← Prev. article Sheet metal bending: what is it, types? Sheet metal bending is metalworking, plastic deformation of rolled metal to give it the desired shape and further use as a workpiece. Replaces welding work where possible, and has a significant advantage over welding: the design is seamless and monolithic.
Track. article →Metal cutting: what is it, types Metal cutting is called the separation of parts of sheet metal or pipes into parts for the production of blanks. Cutting takes into account the characteristics of specific metals and alloys, their physical and chemical characteristics, so that the result is as close as possible to the planned...
Date: 05/19/2020Author: MOP “Complex 1”
Views: 165
Track. article →Metal cutting: what is it, types Metal cutting is called the separation of parts of sheet metal or pipes into parts for the production of blanks. Cutting takes into account the characteristics of specific metals and alloys, their physical and chemical characteristics, so that the result is as close as possible to the planned...
The article is relevant to the services:Bending of round pipesBending of profile pipesBending of sheet metalBending of round and profile pipes
Rating: 5,001 votes
- 1. What is it?
- 2. Types of metal bending
- Video
What it is?
Metal bending (go to service) is plastic deformation of rolled metal, during which one part of it changes its position relative to another, the outer layers of the metal are stretched, and the inner ones are compressed. An effective replacement for welding (go to service), which leaves potentially brittle seams: the bent workpiece is characterized by solidity and strength.
Both sheet metal and pipes can be bent. Almost all types of metals and alloys are amenable to the procedure; it can be carried out manually on home equipment (for example, on a bench vice, using hammers, pliers and pliers) and automatically on special bending machines.
The blanks created by this method are used everywhere, in all areas of industry.
Basic techniques for bending pipe parts
Bending of pipe parts is carried out in cold and hot states by manual and mechanized methods, with and without fillers.
Fillers are used to prevent the formation of folds and flattening of pipe walls. Dried fine sand or synthetic granules are used as fillers.
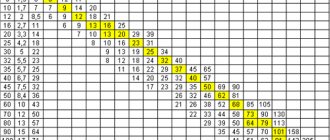
For each pipe, depending on its diameter and material, the minimum permissible bending radius is established. With a smaller radius, bending is unacceptable (Table 1).
Table 1. Values of the minimum permissible bending radii of pipes in a cold state, mm
| Pipe outer diameter, mm | Pipe material | Pipe outer diameter, mm | Pipe material | ||||||
| Steel 45 | Steel 35 | Steel 20 | Steel 10 | Steel 45 | Steel 35 | Steel 20 | Steel 10 | ||
| 18 | 74 | 62 | 56 | 43 | 105 | 450 | 344 | 282 | 240 |
| 24 | 95 | 79 | 65 | 55 | 110 | 510 | 377 | 310 | 264 |
| 32 | 115 | 96 | 79 | 67 | 130 | 536 | 450 | 370 | 315 |
| 38 | 156 | 131 | 107 | 91 | 145 | 578 | 484 | 398 | 339 |
| 50 | 197 | 165 | 136 | 115 | 155 | 620 | 522 | 430 | 360 |
| 60 | 238 | 199 | 165 | 139 | 181 | 720 | 600 | 498 | 425 |
| 75 | 280 | 260 | 194 | 173 | 194 | 752 | 630 | 516 | 444 |
| 80 | 324 | 270 | 224 | 190 | 206 | 835 | 702 | 575 | 488 |
| 90 | 362 | 302 | 250 | 213 | 220 | 920 | 770 | 635 | 540 |
When cold bending pipes with a diameter of up to 25 mm, hand tools are used.
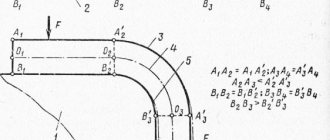
In Fig. 4, a shows a manual machine designed for bending pipes with a diameter of 12 to 20 mm. The machine has an axis 1 and a base plate 2, with which it is bolted to the workbench. The working parts of the machine are a fixed roller 4 with a clamp 5, mounted on axis 1, and a movable roller 3, mounted on a bracket 6 with a handle 7. The end of the bent pipe is placed in the clamp between the rollers, then the bracket with the movable roller is rotated around the axis of the fixed roller until the required bend, after which the bracket is returned to its original position and the pipe is removed.
Rice. 4. Bending using hand tools
To bend copper tubes of different diameters when assembling machines, a multi-strand pipe bender (5.66, b) is used. In this case, the tube is passed between rollers 1 and 2 until it comes into contact with the stop, then when the fork 3 is turned, the movable roller 2 rolls around the stationary one, bending the tube along a radius equal to the radius of roller 1.
Using a manual lever pipe bender (5.66, c), you can bend steel gas pipes with a diameter of 1/2, 3/4 and 1" in a cold state without filler.
For manual bending of steel pipes with a diameter of up to 50 mm at an angle of 180° without filler in a cold state, a special head with a manual drive can be used.
Types of metal bending
- Sheet metal bending (go to service) - processing of rolled metal sheets (go to services) on rolling machines, when the sheet is passed between three or four rolls until it takes the desired shape. Allows you to achieve any bends, including bending sides.
- Pipe bending (go to service) - processing of pipes (go to services) using automatic pipe bending machines, also using the cold rolling method (go to service) (possibly hot, with filler). The machines process profiles of any diameter and shape, of any length.
Basic techniques for bending strip parts
When bending parts manually, it is necessary to take into account that, depending on the properties of the material, the thickness and size of the strip workpiece, it is necessary to apply different forces to complete the work. Therefore, it is necessary to take into account that:
- when bending parts made of thin sheet plastic material, thickness 0.2 mm or less, marks from blows with a hammer may remain on the surface of the parts, therefore, when bending, it is advisable to use pads made of wooden blocks, pieces of steel strip or bar, etc., in some cases In cases, this work can be done without a hammer, but by crimping the workpiece manually using pads;
- when bending parts made of thin sheet plastic material, 0.2–0.5 mm thick, use light hammers, non-ferrous metal pads, pieces of steel strip or bar, etc.;
- for parts made of sheet material with a thickness of 3.0 mm or more, heavier hammers are used for preliminary bending (sledge hammers for material with a thickness of 8 mm or more), and lighter hammers are used for final bending and straightening of parts after bending;
- when manually bending, depending on the effort applied to bending the workpieces, choose a lighter or heavier vice;
- When bending manually, as the thickness of the metal increases, the effort with which it is necessary to clamp the workpiece in a vice increases. As a result, on the surface of the workpiece, the hardened jaws of the vice leave traces of corrugation of the jaw linings, which spoils the appearance of the parts. Therefore, when securing workpieces in a vice, linings made of non-ferrous metal, mild steel, etc. are used;
- when manually bending symmetrical parts, it is possible to shift the axis of symmetry along the length of the workpiece, so it is advisable to leave an allowance at the ends of the workpiece symmetrically, which is removed at the end of bending;
- When bending short flanges (for example, clamps made of material 4–6 mm thick), which are smaller than the width of the hammer head, it is advisable to leave an allowance symmetrically at the ends of the workpiece, which is removed at the end of bending.
Bending of parts is carried out according to a sample of the finished part, or according to a mock-up sample, which is more convenient for work.
To make a layout, a worker draws on a sheet of paper or on a sheet of metal (with a scribe) a life-size profile of the part that will need to be bent. Then the contour of the part profile is bent from wire or a thin strip using pliers according to the pattern (taking into account the radii and angles of inclination of the planes).
To bend parts, mandrels are selected with a minimum bending radius and with radii that should connect straight sections of the part.
On the workpiece, the parts are marked with a scriber to mark the lines along which bending will be done.
When bending shelves, workpiece 1 (Fig. 3, a) is clamped in a vice between two mandrels 2 and 3 so that the bending line faces the bend, at the level of the upper edge of mandrel 3. Hit the top flange of part 1 with a hammer. it is necessary evenly over the entire surface of the striker.
Rice. 3. Bending the workpiece in a vice: a - at an angle; b - along the radius
The angle of inclination of the shelf is checked by applying the template to the vertical face of part 1. The edge of the mandrel 3, on which the workpiece is bent, must be sawn to a radius greater than the critical one for the given thickness of the workpiece.
When bending along a radius, workpiece 1 (Fig. 3, b) is clamped in a vice between the jaw and mandrel 2 so that the bending line faces the bend and protrudes above the generatrix of mandrel 2 by the amount of A mm, if it is necessary for the flanges to be equal length.
where r is the radius of the mandrel.
The direction of hammer blows is shown by arrows.
Manual sheet bending machines and mechanically driven machines are used to bend sheet material blanks. The principle of operation is that a workpiece is secured to the machine table with a clamp, which is positioned at the point of bending relative to the clamp. Then the rotary traverse is set in motion, rotates to the set angle and thereby bends the workpiece to the desired angle. The machine has equipment that allows you to bend various profiles.
Sheet metal bending
The technology of bending metal, which is a sheet, is implemented on special machines - sheet benders. According to the bending method, such mechanisms can be divided into three types:
- Press. The sheet is introduced under pressure into a stationary matrix using a punch and acquires the desired shape. Punches come in several types, differing in shape and bending radius. The matrix, as a rule, has the shape of a corner or groove. A press brake is the most versatile equipment because it can be easily adjusted to different tasks.
- Rotary. Main elements: bed, movable bending beam (crossbeam), pressure beam, back stop. The clamping beam is used to fix the sheet on the frame. To bend the sheet, it is done using a bending beam, which is the main working element.
- Rotary - two, three or four roll devices in which the working elements use rotational motion. The working drive, which creates the necessary force on such machines, can be implemented in one of the following ways:
- manual - human muscular strength is used;
- hydraulic - a hydraulic booster is used;
- pneumatic - compressed air is used;
- mechanical - the energy of a spinning flywheel is used;
- electromechanical - electric motors with gearboxes are used.
One of the widely used types of sheet bending equipment is folding or folding machines, which are designed to work with thin sheets. Such equipment is used in the manufacture of seam roofing, air ducts, and chimneys.
Metal pipe bending
Bending of metal pipes can be done using hot or cold methods. The latter method is more technologically advanced and productive. Devices and machines for this operation use different bending methods. There are the following types of pipe benders:
- lever - for manual bending of pipes made of soft metals, as well as steel pipes of small diameter at an angle of up to 180 degrees;
- crossbow - the pipe is bent by applying force in the middle between two points on which the workpiece rests;
- roller (roller) - a classic example is a three-roller pipe bender.
Roller pipe bending machines use a method of cold deformation of metal called rolling. This machine works with metals of any hardness: from non-ferrous to titanium and its alloys. The bending angle can reach 360 degrees, and the length of the bent workpiece often exceeds 5 meters.
For bending thin-walled pipes, mandrel pipe benders are used, which use special equipment called a mandrel. This device is placed in the pipe cavity at the bend and prevents deformation of the metal walls.
About bending technologies and modern standards
To perform the operation, specialized bending dies are used. The sheet is fixed on a program-controlled press brake, after which uniform pressure is applied to it. The result is a wide range of reliable and durable rolled metal products that do not require welding. In this way, cabinet and other parts are manufactured that are characterized by high strength, arbitrary dimensions and aesthetic appearance.
How is metal bending done at home? Basic Rules:
- The bend radius must be less than the thickness of the prepared material. This requirement protects the workpiece from damage and cracks;
- from available tools, it is allowed to use a hammer and a vice for clamping, the power of which is selected in proportion to the thickness of the metal;
- sheets with a thickness of more than 10 mm are recommended to be bent in production conditions, since they require special equipment and appropriate conditions;
- The most ductile metals should be taken as the basis. Examples: aluminum, gold, iron, which has a minimum of carbon impurities in its chemical formula. In contrast to them are manganese, bismuth and other types of metal alloys, which are difficult to process and break under influence;
- To eliminate mechanical deformation, the plasticity of the raw material is artificially increased. Heating to high temperatures helps with this.