling mills, clutches, wheel pairs, etc.).
Also used in mechanical engineering is structural 60C2, which has similar mechanical properties. The chemical composition of 60C2 differs from 60C2A by thousandths of a percent. An important difference is the content of sulfur and phosphorus.