No material, including steel, can last forever. It must be protected from moisture, sunlight and low temperatures. Oxidation of a metal creates a thin protective film on its surface that prevents oxygen from the air and water from destroying the material. At the same time, the technical characteristics of steels, aluminum and its alloys change.
From a chemical point of view, oxidation is the oxidation reaction of a metal and the formation on the surface of a thin layer of crystals bound by oxygen and other substances. The technology for applying a protective coating has several types of varying complexity. The simplest one was used several centuries ago and is available to anyone who wants to cover a part with a protective film at home. Complex technology requires special equipment and is carried out only in production conditions.
Chemical oxidation
This process involves the processing of metals with solutions, mixtures, melts of chemical elements (oxides such as chromium oxides). This oxidation allows for the so-called passivation of the metal surface. It involves the creation of an inactive (passive) formation in a metal layer close to the surface. A thin surface layer is created that protects the main part of the structure.
Technologically, this process is implemented by lowering the prepared metal part into an alkali or acid solution of a given percentage.
They keep it there for a certain time, which allows the oxidation-reduction reaction to fully occur. Then the part is thoroughly washed, subjected to natural drying, and final processing.
Chemical oxidation of steel
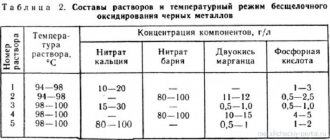
To create an acid bath, three types of chemically active acids are used: hydrochloric, nitric, and orthophosphoric. The acceleration of the chemical reaction is stimulated by adding manganese, potassium, and chromium compounds to the acid solution. The oxidation reaction occurs at a solution temperature in the range from 30 °C to 100 °C.
The use of solutions based on alkaline compounds allows the use of additives of sodium nitrate and manganese dioxide compounds. In this case, the solution temperature must be increased to 180 °C, and with additives up to 300 °C.
After the procedure, the part is washed and dried. Sometimes potassium bichromate is used to consolidate the chemical reaction process. To increase the shelf life of the formed film, chemical oxidation with oiling is carried out. Sometimes this process is called chemical oxidation. The final coating with oil results in a reliable anti-corrosion coating with a striking, highly decorative black color.
Protection of titanium and its alloys
As you know, titanium has low wear resistance. Oxidation of titanium and alloys based on it increases their anti-friction properties and improves the metal’s resistance to corrosion.
As a result of applying a protective layer, thick oxide films (in the range of 20-40 microns) are formed on the metal, which have increased absorption properties. Structures made of titanium alloys are treated at a temperature of 15-25 degrees in a solution containing 50 grams of sulfuric acid. The current density is 1-1.5 Amperes per square decimeter. The duration of the procedure is 50-60 minutes. If the current density exceeds 2 Amperes per square decimeter, the process duration is reduced to 30-40 minutes.
During the application of the protective layer, the recommended current density is maintained for the first 3-6 minutes, and the voltage during this time increases to 90-110 V. Upon reaching this indicator, the current density decreases to 0.2 Amperes per square decimeter. Oxidation continues without current regulation. During the process, the electrolyte is mixed. Lead or steel cathodes are used.
Anodic oxidation
This type is called electrochemical oxidation of steel. Sometimes it is called anodic oxidation of steel. The term anodizing is also used. It is based on the chemical process of electrolysis. It can be carried out in both solid and liquid electrolytes. The prepared workpiece is placed in a container with an oxide solution.
The electrolysis reaction is possible by creating a potential difference between two elements.
The surface of the oxidized product is characterized by a positive potential. Chemically active elements with a negative potential are isolated from the solution. The interaction of oppositely polar elements is called the electrolysis reaction (in our case, anodization).
Anodic oxidation
The anodization reaction can be performed at home. It is required to strictly comply with safety regulations. The reaction involves harmful reactive fluids and unsafe voltage.
The use of anodic oxidation makes it possible to create protective films of various thicknesses. The creation of thick films is possible through the use of a sulfuric acid solution.
Thin films are obtained in solutions of boric or phosphoric acid. Using anodization, you can give the surface layer of metal beautiful decorative shades. For this purpose, the process is carried out in organic acids. Oxalic acid, maleic acid, sulfosalicylic acid are used as such solutions.
Micro-arc oxidation is a special anodizing process. It makes it possible to obtain coatings with high physical and mechanical characteristics. These include: protective, insulating, decorative, heat-resistant and anti-corrosion properties. In this case, oxidation is carried out under the influence of alternating or pulsed current in special baths filled with electrolyte. Such electrolytes are weakly alkaline compounds.
Anodic oxidation at home
Anodizing allows you to obtain a surface layer with the following properties:
- reliable anti-corrosion coating;
- good electrical insulators;
- thin but durable surface layer;
- original color scheme.
Anodizing stainless steel requires a special approach. This is due to the fact that such steel is considered a neutral (inert) alloy. Therefore, in production, when anodizing a large number of parts, a two-step procedure is used.
At the first stage, stainless steel is anodized together with another metal that is more suitable for this process. It may be nickel, copper, other metal or alloy.
At the second stage, the stainless steel itself is oxidized directly. To simplify the oxidation process, special additives, so-called passivating pastes, are being developed today. These compounds speed up the reaction process of stainless steel.
Where are processed products used?
Sometimes a treatment method using alkaline and oxidizing agents is sufficient. Forged fences and fences that are not painted with colored paint, but treated chemically, thermally or electrochemically, look aesthetically attractive.
This method of finishing metal products is used to:
- Protect the surface from corrosion when the product is used for construction purposes. Even when there is no direct negative impact on a metal object, protection of this kind is simply necessary.
- Protect surfaces from aggressive environmental influences, for example, fences, window bars, poles and metal parts of building decor.
- Form a layer that forms an electrical insulating shield. This is applicable in technology and buildings that should protect people from the effects of electric current.
- Change aesthetic or decorative properties if there is no desire to paint parts, changing their unique relief.
Such products and parts are used in everyday life, construction, and jewelry. Resistance can be increased by using an auxiliary coating – paint and varnish.
Often bluing is sufficient. The detail acquires dark shades with a characteristic tint. Additional finishing methods allow you to vary the color scheme.
In any case, oxidation of metal products and parts is simply necessary in order to preserve their positive characteristics. The procedure is carried out at home and in factories, in compliance with specific operating technologies. Auxiliary substances are also necessary: an oxidizing agent and an alkali. The correct temperature conditions and sufficient holding time will lead to high-quality blued metal of any alloy.
Master classes on oxidation at home (2 videos)
Oxidized metal (20 photos)
Thermal oxidation
According to the term, oxidation occurs at relatively high temperatures. The value of this indicator depends on the steel grade. For example, the process of thermal oxidation of ordinary steel occurs in special furnaces. A temperature close to 350 °C is created inside. A class of alloy steels undergo thermal oxidation at higher temperatures. It is necessary to heat the workpiece to 700 °C. Treatment continues for one hour. This process is called steel bluing.
Blueing
Steel pistol after bluing
Protection of brass surfaces
Oxidation of products made of brass and bronze indicates that the parameters of oxide films and the color of surfaces largely depend on the components of these alloys. For example, with equal amounts of zinc and tin in bronze metal, an oxide film is difficult to form, but when lead is added, the quality of the oxide film increases sharply. When treating brass with ammonium sulfide, alloys with high levels of zinc are more difficult to oxidize than brass containing no more than 10% zinc.
The recipe, which has been used for a long time, based on the so-called liver of sulfur, has now been modified: now, after dissolving the crystals, ammonium sulfide is added to it. Based on the amount of solution, you can get a different color of the oxide film: from light brown to dark brown or even black. Moreover, the film is of excellent quality and uniform color.
Also, a 10% thiocarbonate solution can be used for processing alloys. However, the solution is only used for brasses and bronzes with low zinc content.
Another way to protect the surface of bronze and give it an attractive appearance is to treat it with sodium thioantimonate. The result is an evenly coated film with a reddish tint.
Oxidation is a process that requires deep knowledge of chemical and physical processes and, as a rule, expensive equipment. However, the simplest technology for applying a protective film is available to everyone; just follow the simple instructions described in this article.
Plasma oxidation
This oxidation is carried out in an environment with a high concentration of oxygen using low-temperature plasma. Plasma is created due to discharges that occur when high- or ultra-high-frequency currents are applied.
Plasma oxidation is used to form oxidized films on fairly small surfaces.
It is mainly used in electronics and microelectronics. With its help, layers are formed on the surface of semiconductor compounds, the so-called pn junctions. Such films are used in transistors, diodes (including tunnel diodes), and integrated circuits. In addition, it is used to increase the photosensitive effect in photocathodes.
Plasma oxidation
A type of plasma oxidation is oxidation using high-temperature plasma. Sometimes it is replaced by an arc discharge with an increase in temperature to 430 ° C and higher. The use of this technology can significantly improve the quality of the resulting coatings.
Protecting silver surfaces
Silver oxidation is a method of processing silver products, during which the surface is chemically treated with silver sulfide. Layer thickness is approximately 1 micron. The procedure is carried out in solutions of sulfur compounds. The most common solution is liver sulfur.
As a result of processing, silver gets an aged appearance. Its color ranges from light gray to black or brown. In this case, the thickness of the applied layer affects the intensity of the color. You can adjust the color while polishing the metal - the bulges become light, and the depressions remain darker. Contrast allows you to emphasize the relief of the product. Oxidized silver is sometimes confused with blackened silver, although the surface treatment method in these cases is different.
Laser oxidation
This technology is quite complex and requires special equipment. To carry out oxidation use:
- pulsed laser radiation;
- continuous radiation.
In both cases, infrared laser systems are used. Due to laser heating of the top layer of material, it is possible to obtain a fairly resistant protective film. However, this method is only applicable to a small surface area.
Laser oxidation
What is the oxidation method?
Most metallic substances enter into an active phase with various chemicals. In some cases, it occurs with the release of a third-party substance, which can become protection for the main product. In the method under consideration, an oxide film appears after applying a special solution to the surface.
The liquid, under the influence of the redox reaction, leads to the creation of a top layer that increases corrosion resistance and also decorates the plane. It should be noted that there are several varieties of the process; they are selected depending on what effect needs to be achieved, as well as what material is being processed. Let's take a closer look at the views.
Difficulties of blackening work associated with stainless steel
All the methods described above are ideal for ferrous alloys and low alloy steels. A special approach is required, a set of measures for blackening stainless steel as a conditionally inert alloy. The scattered data in the literature on direct blackening of stainless steel is contradictory and does not always work in practice. On a production scale, it is customary to solve this issue with a two-step approach. The first stage is anodizing stainless steel with another metal that is more prone to oxidation. This is mainly nickel, less often copper. The second stage is oxidation of the resulting surface. Chemists in many countries are developing special passivating pastes and compositions for blackening stainless steels that can induce them to oxidize.
To apply a decorative film that does not work when exposed to temperature changes, on a surface that does not experience large mechanical loads, the following oxidation method can be used:
- Etching in 10% oxalic acid solution
- Washing and processing in 1% sodium sulfide solution to the required degree of blackening
- Oiling a stainless steel sample.
Based on the information presented, we can conclude that the use of blackening for stainless steel is in the nature of a commercial decorative coating. The use of oxidation to achieve higher metal characteristics is not justified and cannot be guaranteed. To obtain protective films that expand the scope of application of stainless steels, it is worth considering other methods and methods.
Source
Architectural anodizing
Architectural anodizing produces a finish that is harder than glass, meaning it is less susceptible to damage, wear, and can be sanded down if necessary to restore its original shine. Advantages of anodized aluminum in architecture:
Aesthetics
The clear oxide layer highlights the rich metallic appearance of the aluminum rather than hiding it like paint. The oxide layer, unlike powder painting, does not flake off or peel off.
Corrosion resistance
The oxide layer is resistant to corrosion and this is one of the most important advantages of anodized aluminum.
The aluminum oxide layer is durable, hard and self-renewing because aluminum spontaneously forms a thin but effective protective oxide layer that prevents further oxidation or corrosion when mechanically damaged.
Anodized aluminum will not patina like copper and zinc, and will not rust like steel. It is an excellent material for use in marine and coastal environments.
Anodized aluminum is highly weather resistant, even in many industrial environments where other metals often corrode. The main pollutants in urban environments are carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide, which do not affect anodized aluminum surfaces.
Durability
Featuring a highly durable and abrasion-resistant oxide layer, anodized aluminum is strong enough to withstand harsh and hostile climates.
Resistance to mechanical damage
Aluminum oxide is a very hard compound, ranked second only to diamond on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness. Therefore, the anodized aluminum surface provides excellent scratch and abrasion resistance.
No peeling
Anodizing is an electrolytic process that converts the surface of a metal into an oxide layer integrated into the metal itself. It is not a coating applied to metal surfaces. Consequently, there is no risk of destruction of the anode film associated with processes such as dusting, the formation of bubbles, cracks, chips or peeling.
No fading
Shades such as silver, champagne, bronze, gold and black do not contain organic elements. These coatings do not fade throughout their entire service life.
No dust
Dusting is the formation of a fine powder on the painted surface of a film under the influence of atmospheric phenomena (grains of sand carried by the wind). It can cause significant deterioration in surface appearance with reduced gloss, surface gloss and color.
Anodized aluminum is not subject to this problem: it is resistant to negative environmental influences and is equally stable in hot (desert), sea or humid climates.
No filamentous corrosion
Filiform corrosion is an attack on the hidden area between the aluminum and the paint layer, causing corrosion to spread beneath the paint layer.
When anodizing, the anodic (oxide) layer is integral with the aluminum, and the interlayer layer is simply absent. This means that the coating will never be subject to thread-like corrosion.
Moreover, in the event of surface damage from an impact or puncture, aluminum will simply restore itself through natural oxidation.
Uniform coverage
When anodizing, the product is completely immersed in the bath, which ensures uniform coverage of the surface with an oxide film.
With your own hands
The methods presented above are used only in production, but if you are ready for independent experiments, then you need to create a small home laboratory.
For the experiment, take a small steel piece that will fit into a three-liter jar without any problems.
Stages of work
Do each of them consistently and thoroughly. Prepare all the necessary tools in advance.
Rough stripping
Use a steel brush or coarse sandpaper. You need to remove all rust down to the base, as well as other contaminants. It is better if you then go over it with fine-grained sandpaper to ensure a uniform surface.
Polishing
Special pastes with fine abrasives or discs on hand-held grinders are perfect.
Plaque removal
In other words, rid the element of grease, oil traces, and polishing paste residues.
Treatment
To do this, introduce a solution of sulfuric acid with a 5% content of the substance and place the workpiece there for 1 minute.
Washing
First, rinse the part in regular running water, and then boil it in a soapy water mixture. Now make a 5% solution of caustic soda in a container, place the workpiece there and heat to 150 degrees, hold for 2 hours. Then just let it cool and evaluate the result. You've got an oxidized coating - this is a wonderful effect achieved at home. To clarify the information you are interested in and purchase Russian-made metal bandsaw machines, contact the managers by phone 8 (908) 135-59-82;;. They will answer all your questions.
Metal protective coatings
Anodic metal coatings are metals whose electrochemical potential is lower than that of the materials being processed. On the contrary, it is higher for cathode ones.
Cathodic coatings prevent the penetration of aggressive media into the base metal due to the formation of a mechanical barrier. They better protect surfaces from negative influences, but only if they are undamaged.
Depending on the method of application, metal coatings are divided into the following types.
Electroplating
Galvanization is an electrochemical method of applying a metal protective coating to protect surfaces from corrosion and oxidation, improve their strength and wear resistance, and give an aesthetic appearance.
Galvanic coatings are used in aircraft and mechanical engineering, radio engineering, electronics, and construction.
Depending on the purpose of specific parts, protective, protective-decorative and special galvanic coatings are applied to them.
Protective ones are used to isolate metal parts from aggressive environments and prevent mechanical damage. Protective and decorative are designed to give parts an aesthetic appearance and protect them from destructive external influences.
Special galvanic coatings improve the characteristics of the treated surfaces, increasing their strength, wear resistance, electrical insulating properties, etc.
Thermal spraying
It represents the transfer of molten particles of material to the surface being treated by a gas or plasma stream. Coatings formed by this method are distinguished by heat and wear resistance, good anti-corrosion, anti-friction and extreme pressure properties, electrical insulating or electrical conductivity. The materials to be sprayed are wires, cords, powders made of metals, ceramics and metal-ceramics.
The following methods of thermal spraying are distinguished:
- Flame spraying: the simplest and most inexpensive method used to protect large surface areas from corrosion and restore the geometry of parts
- High-speed flame spraying: used to form dense cermet and metal coatings
- Detonation spraying: used for applying protective coatings and restoring small damaged surface areas
- Plasma spraying: used to create refractory ceramic coatings
- Electric arc metallization: for applying anti-corrosion metal coatings to large surface areas
- Spraying with fusion: used when there is no risk of parts deformation or it is justified
Immersion in melt
When using this method, the workpieces are dipped into molten metal (tin, zinc, aluminum, lead). Before immersion, the surfaces are treated with a mixture of ammonium chloride (52-56%), glycerin (5-6%) and chloride of the metal being coated. This allows you to protect the melt from oxidation, as well as remove oxide and salt films.
This method cannot be called economical, since the applied metal is consumed in large quantities. At the same time, the thickness of the coating is uneven, and it is not possible to apply the melt into narrow gaps and holes, for example, on threads.
Thermal diffusion coating
This coating, the material for which is zinc, provides high electrochemical protection of steel and ferrous metals. It has high adhesion, resistance to corrosion, mechanical stress and deformation.
The thermal diffusion coating layer has the same thickness even on parts of complex shapes and does not peel off during operation.
Cladding
The method is the application of metal using a thermomechanical method: by plastic deformation and strong compression. Most often, protective, contact or decorative coatings are created in this way on parts made of steel, aluminum, copper and their alloys.
Cladding is carried out through the process of hot rolling, pressing, extrusion, stamping or explosion welding.
What does anodizing do?
In some ways, anodizing is similar to the galvanic processes that occur during chrome plating or galvanizing of steel. But there is a significant difference: the use of foreign substances is excluded, even if they are similar in properties and chemical composition. Oxidation is carried out on the basis of the metal itself, which is subjected to electrochemical action.
When anodizing, the process can be regulated, the oxide layer is given predetermined properties, and the result is the strength of the oxidized area.
The best protective layer as a result of anodization is formed on metals such as aluminum, titanium, steel, tantalum. The main requirement for the technology is that the metal has only one oxide with high adhesive properties.
But to ensure adhesion, a porous structure is needed, which will ensure contact of the working mixture with the clean metal surface, which significantly speeds up the oxidation process.
- The first type is the porous surface of the oxide film. It is obtained when metal is exposed to acidic electrolytes. A surface structured with pores serves as an excellent basis for laying paint and varnish materials on it, which, with their structure formed during the polymerization of the base, is fixed in the fractals of the pores. That is, the anodized surface promotes increased adhesion.
- Barrier. Belongs to the second type. This is an independent protective coating that protects the metal from contact with an external aggressive environment.
However, the anodizing process is not limited to creating protective layers. By using different materials and changing the voltage level, you can get different shades of anodized film. What designers actively use when decorating interiors when aluminum is used as the facing material.