- the ability to quickly heat the metal, which makes it possible to introduce a large amount of alloying additives into the furnace;
- the ability to create an oxidizing, reducing, neutral or vacuum atmosphere, which allows you to smelt steel of any composition, deoxidize metal with the formation of a minimum amount of non-metallic inclusions;
- the ability to smoothly and accurately regulate the temperature of the metal.
Therefore, electric furnaces are used for smelting high-alloy, structural, and special steels and alloys.
Features of the use of arc furnaces for steel melting
Electric arc furnaces are used to produce the following types of steels:
- Highly alloyed;
- Instrumental;
- Structural;
- Special weapons and other alloys.
Due to the ability to maintain a high melting temperature, arc furnaces are capable of melting almost any steel and alloy. The main feature of electric arc furnaces is their method of converting electrical energy into heat. It is carried out by an electric arc. It is due to the arc that it becomes possible to achieve such high temperature conditions.
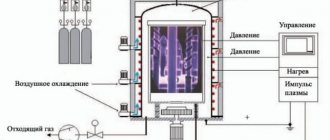
DC electric arc furnaces are the most popular equipment in modern steel mills. The design features of electric arc furnaces make it possible to obtain homogeneous alloys with a minimum amount of non-metallic inclusions. In addition to steel mills, electric arc furnaces are used in specialized laboratories. Laboratory models are compact in size, but by design they are full-fledged arc furnaces. They are used for various kinds of physical and chemical research.
Steel production in electric arc furnaces
Features of the arc furnace for steel production are as follows::
- The electric arc furnace uses three-phase alternating current as a power source;
- A standard furnace has three electrodes made of a special graphitized mass;
- The electric current is conducted from the transformer to the electrode holders through a special cable. Through the electrode holder, current is supplied to the electrodes and the metal bath;
- An electric arc occurs between the electrical charge and the electrodes when the furnace is started. Due to the electric arc, electrical energy is converted into thermal energy, which is transferred to the metal, which melts.
The operating voltage in arc furnaces during steel smelting can fluctuate between 160-600 V. The length of the arc is automatically adjusted by moving the electrodes. In order to monitor and control the melting process, a special working window is provided. Depending on the needs of a particular metallurgical production, the capacity of arc furnaces for steel production can range from 0.5 to 400 tons. Laboratory models are much smaller.
Electric arc furnaces can be used to produce two types of smelting. The first type involves remelting a charge from alloyed waste. For the second type of smelting, a carbonaceous charge is used.
Open hearth method
The essence of this technology is the processing of cast iron and other scrap metal using a reverberatory furnace. The production of various steels in open hearth furnaces can be characterized by the fact that the charge is exposed to high temperatures. To supply high temperature, various fuels are burned.
Scheme of an open hearth furnace
Considering the open-hearth method of steel production, we note the following points:
- Open hearth furnaces are equipped with a system that supplies heat and removes combustion products.
- Fuel is fed into the combustion chamber alternately, from the right and then from the left. This ensures the formation of a torch, which leads to an increase in the temperature of the working environment and its maintenance for a long period.
- At the time of loading the charge, a sufficiently large amount of oxygen enters the combustion chamber, which is necessary for the oxidation of iron.
When producing steel using the open-hearth method, the holding time of the charge is 8-16 hours. Throughout the entire period, the oven operates continuously. Every year the design of the furnace is improved, which makes it possible to simplify the steel production process and produce metals of various qualities.
Features of the smelting process in arc furnaces
Melting of metals or alloys using a charge from alloyed waste is carried out without oxidation of impurities. At the same time, the charge used in the process should not contain more impurities of phosphorus, manganese and silicon than the steel smelted in the process. During the smelting process, most impurities are oxidized, and the charge itself can contain a large amount of oxides. A mandatory procedure that should be carried out after the charge is melted is the removal of sulfur. To do this, you need to clean up the main slag. If necessary, the resulting alloy must be carburized, thereby bringing it to the desired chemical composition.
After carburization of the resulting alloy, diffusion deoxidation must be carried out. For this procedure, ground coke, aluminum and ferrosilicon must be fed to the slag. This is how high-quality alloy steels are smelted from various waste from engineering enterprises.
In order to smelt structural steel, it is impossible to use a charge from alloyed waste. For this purpose, only carbonaceous mixture is used. The composition of the charge used for the production of structural steel in electric arc furnaces must be as follows :
- 90% steel scrap;
- Up to 10% pig iron;
- Coke or scrap electrode, which will be needed for carburizing the metal;
- Lime in an amount of 2-3% of the total composition of the charge.
After the charge is loaded, you need to lower the electrodes and turn on the current. Under the influence of an electric arc, the charge will begin to melt. Molten metal will begin to collect at the bottom of the furnace. During melting, iron, silicon, phosphorus, manganese and some carbon will begin to oxidize. Ferrous slag will begin to form, due to which phosphorus will be removed from the alloy.
After the alloy is heated to a temperature of 1500-1540 degrees Celsius, ore and lime are loaded into it, after which the metal is brought to the so-called “boiling” period. Due to this, further oxidation of carbon will occur. After this, the procedure for removing sulfur and deoxidizing the metal occurs. The ferrous slag is removed, after which silicomanganese and silicocalcium are added to the melt. They are needed as deoxidizers. After this, a deoxidizing mixture is added to the melt. It consists of fluorspar, lime, ground coke and ferrosilicon. During the deoxidation process, the slag becomes white. This deoxidation process under the white slag should last from 30 to 60 minutes.
Steel production
The method of releasing steel into the ladle is determined, first of all, by the design of the chipboard, as well as the presence of a noise-proof casing. When using an EAF of a conventional design, steel is discharged through a conventional chute into a ladle suspended on a crane hook with further after-furnace processing of the steel provided for by the technological regulations. The choice of extra-furnace processing method is determined by the grade of steel and its production technology and will be discussed in more detail in a separate chapter.
According to the technological design standards, the main indicators are developed for two groups of furnaces: 1 - for furnaces with a capacity of 6-25 tons; 2 - for furnaces with a capacity of 50-150 tons. For furnaces of the first group, a classic process is being developed in an EAF with a brick lining, operating only using the heat of arcs using oxygen for trimming scrap metal and purging the bath with oxygen, with the implementation of all necessary technological operations in the EAF using a two-slag process , including oxidative and reduction periods and partial out-of-furnace processing.
Tables 11.2 and 11.3 show the duration of the classical process of electric steel melting and the specific consumption of materials and energy according to the technological design standards for furnaces of the first group.
For furnaces of the second group (50, 100, 150 tons) (Table 11.4-11.9) standards are established for working conditions on cold scrap, using gaseous oxygen and gas-oxygen burners, a single slag process with the removal of processes for finishing steel in complex processing units steel (AKOS) with slag-free production of metal, with casting on a continuous caster. Furnaces are used with water-cooled elements of the roof and walls, eccentric release of steel into a ladle mounted on a steel truck, loading of bulk materials from above through the fifth hole in the roof, and installation of furnaces in smoke- and noise-insulating chambers. Loading of scrap is carried out in two steps. Delivery of scrap in containers and in bulk, with adjustment by magnetic cranes. Filling the slopes and walls of the furnace is carried out by two types of machines: centrifugal, introduced into the furnace by a crane through the top, and pneumomechanical, with material supplied through the working window. Refilling is carried out with periclase powder with special additives. The extension of the electrodes is carried out using a special device on stands, and the bypass of the electrodes is done on the turned-down arch. The electrodes are graphite, with an acceptable current density of 28-35 A/cm2. The furnaces are equipped with three gas-oxygen burners installed in the wall of the furnace casing between the electrodes and operating during the initial period of each of the two fillings. Oxygen is supplied to the furnace bath through the working window; through the wall and bottom of the furnace, temperature measurement and sampling are carried out by a mechanized device using replaceable blocks. Delivery of samples to the laboratory by pneumatic mail.
The lined part of the furnace roof is made of mullite-corundum, thermoanthracite or periclase-chromite bricks, the walls are made of periclase-carbon or periclase-chromite bricks.
Steel-pouring ladles with a capacity of 70, 130 and 175 tons with gate valves, lined with mullite-corundum (working layer) and periclase-graphite (slag belt) bricks are used.
Advantages of electric arc furnaces
Arc furnaces are extremely popular in large steel mills. Steel smelting in arc furnaces is popular due to the following advantages :
- It is possible to obtain a number of refractory and high-quality steels that have a minimum amount of various impurities of non-metallic origin;
- You can work in various modes, using both liquid and solid filling;
- During the production process, minimal waste of metal is obtained;
- Arc furnaces have a simple design, are relatively compact, and their maintenance does not take much time.
In addition to a number of advantages, arc furnaces have one significant drawback - it is not possible to smelt metals and alloys with a very low carbon content. Arc furnaces have no other significant disadvantages.