A series of technologies for controlling the removal of the surface layer of a metal part using specially selected chemical reagents is called metal etching. It allows you to remove scale, rust and oxides from products under the influence of acids, salts and alkalis in solutions. In this way, additional preparation of metal products is carried out for joining or coating, which improves the adhesion of the parts or the applied layer to the base. The most commonly used method is chemical etching of metal, carried out by immersing the workpiece in a bath of dissolved chemical reagents.
Etching methods
- Chemical
- Electrochemical
Chemical etching is performed by immersing products in a solution of sulfuric or hydrochloric acids. When a product is immersed in acid solutions, not only the oxides present on the metal surface, but also metallic iron interact with them.
With the rapid dissolution of oxides, etching of the base metal should be as small as possible. The relative speed of the processes of dissolution of metals and their oxides depends on the composition of the oxides, the concentration of acids, the temperature of the process, etc. An increase in the concentration of sulfuric and hydrochloric acids accelerates the dissolution of both oxides and pure iron.
To remove the FeO film from iron, it is most advisable to use 10% HCl. The optimal pickling temperature for sulfuric acid should be considered 60°, for hydrochloric acid 40°.
- The FeSO4 salt formed in the bath as a result of etching reduces the etching rate;
- An increase in the FeCl2 salt content in the solution increases the etching rate.
During chemical etching of steel, as a result of the interaction of iron with acids, intense release of hydrogen occurs, which diffuses into the surface layer of the metal, making it brittle and causing the formation of so-called “etching bubbles” on the surface.
To eliminate this phenomenon, special additives (retarders KS, MN) are added to the etching bath, which create a protective film during etching that protects the metal from the harmful effects of hydrogen.
Small items are loaded into the bath in baskets or trays. If before soldering you need to clean not the entire product, but only the soldered seam, then it is best to use a 10-15% solution of hydrochloric acid (apply to the seam with a brush) followed by rinsing with water.
For etching products made of copper and copper alloys, solutions of hydrochloric, sulfuric or nitric acids are often used, but more reliable results are obtained by etching in an 8% solution of sulfuric acid with the addition of 10% chromium. It is recommended to etch products made of aluminum and its alloys in an alkali solution, but sometimes hydrochloric acid is also used for this purpose.
Pickling of products made of nickel and its alloys is carried out in a 20% solution of sulfuric acid with the addition of chromic anhydride at a temperature of 60-80°. Products made from cupronickel are etched in a 10% solution of sulfuric acid with the addition of 1.5% chromium. After etching, a mandatory rinse in hot water with a small amount of cream of tartar is necessary.
Electrolytic etching is performed by immersing a product as an anode (anodic etching) or cathode (cathode etching) in an electrolytic bath.
In case of anodic etching:
- the electrolyte is usually a solution of acids or alkali metal salts
- cleaning occurs by rapid electrolytic dissolution
- Strict adherence to the regime is required to avoid excessive dissolution of the metal.
- The cathode is insoluble materials in the electrolyte, mainly lead and sometimes iron.
For cathodic etching:
- Lead or its alloy with 6-10% antimony is usually used as an anode.
- electrolytes are solutions of acids or their mixtures with alkali metal salts
Cleaning the metal surface from oxides using this method occurs through the action of atomic hydrogen formed at the cathode, which reduces the metal oxides, and gaseous hydrogen mechanically removes them from the metal surface.
In order to avoid corrosion, which can begin from the presence of acids and salts on the product, it is advisable to neutralize the remaining etching solutions after etching.
For this purpose, the products are immersed in a 2.5-5.0% soda ash solution for 1/2-1 minute. at room temperature and after washing in cold and hot water, dry thoroughly.
After such treatment, storing the soldered parts in a dry room will not cause corrosion of their surface. To prevent the prepared product from oxidizing again, it is recommended to solder it as soon as possible.
Pickling is the process of cleaning and processing a metal workpiece. Chemical, acidic, alkaline, electrochemical - there are many ways to perform this technological operation. Where is metal etching used, why is it used in industry, what are the processing methods using this technology, all these issues are discussed in detail in the article below.
Cleaning the part
To begin with, the part where the image is planned is cleaned with fine sandpaper and degreased. When the surface is ready, you need to seal the place where the design will be applied with adhesive tape or something similar. After this, the entire remaining surface, where chemical etching should not affect the metal, is painted over. It can be of any color, as long as it is resistant to White Spirit.
Once the paint is dry, you can remove the adhesive tape. Beneath it is clean metal, ready to create a design on it. Now you need to apply an image onto this “mini-canvas”. It is made using resin, which is dissolved in White Spirit until it becomes liquid, like paint. Use it to paint the desired image using a brush. What’s good about this kind of improvised paint is that if something doesn’t work out in the drawing, you can remove it by moistening a cloth or cotton swab in White Spirit. If there are very small details in the drawing that did not turn out well with a brush, they can be corrected with a needle, scraping off the excess after drying.
In this way, you can etch a knife, keys, in general, any metal object. Now that the drawing is completely ready, you can begin the etching itself.
Chemical etching of metal at home - Metalworker's Handbook
Pickling is a metal processing process in which a layer of a certain thickness is removed from the surface under the influence of active chemicals (acids or salts with an acidic reaction), as well as direct current in an electrolyte bath.
Metal etching can serve various purposes and be used in industry and at home.
The surface of an item subjected to etching receives a number of technological and decorative properties and allows one to examine its microstructure in a metallographic microscope, remove scale and other non-metallic inclusions from the surface, obtain the necessary jewelry ornament or prepare it for soldering.
Etching, also called electrochemical engraving, is most often used at home or in the garage to obtain relief images on various objects with decorative functions.
Most often, it is used on steels with high hardness, the processing of which with conventional engraving tools requires great effort.
This process is not very difficult even in the absence of artistic skills, if you follow its technology.
What is metal etching used for?
A series of technologies for controlling the removal of the surface layer of a metal part using specially selected chemical reagents is called metal etching. It allows you to remove scale, rust and oxides from products under the influence of acids, salts and alkalis in solutions.
In this way, additional preparation of metal products is carried out for joining or coating, which improves the adhesion of the parts or the applied layer to the base.
The most commonly used method is chemical etching of metal, carried out by immersing the workpiece in a bath of dissolved chemical reagents.
Methods of chemical etching of metal
There are also types of it that provide for additional activation of toxic substances using physical factors.
This is metal etching electrochemical (or galvanic) under the influence of an electric field or ion-plasma through the ionization of reagent particles.
If the word “etching” is used without indicating its type, then we are talking about chemical etching in an aqueous electrolyte. It is also called “liquid”, in contrast to “dry” ion-plasma.
When etching metal with an acid, usually sulfuric or hydrochloric, the workpiece is immersed in its solution. In this case, both the oxides existing on the surface of the part and the base metal enter into an acid reaction. As the acid content increases, the dissolution operations are accelerated simultaneously for the oxides and the base metal.
In addition to the acid concentration, the speed of the metal etching process is also influenced by its temperature regime, as well as the chemical composition of the oxides. The most optimal combination of these factors allows etching to be carried out so that, with the fastest possible dissolution of the oxides, it affects the base metal as little as possible.
Types of etching
Depending on the substance used to destroy the surface of the material, the following etching methods are distinguished.
1. Chemical method (also called liquid method). In this case, special acid-based solutions are used. In this way, ornaments and inscriptions are applied to alloys.
2. Electrochemical etching of metal - involves the use of an electrolyte bath. It is filled with a special solution. Lead salts are also often used to prevent over-etching. This method has a number of advantages. Firstly, the drawing is clearer, and the time required to complete the process is significantly reduced. In addition, this metal processing is economical: the volume of acid used is much less than with the first method. Another undoubted advantage is the absence of harmful gases (the mordant does not contain caustic acids).
3. There is also an ion plasma method (the so-called dry method). In this case, the surface is damaged minimally. This method is used in microelectronics.
Features of the method
Preparing a drawing (lettering)
Everything you need can be easily found on the Internet and copied. For those who know computer graphics, this is not a problem at all. The main thing is to have a printer at hand for printing.
- You will have to do a mirror image conversion. For this technology, only a laser printer can be used. Any other type of device is not suitable. You will need not ordinary paper, but thin glossy paper. As an option - self-adhesive film. In this case, you need to refill so that the print falls on the substrate. You can also attach it to standard (office) paper with pieces of this film. The printer “brightness” mode is set to maximum.
After printing, the image is carefully cut out.
The essence of the method
A special coating that is resistant to chemicals is applied to areas of the blade that should not be touched. Then the metal is immersed in an aggressive liquid (this can be acid, electrolytes). The unprotected layer of metal is “eaten away”, leaving a design or inscription under the protective coating. Etching can be multi-layered - in this case it is carried out in several stages.
The process can be carried out in two ways: to etch the “field”, protecting the contours of the design, or to etch only the contours of the ornament.
Steel pickling
In addition to the artistic etching of metal, which allows one to obtain exquisite images on steel surfaces, steel etching is also used to remove scale and oxide films. In this case, you should especially carefully observe the requirements of the technological process in everything related to the concentration of etchant solutions and the time of exposure of the part in the mordant or in the electrolyte bath. Over-etching during such an operation is extremely undesirable.
When etching steel, both liquid and electrochemical methods are used. The mordant is prepared on the basis of strong acids, such as hydrochloric or sulfuric
Particular attention should be paid to thoroughly degreasing the surface. A missed oil or grease stain can render the workpiece unusable.
To protect parts of the workpiece that are not subject to etching, I use varnishes based on rosin, turpentine, and tar.
These components are highly flammable, so you should be especially careful and careful when working with varnish. After etching is completed, the unetched areas of the workpiece are cleaned of the protective varnish with a solvent.
Nitric acid is very popular among home picklers. It is used as the only base for mordant, or in a mixture with tartar or salt.
A metal etching solution based on a mixture of nitric and hydrochloric acid is very reactive and must be handled with extreme care.
Nitric acid
For processing hard and special grades of steel, mixtures of nitric and acetic acid are used. The processing is carried out in two stages. First, a special preliminary mordant is prepared - glyphogen, which is a mixture of water, nitric acid and ethyl alcohol. The part is kept in it for several minutes. Next, the workpiece is washed with a solution of wine alcohol in distilled water and thoroughly dried. After this, the main etching is carried out.
Based on their atomic weight and the physical and chemical properties of the substance determined by it, for each metal and alloy they select its own mordant that best affects it.
Pickling copper alloys
Both pure copper and copper alloys are etched using sulfuric, hydrochloric, phosphoric, and nitric acid. To increase the reaction rate, chromium or nitrogen compounds are added to solutions. At the first stage of etching, scale and oxide film are removed from the workpiece, then proceed to the actual etching of the metal
Be careful when etching copper at home
Aluminum and alloys based on it stand out among other metals in that they are etched using alkaline rather than acidic solutions. For molybdenum, alkaline solutions based on sodium hydroxide and hydrogen peroxide are also used.
Titanium stands even more apart - at the first stage of preliminary etching, alkali is used, and at the main stage, acid is used. For titanium I use the strongest acids - hydrofluoric and concentrated sulfuric and nitric. Titanium blanks are etched to remove the surface layer of oxides immediately before electroplating.
A blank for a printed circuit board is a sheet of textolite, coated on one or both sides with a layer of copper foil. The purpose of etching printed circuit boards is to create conductive traces from copper foil in exact accordance with the drawing. The tracks are covered with a protective varnish, the rest of the foil is removed by etching.
At home he uses several methods:
- Ferric chloride. The reagent can be purchased at a chemical store or made independently. Iron filings should be dissolved in hydrochloric acid. Before use, the solution should be kept until the iron is completely dissolved and mixed thoroughly.
- Nitric acid.
- An aqueous solution of sulfuric acid mixed with tableted hydrogen peroxide.
- Copper sulfate with the addition of hot water and sodium chloride. This option is the safest, but also the longest. Throughout the entire process, the pickling temperature should be maintained at least 40°C, otherwise the pickling will take many hours.
- Electrolytic method. You should take a dielectric container (cuvettes are good for developing photographs), fill it with a solution of table salt, place a board and a piece of copper foil there, which will serve as a cathode.
After etching with the liquid method is completed, the board should be thoroughly washed with a soda solution to extinguish any remaining acid.
PCB etching
There are several ways to etch boards. In the first case, water and ferric chloride are used. You can make it yourself. To do this, iron filings are dissolved in hydrochloric acid. The mixture is kept for some time. Printed circuit boards are also etched using nitric acid. The whole process lasts about 10 minutes. At the end of the process, the board must be thoroughly wiped with baking soda, as it perfectly neutralizes the remaining caustic substance. Another etching composition includes sulfuric acid, water, hydrogen peroxide (in tablets). Etching boards with the following composition takes much more time: hot water, table salt, copper sulfate. It is worth noting that the solution temperature must be at least 40 degrees. Otherwise, etching will take longer. You can also etch boards using direct current. Glass or plastic containers can be used as dishes for this process (they do not conduct current). Fill the container with a solution of table salt. It is this that is the electrolyte. You can use copper (brass) foil as a cathode.
Development and drawing
Sketch
A subject drawing, a floral ornament, a logo or just a phrase - this is just a small list of design ideas that will be beautifully imprinted on the blade. Choose what pattern you want to see on the blade and start creating a sketch. You can draw it yourself or ask a professional.
Then you need to transfer the design to the blade. To do this, we place the blade in the scanner, transfer the image to the CorelDraw program, where we outline the contours of the blade. Next, apply a suitable ornament. The result should be duplicated in a mirror image and sent for printing.
Blade varnishing and pattern transfer
The blade must be varnished in advance. You can use matte varnish for plastic replica models. The varnish needs to be diluted with a nitro thinner to dry faster, and applied with an airbrush (you can also use a brush). The varnish is used because it retains its plasticity throughout the day and does not crumble under the scrubber.
We cut out the sketch to make it easier to fit to the blade, “black out” the reverse side with a pencil, and attach it to the blade with masking tape. Afterwards we draw the ornament with a thin pen. The result is a drawing on the varnish.
Scratching a drawing
We scratch the pattern on the surface of the varnish using scrubbers with different sharpenings.
It is important that the metal of the scrubber is not harder than the metal of the blade, otherwise there will be scratches
Features of the drawing
Interesting: Active low pass filter (LPF) for a subwoofer
In our example, a “field” is etched (this is the most difficult option, since it is more difficult to scratch the design), although a more accessible option is also possible, when only the contours of the design are etched.
Actions during a chemical reaction
During the reaction, a plaque forms, which will become more and more numerous. It slows down the whole process, so you need to periodically wash it off with water. You should not do this using various brushes, brushes and other tools, because you can damage the paint. But it seems to hold the entire design, and it would be a shame if, while etching a knife, for example, you inadvertently damage the design on it. This is a very delicate work that requires a steady hand and patience.
The depth of the pattern directly depends on the time during which the metal remains in the solution. There are no exact criteria, so each master must observe the progress of the chemical reaction himself. And only after doing this several times will it be possible to say with confidence how much time is needed to develop the desired pattern to the intended depth.
Oxidation with citric acid
Blackening with citric acid protects against corrosion, oxide films and rust. This is an old method suitable for steel with a high carbon content. If you oxidize a knife in this way, then in the places where it will be sharpened, all the coating will come off. It is not too durable, suitable for items that are rarely used.
For this you will need:
- a pack of citric acid;
- hot water (90-95 degrees);
- machine oil.
Pour the entire sachet of citric acid (20 g) into a stainless steel or glass container, add hot water (about 200 g) and stir thoroughly. Dip the product into the prepared mixture and leave for 50 minutes. After some time, the beginning of the reaction can be observed. Bubbles will begin to actively form around the part. They can prevent air from reaching the product, so you can periodically (every 10-15 minutes) move the knife so that they disappear from the surface.
After 50 minutes, you can remove the part; it will turn black at the end of the process. It needs to be rinsed, oiled and wiped.
Equipment
You need to take a power supply or transformer that can output from 4 to 7 V. In addition, you will need a dielectric bath; it must contain the necessary part and a second metal object that is connected to the anode.
To etch a pattern on metal, you must use iron sulfate. If the design is needed on a copper or brass surface, then use it. You can also use it. The main thing is that the water is distilled.
Engraving method 1
- Glass container (according to the size of the workpiece being processed). Naturally, not a bottle with a narrow neck, but a jar, glass or bath. Constant voltage source (up to 15 V). It should provide a current of 0.5 A, at a minimum. The best option is a battery charger for a personal car. This is exactly what the author used. Although some craftsmen use battery chargers for household tools (screwdrivers, etc.) and even cell phones for these purposes. A couple of wires for connection and clamps (for example, alligator clips). Any metal workpiece (the same spoon) that will play the role of a second electrode. Saline solution. The concentration is determined by eye, so the general recommendation is as follows: per glass of water – 2 teaspoons. Varnish. You will need it to paint the segment of metal on which you plan to engrave. Most articles devoted to the electro/chemical method contain tips on using the nail composition. The author, in order not to “injure” his wife with such extravagance, used the so-called tsapon-varnish, which is well known to radio amateurs and electrical installers. It costs a penny, is not in short supply, and can be easily removed with a solvent.
Layout development
The tasks were as follows: try to make railings, make steering wheels for davits, stop anchors, ladders, anchor chains, ladders for pipes, five-pointed stars and a double-headed eagle. I drew in CorelDRAW.
On the model, I made all the lines at least 0.18 mm thick, only on 4 lines for the experiment I made 0.10 mm (looking ahead, I will say that I was not able to feel the difference here). This is what happened:
At the end, to “clog” the free space, I printed a steering wheel and a star from symbolic fonts. I was too lazy to pull the sprues to them.
Thermal bluing of parts
In industrial conditions, they prefer to perform bluing using a thermal method. Usually this operation is combined with low tempering, which relieves internal stresses inside steel products:
- The part is heated in a muffle furnace for 20...30 minutes to a temperature of 180...220 ⁰C.
- The removed part is wiped with machine oil using a swab. It is advisable to treat all surfaces.
- If necessary, the treatments are repeated.
- Usually, a double heat treatment is sufficient to obtain a high-quality blued surface.
Information: weapons factories producing firearms and bladed weapons use thermal bluing. The coating on many products lasts more than 100 years. Example, Mosin rifles manufactured in 1891 and Nagan revolvers released at the end of 1888.
Transferring the layout to foil
The printer, as luck would have it, printed disgustingly.
I just refilled the cartridge and, apparently, the remnants of spilled toner were making themselves felt... But there was nothing to do - I chose a more or less clean place on the sheet and placed it there.
I cut out an A4 sheet from the ORACAL film backing, the master printed it on it and ran to iron it. I placed foil on top of the printout and ironed it through a couple of sheets of paper with an iron (at maximum heat) for about two minutes. The master didn’t fit on a piece of foil :(, but that’s okay...
Again, I used film backing due to availability. Many people use glossy magazines and even aluminum foil - there is a lot of room for experimentation. I was afraid to push the foil into the printer in case the edges scratched the drum.
Mordants used for steel
Very often, a solution of nitric acid is used for pickling steel. Salt and tartar are also used (with small additions of nitrogen). Hard steel grades are pickled with a mixture of nitric and acetic acids. Glyphogen is a special liquid based on water, nitric acid and alcohol. The surface is treated with this composition for several minutes. Then they are washed (a solution of wine alcohol in purified water) and quickly dried. This is pre-etching. Only after such manipulations are the workpieces placed in the etching solution. Cast iron pickles well in a sulfuric acid solution.
Preparation of materials
I diluted ferric chloride in a mayonnaise jar (poured a third of the jar of powder and filled two-thirds with boiled water (warm)). It said on the can: “Dilute 1 to 3,” but I decided not to bother with that. I chose ferric chloride as the most affordable.
for me (I came across the RADIO PARTS store sooner than HOUSEHOLD SUPPLIES) You can also poison with copper sulfate, hydrochloric acid with hydroperite, and nitric acid. Cut from copper? (maybe some kind of alloy, because it was wildly springy) a piece of foil about 0.2 mm thick according to the size of the master and carefully cleaned it.
Etching process for other materials
In addition to metals, other materials are also subjected to etching. The most common etching of glass is for decorative purposes. Etching is carried out in hydrofluoric acid vapor, the only one capable of dissolving glass. At the preparation stages, preliminary acid polishing of the surface of the product is carried out, then the outline of the future image is transferred to it. Protective coatings for glass are made from a mixture of wax, rosin and paraffins. After applying the protective coating, the workpiece is dipped into an etching tank.
The use of hydrofluoric acid creates a beautiful matte structure on the surface. To obtain a smooth, transparent surface, concentrated sulfuric acid is added to the etching mixture. To obtain a relief, deep pattern, the operation is repeated.
In metal etching, extremely chemically active substances are used - strong acids, alkalis and their solutions. If handled incorrectly, they can cause serious injury and damage to property.
Using rubber gloves
Therefore, when working with them, you need to take special precautions and strictly follow the safety rules when carrying out work:
- Work is carried out only in the presence of good ventilation, preferably a fume hood.
- It is mandatory to use personal protective equipment: rubber gloves and an apron, thick work clothing, a respirator, and a protective face shield.
- Do not place jars containing acids and alkalis on high shelves and cabinets.
- When diluting acids, ACID is POURED into WATER, and never water into acid.
- When working with acid, have a soda solution on hand, and when working with alkali, have a weak vinegar solution to wash areas of the skin where drops of the solution accidentally fall.
- When working using the galvanic method, before starting work, carefully inspect all electrical equipment used for the absence of mechanical damage and integrity of the insulation.
- Have a working fire extinguisher on hand.
Read also: Torch for brazing copper
If the etching solution comes into contact with the skin, immediately wash the affected area with an appropriate neutralizing solution. If acid or alkali splashes onto clothing, it should be removed immediately.
Rinse the affected area with water
If the etching solution gets on the mucous membranes, you should immediately seek medical help. Delay in such cases can cost health or even life.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Removing oxides, rust and scale from the surface of metals in solutions of acids, salts or alkalis is called etching.
Pickling safety precautions
Metal etching is a rather unsafe activity that requires a lot of concentration. This is due to working with aggressive materials – acids and their mixtures. First of all, for this process it is necessary to wisely choose a room with good ventilation. Ideally, a fume hood will be used for etching. If one is not available, then you need to take care of a respirator to avoid inhaling harmful fumes. When working with acids, you should wear rubber gloves and an apron. You should always have baking soda on hand, which - if necessary - can neutralize the effect of the acid. All etching solutions must be stored in special containers (glass or plastic). Don’t forget about the stickers that will indicate the composition of the mixture and the date of preparation. There is one more rule: jars of acids should not be placed on high shelves. Their fall from a height is fraught with serious consequences. Artistic metal etching is not complete without the use of nitric acid, which is quite caustic. In addition, in some mixtures it can be explosive. Nitric acid is most often used for sterling silver. Etching solutions are prepared by mixing acids with water. It is also worth remembering that in all cases the acid is added to the water, and not vice versa.
Types of etching
The main types of metal processing used in industry:
- electrolytic - there are cathode and anodic;
- chemical;
- plasma.
Electrolytic etching
Electrolytic or galvanic metal processing is used to quickly clean parts, apply engravings and produce grooves. Metal parts are immersed in an acid or salt electrolyte. The part becomes a cathode - a negative electrode or an anode - a positive electrode. Therefore, two types of electrolytic etching are classified - cathodic and anodic.
- Cathodic etching. The method is used to remove scale from the surface of carbon steel products after hot rolling or oil quenching. In cathodic etching, the material for the anode is lead, and the electrolyte is a solution of hydrochloric, sulfuric acid or an alkali metal salt. During the electrolysis process, hydrogen gas is actively released at the cathode, which interacts with iron and removes scale. During the cathode method, the metal surface is actively saturated with hydrogen, which increases the fragility of the workpiece. Therefore, the cathode method is not used for thin-walled products.
- Anodic electrochemical cleaning. This is the most common method in mechanical engineering. The process involves mechanically tearing off the oxide film on the anode with oxygen and mixing metal molecules with the electrolyte. An electrolyte is a solution of acids or salts of the metal being processed. Lead, copper and other metals are used as the cathode. During anodic treatment, the surface of the product becomes clean, with slight roughness, and the metal dissolves in the electrolyte. With this method, there is a risk of reducing the thickness of the workpiece and over-etching.
Chemical etching
The chemical treatment method is used to clean the surface of a part from oxide film, scale and rust for workpieces made of the following materials:
- ferrous metals;
- stainless and heat-resistant steels;
- titanium and its alloys;
- aluminum
For etching, sulfuric, hydrochloric or nitric acid is used. The workpiece is immersed in an acid or alkaline solution, molten salt and kept for the required time interval. The required cleaning time can range from 1 to 120 minutes.
The cleaning process occurs due to the release of hydrogen when the acid interacts with the metal. Acid molecules penetrate through pores and cracks under the oxide film. There they interact with the metal surface and hydrogen is released. The released gas tears off the oxide film and cleans the part.
Simultaneously with the oxides, the metal being treated dissolves in the acid. To prevent this process, corrosion inhibitors are used.
Plasma etching
With the ion-plasma method, cleaning and removal of the surface layer occurs by bombarding the part with ions of inert gases that do not react chemically with the molecules of the material being processed. Allows you to make high-precision notches and grooves with an accuracy of up to 10 nm. The technology is used in microelectronics.
The plasma-chemical method involves excitation of plasma in a chemically active medium, which causes the formation of ions and radicals. Active particles falling on a metal surface cause a chemical reaction. In this case, light compounds are formed, which are removed from the surrounding air by vacuum pumps.
The method is based on chemical reactions that occur when using reactive gases, such as oxygen, which are highly reactive. These gases actively interact in the gas discharge plasma. Unlike plasma treatment in inert gases, with this cleaning method, the active gas reacts only with certain molecules.
The disadvantage of this method is the lateral expansion of the grooves.
Etching solution
We need a liter of water, in which we need to dissolve 100 g of copper sulfate, and then add salt. It needs to be sprinkled until it stops dissolving. The resulting mixture will have a blue color. However, after a metal object is immersed in it, the color will begin to change to green.
So, let's dive into the detail. The chemical process begins immediately. In all this production, no substances harmful to health are released, so this metal etching at home is safe.
Types of etching
Let's present common methods. Most of them can be implemented at home. But it is necessary to adhere to safety rules - we will be dealing with chemicals.
Electrolytic
The second name is galvanic processing. The easiest way to use this technology is on small parts when it is necessary to urgently clean the surface. The essence of the procedure is as follows: a saline or acid electrolytic solution is introduced, and the workpiece is placed in it. Then a shock is given. Depending on how it is charged, etching is distinguished:
Cathode. In an environment with the addition of chemical elements, hydrogen is formed at the cathode in the form of a gas; a reaction occurs with its release. It saturates the liquid and reacts with the alloys, removing scale. It should be taken into account that the strength of the surface suffers and it becomes more fragile, so it is better not to treat thin steel sheets this way. Suitable materials are high carbon steel, heat treated samples. Anode. Used more often. At the anode, the oxide film comes off with the release of oxygen. All “extra” particles melt in the solution. The top layer becomes slightly rough
There is a possibility of losing an excessively large amount of metal; it is important not to overexpose the product in a container under voltage.
Chemical
If the previous option was great for steel, especially carbon, then this procedure has the same goals, but a completely different audience. You can start processing if you have in your hands:
- ferrous metal;
- stainless steel;
- titanium;
- aluminum.
Suitable: H2SO4, HCl, HNO3. The duration of immersion in the bath depends on the concentration of the composition and the degree of contamination of the workpiece. The interval is quite large - cosmetic cleaning of a thin-walled product may take only 1 minute, and for a thick cast-iron part - up to 2 hours.
The technology is simple. There is metal. An oxide film has formed on it, which needs to be removed. Acids penetrate through the pores under oxidation and interact with the steel surface. During a chemical reaction with iron, hydrogen is released. It repels pollution. But the metal surface can also be damaged. This can be avoided if you pre-treat the part with special rust inhibitors.
Plasma
The procedure also takes place in a chemical environment. But the chemical reaction is excited by a plasma flow generated on the basis of inert gases (containing fluorine). When they interact with corrosion (or silicon), they do not affect the iron itself. This is a very accurate method, but it requires special equipment. The degree of accuracy is up to 10 nanomicrons.
Let's watch a video on this topic:
Galvanic
This is a very fast method, which is why it has gained popularity, especially among those who do it at home. Speed isn't the only advantage. Other advantages:
- fairly clear boundaries and contours;
- no acids are required, so it is a more environmentally friendly method for humans.
First, let's determine the composition of the liquid for immersion; it depends on the material of the workpiece:
| Substance | Mordant |
| Steel, iron | A mixture of ammonia and iron sulfate |
| Copper, bronze, brass | Copper sulfate solution |
| Zinc | Zinc sulfate |
The immersion bath must be made of dielectric. For example, a glass jar for small parts.
Place the element in a container and pour in a product with good conductive properties. We attach the anode to the product. You will definitely need a source of energy. The procedure takes no more than 2 minutes, then rinse the sample under water.
Artistic
The procedure is suitable for etching a knife at home. The process is very common among restorers and weapon connoisseurs. It can be used to engrave, write the owner’s initials, or add picturesque patterns.
The operation is very simple. You can use any of the above methods, but the fastest and safest is galvanic. A stencil of tape should be left on the surface of the metal. It's easy to do with a good inkjet printer. When the necessary areas are protected (make sure that there are no traces of air under the tape), classic etching can be carried out.
Let's look at the photo:
Electrochemical etching of metal
We need to protect areas that should not be etched. To do this, you need to apply a special mastic to these surface areas. It is made from three parts of wax and two parts of rosin, they are melted in a tin can, stirring. After everything turns into a homogeneous mass, it is allowed to cool and divided into fragments. Each of them is placed in gauze so that later, when pressed, as much mastic as necessary can seep through it. After this, the workpiece that we will etch heats up. Now we take the created mixture, which was placed in gauze, and rub the surface with an even layer.
After cooling, the mastic becomes hard. The top is coated with light water-soluble paint. This can be watercolor or gouache white. After which the coating should dry. Then you can apply the design; it will stick well to the paint. It can be depicted using a pencil or translated using carbon paper. Then this outline needs to be scratched with a needle all the way to the metal.
Now the etching of the metal by electrolysis begins, we connect one rod to the anode - plus, the other to the cathode - minus. We connect the part on which the image will be applied to the first, and any steel plate to the second. After this, the process of etching the metal begins where the image was scratched.
If you need to create a multi-level drawing, everything is done in the same way as described above. Only the contours are checked each time, and when the smallest of them have been etched to the required depth, the part is removed and painted over with heated mastic using a brush. When it hardens, everything is repeated again until the next level of the drawing. In this process, an image is gradually created.
In this way, metal is etched at home, after which the surface is washed with turpentine and then polished, giving the product a finished look.
Types of etching
The main types of metal processing used in industry:
- electrolytic - there are cathode and anodic;
- chemical;
- plasma.
Electrolytic etching
Electrolytic or galvanic metal processing is used to quickly clean parts, apply engravings and produce grooves. Metal parts are immersed in an acid or salt electrolyte. The part becomes a cathode - a negative electrode or an anode - a positive electrode. Therefore, two types of electrolytic etching are classified - cathodic and anodic.
- Cathodic etching. The method is used to remove scale from the surface of carbon steel products after hot rolling or oil quenching. In cathodic etching, the material for the anode is lead, and the electrolyte is a solution of hydrochloric, sulfuric acid or an alkali metal salt. During the electrolysis process, hydrogen gas is actively released at the cathode, which interacts with iron and removes scale. During the cathode method, the metal surface is actively saturated with hydrogen, which increases the fragility of the workpiece. Therefore, the cathode method is not used for thin-walled products.
- Anodic electrochemical cleaning. This is the most common method in mechanical engineering. The process involves mechanically tearing off the oxide film on the anode with oxygen and mixing metal molecules with the electrolyte. An electrolyte is a solution of acids or salts of the metal being processed. Lead, copper and other metals are used as the cathode. During anodic treatment, the surface of the product becomes clean, with slight roughness, and the metal dissolves in the electrolyte. With this method, there is a risk of reducing the thickness of the workpiece and over-etching.
Chemical etching
The chemical treatment method is used to clean the surface of a part from oxide film, scale and rust for workpieces made of the following materials:
- ferrous metals;
- stainless and heat-resistant steels;
- titanium and its alloys;
- aluminum
For etching, sulfuric, hydrochloric or nitric acid is used. The workpiece is immersed in an acid or alkaline solution, molten salt and kept for the required time interval. The required cleaning time can range from 1 to 120 minutes.
The cleaning process occurs due to the release of hydrogen when the acid interacts with the metal. Acid molecules penetrate through pores and cracks under the oxide film. There they interact with the metal surface and hydrogen is released. The released gas tears off the oxide film and cleans the part.
Simultaneously with the oxides, the metal being treated dissolves in the acid. To prevent this process, corrosion inhibitors are used.
Plasma etching
With the ion-plasma method, cleaning and removal of the surface layer occurs by bombarding the part with ions of inert gases that do not react chemically with the molecules of the material being processed. Allows you to make high-precision notches and grooves with an accuracy of up to 10 nm. The technology is used in microelectronics.
The plasma-chemical method involves excitation of plasma in a chemically active medium, which causes the formation of ions and radicals. Active particles falling on a metal surface cause a chemical reaction. In this case, light compounds are formed, which are removed from the surrounding air by vacuum pumps.
The method is based on chemical reactions that occur when using reactive gases, such as oxygen, which are highly reactive. These gases actively interact in the gas discharge plasma. Unlike plasma treatment in inert gases, with this cleaning method, the active gas reacts only with certain molecules.
The disadvantage of this method is the lateral expansion of the grooves.
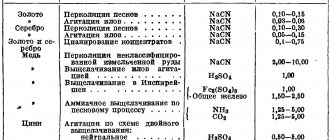
Purposes of Stainless Steel Pickling
To improve the performance and aesthetic properties of the stainless steel surface, special treatment is required. Modern enterprises most often use the etching method, which is applied after thermal or mechanical treatment of the metal. The process is complicated by the presence of a protective film on stainless steel, because it forms hard scale that does not interact well with reagents.
During technological procedures, a change in color may occur on the metal. Traces of tarnish can be removed by etching. To achieve maximum effect, various methods and compositions have been developed that take into account the chemical composition of stainless steel.
The stainless steel pickling process is used in production to clean the top layers of steel from welds, scale, oxides and rust. The procedure ensures that the stainless steel is cleaned, thereby increasing the adhesion of the top layer. This allows the metal part to be successfully connected to another surface. After etching, a protective coating is applied to the product.
are used at production sites :
- Electrochemical;
- Chemical.
The stainless steel pickling methods used by our company are described in the article “Pickling and passivation of stainless steel.”
It is important to follow all technologies when processing stainless steel, since over-etching renders the material unusable. The etching process is divided into several stages:
- Surface preparation;
- Interaction of metal with etchant or electrolyte;
- Cleaning the surface from etching products.
What is surface degreasing?
It is known that contaminants are always present on the surface of products entering electroplating after manufacturing and mechanical processing. They can be polishing paste residues, oil and grease stains, coolant, scale, old paint or coating, as well as ordinary dirt. Before applying a high-quality galvanic coating, all contaminants must be removed. Cleaning occurs through degreasing and etching. Next, we will consider the process of degreasing metal surfaces in more detail.
The types of contaminants removed by degreasing can be of different origins:
- Mineral.
These include mineral oils, polishing pastes, coolants. The peculiarity is that they do not dissolve in water, so it is advisable to use organic solvents to remove them; - Plant and animal.
Dissolves only in aqueous degreasing solutions. Let's look at them in more detail.
Often the contaminants are of a combined nature, and solid particles are added to the liquid phase - dust, asphalts, carbenes, oxides, etc.
A full degreasing cycle usually includes the following stages:
- Solvent treatment;
- Chemical;
- Electrochemical degreasing.
A clean, degreased steel surface looks like this: